论文地址:implementing Lock-Free Queue
论文大体讲的意思是:Lock-Base的程序的performance不好,并且a process inside the critical section can delay all operations inde nitely;所以基于以上的弊端,他们提出了Non-Blocking的算法,也就是CSW和FAA,当然就是CAS,而CAS也有最难以handler的情况,也就是ABA问题,他们给出了solution,也就是检查引用;他们分别给出了链表场景和数组场景的algorithm,最后是性能分析。
这篇笔记主要为了给Lock-Free提供一些实现方法和思路。
我们先看链表的情况:
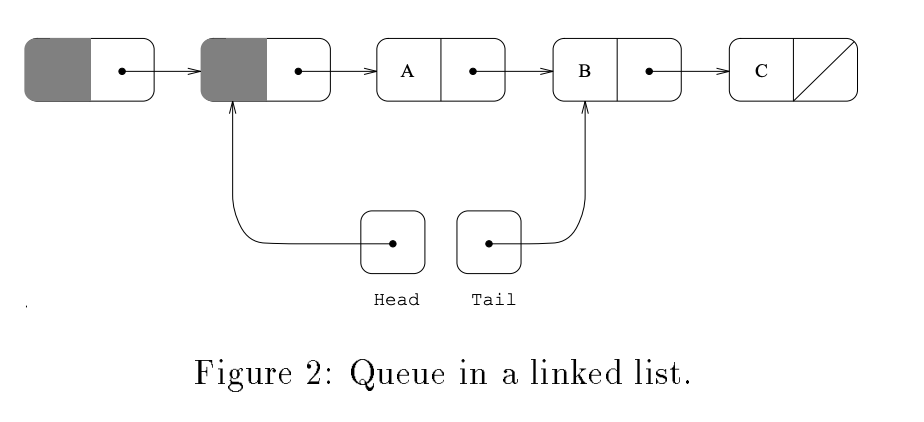
双端链表,入队Enqueue方法是tail移动,出队Dequeue是Head移动,下面记录一下伪代码。
Enqueue(x) q new record q^:value x q^:next NULL repeat p tail succ Compare&Swap(p^:next, NULL, q) if succ 6= TRUE Compare&Swap(tail ; p; p^:next) until succ = TRUE Compare&Swap(tail ; p; q) end
Dequeue() repeat p head if p^:next = NULL error queue empty until Compare&Swap(head ; p; p^:next) return p^:next^:value end
Enqueue的思路是,先设置tail的next指针,如果成功,则把tail指针移动;Dequeue的思路是,如果head的copy p的next不为空,则进行移动,并在成功之后返回之前p的next的值,Java没有指针操作,只有使用unSafe类进行内存操作。(数组实现要比链表实现稳定多了)在跑线程的时候,add会有几率出现Runnable的情况,目前还不知道什么原因,最初的原因是把变量赋值写在for(;;)里,导致它一直不取值,只做循环体,将赋值写在循环体里好了一些,但还是会出现死循环问题。
import sun.misc.Unsafe; import java.lang.reflect.Field; /** * Created by MacBook on 2019/4/14. */ public class MyLockFreeLinkQueue<E> implements MyQueue<E>{ Node<E> head; Node<E> tail; static Unsafe unsafe; private static final long headOffset; private static final long tailOffset; private static final long nextOffset; static{ try{ Field singleoneInstanceField = Unsafe.class.getDeclaredField("theUnsafe"); singleoneInstanceField.setAccessible(true); unsafe = (Unsafe)singleoneInstanceField.get(null); headOffset = unsafe.objectFieldOffset (MyLockFreeLinkQueue.class.getDeclaredField("head")); tailOffset = unsafe.objectFieldOffset (MyLockFreeLinkQueue.class.getDeclaredField("tail")); nextOffset = unsafe.objectFieldOffset (MyLockFreeLinkQueue.Node.class.getDeclaredField("next")); }catch (Exception e){ throw new Error(e); } } static class Node<E>{ E data; Node<E> next; public Node(E data, Node<E> next) { this.data = data; this.next = next; } public E getData() { return data; } public void setData(E data) { this.data = data; } public Node<E> getNext() { return next; } public void setNext(Node<E> next) { this.next = next; } } public MyLockFreeLinkQueue() { head = tail = new Node<>(null,null); } /** * Enqueue(x) q new record q^:value x q^:next NULL repeat p tail succ Compare&Swap(p^:next, NULL, q) if succ 6= TRUE Compare&Swap(tail ; p; p^:next) until succ = TRUE Compare&Swap(tail ; p; q) end * @param e * @return */ @Override public boolean add(E e) { Node<E> q = new Node<>(e,null); for(;;){ Node<E> p = tail; if(unsafe.compareAndSwapObject(p,nextOffset,null,q)){ while(unsafe.compareAndSwapObject(this,tailOffset,p,q)); break; } } return true; } /** * Dequeue() repeat p head if p^:next = NULL error queue empty until Compare&Swap(head ; p; p^:next) return p^:next^:value end * @return */ @Override public E take() { for(;;){ Node<E> p = head,next = p.getNext(); if(next == null){ return null; }else if(unsafe.compareAndSwapObject(this,headOffset,p,next)){ p.setNext(null);// help gc return next.getData(); } } } }
这里我跑了2个生产者线程,2个消费者线程,数据有序的被消费了。
...
pool-1-thread-3 send [62] to queue; total 193 pool-1-thread-3 send [97] to queue; total 194 pool-1-thread-3 send [25] to queue; total 195 pool-1-thread-3 send [17] to queue; total 196 pool-1-thread-3 send [50] to queue; total 197 pool-1-thread-3 send [72] to queue; total 198 pool-1-thread-3 send [46] to queue; total 199 pool-1-thread-3 send [83] to queue; total 200 pool-1-thread-4 consumer [62],count 2n+1 result :125; total 193 pool-1-thread-4 consumer [97],count 2n+1 result :195; total 194 pool-1-thread-4 consumer [25],count 2n+1 result :51; total 195 pool-1-thread-4 consumer [17],count 2n+1 result :35; total 196 pool-1-thread-4 consumer [50],count 2n+1 result :101; total 197 pool-1-thread-4 consumer [72],count 2n+1 result :145; total 198 pool-1-thread-4 consumer [46],count 2n+1 result :93; total 199 pool-1-thread-4 consumer [83],count 2n+1 result :167; total 200
接下来,我实践了环形数组的实现,基于我之前实现的BlockingQueue,这个Lock-Free Queue会变得比较简单。

import java.util.concurrent.atomic.AtomicInteger;
/**
* Created by MacBook on 2019/4/13.
*/
public class MyLockFreeQueue<E> implements MyQueue<E>{
private Object[] data;
private AtomicInteger takeIndex;
private AtomicInteger putIndex;
private AtomicInteger size;
private static final int DEFAULT_CAPACITY = 10;
public MyLockFreeQueue (){
this(DEFAULT_CAPACITY);
}
public MyLockFreeQueue(int initCapacity){
if(initCapacity < 0){
throw new IllegalStateException("initCapacity must not be negative");
}
data = new Object[initCapacity];
takeIndex = new AtomicInteger(0);
putIndex = new AtomicInteger(0);
size = new AtomicInteger(0);
}
public boolean add(E e){
if(e == null){
throw new NullPointerException("the element you put can't be null");
}
for(int index = putIndex.get();;){
if(size.get() == data.length){
return false;
}
int expect = (index == data.length - 1)?0:(index+1);
if(putIndex.compareAndSet(index,expect)){
data[index] = e;
size.incrementAndGet();
return true;
}
}
}
public E take(){
for(int index = takeIndex.get();;){
if(size.get() == 0){
return null;
}
int expect = (index == data.length - 1)?0:(index+1);
E e = (E)data[index];
if(takeIndex.compareAndSet(index,expect)){
size.decrementAndGet();
return e;
}
}
}
}
思路就是,使用两个标记入队和出队的Atom Integer对象,在成功申请当前格子之后,给当前格子赋值,使用size来判断是否EMPTY和FULL。这里依然有一点缺陷,就是index和size不同步的问题,不过我也是跑了2+2线程,也是有序消费了。
...pool-1-thread-3 send [81] to queue; total 188 pool-1-thread-2 consumer [81],count 2n+1 result :163; total 188 pool-1-thread-3 send [1] to queue; total 189 pool-1-thread-2 consumer [1],count 2n+1 result :3; total 189 pool-1-thread-2 consumer [19],count 2n+1 result :39; total 190 pool-1-thread-3 send [19] to queue; total 190 pool-1-thread-3 send [61] to queue; total 191 pool-1-thread-2 consumer [61],count 2n+1 result :123; total 191 pool-1-thread-3 send [16] to queue; total 192 pool-1-thread-2 consumer [16],count 2n+1 result :33; total 192 pool-1-thread-3 send [74] to queue; total 193 pool-1-thread-2 consumer [74],count 2n+1 result :149; total 193 pool-1-thread-3 send [38] to queue; total 194 pool-1-thread-2 consumer [38],count 2n+1 result :77; total 194 pool-1-thread-3 send [32] to queue; total 195 pool-1-thread-2 consumer [32],count 2n+1 result :65; total 195 pool-1-thread-3 send [9] to queue; total 196 pool-1-thread-2 consumer [9],count 2n+1 result :19; total 196 pool-1-thread-3 send [77] to queue; total 197 pool-1-thread-2 consumer [77],count 2n+1 result :155; total 197 pool-1-thread-3 send [69] to queue; total 198 pool-1-thread-2 consumer [69],count 2n+1 result :139; total 198 pool-1-thread-3 send [52] to queue; total 199 pool-1-thread-2 consumer [52],count 2n+1 result :105; total 199 pool-1-thread-3 send [81] to queue; total 200 pool-1-thread-2 consumer [81],count 2n+1 result :163; total 200
ExecutorService executor = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(6); MyLockFreeQueue<Integer> queue = new MyLockFreeQueue(); Worker<Integer> pro = new Provider(queue); Worker<Integer> con = new Consumer(queue); executor.submit(pro); executor.submit(con); executor.submit(pro); executor.submit(con); executor.submit(pro); executor.submit(con); executor.shutdown();