AngularJS使用directive自定义指令
directive
除了AngularJS的内置指令,我们也可以通过.directive来创建自定义的指令。
app.directive("myDir",function(){
return {
template:"<h1>这是自定义指令</h1>"
}
})
命名
AngularJS要求自定义的Directive命名使用驼峰式语法。也就是从第二个单词开始,每个单词首字母大写,并且不用任何连接符号。
| 命名 | 使用 |
|---|---|
| dir | dir |
| myDir | my-dir |
| myDirArray | my-dir-array |
参数
restrict:String,
priority:Number,
terminal:Boolean,
template:String or Template Function,
templateUrl:String or Template Function,
replace:Boolean or String,
transclude:Boolean,
scope:Boolean or Object,
controller:String or function(scope, element, attrs, transclude, otherInjectables) { ... },
controllerAs:String,
require:String,
link: function(scope, iElement, iAttrs) { ... },
compile:function(tElement, tAttrs, transclude) {
return {
pre: function(scope, iElement, iAttrs, controller) { ... },
post: function(scope, iElement, iAttrs, controller) { ... }
}
return function postLink(...) { ... }
}
这里是Directive的所有参数,下面我们主要介绍一下常用的参数restrict,template,scope,link,compile
组合使用例子
restrict
restrict描述了我们怎么使用自定义指令,以上面自定义的myDir为例
| 参数 | 使用 |
|---|---|
| E(Element) | <my-dir></my-dir> |
| A(attribute) | <div my-dir></div> |
| C(class) | <div class="my-dir"></div> |
EAC可以组合使用
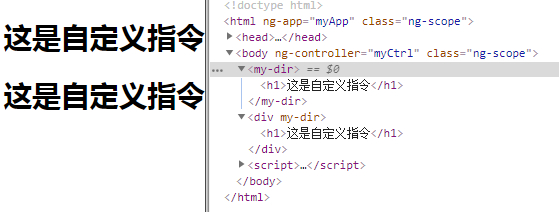
<body ng-controller="myCtrl">
<my-dir></my-dir>
<div my-dir></div>
<script>
angular.module('myApp', [])
.controller("myCtrl", function($scope) {})
.directive("myDir", function() {
return {
template: "<h1>这是自定义指令</h1>",
restrict: "EA"
}
});
</script>
</body>
scope
scope:为directive指定相关联的作用域
| 参数 | 使用 |
|---|---|
| false(默认值) | 将使用parent的scope;改变scope中的值,directive的值也会发生变化,反之亦如此 |
| true | 创建一个继承parent``scope的子scope ;改变parent``scope中的值,子scope会发生变化;改变子scope中的值,parent``scope不会发生变化 |
| {} | 创建一个独立的scope,可以使用 @ = &和parent``scope进行属性绑定;不继承parent``scope改变任何一方都不影响对方 |
false和true
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html ng-app ="myApp">
<head>
<meta charset="utf-8">
<script src="http://cdn.static.runoob.com/libs/angular.js/1.4.6/angular.min.js"></script>
<style>
body{
border: 5px solid #FF851B;
padding: 10px;
}
.info{
color:#0074D9;
}
.age{
color:#FF4136;
}
</style>
</head>
<body ng-controller="myCtrl">
<div><my-dire></my-dire></div>
<div class="my-dirc"></div>
<button ng-click="changeMyinfo()">changeInfo</button>
<script>
angular.module('myApp', [])
.controller("myCtrl", function($scope) {
$scope.myage = 16;
$scope.myInfo = {
name:"chenjy"
};
$scope.changeMyinfo = function(){
$scope.myage++;
$scope.myInfo.name += "_";
}
})
.directive("myDire", function() {
return {
template:"<h3>directive E</h3><div>my name:<span class='info'>{{myInfo.name}}</span>,my age:<span class='age'>{{myage}}</span></div>",
restrict:"E",
scope:false
};
}).directive("myDirc", function() {
return {
template:"<h3>directive C</h3><div>my name:<span class='info'>{{myInfo.name}}</span>,my age:<span class='age'>{{myage}}</span></div><div><input type='text' ng-model='myInfo.name'/><input type='text' ng-model='myage'/></div>",
restrict:"C",
scope:true
};
})
</script>
</body>
</html>
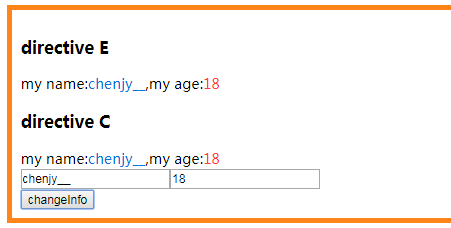
- 我们点击
button会发现directive E``directive C的值都会发生变化,
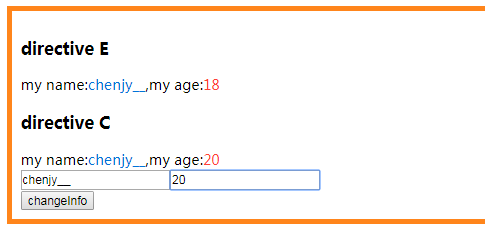
- 修改
age对应的input框只有directive C的age会发生变化
@ = &
What is the difference between '@' and '=' in directive scope in AngularJS?
scope为{}时,用三者的主要区别为
| type | describe |
|---|---|
| @ (@attr) | Text binding / one-way binding |
| = (=attr) | Direct model binding / two-way binding |
| & | Behaviour binding / Method binding |
@传递的是字符串不是对象
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="utf-8">
<script src="http://cdn.static.runoob.com/libs/angular.js/1.4.6/angular.min.js"></script>
<style>
.app{
border: 5px solid #FF851B;
padding: 10px;
}
.info{
color:#0074D9;
}
.age{
color:#FF4136;
}
</style>
</head>
<body ng-controller="myCtrl">
<div ng-app="App" ng-controller="Ctrl" class="app">
<div ng-repeat = "info in infoList">
<my-dir name="info.name" age="{{info.age}}" change-age="changeAge(info)"></my-dir>
</div>
</div>
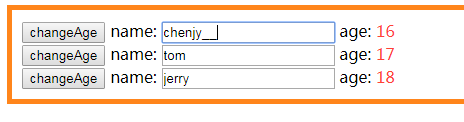
<script>
angular.module("App", []).controller("Ctrl", ["$scope","$log","$sce",function($scope,$log, $sce) {
$scope.infoList = [{
name:"chenjy",
age:16
},{
name:"tom",
age:17
},{
name:"jerry",
age:18
}];
$scope.changeAge = function(info){
info.age++;
}
$scope.showLog = function(name){
$log.info(name);
}
}]).directive("myDir", function() {
return {
template:"<div>"+
" <button ng-click='changeAge(info)'>changeAge</button> name:"+
" <input type='text' ng-model='name'/> age:"+
" <span class='age'>{{age}}</span>"+
"</div>",
restrict:"E",
scope:{
name:"=",
age:"@",
changeAge:"&"
}
};
});
</script>
</body>
</html>
//html
<my-dir new-name="info.name" naw-age="{{info.age}}" change-age="changeAge(info)"></my-dir>
//directive
scope:{
name:"=newName",
age:"@nawAge",
changeAge:"&"
}
两种写法是相同的
@也可以定义在link
.directive("myDir", function() {
return {
template:"<div>"+
" <button ng-click='changeAge(info)'>changeAge</button> name:"+
" <input type='text' ng-model='name'/> age:"+
" <span class='age'>{{age}}</span>"+
"</div>",
restrict:"E",
scope:{
name:"=",
/*age:"@",*/
changeAge:"&"
},
link:function(scope, iElement, iAttrs){
//scope.age = iAttrs.age; 这么写 只有在第一次加载的时候等于`scope age`但是不会随着changeAge事件更新
iAttrs.$observe('age', function(value) {
scope.age = value;
})
}
};
});
- 如果用使用&绑定函数传参数需要json 否则会报错
TypeError: Cannot use 'in' operator to search for 'editWebsite' in 1
template:"<div>"+
" <button ng-click='changeAge({age:age})'>changeAge</button> name:"+
" <input type='text' ng-model='name'/> age:"+
" <span class='age'>{{age}}</span>"+
"</div>"
compile、link
在使用前我们先简单了解一下下面两个阶段-编译和链接阶段
第一个阶段是编译阶段,AngularJS会递归的遍历DOM,并从JavaScript中的指令定义知道需要执行的操作。
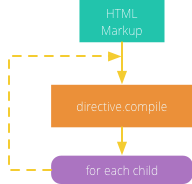
如图(from stackoverflow)所示原始DOM模板作为函数的参数传给compile编译函数,编译后会返回它的实例。我们有机会在它被返回前对DOM模板进行操作。
1.1 我们以ng-repeat为例,HTML中生成的重复元素就是DOM模板的实例。实例有多个但是模板元素只有一个。
<body ng-controller="myCtrl">
<div ng-app="App" ng-controller="Ctrl" class="app">
<div ng-repeat="info in infoList">
<my-dir info ="info"></my-dir>
</div>
<script>
angular.module("App", []).controller("Ctrl", ["$scope",function($scope) {
$scope.infoList = [{
name:"chenjy",
age:16
},{
name:"tom",
age:17
},{
name:"jerry",
age:18
}];
}]).directive("myDir", function() {
return {
template:"<span>{{info.name}}:</span>",
restrict:"E",
scope:{
info:"="
},
compile:function(tELe ,tAttrs,transcludeFn){
// 对原始DOM模板进行操作
tELe.append(angular.element("<span class='age'>{{info.age}}</span>"));
return{
pre:function(scope, iElement, iAttrs, controller){},
post:function(scope, iElement, iAttrs, controller){}
}
}
};
});
</script>
</body>

第二个阶段是链接阶段,链接函数link将模板与作用域链接起来。负责设置事件监听器、监视数据变化和实时的DOM操作。
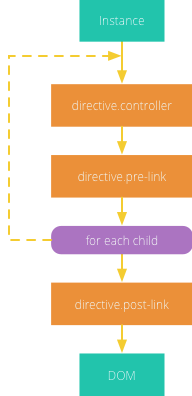
-
如果定义了编译函数
compile它会返回pre-link和post-link函数 -
如果只定义了链接函数
link,则会被视为post-link
If you create a directive that only has a link function, AngularJS treats the function as a post-link function. Hence the reason to discuss it here first.
post-link会和前面DOM遍历相反的顺序调用。这个顺序保证所有子元素的post-link在父元素post-link运行时都已经被执行了。
pre-link是AngularJS提供了一个额外的钩子。它可以让你在子元素的post-link函数之前运行你的代码。
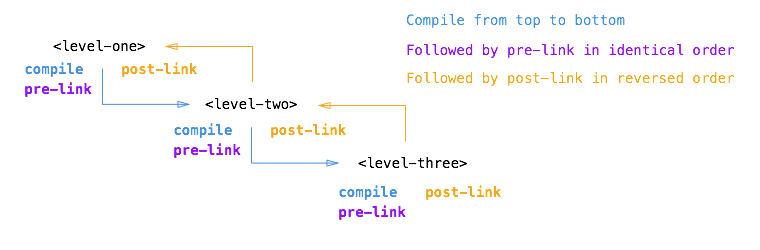
post-link被认为是最安全的,因为此时所有子元素都已经被编译compile并且所有子元素的pre-link和post-link都已经执行结束。
所以这里是自定义指令最常用的地方,大多数情况下我们只需要编写link函数即可
.directive("myDir", function() {
return {
template:"<span>{{info.name}}:</span>"+
"<span class='age'>{{info.age}}</span>",
restrict:"E",
compile:function(tELe ,tAttrs,transcludeFn){
return{
// 子元素被链接之前执行
pre:function(scope, iElement, iAttrs, controller){},
// 子元素被链接之后执行
post:function(scope, iElement, iAttrs, controller){
// 绑定DOM事件
iElement.on('click',function(){
scope.$apply(function(){
scope.infoList[0].name += "_";
scope.infoList[0].age ++;
});
});
}
}
}
};
});
等于下面这种写法
.directive("myDir", function() {
return {
template: "<span>{{info.name}}:</span>" +
"<span class='age'>{{info.age}}</span>",
restrict: "E",
link: function(scope, iElement, iAttrs) {
iElement.on('click', function() {
scope.$apply(function() {
scope.infoList[0].name += "_";
scope.infoList[0].age++;
});
});
}
};
});

<body ng-controller="myCtrl">
<div ng-app="App" ng-controller="Ctrl" class="app">
<input type="text" focus-me="{{shouldBeFocus}}">
</div>
<script>
angular.module("App", []).controller("Ctrl", function($scope) {
$scope.shouldBeFocus = true;
}).directive('focusMe', function() {
return {
link: function(scope, element, iAttrs) {
iAttrs.$observe("focusMe", function(value) {
element[0].focus();
});
element.bind("blur", function() {
scope.$apply(function() {
scope.shouldBeFocus = !scope.shouldBeFocus;
});
});
}
};
});
</script>
</body>