MCUNet
2020-NIPS-MCUNet Tiny Deep Learning on IoT Devices
来源:ChenBong 博客园
- Institute:MIT、NTU、MIT-IBM Watson AI Lab
- Author:Ji Lin、Song Han
- GitHub:/
- Citation:1
Introduction
- MCU(单片机)上的网络
- 极低的内存(SRAM)和硬盘(Flash,read only)
- 没有操作系统
- 目前的轻量化网络主要为移动端(如智能手机)设计,而单片机的价格($5)比智能手机($500)低了几个数量级,应用范围也更加广泛,同时性能也低了N个数量级,因此如何在MCU上部署神经网络是一个巨大的挑战。

- 我们提出了MCUNet,一种专为MCU设计的 model design(TinyNAS)与 inference library(TinyEngine)联合设计的方法,可在MCU上进行 ImageNet scale 的推理。
- 首次在MCU上达到 ImageNet 的 70.2% top-1 acc
DL in MCU
现有的框架:
- TF Lite Micro
- CMSIS-NN
- CMix-NN
- MicroTVM
缺点:
- 运行时编译 network graph,消耗大量的 SRAM 和 Flash
- layer-level optimization,没有利用整个网络的信息来进一步减少 memory usage(例如某些网络没有用到 5*5 conv,但 library 中依然保留这部分的功能以保证通用性)
Efficient Neural Network Design
- Model Compression
- Pruning
- Quantization
- Tensor decomposition
- Efficient Network Design
- MobileNet,EfficientNet
- NAS(dominate)
Method
TinyNAS: Two-Stage NAS for Tiny Memory Constraints
- first optimizes the search space
- then performs neural architecture search within the optimized space
Optimize Search Space
R = {48, 64, 80, ..., 192, 208, 224}
W = {0.2, 0.3, 0.4, ..., 1.0}
This leads to S = W×R = 12×9 = 108 possible search space
Each search space configuration contains (3.3 × 10^{25}) possible sub-networks
Our goal is to find the best search space configuration S* that contains the model with the highest accuracy while satisfying the resource constraints.
如何找到S*?
- Perform NAS on each of the search spaces and compare the final results
- Search Speace ==> (under memory constrain) Searching ==> Compare Best Acc?
- Evaluate the quality of the search space by randomly sampling m networks from the search space and comparing the distribution of satisfying networks
- Search Speace ==> (under memory constrain) Sample ==> Training ==> Compare Acc?
- (RegNet,一个 search space sample 500 model,训练10个epoch的acc 的 EDF,足以刻画 search space 的质量)

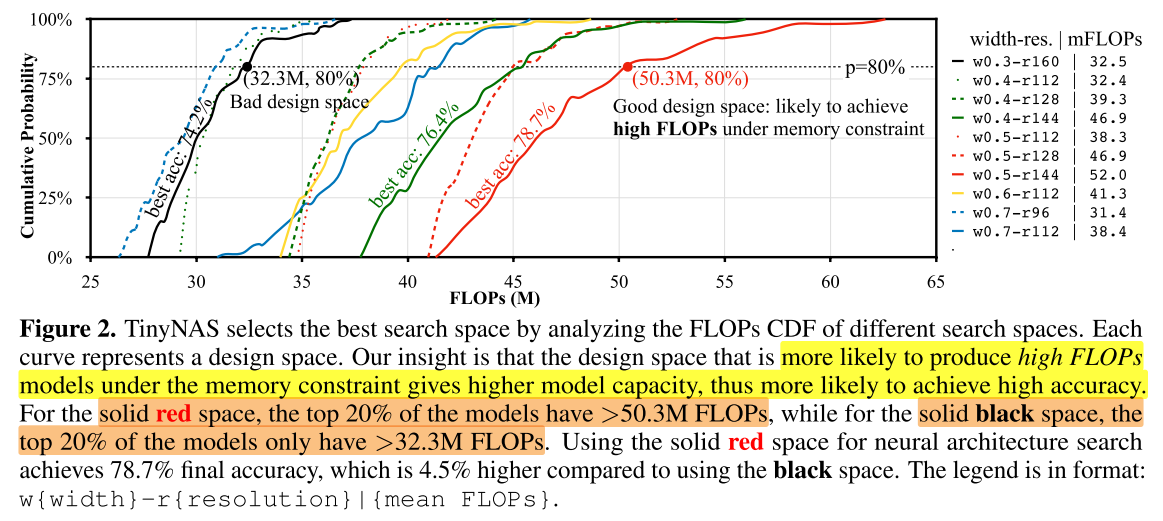
- 我们使用评估策略:Search Speace ==> (under memory constrain) Sample ==> Compare FLOPs (No training!)
- Search Speace ==> (under memory constrain) Sample ==> Training ==> Compare Acc?
Assumption: A model with larger computation has a larger capacity, which is more likely to achieve higher accuracy.
We only collect the CDF of FLOPs:
TinyEngine: A Memory-Efficient Inference Library
compilation vs. interpreter
编译 vs. 解释
memory scheduling
layer-wise vs. model-wise
kernel specialization
the inner loop unrolling is also specialized for different kernel sizes (e.g., 9 repeated code segments for 3×3 kernel, and 25 for 5×5 ) to eliminate the branch instruction overheads
Operation fusion is performed for Conv+Padding+ReLU+BN layers.
Experiments
Setup
- Datasets
- ImageNet
- Visual Wake Words (VWW) 视觉唤醒词
- Speech Commands (V2) 音频唤醒词
- (did not use cifar)
- Deployment
- 320kB SRAM / 1MB Flash
- 512kB SRAM / 2MB Flash
Large-Scale Image Recognition
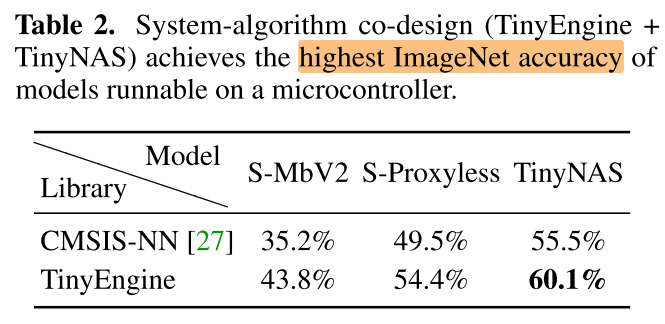
Co-design
Lower bit precision
Under the same memory constraints, 4-bit MCUNet outperforms 8-bit by 2.2% by fitting a larger model in the memory

Visual & Audio Wake Words
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=YvioBgtec4U&feature=youtu.be
Analysis
Search space optimization
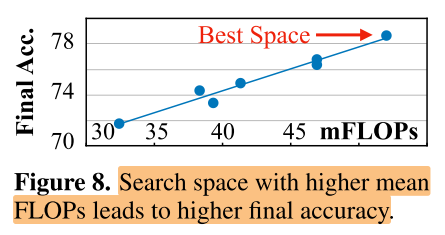
Sensitivity analysis on search space optimization
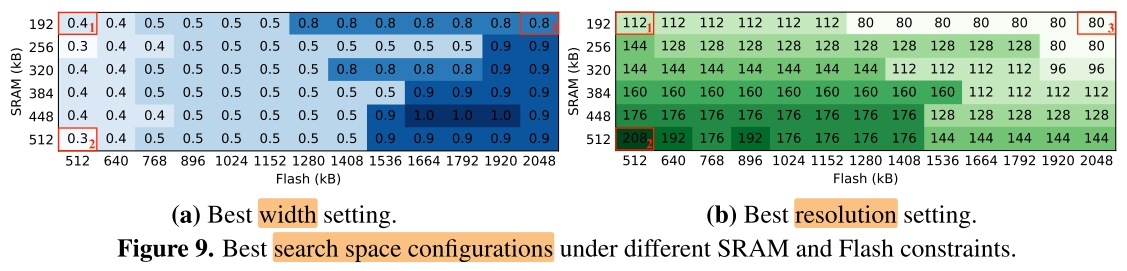
- x轴:Flash(硬盘,存储模型)512kB~2048kB
- y轴:SRAM(内存/显存,推理时存储 feature map)192kB~512kB
1-2: SRAM 增大,input 分辨率增加,但由于Flash的限制,模型参数不能增加,因此 width 没有增加
1-3: Flash 增大,模型参数可以增加,因此width增加,但 input 分辨率反而减少(由于模型宽度增大,卷积核变多,每层的 feature map 通道数也会增加,但由于 SRAM 不变,因此要减小 feature map 分辨率大小