LRU算法实现
介绍
LRU是Least Recently Used的缩写,即最近最少使用,是一种常用的页面置换算法,选择最近最久未使用的页面予以淘汰。该算法赋予每个页面一个访问字段,用来记录一个页面自上次被访问以来所经历的时间 t,当须淘汰一个页面时,选择现有页面中其 t 值最大的,即最近最少使用的页面予以淘汰。
如图(摘自百度百科)为LRU置换策略思想
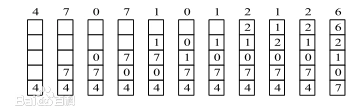
分析
1)加入缓存
当缓存未满时,先查找要缓存得数据是否已经存在,若存在,则将该数据移动到链表头部;若不存在,则直接将数据插入链表头部;
当缓存已满时,先查找要缓存得数据是否已经存在,若存在,则将该数据移动到链表头部;若不存在,则先删除链表尾部的数据,再将要缓存的数据插入链表头部;
2)获取缓存
每次获取时,总是从最近使用的缓存数据开始查找(即从链表头部向尾部反向查找)
实现
下面是用双向链表实现一个LRU缓存淘汰算法:
public class LRUTest { public static final int MAX_SIZE = 10; public static int size = 0; public static Node head = null; public static Node tail = null; /** * 用双向链表构建一个LRU缓存机制 * @param s */ public static void put(String s) { if (tail == null) { tail = new Node(s, null, null); head = tail; size++; return; } Node node = get(s); if (node == null) { if (size >= MAX_SIZE) { tail = tail.next; tail.pre = null; size--; } head.next = new Node(s, head, null); head = head.next; size++; return; } if (size > 1 && node != head) { if (node == tail) { tail = tail.next; tail.pre = null; } else { Node pre = node.pre; Node next = node.next; pre.next = next; next.pre = pre; } node.pre = head; node.next = null; head.next = node; head = head.next; return; } } public static Node get(String s) { Node k = head; while (k != null) { if (s.equals(k.value)) return k; k = k.pre; } return null; } } class Node { String value; Node pre; Node next; public Node(String value, Node pre, Node next) { this.value = value; this.pre = pre; this.next = next; } }