1.插入元素进入队列时,将元素push到stack1中。当有元素出队列时,先将所有元素插入到stack2中,然后进行出栈。出栈结束后,再将剩余元素放回stack1中。这个算法不是最优的。接下来介绍一个从剑指offer中看到的一种算法。
2
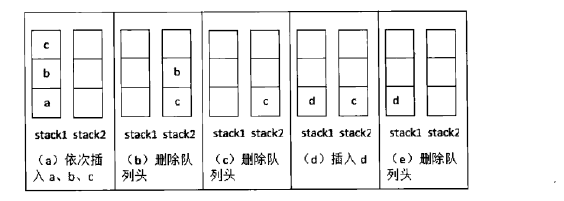
入队列:直接将元素插入stack1中。 出队列:如果stack2为空,就将stack1中的全部元素,压入stack2中。如果stack2还为空,就说明当前队列为空。如果stack2不为空,就弹出stack2栈顶元素。
import java.util.Stack;
public class Queue {
private Stack<Integer> stack1 = new Stack<Integer>();
private Stack<Integer> stack2 = new Stack<Integer>();
public void appendTail(int element){
stack1.push(element);
}
public int deleteHead(){
if(stack2.size() <= 0){
while(stack1.size() > 0){
int data = stack1.pop().intValue();
stack2.push(data);
}
}
if(stack2.size() == 0){
System.out.println("队列为空");
return -1;
}
int data = stack2.pop().intValue();
return data;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
Queue q = new Queue();
q.appendTail(1);
q.appendTail(2);
q.appendTail(3);
System.out.println(q.deleteHead());
System.out.println(q.deleteHead());
System.out.println(q.deleteHead());
//q.deleteHead();
}
}
/**思想:
*入队:直接将元素入栈1;
*出队:判断栈2是否为空,若为空,则将栈1中的元素全部pop,然后push到栈2,栈2出栈;若栈2不为空,则栈2直接出栈。
*/
import java.util.Stack;
public class Solution {
Stack<Integer> stack1 = new Stack<Integer>();
Stack<Integer> stack2 = new Stack<Integer>();
public void push(int node) {
stack1.push(node);
}
public int pop() {
if(stack2.isEmpty()) {
while(!stack1.isEmpty()) {
int temp = stack1.pop();
stack2.push(temp);
}
}
return stack2.pop();
}
}
扩展:用两队列1、2实现栈
思想:
入栈:直接将元素push到队列1;
出栈:判断队列1中是否只有一个元素,若是,则队列1出队pop;若不是,则将队列1中元素依次出队并入队到队列2,直到队列1中只剩一个元素,然后队列1出队pop,然后将队列2中全部元素出队并入队到队列1;
优化:为避免出栈时,最后将队列2中元素频繁出队并入队到队列1。根据出栈后,每次有一个队列为空, 可做以下调整:
入栈:先判断队列1是否为空,若不为空,则直接 将元素push到队列1 ;若队列1为空,则 将元素push到队列2;
出栈:先判断队列1是否为空。
若队列1 不为空,再判断队列1中是 否只有一个元素,若是,则队列1出队;若不是,则将队列1中元素依次出队并入队到队列2,直到队列1中只剩一个元素,然后队列1出队,此时队列1为空;
若队列1为空,再判断队列2中是否只有一个元素,若是,则队列2出队;若不是,则将队列2中元素依次出队并入队到队列1,直到队列2中只剩下一个元素,然后队列2出队,此时队列2为空。
import java.util.Stack; public class Solution { Stack<Integer> stack1 = new Stack<Integer>(); Stack<Integer> stack2 = new Stack<Integer>(); public void push(int node) { stack1.push(node); } public int pop() { if(stack2.isEmpty()) { while(!stack1.isEmpty()) { int temp = stack1.pop(); stack2.push(temp); } } return stack2.pop(); } }