前言
最近打算花点时间好好看看spring的源码,然而现在Spring的源码经过迭代的版本太多了,比较庞大,看起来比较累,所以准备从最初的版本(interface21)开始入手,仅用于学习,理解其设计思想,后续慢慢研究其每次版本变更的内容。。。
先从interface21的一个典型web工程例子看起,宠物诊所 - petclinic,因为该工程基本涵盖了Spring的APO、IOC、JDBC、Web MVC、事务、国际化、主题切换、参数校验等主要功能。。。
先从简单的走起,看下该web工程中, Log4j是如何加载的吧~~~~~~~
对应的web.xml配置
<context-param> <param-name>webAppRootKey</param-name> <param-value>petclinic.root</param-value> </context-param> <context-param> <param-name>log4jConfigLocation</param-name> <param-value>/WEB-INF/classes/log4j.properties</param-value> </context-param> <listener> <listener-class>com.interface21.web.util.Log4jConfigListener</listener-class> </listener>
执行时序图(看不清的话可以点击查看原图)
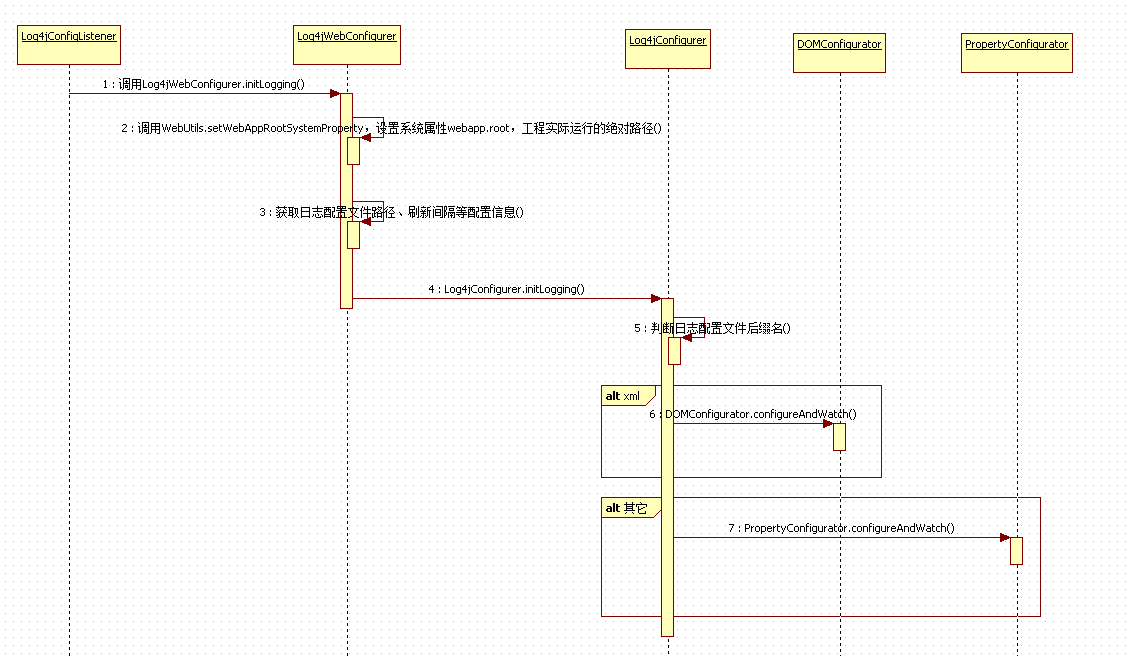
时序图中的各个步骤简要分析
执行的入口在Log4jConfigListener类的contextInitialized方法,由于Log4jConfigListener类实现了ServletContextListener接口,所以在Servlet容器(tomcat)启动时,会自动调用contextInitialized方法。
步骤描述:
- 进入Log4jConfigListener类的contextInitialized方法,该类只有一句代码,执行Log4jWebConfigurer.initLogging方法;
public void contextInitialized(ServletContextEvent event) { Log4jWebConfigurer.initLogging(event.getServletContext()); }
- 进入Log4jWebConfigurer类的initLogging方法,首先,调用WebUtils.setWebAppRootSystemProperty方法,内部调用servletContext.getRealPath("/")方法获取工程实际运行的绝对路径(如:F:�04_SVNIBPspringweb argetspring-web-1.0-SNAPSHOT),设置到系统变量中(System.setProperty),注意这里的key值是可以配置的,通过webAppRootKey参数配置,如在本例子的web.xml中配成了petclinic.root;
public static void setWebAppRootSystemProperty(ServletContext servletContext) { String param = servletContext.getInitParameter(WEB_APP_ROOT_KEY_PARAM); String key = (param != null ? param : DEFAULT_WEB_APP_ROOT_KEY); String oldValue = System.getProperty(key); if (oldValue != null) { servletContext.log("WARNING: Web app root system property already set: " + key + " = " + oldValue); servletContext.log("WARNING: Choose unique webAppRootKey values in your web.xml files!"); } else { String root = servletContext.getRealPath("/"); System.setProperty(key, root); servletContext.log("Set web app root system property: " + key + " = " + root); } }
- 获取日志配置文件路径、刷新间隔等配置信息,日志配置文件路径可根据log4jConfigLocation参数配置,这里配置的是相对路径,通过调用ServletContext.getRealPath()获得完整路径,注意getRealPath方法的参数要以“/”开头;刷新间隔可根据log4jRefreshInterval参数配置,默认为60s;
public static void initLogging(ServletContext servletContext) { // set the web app root system property WebUtils.setWebAppRootSystemProperty(servletContext); // only perform custom Log4J initialization in case of a config file String location = servletContext.getInitParameter(CONFIG_LOCATION_PARAM); if (location != null) { // interpret location as relative to the web application root directory if (location.charAt(0) != '/') { location = "/" + location; } location = servletContext.getRealPath(location); // use default refresh interval if not specified long refreshInterval = Log4jConfigurer.DEFAULT_REFRESH_INTERVAL; String intervalString = servletContext.getInitParameter(REFRESH_INTERVAL_PARAM); if (intervalString != null) { refreshInterval = Long.parseLong(intervalString); } // write log message to server log servletContext.log("Initializing Log4J from " + location); // perform actual Log4J initialization try { Log4jConfigurer.initLogging(location, refreshInterval); } catch (FileNotFoundException ex) { throw new IllegalArgumentException("Invalid log4jConfigLocation parameter: " + ex.getMessage()); } } }
- 进入Log4jConfigurer类的initLogging方法,initLogging比较简单,根据配置文件后缀名,使用相应的解析器解析配置文件中的元素。
public static void initLogging(String location, long refreshInterval) throws FileNotFoundException { if (!(new File(location)).exists()) { throw new FileNotFoundException("Log4j config file [" + location + "] not found"); } if (location.toLowerCase().endsWith(XML_FILE_EXTENSION)) { DOMConfigurator.configureAndWatch(location, refreshInterval); } else { PropertyConfigurator.configureAndWatch(location, refreshInterval); } }
另外补充下,当Servlet容器销毁时,会调用Log4jConfigListener的contextDestroyed方法,最终是调用LogManager.shutdown,执行一些资源关闭等操作;