十三、PL/SQL程序设计
PL/SQL(Procedure Language/Structured Query Language)
1、PL/SQL是一种高级数据库程序设计语言,专门用于在各种环境下对Oracle数据库进行访问。该语言集成于数据库服务器中,所以PL/SQL代码可以对数据进行快速高效的处理。
2、PL/SQL是对SQL语言存储过程语言的扩展,是Oracle系统的核心语言。
3、PL/SQL程序由三个块组成:声明部分、执行部分、异常处理部分。
13.1、sqldeveloper工具的使用
先去Oracle官网去下载最新版本的sqldeveloper,下载地址:https://www.oracle.com/technetwork/developer-tools/sql-developer/downloads/index.html
得到2个zip压缩包,如下图所示:
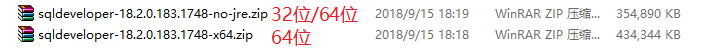
解压缩后,找到sqldeveloper.exe点击打开即可。
新建数据库连接
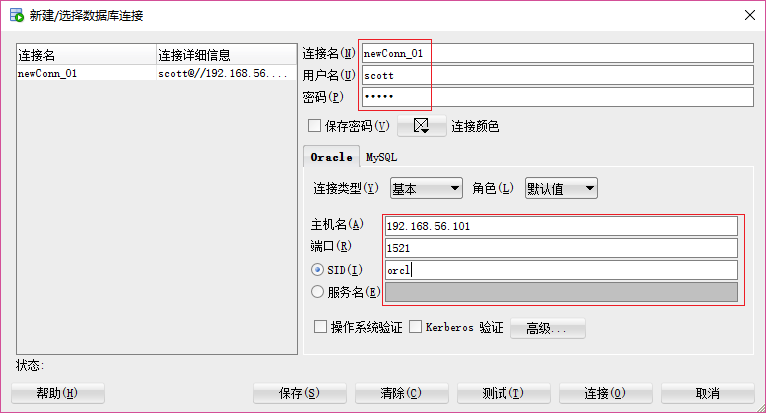
就可以使用了。
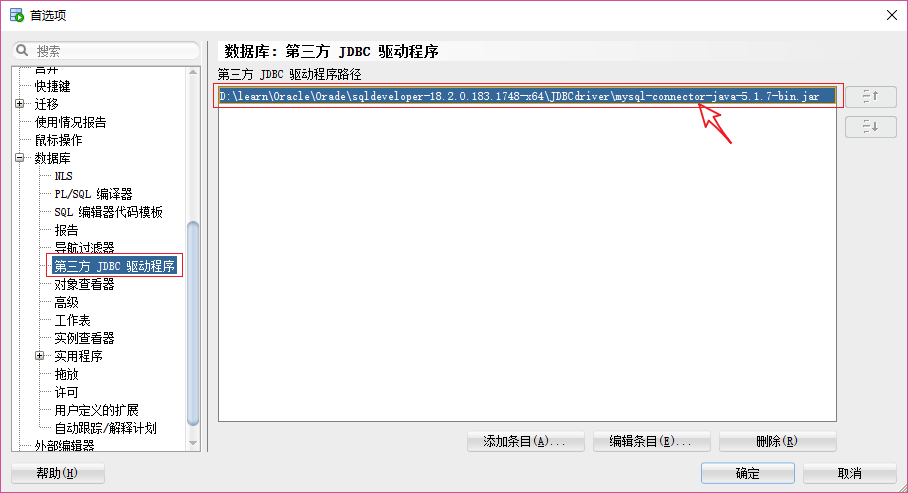
如果想要连接Mysql数据库,需要进行配置:工具 --> 首选项 --> 数据库 --> 第三方 JDBC 驱动包 --> 添加条目,添加所需要的jar包。如下图所示:
13.2、小案例
小案例-回顾条件表达式:
给员工涨工资:总裁涨1000元 经理涨800元 其他涨400元
写一段java的JDBC程序,我们这里写的是伪代码,伪代码不能够执行,但是可以帮助我们分析程序执行的过程和结构。
ResultSet rs = "select empno,job from emp";
while(rs.next()) {
int eno = rs.getInt("empno");
String job = rs.getString("job");
if("PRESIDENT".eauals(job)) {
update emp sal=sal+1000 where empno=eno;
} else if ("MANAGER".eauals(job)) {
update emp sal=sal+800 where empno=eno;
} else {
update emp sal=sal+400 where empno=eno;
}
PL/SQL = Procedure Language/SQL = 过程语言/SQL
PL/SQL程序从功能上来讲,与上面JDBC的程序想要完成的功能是一样的。
学习PL/SQL程序的目的:
1、PL/SQL是Oracle对SQL语言的过程化扩展,操作效率更高。
2、PL/SQL在SQL命令语言中增加了过程处理语句(分支、循环等),使SQL语言具有过程处理能力。
我们把SQL语言的数据操纵能力与过程语言的数据处理能力结合起来,使得PL/SQL面向过程但比过程语言简单、高效、灵活和实用。
Oracle中对SQL语言的扩展叫做PL/SQL。
SQL Server中对SQL语言的扩展叫做Transact-sql。
13.3、PL/SQL程序--打印输出Hello World
示例代码如下:
SQL> --声明部分
SQL> declare
2 --说明部分
3 begin
4 --程序部分
5 dbms_output.put_line('Hello World');
6 end;
7 --退出编辑环境,并执行PL/SQL程序
8 /
PL/SQL 过程已成功完成。
SQL> --默认情况下,Oracle的输出开关是关闭的。
SQL> --如果要在屏幕上输出信息,需要将 serveroutput开关打开 set serveroutput on
SQL> set serveroutput on
SQL> /
Hello World
PL/SQL 过程已成功完成。
SQL>
13.4、变量和常量说明
PL/SQL程序结构截图如下:

PL/SQL程序结构完整截图如下:

变量和常量说明:
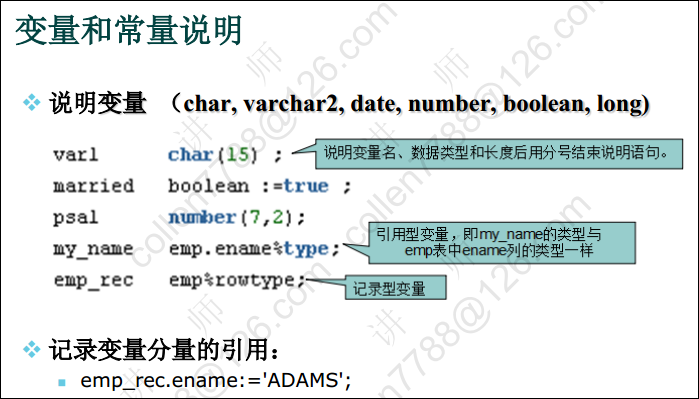
引用型变量示例代码:
--查询员工编号为7839的姓名和薪水
set serveroutput on
declare
--定义变量保存姓名和薪水
--pename varchar2(20);
--psal number;
--定义引用型变量保存姓名和薪水
pename emp.ename%type;
psal emp.sal%type;
begin
--得到姓名和薪水
--在PL/SQL中,赋值方式有两种方式,一种是 := 一种是 使用关键字into
select ename,sal into pename,psal from emp where empno=7839;
dbms_output.put_line(pename||'的薪水是'||psal);
end;
/
记录型变量示例代码:
--查询员工编号为7839的姓名和薪水
set serveroutput on
declare
--定义记录型变量:代表一行
emp_rec emp%rowtype;
begin
select * into emp_rec from emp where empno=7839;
dbms_output.put_line(emp_rec.ename||'的薪水是'||emp_rec.sal);
end;
/
如何定义常量呢?
pename emp.ename%type;
psal emp.sal%type;
加一个constant,就变成常量了。
pename constant emp.ename%type;
psal constant emp.sal%type;
13.5、分支
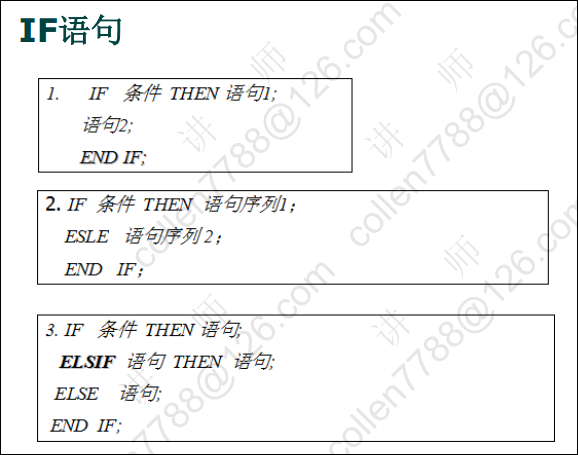
if语句示例代码:
set serveroutput on
--判断用户从键盘输入的数字
--接收键盘输入
--num: 地址值,在该地址上保存了输入的值。
accept num prompt '请输入一个数字';
declare
--定义变量保存输入的数字
pnum number := #
begin
if pnum = 0 then dbms_output.put_line('您输入的是0');
elsif pnum = 1 then dbms_output.put_line('您输入的是1');
elsif pnum = 2 then dbms_output.put_line('您输入的是2');
else dbms_output.put_line('其他数字');
end if;
end;
/
13.6、循环
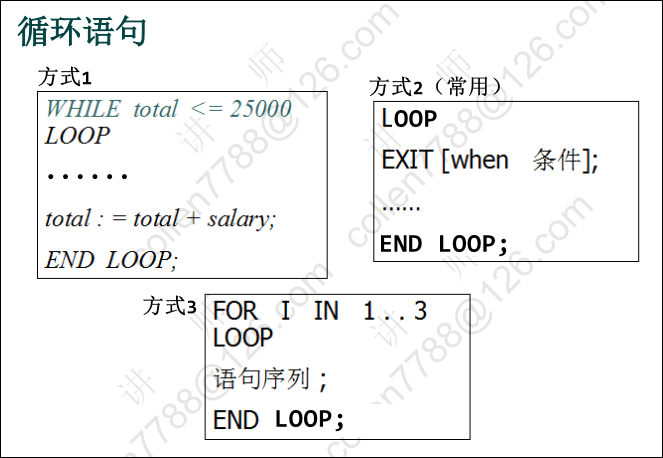
循环语句示例代码:
--打印1~10
set serveroutput on
declare
pnum number := 1;
begin
loop
--退出条件
exit when pnum > 10;
dbms_output.put_line(pnum);
--加一
pnum := pnum + 1;
end loop;
end;
/
13.7、光标Cursor(游标)== ResultSet
示例:按员工的工种长工资,总裁涨1000元,经理涨800元,其他员工涨400元。
示例代码截图:

光标Cursor(游标)详解如下图所示:

示例代码:
--查询并打印员工的姓名和薪水
/*
1. 光标的属性:
%isopen(光标是否打开)
%rowcount(光标影响的行数)
%found(光标找到内容)
%notfound(光标没有找到内容)
2. Oracle中默认,一个会话中只能打开300个光标
SQL> --修改光标个数需要管理员权限
SQL> show user
USER 为 "SCOTT"
SQL> conn sys/password@192.168.56.101:1521/orcl as sysdba
已连接。
SQL> show user
USER 为 "USER"
SQL> show parameter cursor
NAME TYPE VALUE
------------------------------------ -------------------------------- -----------
cursor_sharing string FORCE
cursor_space_for_time boolean FALSE
open_cursors integer 300
session_cached_cursors integer 20
修改: alter system set open_cursors=400;
3. (思考):上面参数 cursor_sharing 什么作用? --> 对于数据库性能优化非常有用。
EXACT(默认值), FORCE(应急使用), SIMILAR
*/
--示例:使用光标查询员工姓名和工资,并打印
set serveroutput on
declare
--定义一个光标
cursor cemp is select ename,sal from emp;
--为这个光标定义所需要用到的对应的变量
pename emp.ename%type;
psal emp.sal%type;
begin
--打开光标
open cemp;
loop
--取一条记录到变量中
fetch cemp into pename,psal;
--退出条件
--exit when 没有取到记录;
exit when cemp%notfound;
--打印
dbms_output.put_line(pename||'的薪水是'||psal);
end loop;
--关闭光标
close cemp;
end;
/
再来给员工涨工资代码:
--示例:按员工的工种长工资,总裁涨1000元,经理涨800元,其他员工涨400元。
set serveroutput on
declare
--alter table "SCOTT"."EMP" rename column "JOB" to empjob
cursor cemp is select empno,empjob from emp;
--为这个光标定义所需要用到的对应的变量
pempno emp.empno%type;
pjob emp.empjob%type;
begin
open cemp;
loop
--取一条记录到变量中
fetch cemp into pempno,pjob;
exit when cemp%notfound;
--判断职位
if pjob = 'PRESIDENT' then update emp set sal=sal+1000 where empno=pempno;
elsif pjob = 'MANAGER' then update emp set sal=sal+800 where empno=pempno;
else update emp set sal=sal+400 where empno=pempno;
end if;
end loop;
close cemp;
--Oracle是自动开启事务的
--Oracle默认的隔离级别是:read committed
--why? --> ACID
commit;
dbms_output.put_line('涨工资完成');
end;
/
带参数的光标
示例代码如下:
--查询某个部门的员工姓名
set serveroutput on
declare
cursor cemp(dno number) is select ename from emp where deptno=dno; --不一样的地方
pename emp.ename%type;
begin
open cemp(20); --不一样的地方
loop
fetch cemp into pename;
exit when cemp%notfound;
dbms_output.put_line(pename);
end loop;
close cemp;
end;
/
13.8、例外
例外:是程序设计语言提供的一种功能,用来增强程序的健壮性和容错性。
Oracle中对异常的处理
1、系统定义的例外
No_data_found (没有找到数据)
Too_many_rows (select … into 语句中匹配多个行)
Zero_Divide (被零除)
Value_error (算术或转换错误)
Timeout_on_resource (在等待资源时发生超时)
2、用户定义的例外
演示:系统定义的例外(被0除)
--系统例外:被0除
set serveroutput on
declare
pnum number;
begin
pnum := 1/0;
exception
when zero_divide then dbms_output.put_line('1:0不能做分母');
dbms_output.put_line('2:0不能做分母');
when value_error then dbms_output.put_line('算术或转换错误');
when others then dbms_output.put_line('其他例外');
end;
/
演示:用户定义的例外以及处理例外
--查询50号部门的员工姓名
set serveroutput on
declare
cursor cemp is select ename from emp where deptno=50;
pename emp.ename%type;
--自定义例外
no_emp_found exception;
begin
open cemp;
--取第一条记录
fetch cemp into pename;
if cemp%notfound then
--抛出例外
raise no_emp_found;
end if;
--回顾
--Java中是通过IO流来操作硬盘中的文件,
--Java中IO最终是通过什么方式操作硬盘上的文件呢?答:通过操作系统的进程。
--Oracle中通过内存中的实例操作硬盘中的文件,
--而内存中实例最终是怎么操作硬盘上的文件呢?答:也是通过操作系统的进程。
--这句执行不到,Oracle中怎么办呢?答:通过进程监视器
--pmon: process monitor 进程监视器
close cemp;
exception
when no_emp_found then dbms_output.put_line('没有找到员工');
when others then dbms_output.put_line('其他例外');
end;
/
13.9、实例
瀑布模型图解:

实例1:统计每年入职的员工人数
/*
SQL语句:
select to_char(hiredate,'yyyy') from emp;
--> 集合 --> 光标 --> 循环 --> 退出条件:notfound
变量:
1. 初始值
2. 最终怎么得到
每年入职的员工人数:
count80 number := 0;
count81 number := 0;
count82 number := 0;
count87 number := 0;
*/
set serveroutput on
declare
cursor cemp is select to_char(hiredate,'yyyy') from emp;
phiredate varchar2(4);
--每年入职的员工人数:
count80 number := 0;
count81 number := 0;
count82 number := 0;
count87 number := 0;
begin
open cemp;
loop
--取一个员工的入职年份到变量中
fetch cemp into phiredate;
--退出条件:notfound
exit when cemp%notfound;
--判断年份
if phiredate = '1980' then count80:=count80+1;
elsif phiredate = '1981' then count81:=count81+1;
elsif phiredate = '1982' then count82:=count82+1;
else count87:=count87+1;
end if;
end loop;
close cemp;
dbms_output.put_line('Total:'||(count80+count81+count82+count87));
dbms_output.put_line('1980年入职的有:'||count80);
dbms_output.put_line('1981年入职的有:'||count81);
dbms_output.put_line('1982年入职的有:'||count82);
dbms_output.put_line('1987年入职的有:'||count87);
end;
/
实例2:为员工涨工资,从最低工资调起每人涨10%,但工资总额不能超过5万元,请计算涨工资的人数和涨工资后的工资总额,并输出涨工资人数及工资总额。
/*
SQL语句:
select empno,sal from emp order by sal;
--> 光标 --> 退出条件:1. 工资总额 > 5w 2. notfound
变量:
1. 初始值
2. 最终得到
涨工资的人数: countEmp number := 0;
涨后的工资总额: salTotal number;
方式1. select sum(sal) into salTotal from emp;
方式2. 涨后=涨前 + sal * 0.1
写程序的原则:能不操作数据库就不要操作数据库。
练习:人数:7 总额:50205.325
*/
set serveroutput on
declare
cursor cemp is select empno,sal from emp order by sal;
pempno emp.empno%type;
psal emp.sal%type;
--涨工资的人数:
countEmp number := 0;
--涨后的工资总额:
salTotal number;
begin
--得到初始的工资总额
select sum(sal) into salTotal from emp;
open cemp;
loop
--取一个员工出来到变量中
fetch cemp into pempno,psal;
--1. 工资总额 > 5w
exit when salTotal > 50000;
--2. notfound
exit when cemp%notfound;
--涨工资操作
update emp set sal=sal*1.1 where empno=pempno;
--人数+1
countEmp := countEmp + 1;
--2. 涨后工资总额=涨前工资总额 + sal * 0.1
salTotal := salTotal + psal * 0.1;
end loop;
close cemp;
commit;
dbms_output.put_line('人数:'||countEmp||' 总额:'||salTotal);
end;
/
实例3:用PL/SQL语言编写一程序,实现按部门分段(6000以上、(6000,3000)、3000元以下)统计各工资段的职工人数、以及各部门的工资总额(工资总额中不包括奖金)
/*
SQL语句:
部门: select deptno from dept;
部门中员工的薪水:select sal from emp where deptno=???; 问号是部门编号
变量:
1. 初始值
2. 最终得到
每个段的人数:
count1 number;
count2 number;
count3 number;
部门的工资总额:
salTotal number := 0;
得到部门的工资总额的方式:
1.select sum(sal) into salTotal from emp where deptno=???;
2.累加
*/
set serveroutput on
declare
--部门
cursor cdept is select deptno from dept;
pdeptno dept.deptno%type;
--部门中员工的薪水
cursor cemp(dno number) is select sal from emp where deptno=dno;
psal emp.sal%type;
--每个段的人数:
count1 number;
count2 number;
count3 number;
--部门的工资总额:
salTotal number := 0;
begin
open cdept;
loop
--取一个部门
fetch cdept into pdeptno;
exit when cdept%notfound;
--初始化
--每个段的人数
count1:=0;
count2:=0;
count3:=0;
--得到部门的工资总额
select sum(sal) into salTotal from emp where deptno=pdeptno;
--取部门中员工的薪水
open cemp(pdeptno);
loop
--取一个员工
fetch cemp into psal;
exit when cemp%notfound;
--判断
if psal < 3000 then count1:=count1+1;
elsif psal>=3000 and psal<6000 then count2:=count2+1;
else count3:=count3+1;
end if;
end loop;
close cemp;
--保存结果
insert into msg values(pdeptno,count1,count2,count3,nvl(saltotal,0));
end loop;
close cdept;
commit;
dbms_output.put_line('完成');
end;
/
13.10、笔试题2道
笔试1脚本.txt
create table test1
(id int primary key,
name varchar(20),
money int);
insert into test1 values(1,'Tom',1000);
insert into test1 values(2,'Mary',2000);
insert into test1 values(3,'Mike',3000);
insert into test1 values(4,'Jeff',4000);
commit;
示例代码如下:
SQL> select * from test1;
ID NAME MONEY
---------- -------------------- ----------
1 Tom 1000
2 Mary 2000
3 Mike 3000
4 Jeff 4000
SQL> select id,name,money,(select money from test1 where id=t.id-1) money1 from test1 t;
ID NAME MONEY MONEY1
---------- -------------------- ---------- ----------
1 Tom 1000
2 Mary 2000 1000
3 Mike 3000 2000
4 Jeff 4000 3000
SQL>
笔试2脚本.txt
create table pm_ci
(ci_id varchar(20) primary key,
stu_ids varchar(100));
insert into pm_ci values('1','1,2,3,4');
insert into pm_ci values('2','1,4');
create table pm_stu
(stu_id varchar(20) primary key,
stu_name varchar(20));
insert into pm_stu values('1','张三');
insert into pm_stu values('2','李四');
insert into pm_stu values('3','王五');
insert into pm_stu values('4','赵六');
commit;
示例代码如下:
SQL> select * from pm_ci;
CI_ID STU_IDS
-------------------- ----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 1,2,3,4
2 1,4
SQL> select * from pm_stu;
STU_ID STU_NAME
-------------------- --------------------
1 张三
2 李四
3 王五
4 赵六
SQL> select c.ci_id,s.stu_name
2 from pm_ci c,pm_stu s
3 where instr(c.stu_ids,s.stu_id)>0;
CI_ID STU_NAME
-------------------- --------------------
1 张三
1 李四
1 王五
1 赵六
2 张三
2 赵六
已选择 6 行。
SQL> select ci_id,wm_concat(stu_name) namelist
2 from(select c.ci_id,s.stu_name
3 from pm_ci c,pm_stu s
4 where instr(c.stu_ids,s.stu_id)>0)
5 group by ci_id;
CI_ID
--------------------
NAMELIST
------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1
张三,李四,王五,赵六
2
张三,赵六
SQL> --设置列的宽度
SQL> col namelist for a50
SQL> select ci_id,wm_concat(stu_name) namelist
2 from(select c.ci_id,s.stu_name
3 from pm_ci c,pm_stu s
4 where instr(c.stu_ids,s.stu_id)>0)
5 group by ci_id;
CI_ID NAMELIST
-------------------- --------------------------------------------------
1 张三,李四,王五,赵六
2 张三,赵六
SQL>
十四、存储过程和存储函数
14.1、存储过程
详解如下:
存储在数据库中供所有用户程序调用的子程序(用PL/SQL写的)叫存储过程、存储函数。
创建存储过程的语法:
create [or replace] PROCEDURE 过程名(参数列表)
as PL/SQL子程序体;
示例代码1:
--打印Hello World,不传递参数
/*
调用存储过程的方式:
1. exec sayHelloWorld();
2. begin
sayHelloWorld();
sayHelloWorld();
sayHelloWorld();
end;
/
*/
create or replace procedure sayHelloWorld --注意Oracle中的命名规范,但是这里为了简便,我们使用java的命名规范
as
--说明部分
begin
dbms_output.put_line('Hello World');
end;
/
示例代码2:
--给指定的员工涨100,并且打印涨前和涨后的工资,传递单个参数
create or replace procedure raisesalary(eno in number) --注意:需要指明参数是输入参数,还是输出参数
as
--定义变量保存涨前的薪水
psal emp.sal%type;
begin
--得到涨前的薪水
select sal into psal from emp where empno=eno;
--涨100
update emp set sal=sal+100 where empno=eno;
--要不要commit呢?答:不要。
--原则:一般情况下,我们不在存储过程和存储函数中commit和rollback数据,应该交由调用者去做。
dbms_output.put_line('涨前:'||psal||' 涨后:'||(psal+100));
end;
/
示例代码3:
--给指定的员工涨指定额度的工资,传递多个参数
create or replace procedure raiseSalary(eno in number,rate in number)
as
psal emp.sal%type;
begin
--得到涨前的薪水
select sal into psal from emp where empno=eno;
--涨指定额度的工资
update emp set sal=sal*rate where empno=eno;
dbms_output.put_line('涨前:'||psal||' 涨后:'||(psal*rate));
end;
14.2、存储函数
详解如下:
存储函数和存储过程的结构类似,但必须有一个return子句,用于返回函数值。
函数说明要指定函数名、结果值的类型,以及参数类型等。
创建存储函数的语法:
create [or replace] FUNCTION 函数名(参数列表)
return 函数返回值类型
as PL/SQL子程序体;
示例代码1:
--查询某个员工的年收入
create or replace function queryempincome(eno in number)
return number
as
--定义变量保存月薪和奖金
psal emp.sal%type;
pcomm emp.comm%type;
begin
select sal,comm into psal,pcomm from emp where empno=eno;
--返回年收入
return psal*12+nvl(pcomm,0);
end;
/
14.3、存储过程和存储函数中的in和out参数
详解如下:
一般来讲,存储过程和存储函数区别在于存储函数可以有一个返回值,而存储过程没有返回值。
但存储过程和存储函数都可以通过out指定一个或多个输出参数。我们可以利用out参数,在存储过程和存储函数中实现返回多个值。
这时存储函数的功能就被存储过程取代了,那为什么还要保留存储函数呢?答:为了版本的向下兼容。
什么时候使用存储过程/存储函数呢?
原则:
一般而言,如果只有一个返回值,就用存储函数;否则,就用存储过程。
示例代码如下:
--查询某个员工的姓名 月薪 职位
create or replace procedure queryempinfo(eno in number,
pename out varchar2,
psal out number,
pjob out varchar2)
as
begin
select ename,sal,empjob into pename,psal,pjob from emp where empno=eno;
end;
/
思考:
1. 查询某个员工的所有信息 --> 问题:out参数太多
2. 查询某个部门中的所有员工信息 --> 问题:返回的是集合
14.4、在Java中调用存储过程和存储函数
- 在java中想要访问数据库,首先要得到Connection对象,通过该对象得到Statement对象(接口),我们使用Statement的子接口CallableStatement。
在Java中调用存储过程和存储函数 的示例代码:
/*
create or replace procedure queryempinfo(eno in number,
pename out varchar2,
psal out number,
pjob out varchar2)
as
begin
select ename,sal,empjob into pename,psal,pjob from emp where empno=eno;
end;
*/
@Test
public void testProcedure() {
// {call <procedure-name>[(<arg1>,<arg2>, ...)]}
String sql = "{call queryempinfo(?,?,?,?)}";
Connection conn = null;
CallableStatement call = null;
try {
conn = JDBCUtils.getConnection();
call = conn.prepareCall(sql);
// 对于in参数,需要赋值
call.setInt(1, 7839);
// 对于out参数,需要声明
call.registerOutParameter(2, OracleTypes.VARCHAR);
call.registerOutParameter(3, OracleTypes.NUMBER);
call.registerOutParameter(4, OracleTypes.VARCHAR);
// 执行存储过程
call.execute();
// 取出结果
String name = call.getString(2);
double sal = call.getDouble(3);
String job = call.getString(4);
System.out.println(name + " " + sal + " " + job);
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}finally{
JDBCUtils.release(conn, call, null);
}
}
/*
create or replace function queryempincome(eno in number)
return number
as
--定义变量保存月薪和奖金
psal emp.sal%type;
pcomm emp.comm%type;
begin
select sal,comm into psal,pcomm from emp where empno=eno;
--返回年收入
return psal*12+nvl(pcomm,0);
end;
*/
@Test
public void testFunction(){
// {?= call <procedure-name>[(<arg1>,<arg2>, ...)]}
String sql = "{?=call queryempincome(?)}";
Connection conn = null;
CallableStatement call = null;
try {
conn = JDBCUtils.getConnection();
call = conn.prepareCall(sql);
// 第一个是out参数,需要声明
call.registerOutParameter(1, OracleTypes.NUMBER);
// 第二个是in参数,需要赋值
call.setInt(2, 7839);
// 执行存储函数
call.execute();
// 取出年收入
double income = call.getDouble(1);
System.out.println(income);
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}finally{
JDBCUtils.release(conn, call, null);
}
}
14.5、在out参数中使用光标
查询某个部门中所有员工的所有信息,返回的是集合。
我们需要声明包结构和创建包体,其中包和包体也是数据库的对象。
示例代码如下:
/*
1. 查询某个员工的所有信息 --> 问题:out参数太多
2. 查询某个部门中的所有员工信息 --> 问题:返回的是集合
*/
// 在out参数中使用光标
// 查询某个部门中所有员工的所有信息
/*
--声明包结构
create or replace
package myPackage as
type empcursor is ref cursor;
procedure queryEmpList(dno in number,emplist out empcursor);
end myPackage;
--创建包体
create or replace
package body myPackage as
procedure queryEmpList(dno in number,emplist out empcursor) as
begin
open emplist for select * from emp where deptno=dno;
end queryEmpList;
end myPackage;
*/
@Test
public void testCursor(){
String sql = "{call myPackage.queryEmpList(?,?)}";
Connection conn = null;
CallableStatement call = null;
ResultSet rs = null;
try {
conn = JDBCUtils.getConnection();
call = conn.prepareCall(sql);
// 对于in参数,需要赋值
call.setInt(1, 20);
// 对于out参数 ,需要声明
call.registerOutParameter(2, OracleTypes.CURSOR);
// 执行存储函数
call.execute();
// 取出结果
rs = ((OracleCallableStatement)call).getCursor(2);
while (rs.next()) {
// 取出一个员工,示例只取出了两列
String name = rs.getString("ename");
double sal = rs.getDouble("sal");
System.out.println(name + " " + sal);
}
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}finally{
JDBCUtils.release(conn, call, rs);
}
}
十五、触发器
详解如下:
数据库触发器是一个与表相关联的、存储的PL/SQL程序。
每当一个特定的数据操作语句(insert、update、delete)在指定的表上发出时,Oracle自动地执行触发器中定义的语句序列。
触发器的类型:
语句级(表级)触发器:在指定的操作语句操作之前或之后执行一次,不管这条语句影响了多上行。
行级触发器(for each row):触发语句作用的每一条记录都被触发。在行级触发器中使用 :old 和 :new 伪记录变量来识别值的状态。
创建触发器的语法:
create or replace trigger 触发器名
before | after
insert | update | delete [of 列名]
on 表名
[for each row [when(条件)]] --触发器的类型
declare
begin
......
end;
触发器的用途:
1. 数据确认
2. 实施复杂的安全性检查
3. 做审计,跟踪表上所做的数据操作等(想要做什么事,不被查到,需要关闭数据库的审计功能)
4. 数据的备份和同步
示例1:
--每当成功插入新员工后,自动打印“成功插入了新员工”
create or replace trigger abcd
after insert
on emp
declare
begin
dbms_output.put_line('成功插入了新员工');
end;
15.1、触发器应用一:实施复杂的安全性检查
禁止在非工作时间向数据库中插入数据
周末:to_char(sysdate,'day') in ('星期六','星期日')
上班前 下班后:to_number(tochar(sysdate,'hh24')) not between 9 and 17
------------------------------------------------------------------
create or replace trigger securityemp
before insert
on emp
declare
begin
if to_char(sysdate,'day') in ('星期六','星期日') or
to_number(to_char(sysdate,'hh24')) not between 9 and 17 then
--禁止insert
raise_application_error(-20002,'禁止在非工作时间向数据库中插入数据'); -- -20000到-20999之间
end if;
end;
------------------------------------------------------------------
SQL> insert into emp(empno,ename,sal,deptno) values(1001, 'tom',3000, 20);
insert into emp(empno,ename,sal,deptno) values(1001, 'tom',3000, 20)
*
第 1 行出现错误:
ORA-20002: 禁止在非工作时间向数据库中插入数据
ORA-06512: 在 "SCOTT.SECURITYEMP", line 6
ORA-04088: 触发器 'SCOTT.SECURITYEMP' 执行过程中出错
SQL>
15.2、触发器应用二:数据确认
检查emp表中的sal的修改值不低于原值
------------------------------------------------------------------
create or replace trigger checksalary
before update
on emp
for each row
declare
begin
if :new.sal<:old.sal then
raise_application_error(-20001,'涨后的工资不能少于涨前的工资。涨前:'||:old.sal||' 涨后:'||:new.sal); -- -20000到-20999之间
end if;
end;
------------------------------------------------------------------
测试代码:
SQL> update emp set sal=sal+1 where empno=7839;
已更新 1 行。
SQL> update emp set sal=sal-1 where empno=7839;
update emp set sal=sal-1 where empno=7839
*
第 1 行出现错误:
ORA-20001: 涨后的工资不能少于涨前的工资。涨前:7987 涨后:7986
ORA-06512: 在 "SCOTT.CHECKSALARY", line 4
ORA-04088: 触发器 'SCOTT.CHECKSALARY' 执行过程中出错
SQL>
15.3、练习:限制每个部门只招聘10名员工,超过计划则报出错误信息
限制每个部门只招聘10名员工,超过计划则报出错误信息
------------------------------------------------------------------
create or replace trigger limitEmpCount
before insert
on emp
declare
count10 number := 0;
count20 number := 0;
count30 number := 0;
begin
select count(*) into count10 from emp where deptno=10;
select count(*) into count20 from emp where deptno=20;
select count(*) into count30 from emp where deptno=30;
if count10>=10 then raise_application_error(-20005,'部门:10,员工已有'||count10||'人');
elsif count20>=10 then raise_application_error(-20005,'部门:20,员工已有'||count20||'人');
elsif count30>=10 then raise_application_error(-20005,'部门:30,员工已有'||count30||'人');
end if;
end;
------------------------------------------------------------------
测试代码:
SQL> insert into emp(empno,ename,sal,deptno) values(1030,'tom',3000, 30);
insert into emp(empno,ename,sal,deptno) values(1030,'tom',3000, 30)
*
第 1 行出现错误:
ORA-20005: 部门:30,员工已有10人
ORA-06512: 在 "SCOTT.LIMITEMPCOUNT", line 12
ORA-04088: 触发器 'SCOTT.LIMITEMPCOUNT' 执行过程中出错
SQL>