ASP.NET Core实现OAuth2的AuthorizationCode模式
授权服务器
Program.cs --> Main方法中:需要调用UseUrls设置IdentityServer4授权服务的IP地址
1 var host = new WebHostBuilder()
2 .UseKestrel()
3 //IdentityServer4的使用需要配置UseUrls
4 .UseUrls("http://localhost:5114")
5 .UseContentRoot(Directory.GetCurrentDirectory())
6 .UseIISIntegration()
7 .UseStartup<Startup>()
8 .Build();
Startup.cs -->ConfigureServices方法中的配置:
1 //RSA:证书长度2048以上,否则抛异常 2 //配置AccessToken的加密证书 3 var rsa = new RSACryptoServiceProvider(); 4 //从配置文件获取加密证书 5 rsa.ImportCspBlob(Convert.FromBase64String(Configuration["SigningCredential"])); 6 //配置IdentityServer4 7 services.AddSingleton<IClientStore, MyClientStore>(); //注入IClientStore的实现,可用于运行时校验Client 8 services.AddSingleton<IScopeStore, MyScopeStore>(); //注入IScopeStore的实现,可用于运行时校验Scope 9 //注入IPersistedGrantStore的实现,用于存储AuthorizationCode和RefreshToken等等,默认实现是存储在内存中, 10 //如果服务重启那么这些数据就会被清空了,因此可实现IPersistedGrantStore将这些数据写入到数据库或者NoSql(Redis)中 11 services.AddSingleton<IPersistedGrantStore, MyPersistedGrantStore>(); 12 services.AddIdentityServer() 13 .AddSigningCredential(new RsaSecurityKey(rsa)); 14 //.AddTemporarySigningCredential() //生成临时的加密证书,每次重启服务都会重新生成 15 //.AddInMemoryScopes(Config.GetScopes()) //将Scopes设置到内存中 16 //.AddInMemoryClients(Config.GetClients()) //将Clients设置到内存中
Startup.cs --> Configure方法中的配置:
1 //使用IdentityServer4
2 app.UseIdentityServer();
3 //使用Cookie模块
4 app.UseCookieAuthentication(new CookieAuthenticationOptions
5 {
6 AuthenticationScheme = IdentityServerConstants.ExternalCookieAuthenticationScheme,
7 AutomaticAuthenticate = false,
8 AutomaticChallenge = false
9 });
Client配置
方式一:
.AddInMemoryClients(Config.GetClients()) //将Clients设置到内存中,IdentityServer4从中获取进行验证
方式二(推荐):
services.AddSingleton<IClientStore, MyClientStore>(); //注入IClientStore的实现,用于运行时获取和校验Client
IClientStore的实现
1 public class MyClientStore : IClientStore
2 {
3 readonly Dictionary<string, Client> _clients;
4 readonly IScopeStore _scopes;
5 public MyClientStore(IScopeStore scopes)
6 {
7 _scopes = scopes;
8 _clients = new Dictionary<string, Client>()
9 {
10 {
11 "auth_clientid",
12 new Client
13 {
14 ClientId = "auth_clientid",
15 ClientName = "AuthorizationCode Clientid",
16 AllowedGrantTypes = new string[] { GrantType.AuthorizationCode }, //允许AuthorizationCode模式
17 ClientSecrets =
18 {
19 new Secret("secret".Sha256())
20 },
21 RedirectUris = { "http://localhost:6321/Home/AuthCode" },
22 PostLogoutRedirectUris = { "http://localhost:6321/" },
23 //AccessTokenLifetime = 3600, //AccessToken过期时间, in seconds (defaults to 3600 seconds / 1 hour)
24 //AuthorizationCodeLifetime = 300, //设置AuthorizationCode的有效时间,in seconds (defaults to 300 seconds / 5 minutes)
25 //AbsoluteRefreshTokenLifetime = 2592000, //RefreshToken的最大过期时间,in seconds. Defaults to 2592000 seconds / 30 day
26 AllowedScopes = (from l in _scopes.GetEnabledScopesAsync(true).Result select l.Name).ToList(),
27 }
28 }
29 };
30 }
31
32 public Task<Client> FindClientByIdAsync(string clientId)
33 {
34 Client client;
35 _clients.TryGetValue(clientId, out client);
36 return Task.FromResult(client);
37 }
38 }
Scope配置
方式一:
.AddInMemoryScopes(Config.GetScopes()) //将Scopes设置到内存中,IdentityServer4从中获取进行验证
方式二(推荐):
services.AddSingleton<IScopeStore, MyScopeStore>(); //注入IScopeStore的实现,用于运行时获取和校验Scope
IScopeStore的实现
1 public class MyScopeStore : IScopeStore
2 {
3 readonly static Dictionary<string, Scope> _scopes = new Dictionary<string, Scope>()
4 {
5 {
6 "api1",
7 new Scope
8 {
9 Name = "api1",
10 DisplayName = "api1",
11 Description = "My API",
12 }
13 },
14 {
15 //RefreshToken的Scope
16 StandardScopes.OfflineAccess.Name,
17 StandardScopes.OfflineAccess
18 },
19 };
20
21 public Task<IEnumerable<Scope>> FindScopesAsync(IEnumerable<string> scopeNames)
22 {
23 List<Scope> scopes = new List<Scope>();
24 if (scopeNames != null)
25 {
26 Scope sc;
27 foreach (var sname in scopeNames)
28 {
29 if (_scopes.TryGetValue(sname, out sc))
30 {
31 scopes.Add(sc);
32 }
33 else
34 {
35 break;
36 }
37 }
38 }
39 //返回值scopes不能为null
40 return Task.FromResult<IEnumerable<Scope>>(scopes);
41 }
42
43 public Task<IEnumerable<Scope>> GetScopesAsync(bool publicOnly = true)
44 {
45 //publicOnly为true:获取public的scope;为false:获取所有的scope
46 //这里不做区分
47 return Task.FromResult<IEnumerable<Scope>>(_scopes.Values);
48 }
49 }
资源服务器
资源服务器的配置在上一篇中已介绍(http://www.cnblogs.com/skig/p/6079457.html ),详情也可参考源代码。
测试
AuthorizationCode模式的流程图(来自:https://tools.ietf.org/html/rfc6749):

流程实现
步骤A
第三方客户端页面简单实现:
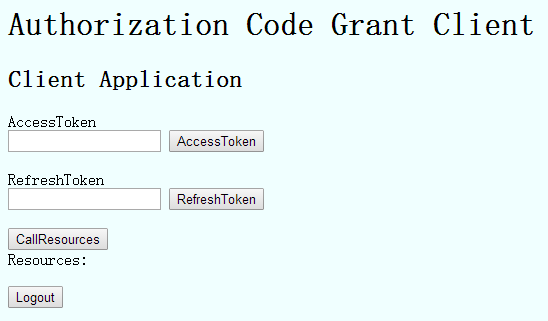
点击AccessToken按钮进行访问授权服务器,就是流程图中步骤A:
1 //访问授权服务器 2 return Redirect(OAuthConstants.AuthorizationServerBaseAddress + OAuthConstants.AuthorizePath + "?" 3 + "response_type=code" 4 + "&client_id=" + OAuthConstants.Clientid 5 + "&redirect_uri=" + OAuthConstants.AuthorizeCodeCallBackPath 6 + "&scope=" + OAuthConstants.Scopes 7 + "&state=" + OAuthConstants.State);
步骤B
授权服务器接收到请求后,会判断用户是否已经登陆,如果未登陆那么跳转到登陆页面(如果已经登陆,登陆的一些相关信息会存储在cookie中):

1 /// <summary>
2 /// 登陆页面
3 /// </summary>
4 [HttpGet]
5 public async Task<IActionResult> Login(string returnUrl)
6 {
7 var context = await _interaction.GetAuthorizationContextAsync(returnUrl);
8 var vm = BuildLoginViewModel(returnUrl, context);
9 return View(vm);
10 }
11
12 /// <summary>
13 /// 登陆账号验证
14 /// </summary>
15 [HttpPost]
16 [ValidateAntiForgeryToken]
17 public async Task<IActionResult> Login(LoginInputModel model)
18 {
19 if (ModelState.IsValid)
20 {
21 //账号密码验证
22 if (model.Username == "admin" && model.Password == "123456")
23 {
24 AuthenticationProperties props = null;
25 //判断是否 记住登陆
26 if (model.RememberLogin)
27 {
28 props = new AuthenticationProperties
29 {
30 IsPersistent = true,
31 ExpiresUtc = DateTimeOffset.UtcNow.AddMonths(1)
32 };
33 };
34 //参数一:Subject,可在资源服务器中获取到,资源服务器通过User.Claims.Where(l => l.Type == "sub").FirstOrDefault();获取
35 //参数二:账号
36 await HttpContext.Authentication.SignInAsync("admin", "admin", props);
37 //验证ReturnUrl,ReturnUrl为重定向到授权页面
38 if (_interaction.IsValidReturnUrl(model.ReturnUrl))
39 {
40 return Redirect(model.ReturnUrl);
41 }
42 return Redirect("~/");
43 }
44 ModelState.AddModelError("", "Invalid username or password.");
45 }
46 //生成错误信息的LoginViewModel
47 var vm = await BuildLoginViewModelAsync(model);
48 return View(vm);
49 }
登陆成功后,重定向到授权页面,询问用户是否授权,就是流程图的步骤B了:
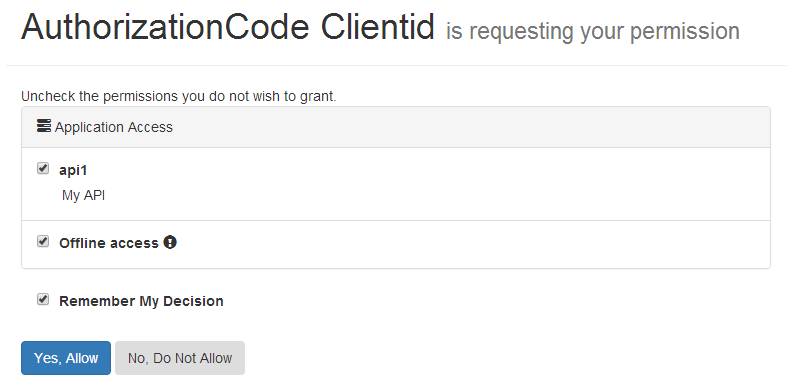
1 /// <summary>
2 /// 显示用户可授予的权限
3 /// </summary>
4 /// <param name="returnUrl"></param>
5 /// <returns></returns>
6 [HttpGet]
7 public async Task<IActionResult> Index(string returnUrl)
8 {
9 var vm = await BuildViewModelAsync(returnUrl);
10 if (vm != null)
11 {
12 return View("Index", vm);
13 }
14
15 return View("Error", new ErrorViewModel
16 {
17 Error = new ErrorMessage { Error = "Invalid Request" },
18 });
19 }
步骤C
授权成功,重定向到redirect_uri(步骤A传递的)所指定的地址(第三方端),并且会把Authorization Code也设置到url的参数code中:
1 /// <summary>
2 /// 用户授权验证
3 /// </summary>
4 [HttpPost]
5 [ValidateAntiForgeryToken]
6 public async Task<IActionResult> Index(ConsentInputModel model)
7 {
8 //解析returnUrl
9 var request = await _interaction.GetAuthorizationContextAsync(model.ReturnUrl);
10 if (request != null && model != null)
11 {
12 if (ModelState.IsValid)
13 {
14 ConsentResponse response = null;
15 //用户不同意授权
16 if (model.Button == "no")
17 {
18 response = ConsentResponse.Denied;
19 }
20 //用户同意授权
21 else if (model.Button == "yes")
22 {
23 //设置已选择授权的Scopes
24 if (model.ScopesConsented != null && model.ScopesConsented.Any())
25 {
26 response = new ConsentResponse
27 {
28 RememberConsent = model.RememberConsent,
29 ScopesConsented = model.ScopesConsented
30 };
31 }
32 else
33 {
34 ModelState.AddModelError("", "You must pick at least one permission.");
35 }
36 }
37 else
38 {
39 ModelState.AddModelError("", "Invalid Selection");
40 }
41 if (response != null)
42 {
43 //将授权的结果设置到identityserver中
44 await _interaction.GrantConsentAsync(request, response);
45 //授权成功重定向
46 return Redirect(model.ReturnUrl);
47 }
48 }
49 //有错误,重新授权
50 var vm = await BuildViewModelAsync(model.ReturnUrl, model);
51 if (vm != null)
52 {
53 return View(vm);
54 }
55 }
56 return View("Error", new ErrorViewModel
57 {
58 Error = new ErrorMessage { Error = "Invalid Request" },
59 });
60 }
步骤D
授权成功后重定向到指定的第三方端(步骤A所指定的redirect_uri),然后这个重定向的地址中去实现获取AccessToken(就是由第三方端实现):
1 public IActionResult AuthCode(AuthCodeModel model)
2 {
3 GrantClientViewModel vmodel = new GrantClientViewModel();
4 if (model.state == OAuthConstants.State)
5 {
6 //通过Authorization Code获取AccessToken
7 var client = new HttpClientHepler(OAuthConstants.AuthorizationServerBaseAddress + OAuthConstants.TokenPath);
8 client.PostAsync(null,
9 "grant_type=" + "authorization_code" +
10 "&code=" + model.code + //Authorization Code
11 "&redirect_uri=" + OAuthConstants.AuthorizeCodeCallBackPath +
12 "&client_id=" + OAuthConstants.Clientid +
13 "&client_secret=" + OAuthConstants.Secret,
14 hd => hd.ContentType = new System.Net.Http.Headers.MediaTypeHeaderValue("application/x-www-form-urlencoded"),
15 rtnVal =>
16 {
17 var jsonVal = JsonConvert.DeserializeObject<dynamic>(rtnVal);
18 vmodel.AccessToken = jsonVal.access_token;
19 vmodel.RefreshToken = jsonVal.refresh_token;
20 },
21 fault => _logger.LogError("Get AccessToken Error: " + fault.ReasonPhrase),
22 ex => _logger.LogError("Get AccessToken Error: " + ex)).Wait();
23 }
24
25 return Redirect("~/Home/Index?"
26 + nameof(vmodel.AccessToken) + "=" + vmodel.AccessToken + "&"
27 + nameof(vmodel.RefreshToken) + "=" + vmodel.RefreshToken);
28 }
步骤E
授权服务器对步骤D请求传递的Authorization Code进行验证,验证成功生成AccessToken并返回:
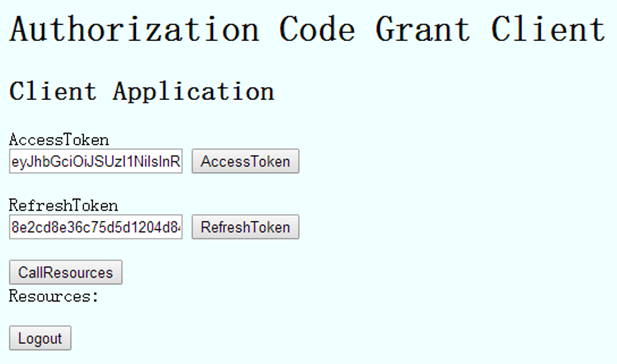
其中,点击RefreshToken进行刷新AccessToken:
1 //刷新AccessToken
2 var client = new HttpClientHepler(OAuthConstants.AuthorizationServerBaseAddress + OAuthConstants.TokenPath);
3 client.PostAsync(null,
4 "grant_type=" + "refresh_token" +
5 "&client_id=" + OAuthConstants.Clientid +
6 "&client_secret=" + OAuthConstants.Secret +
7 "&refresh_token=" + model.RefreshToken,
8 hd => hd.ContentType = new System.Net.Http.Headers.MediaTypeHeaderValue("application/x-www-form-urlencoded"),
9 rtnVal =>
10 {
11 var jsonVal = JsonConvert.DeserializeObject<dynamic>(rtnVal);
12 vmodel.AccessToken = jsonVal.access_token;
13 vmodel.RefreshToken = jsonVal.refresh_token;
14 },
15 fault => _logger.LogError("RefreshToken Error: " + fault.ReasonPhrase),
16 ex => _logger.LogError("RefreshToken Error: " + ex)).Wait();
点击CallResources访问资源服务器:
1 //访问资源服务
2 var client = new HttpClientHepler(OAuthConstants.ResourceServerBaseAddress + OAuthConstants.ResourcesPath);
3 client.GetAsync(null,
4 hd => hd.Add("Authorization", "Bearer " + model.AccessToken),
5 rtnVal => vmodel.Resources = rtnVal,
6 fault => _logger.LogError("CallResources Error: " + fault.ReasonPhrase),
7 ex => _logger.LogError("CallResources Error: " + ex)).Wait();
点击Logout为注销登陆:
1 //访问授权服务器,注销登陆 2 return Redirect(OAuthConstants.AuthorizationServerBaseAddress + OAuthConstants.LogoutPath + "?" 3 + "logoutId=" + OAuthConstants.Clientid);
授权服务器的注销实现代码:
1 /// <summary>
2 /// 注销登陆页面(因为账号的一些相关信息会存储在cookie中的)
3 /// </summary>
4 [HttpGet]
5 public async Task<IActionResult> Logout(string logoutId)
6 {
7 if (User.Identity.IsAuthenticated == false)
8 {
9 //如果用户并未授权过,那么返回
10 return await Logout(new LogoutViewModel { LogoutId = logoutId });
11 }
12 //显示注销提示, 这可以防止攻击, 如果用户签署了另一个恶意网页
13 var vm = new LogoutViewModel
14 {
15 LogoutId = logoutId
16 };
17 return View(vm);
18 }
19
20 /// <summary>
21 /// 处理注销登陆
22 /// </summary>
23 [HttpPost]
24 [ValidateAntiForgeryToken]
25 public async Task<IActionResult> Logout(LogoutViewModel model)
26 {
27 //清除Cookie中的授权信息
28 await HttpContext.Authentication.SignOutAsync();
29 //设置User使之呈现为匿名用户
30 HttpContext.User = new ClaimsPrincipal(new ClaimsIdentity());
31 Client logout = null;
32 if (model != null && !string.IsNullOrEmpty(model.LogoutId))
33 {
34 //获取Logout的相关信息
35 logout = await _clientStore.FindClientByIdAsync(model.LogoutId);
36 }
37 var vm = new LoggedOutViewModel
38 {
39 PostLogoutRedirectUri = logout?.PostLogoutRedirectUris?.FirstOrDefault(),
40 ClientName = logout?.ClientName,
41 };
42 return View("LoggedOut", vm);
43 }
