=============================================================================
=============================================================================
涉及到的知识点有:
项目实战:做一个电子词典,快易通电子词典。
方案零:固定字典词条数目。(出现问题:多了的词条数解决不了,少了的词条数浪费内存。)
方案一:读2次文件,第一次读文件得到文件的词条数(每个循环读两行数据),第二次打开文件后根据文件实际的词条数来分配堆内存。
方案二:边读边随时增加struct dict在堆中的数量。
方案三:链表也可以实现。(基础班没有讲到哦!)
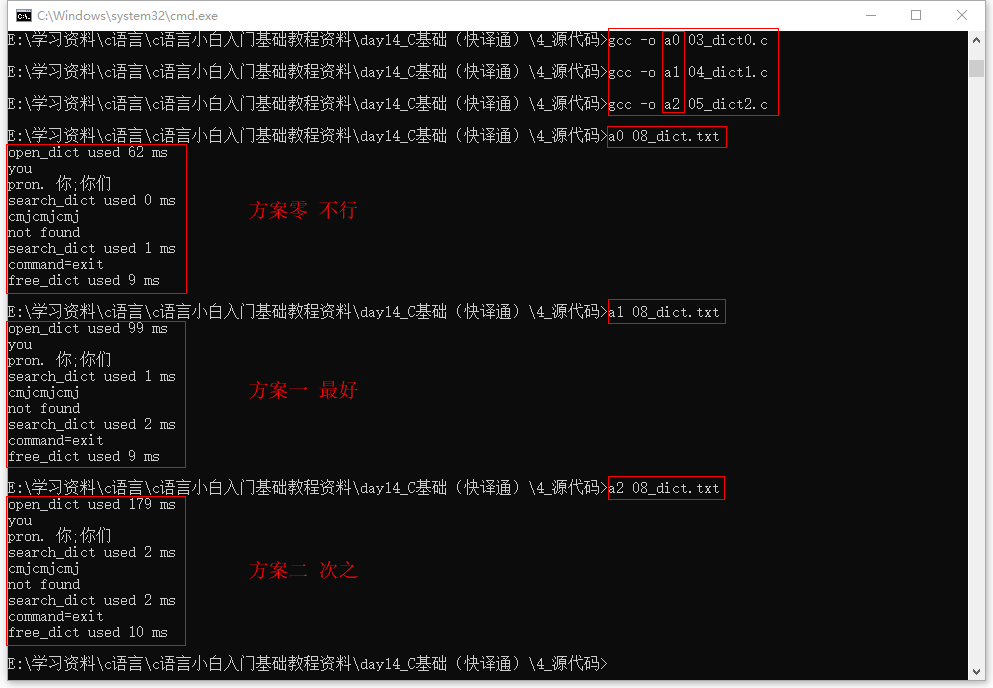
四种实现方案的效率比较
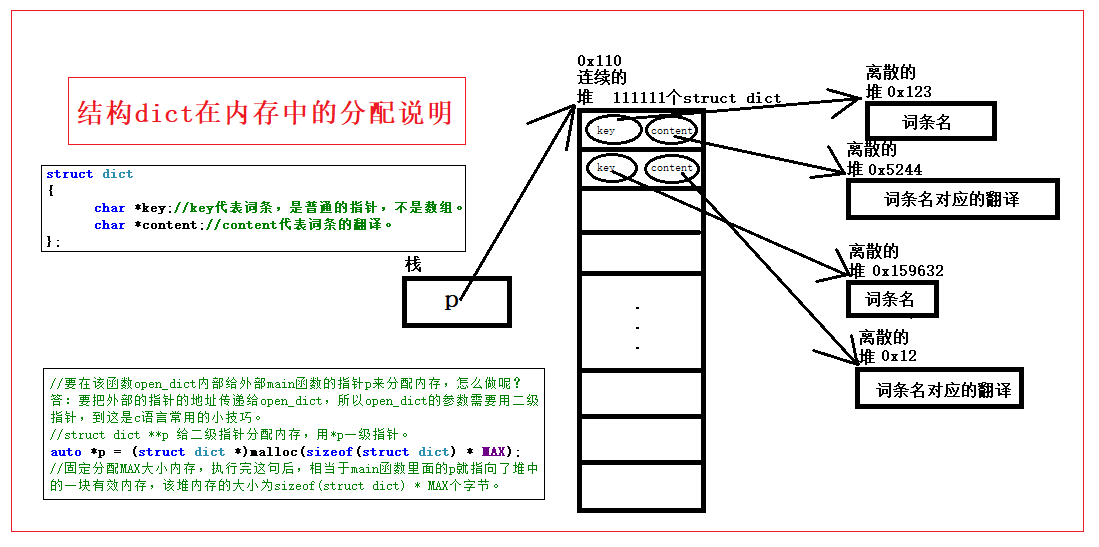
结构dict在内存中的分配说明图
=============================================================================
=============================================================================
08_dict.txt是个文本文件,汉字的格式是GBK格式的。
第一行
#a 代表一个词条。
第二行
Trans:art. 一;字母A 代表词条对应的翻译。
第三行
#a.m.
第四行
Trans:n. 上午
......
--------------------------------------
方案零:固定字典词条数目。
vs2017下示例代码:
1 #define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS 2 #include <stdio.h> 3 #include <stdlib.h> 4 #include <string.h> 5 #include <time.h> 6 7 #define MAX 111111 //最大记录数 8 9 struct dict 10 { 11 char *key;//key代表词条,是普通的指针,不是数组,目前还不是字符串,只是char类型的指针变量。 12 char *content;//content代表词条的翻译,是普通的指针,不是数组,目前还不是字符串,只是char类型的指针变量。 13 }; 14 15 16 void format_string(char *str)//去掉字符串结尾的回车和空格字符 17 { 18 size_t i; 19 for(i = strlen(str) - 1; i >= 0; i--)//从右往左遍历字符串 20 { 21 if (str[i] != ' ' && str[i] != ' ' && str[i] != ' ') 22 { 23 str[i + 1] = '�'; 24 break; 25 } 26 } 27 } 28 29 //打开字典文件,并读取文件内容 30 int open_dict(struct dict **p, const char *dict_filename) 31 { 32 FILE *pfile = fopen(dict_filename, "r"); 33 if (pfile == NULL) 34 return 0;//打开文件失败,函数返回0。说明打开的文件不存在。目的是:为了避免乱操作、误操作,导致程序崩溃,这也是程序的健壮性。 35 36 //要在该函数open_dict内部给外部main函数的指针p来分配内存,怎么做呢?答:要把外部的指针的地址传递给open_dict,所以open_dict的参数需要用二级指针,到这是c语言常用的小技巧。 37 //struct dict **p 给二级指针分配内存,用*p一级指针。 38 *p = (struct dict *)malloc(sizeof(struct dict) * MAX);//固定分配MAX大小内存,执行完这句后,相当于main函数里面的p就指向了堆中的一块有效内存,该堆内存的大小为sizeof(struct dict) * MAX个字节。 39 memset(*p, 0, sizeof(struct dict) * MAX);//将分配到的堆内存初始化为0 40 41 char buf[1024] = { 0 }; 42 size_t len = 0; 43 int i = 0;//计数器 44 while (!feof(pfile))//循环读取文件,直到文件末尾 45 { 46 memset(buf, 0, sizeof(buf));//读之前先把缓存buf清零(清空)。 47 fgets(buf, sizeof(buf), pfile);//从文件读取文件一行 48 len = strlen(buf);//得到读取到的字符串长度 49 if (len > 0)//如果读到的这一行不是空行,就执行以下代码。 50 { 51 //*p相当于堆内存中的一个数组名。(*p)[i]的意思是:数组里面下标为i的结构变量。(*p)[i].key结构变量的成员key。 52 (*p)[i].key = (char *)malloc(len);//根据字符串长度分配相应的堆内存 53 memset((*p)[i].key, 0, len);//好习惯:任何分配出来的一块内存后,都要先把它清空(置零)后再使用。 54 format_string(buf);//去掉字符串结尾的空格和回车 55 strcpy((*p)[i].key, &buf[1]);//将读取到的内容拷贝到key中 56 //free((*p)[i].key);//有专门的释放堆内存的函数。 57 } 58 59 memset(buf, 0, sizeof(buf)); 60 fgets(buf, sizeof(buf), pfile); 61 len = strlen(buf); 62 if (len > 0) 63 { 64 (*p)[i].content = (char *)malloc(len); 65 memset((*p)[i].content, 0, len); 66 format_string(buf); 67 strcpy((*p)[i].content, &buf[6]); 68 //free((*p)[i].key);//有专门的释放堆内存的函数。 69 } 70 71 i++;//计数器加1 72 } 73 fclose(pfile);//关闭字典文件 74 75 return i;//返回读取到的字典词条数 76 } 77 78 //根据关键字key,在字典中查找内容 79 int search_dict(const struct dict *p, int size, const char *key, char *content) 80 { 81 int i = 0; 82 for (i = 0; i < size; i++)//遍历字典 83 { 84 //容错代码。 85 if ((p[i].key == NULL) || (p[i].content == NULL)) 86 continue; 87 88 if (strcmp(p[i].key, key) == 0) 89 { 90 strcpy(content, p[i].content); 91 return 1;//找到符合条件记录,返回1 92 } 93 } 94 return 0;//没有找到符合条件记录,返回0 95 } 96 97 //释放内存 98 void free_dict(struct dict *p, int size) 99 { 100 int i = 0; 101 for (i = 0; i < size; i++)//循环释放key与content成员内存 102 { 103 if (p[i].key) 104 free(p[i].key); 105 if (p[i].content) 106 free(p[i].content); 107 } 108 free(p);//释放p内存 109 } 110 111 int main(int argc, char *args[]) 112 { 113 if (argc < 2) 114 { 115 printf("usage: %s dict-filename ", args[0]); 116 return 0;//参数不足,程序退出 117 } 118 long start_ms = 0;//记录函数执行的开始时间 119 long end_ms = 0;//记录函数执行的结束时间 120 auto struct dict *p = NULL; 121 start_ms = clock();//得到系统当前时间,单位是ms。是long类型的一个值。 122 123 //要通过在函数open_dict的内部给main函数里面的指针p分配内存,需要传递指针p的地址给该函数open_dict,这是c语言里面一个最基本的技巧。 124 int dict_size = open_dict(&p, args[1]);//根据命令行第一个参数作为字典文件名,打开字典文件 125 if (dict_size == 0) 126 return 0;//打开字典文件失败,程序退出,表示要打开的文件不存在。目的是:为了避免乱操作、误操作,导致程序崩溃,这也是程序的健壮性。 127 128 end_ms = clock();//得到系统当前时间,单位是ms。是long类型的一个值。 129 printf("open_dict used %ld ms ", end_ms - start_ms);//打印函数执行时间,单位:毫秒,是long类型的一个值。 130 131 char key[1024]; 132 char content[1024]; 133 while (1) 134 { 135 memset(key, 0, sizeof(key)); 136 memset(content, 0, sizeof(content)); 137 fgets(key, sizeof(key), stdin);//从键盘得到用户输入 138 format_string(key);//去掉字符串结尾的空格和回车 139 if (strncmp(key, "command=exit", 12) == 0) 140 break; 141 142 start_ms = clock();//得到系统当前时间,单位是ms。是long类型的一个值。 143 //dict_size是读取到的字典词条数。 144 if (search_dict(p, dict_size, key, content))//根据用户输入,在字典中检索 145 { 146 printf("%s ", content); 147 } else 148 { 149 printf("not found "); 150 } 151 end_ms = clock();//得到系统当前时间,单位是ms。是long类型的一个值。 152 printf("search_dict used %ld ms ", end_ms - start_ms);//打印函数执行时间,单位:毫秒 153 } 154 155 start_ms = clock(); 156 free_dict(p, dict_size); 157 end_ms = clock(); 158 printf("free_dict used %ld ms ", end_ms - start_ms);//打印函数执行时间,单位:毫秒 159 return 0; 160 }
-----------------------------------------------------------------------------
方案一:读2次文件,第一次读文件得到文件的词条数(每个循环读两行数据),第二次打开文件后根据文件实际的词条数来分配堆内存。
vs2017下示例核心代码:
...... ...... //第一次读文件得到文件的词条数(每个循环读两行数据)。 int get_dict_size(FILE *pfile)//得到字典文件中词条总数 { if (pfile == NULL) return 0; int i = 0; char buf[2048]; while (!feof(pfile)) { fgets(buf, sizeof(buf), pfile); fgets(buf, sizeof(buf), pfile); i++;//读取两行后,计数器加1 } return i; //执行过该函数后,指针到了文件的末尾了,为了能再次从文件中读出内容,需要在main函数的循环读取文件之前将指针设置在文件的开始位置。如下: //fseek(pfile, 0L, SEEK_SET);//设置读取位置为字典文件的开始位置。 } //打开字典文件,并读取文件内容 int open_dict(struct dict **p, const char *dict_filename) { FILE *pfile = fopen(dict_filename, "r"); if (pfile == NULL) return 0;//打开文件失败,函数返回 int dict_size = get_dict_size(pfile);//得到字典文件中词条总数 if (dict_size == 0) return 0; //第二次打开文件后根据文件实际的词条数来分配堆内存。 *p = (struct dict *)malloc(sizeof(struct dict) * dict_size);//根据字典文件词条总数分配内存 memset(*p, 0, sizeof(struct dict) * dict_size);//将分配内存初始化为0 char buf[2048] = { 0 }; size_t len = 0; int i = 0; fseek(pfile, 0L, SEEK_SET);//设置读取位置为字典文件的开始位置 while (!feof(pfile))//循环读取文件,直到文件末尾 { memset(buf, 0, sizeof(buf)); fgets(buf, sizeof(buf), pfile);//读取文件一行 len = strlen(buf);//得到读取到字符串长度 if (len > 0) { (*p)[i].key = (char *)malloc(len);//根据字符串长度分配内存 memset((*p)[i].key, 0, len); format_string(buf);//去掉字符串结尾的空格和回车 strcpy((*p)[i].key, &buf[1]);//将读取到的内容拷贝到key中 } memset(buf, 0, sizeof(buf)); fgets(buf, sizeof(buf), pfile); len = strlen(buf); if (len > 0) { (*p)[i].content = (char *)malloc(len); memset((*p)[i].content, 0, len); strcpy((*p)[i].content, &buf[6]); } i++; } fclose(pfile);//关闭字典文件 return i;//返回读取到的字典词条数 } ...... ......
-----------------------------------------------------------------------------
方案二:边读边随时增加struct dict在堆中的数量。
vs2017下示例核心代码:
...... ...... //打开字典文件,并读取文件内容 int open_dict(struct dict **p, const char *dict_filename) { FILE *pfile = fopen(dict_filename, "r"); if (pfile == NULL) return 0;//打开文件失败,函数返回 //一开始就分配一个结构体struct dict的堆内存。读完一个词条后再读的时候我再加一个词条的内存。 *p = (struct dict *)malloc(sizeof(struct dict)); memset(*p, 0, sizeof(struct dict)); char buf[2048] = { 0 }; size_t len = 0; int i = 0; while (!feof(pfile))//循环读取文件,直到文件末尾 { memset(buf, 0, sizeof(buf)); fgets(buf, sizeof(buf), pfile);//读取文件一行 len = strlen(buf);//得到读取到字符串长度 if (len > 0) { (*p)[i].key = (char *)malloc(len);//根据字符串长度分配内存 memset((*p)[i].key, 0, len); format_string(buf);//去掉字符串结尾的空格和回车 strcpy((*p)[i].key, &buf[1]);//将读取到的内容拷贝到key中 } memset(buf, 0, sizeof(buf)); fgets(buf, sizeof(buf), pfile); len = strlen(buf); if (len > 0) { (*p)[i].content = (char *)malloc(len); memset((*p)[i].content, 0, len); strcpy((*p)[i].content, &buf[6]); } i++; //边读边随时增加struct dict在堆中的数量。 *p = (struct dict *)realloc(*p, (1 + i) * sizeof(struct dict)); //把新增的堆内存清零(置零)。 memset(*p + i, 0, sizeof(struct dict)); } fclose(pfile);//关闭字典文件 return i;//返回读取到的字典词条数 } ...... ......
-----------------------------------------------------------------------------
方案三:链表也可以实现。(基础班没有讲到哦!)
vs2017下示例核心代码:
......
......
-----------------------------------------------------------------------------
结构dict在内存中的分配说明图如下所示:
=============================================================================
四种实现方案的效率比较:
如下图所示:
=============================================================================