- 前言
作为电商网站,必然要有商品类目表,以便商品分类检索。而设计商品类目表,又是一件特别繁杂的事情。一件商品可能有多个类目来检索出来,比如苹果手机,可以从品牌检索也可以从手机检索。一个类目对应多个商品,比如手机下对应了多款属于手机类的商品。而类目是一个多叉树结构,类似于文件夹的结构。通常大电商都是把类目整理好了放在cache上,就不用频繁访问数据库和整理排序了。
- 个人类目标的结构设计
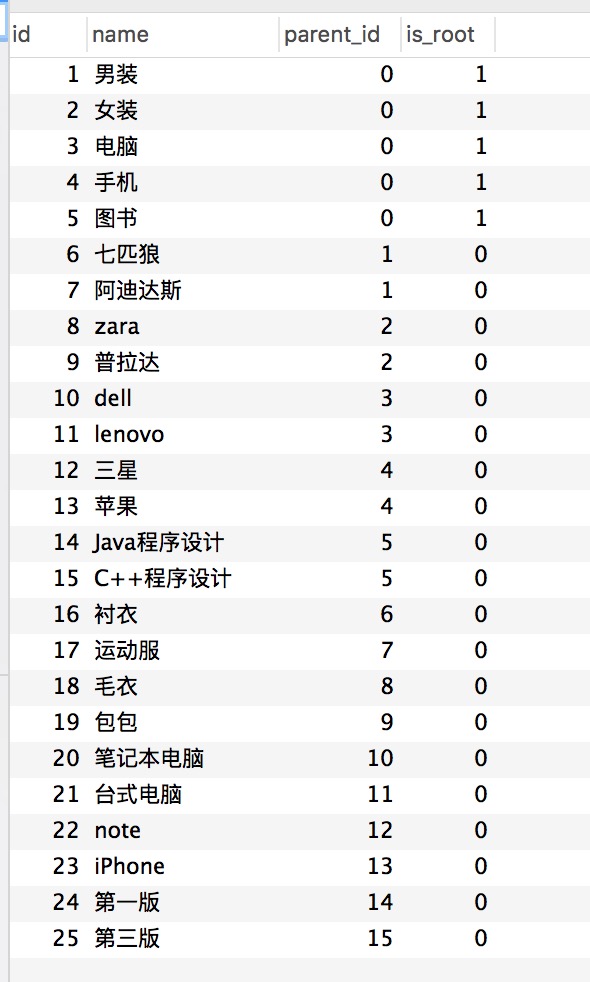
参考了一下网上无限级分类的表设计,简化模型为一个表内存在父子级从属关系。

表中的isRoot可以去掉,只要parent为0就认为是根节点就好了。而为什么不存子节点而是存父节点,因为子节点的映射类,生成整理的时候比存父节点要复杂一些,当然程序写的不复杂而是这个问题需要花费的时间就会多一些。
表设计好了之后,就需要查询数据并且整理出他们的从属关系。为了减少数据库的查询次数,我采用了全部查询,在内存中生成多叉树的形式。节点类的定义想法非常直接,它存在唯一识别:id,真实信息:name,以及它的子树:List or Map。
/* * 树型存储 */ class CategoryTree{ private long id; private String name; private List<CategoryTree> children; public CategoryTree(){ children = new ArrayList<>(); } public long getId() { return id; } public void setId(long id) { this.id = id; } public String getName() { return name; } public void setName(String name) { this.name = name; } public List<CategoryTree> getChildren() { return children; } public void setChildren(List<CategoryTree> children) { this.children = children; } } /* * 哈希表存储 */ class CategoryMap{ private long id; private String name; private Map<Long,CategoryMap> children; public CategoryMap(){ children = new HashMap<>(); } public long getId() { return id; } public void setId(long id) { this.id = id; } public String getName() { return name; } public void setName(String name) { this.name = name; } public Map<Long, CategoryMap> getChildren() { return children; } public void setChildren(Map<Long, CategoryMap> children) { this.children = children; } }
在对乱序数组生成三级n叉树这个过程中,最快的方式是用map。在生成过程中,只能一级级生成,因为没有父节点不可能有子节点跟随这个逻辑的存在。
//集合存储 public void test1(){ tool.connection2MYSQL(); Connection conn = tool.getCon(); String sql = "select * from category"; Statement stm = null; List<category> clist = new ArrayList<>(); try { stm = conn.createStatement(); ResultSet rs = stm.executeQuery(sql); while(rs.next()){ category c = new category(); c.setId(rs.getLong("id")); c.setName(rs.getString("name")); c.setParentId(rs.getLong("parent_id")); c.setIsRoot(rs.getInt("is_root")); clist.add(c); } tool.closeConn(conn); } catch (SQLException e1) { // TODO Auto-generated catch block e1.printStackTrace(); } /* * 检查集合 */ // for(category ca:clist){ // System.out.println("id: "+ca.getId()+" name: "+ca.getName()+" parentId: "+ca.getParentId()+" isRoot: "+ca.getIsRoot()); // } /** * 逻辑尝试===== */ List<CategoryTree> roots = new ArrayList<>(); List<CategoryTree> second = new ArrayList<>(); List<CategoryTree> third = new ArrayList<>(); //一次遍历 添加根节点 int i = 0; while(i != clist.size()-1){ if(clist.get(i).getParentId() == 0){ CategoryTree ct = new CategoryTree(); ct.setId(clist.get(i).getId()); ct.setName(clist.get(i).getName()); roots.add(ct); clist.remove(i); }else i++; } //二次遍历 添加二级节点 for(int j=0;j<roots.size();j++){ i = 0; while(i < clist.size()){ if(clist.get(i).getParentId() == roots.get(j).getId()){ CategoryTree ct = new CategoryTree(); ct.setId(clist.get(i).getId()); ct.setName(clist.get(i).getName()); roots.get(j).getChildren().add(ct); second.add(ct);//用空间换 clist.remove(i); }else i++; } } //三次遍历 添加三级节点 for(int j=0;j<second.size();j++){ i = 0; while(i < clist.size()){ if(clist.get(i).getParentId() == second.get(j).getId()){ CategoryTree ct = new CategoryTree(); ct.setId(clist.get(i).getId()); ct.setName(clist.get(i).getName()); second.get(j).getChildren().add(ct); third.add(ct);//用空间换 clist.remove(i); }else i++; } } for(category ca:clist){ System.out.println("id: "+ca.getId()+" name: "+ca.getName()+" parentId: "+ca.getParentId()+" isRoot: "+ca.getIsRoot()); } for(CategoryTree ct:roots){ System.out.println("id: "+ct.getId()+" name: "+ct.getName()); { for(CategoryTree ct1:ct.getChildren()) { System.out.println("二级 id: "+ct1.getId()+" name: "+ct1.getName()); for(CategoryTree ct2:ct1.getChildren()) System.out.println("三级 id: "+ct2.getId()+" name: "+ct2.getName()); } } }/** * 逻辑尝试===== */ }
我对每一级的节点做了一个额外的存储,在第三级生成的时候简化一个循环,也就是n平方的复杂度。
使用map生成的话,仅在生成这个过程,就可以把问题化简成n的复杂度。因为Map“知道”自己存储的对象的id,而List要通过遍历才知道它的自己存的元素的id。
public void test2(){ tool.connection2MYSQL(); Connection conn = tool.getCon(); String sql = "select * from category"; Statement stm = null; List<category> clist = new ArrayList<>(); try { stm = conn.createStatement(); ResultSet rs = stm.executeQuery(sql); while(rs.next()){ category c = new category(); c.setId(rs.getLong("id")); c.setName(rs.getString("name")); c.setParentId(rs.getLong("parent_id")); c.setIsRoot(rs.getInt("is_root")); clist.add(c); } tool.closeConn(conn); } catch (SQLException e1) { // TODO Auto-generated catch block e1.printStackTrace(); } /** * 逻辑尝试===== */ Map<Long,CategoryMap> rootMap = new HashMap<>(); Map<Long,CategoryMap> secondMap = new HashMap<>(); //遍历一级 int i = 0; while(i < clist.size()){ if(clist.get(i).getParentId() == 0){ CategoryMap cm = new CategoryMap(); cm.setId(clist.get(i).getId()); cm.setName(clist.get(i).getName()); rootMap.put(cm.getId(),cm); clist.remove(i); }else i++; } //遍历二级 i = 0; while (i < clist.size()) { if (rootMap.get(clist.get(i).getParentId()) != null) { CategoryMap cm = new CategoryMap(); cm.setId(clist.get(i).getId()); cm.setName(clist.get(i).getName()); rootMap.get(clist.get(i).getParentId()).getChildren().put(cm.getId(), cm); secondMap.put(cm.getId(), cm); clist.remove(i); } else i++; } //遍历三级 i = 0; while (i < clist.size()) { if (secondMap.get(clist.get(i).getParentId()) != null) { CategoryMap cm = new CategoryMap(); cm.setId(clist.get(i).getId()); cm.setName(clist.get(i).getName()); secondMap.get(clist.get(i).getParentId()).getChildren().put(cm.getId(), cm); clist.remove(i); } else i++; } // for (Map.Entry<Long, CategoryMap> entry : rootMap.entrySet()) { // System.out.println("Key = " + entry.getKey() + ", id : " + entry.getValue().getId()+" name : "+entry.getValue().getName()); // for (Map.Entry<Long, CategoryMap> entry1 : entry.getValue().getChildren().entrySet()){ // System.out.println("二级 Key = " + entry1.getKey() + ", id : " + entry1.getValue().getId()+" name : "+entry1.getValue().getName()); // for (Map.Entry<Long, CategoryMap> entry2 : entry1.getValue().getChildren().entrySet()){ // System.out.println("三级 Key = " + entry2.getKey() + ", id : " + entry2.getValue().getId()+" name : "+entry2.getValue().getName()); // } // } // // } JSONArray json = new JSONArray(); for (CategoryMap entry : rootMap.values()) { JSONObject job1 = new JSONObject(); job1.put("id", entry.getId()); job1.put("name", entry.getName()); JSONArray joa1 = new JSONArray(); // System.out.println("id : " + entry.getId()+" name : "+entry.getName()); for (CategoryMap entry1 : entry.getChildren().values()){ JSONObject job2 = new JSONObject(); job2.put("id", entry1.getId()); job2.put("name", entry1.getName()); JSONArray joa2 = new JSONArray(); // System.out.println("二级 id : " + entry1.getId()+" name : "+entry1.getName()); for (CategoryMap entry2 : entry1.getChildren().values()){ JSONObject job3 = new JSONObject(); job3.put("id", entry2.getId()); job3.put("name", entry2.getName()); joa2.add(job3); // System.out.println("三级 id : " + entry2.getId() + " name : "+entry2.getName()); } job2.put("chird", joa2); joa1.add(job2); } job1.put("chird", joa1); json.add(job1); } for(int k=0;k<json.size();k++){ JSONObject jo = json.getJSONObject(k); System.out.println(jo.toString()); } /** * 逻辑尝试===== */ }
最后的生成json的时候,仍然需要三次方的复杂度,我在考虑如何能在整理过程中顺带生成json,现在还没做出来,不过优化成n应该还是有机会的。
另外,遍历源数据的时候,把抽掉的节点remove掉也是一种减少重复遍历的方式。
最后生成的结果如同预期。
连接成功
{"chird":[{"chird":[{"name":"衬衣","id":16}],"name":"七匹狼","id":6},{"chird":[{"name":"运动服","id":17}],"name":"阿迪达斯","id":7}],"name":"男装","id":1}
{"chird":[{"chird":[{"name":"毛衣","id":18}],"name":"zara","id":8},{"chird":[{"name":"包包","id":19}],"name":"普拉达","id":9}],"name":"女装","id":2}
{"chird":[{"chird":[{"name":"笔记本电脑","id":20}],"name":"dell","id":10},{"chird":[{"name":"台式电脑","id":21}],"name":"lenovo","id":11}],"name":"电脑","id":3}
{"chird":[{"chird":[{"name":"note","id":22}],"name":"三星","id":12},{"chird":[{"name":"iPhone","id":23}],"name":"苹果","id":13}],"name":"手机","id":4}
{"chird":[{"chird":[{"name":"第一版","id":24}],"name":"Java程序设计","id":14},{"chird":[{"name":"第三版","id":25}],"name":"C++程序设计","id":15}],"name":"图书","id":5}
- 总结
对于表设计和这个问题的解决不知道有没有更加规范一点的方式,还需要继续探讨。对于我们项目来说,这个方法已经可以适应了,商品分类我打算用个分类表来做映射,类目表叶子节点的id和商品的id存入,检索的时候根据叶子节点id检索所有商品。本次问题,在于对乱序数组转化为多叉树的模型建立,解决了这个问题,对转化思维又有了进一步的提高。(在这里其实问题的阶并不重要,因为这是有穷集合,类目表的条目基本不会超过几百,考虑的最多的就是访问量的问题,因为小电商不会做cache,每一次访问都生成三级树,所以本次问题重在如何用更好的运算模型去解决同一个问题)
- 追加
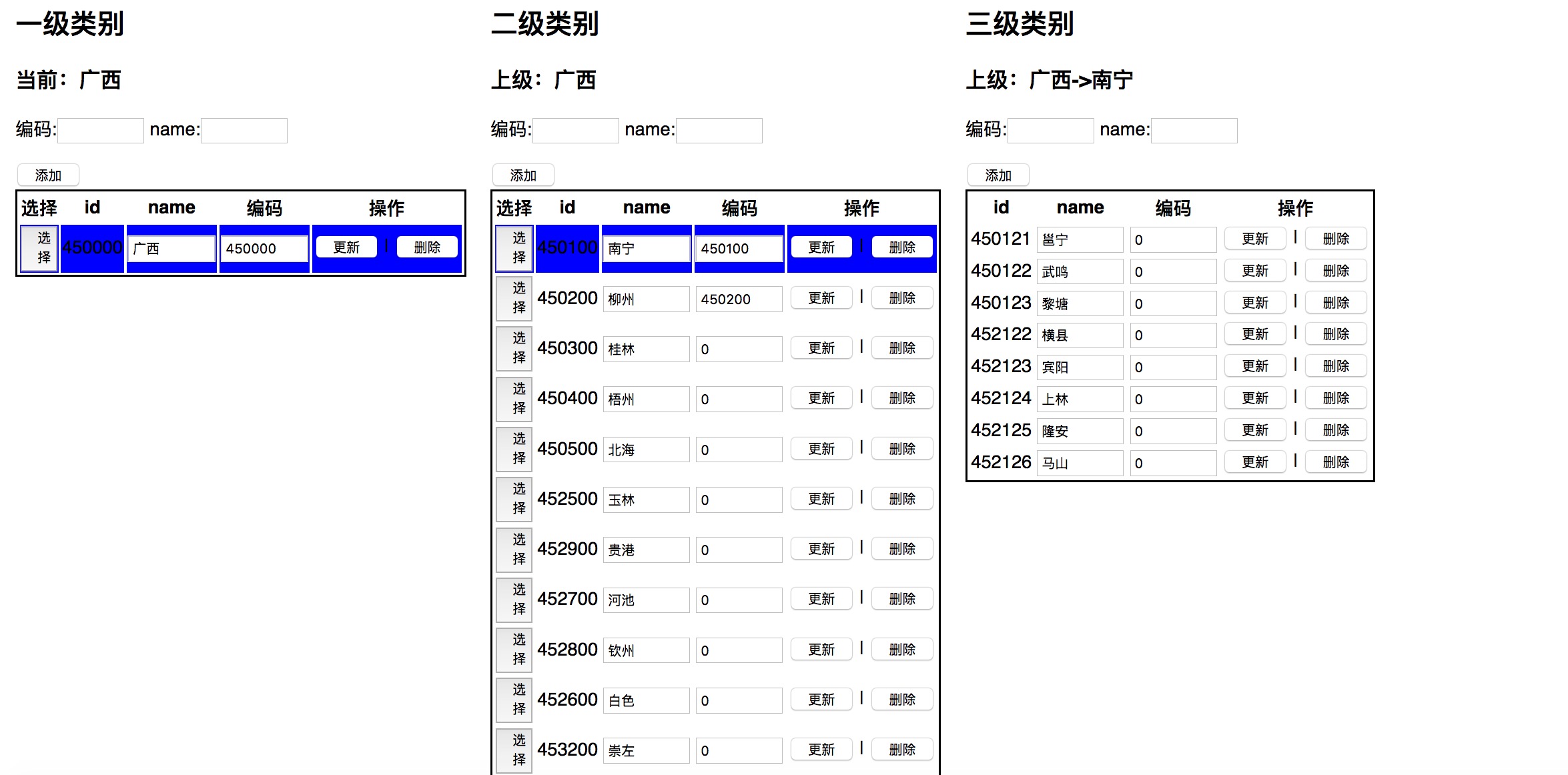
关于三级关系树的运用,我做了一个小的地域管理页面,与类目树是一样的结构。
<%@ page language="java" contentType="text/html; charset=UTF-8" pageEncoding="UTF-8"%> <%@include file="/common.jsp" %> <!DOCTYPE html PUBLIC "-//W3C//DTD HTML 4.01 Transitional//EN" "http://www.w3.org/TR/html4/loose.dtd"> <html> <head> <script type="text/javascript" src="js/jquery.js" ></script> <script type="text/javascript" src="js/jquery.form.js"></script> <meta http-equiv="Content-Type" content="text/html; charset=UTF-8"> <title>地域信息</title> <style> .chosen{ background:blue; } .select{ width:30px; } </style> </head> <body> <div> <div style="margin-left:20px;float:left;"> <h2>一级类别</h2> <h3>当前:${current1.name}</h3> <form action="letao_DevelopmentModelArea_addArea" id="addForm1"> 编码:<input size="8" name="code"> name:<input size="8" name="name"> <input size="8" name="parent" type="hidden" value="0"> <br/> </form> <br/> <button class="add1">添加</button> <table style="border: 2px solid BLACK;"> <thead> <tr> <th>选择</th> <th>id</th> <th>name</th> <th>编码</th> <th>操作</th> </tr> </thead> <s:iterator id="r1" value="#rank1"> <s:if test="#current1.id == #r1.id"> <tr class="chosen" type="${ r1.id}"> <td><button class="select" id="${ r1.id}" type="1">选择</button></td> <td>${ r1.id}</td> <td><input value ="${ r1.name}" id="name${ r1.id}" size="8" ></td> <td><input value ="${ r1.code}" id="code${ r1.id}" size="8"></td> <td><button type="${ r1.id}" class="update">更新</button> | <button type="${ r1.id}" class="del">删除</button></td> </tr> </s:if> <s:else> <tr type="${ r1.id}"> <td><button class="select" id="${ r1.id}" type="1">选择</button></td> <td>${ r1.id}</td> <td><input value ="${ r1.name}" id="name${ r1.id}" size="8" ></td> <td><input value ="${ r1.code}" id="code${ r1.id}" size="8"></td> <td><button type="${ r1.id}" class="update">更新</button> | <button type="${ r1.id}" class="del">删除</button></td> </tr> </s:else> </s:iterator> </table> </div> <div style="margin-left:20px;float:left;"> <h2>二级类别</h2> <h3>上级:${current1.name}</h3> <form action="letao_DevelopmentModelArea_addArea" id="addForm2"> 编码:<input size="8" name="code"> name:<input size="8" name="name"><input size="8" name="parent" type="hidden" value="${current1.id}"> <br/> </form> <br/> <button class="add2">添加</button> <table style="border: 2px solid BLACK;"> <thead> <tr> <th>选择</th> <th>id</th> <th>name</th> <th>编码</th> <th>操作</th> </tr> </thead> <s:iterator id="r2" value="#rank2"> <s:if test="#current2.id == #r2.id"> <tr class="chosen" type="${ r2.id}"> <td><button class="select" id="${ r2.id}" type="2">选择</button></td> <td>${ r2.id}</td> <td><input value ="${ r2.name}" id="name${ r2.id}" size="8"></td> <td><input value ="${ r2.code}" id="code${ r2.id}" size="8"></td> <td><button type="${ r2.id}" class="update">更新</button> | <button type="${ r2.id}" class="del">删除</button></td> </tr> </s:if> <s:else> <tr type="${ r2.id}"> <td><button class="select" id="${ r2.id}" type="2">选择</button></td> <td>${ r2.id}</td> <td><input value ="${ r2.name}" id="name${ r2.id}" size="8"></td> <td><input value ="${ r2.code}" id="code${ r2.id}" size="8"></td> <td><button type="${ r2.id}" class="update">更新</button> | <button type="${ r2.id}" class="del">删除</button></td> </tr> </s:else> </s:iterator> </table> </div> <div style="margin-left:20px;float:left;"> <h2>三级类别</h2> <h3>上级:${current1.name}->${current2.name}</h3> <form action="letao_DevelopmentModelArea_addArea" id="addForm3"> 编码:<input size="8" name="code"> name:<input size="8" name="name"> <input size="8" name="parent" type="hidden" value="${current2.id }"> <br/> </form> <br/> <button class="add3">添加</button> <table style="border: 2px solid BLACK;"> <thead> <tr> <th>id</th> <th>name</th> <th>编码</th> <th>操作</th> </tr> </thead> <s:iterator id="r3" value="#rank3"> <tr> <td>${ r3.id}</td> <td><input value ="${ r3.name}" id="name${ r3.id}" size="8"></td> <td><input value ="${ r3.code}" id="code${ r3.id}" size="8"></td> <td><button type="${ r3.id}" class="update">更新</button> | <button type="${ r3.id}" class="del">删除</button></td> </tr> </s:iterator> </table> </div> </div> <form action="letao_DevelopmentModelArea_updateInfo" method="post" id="updateForm" style="display:none;"> <input id="hideId" type="hidden" name="id" type="hidden"> <input id="updateCode" type="hidden" name="code"> <input id="updateName" type="hidden" name="name"> </form> <form action = "letao_DevelopmentModelArea_listArea" method="post" id="listForm"> <input id="firstRankId" type="hidden" name="firstRankId" value="${current1.id }"> <input id="secondRankId" type="hidden" name="secondRankId" value="${current2.id }"> </form> </body> <script> $('.update').click(function(e){ var dataId = $(e.target).attr("type"); $("#hideId").val(dataId); $("#updateCode").val($("#code"+dataId).val()); $("#updateName").val($("#name"+dataId).val()); $('#updateForm').ajaxSubmit({ type:'post', dataType: 'json', success: function (data) { if(data.status==1){ alert(data.info); location.reload(); }else{ alert(data.info); } }, error: function (XMLResponse) { //alert(XMLResponse.responseText); var ss =JSON.stringify(XMLResponse); alert('操作失败!'+ss); } }); }); $('.del').click(function(e){ var dataId = $(e.target).attr("type"); $.getJSON("letao_DevelopmentModelArea_deleteInfo?id=" + dataId, function(data) { if (data.status == 1) { alert(data.info); location.reload(); } else { alert(data.info); } }); }); $('.add1').click(function(){ $('#addForm1').ajaxSubmit({ type:'post', dataType: 'json', success: function (data) { if(data.status==1){ alert(data.info); location.reload(); }else{ alert(data.info); } }, error: function (XMLResponse) { //alert(XMLResponse.responseText); var ss =JSON.stringify(XMLResponse); alert('操作失败!'+ss); } }); }); $('.add2').click(function(){ $('#addForm2').ajaxSubmit({ type:'post', dataType: 'json', success: function (data) { if(data.status==1){ alert(data.info); location.reload(); }else{ alert(data.info); } }, error: function (XMLResponse) { //alert(XMLResponse.responseText); var ss =JSON.stringify(XMLResponse); alert('操作失败!'+ss); } }); }); $('.add3').click(function(){ $('#addForm3').ajaxSubmit({ type:'post', dataType: 'json', success: function (data) { if(data.status==1){ alert(data.info); location.reload(); }else{ alert(data.info); } }, error: function (XMLResponse) { //alert(XMLResponse.responseText); var ss =JSON.stringify(XMLResponse); alert('操作失败!'+ss); } }); }); $('.select').click(function(e){ if($(e.target).attr("type") === "1"){ $('#firstRankId').val($(e.target).attr("id")); }else if($(e.target).attr("type") === "2"){ $('#secondRankId').val($(e.target).attr("id")); } $('#listForm').submit(); }); </script> </html>
查询用的sql语句使用in来构造。页面控制使用一级当前id和二级当前id作为请求参数刷新页面。
action的设计也是一般操作数据库的形式,不过列表作为页面展示,而其他作为REST接口。
package com.dijing.letao.action; import java.util.List; import com.dijing.letao.DJActionSupport; import com.dijing.letao.NoNeedLogin; import com.dijing.letao.dao.AreaDao; import com.dijing.letao.model.Headquarters.Area; import com.dijing.server.web.DJAction; import com.dijing.server.web.action.JsonResult; import com.opensymphony.xwork2.ActionContext; /** * 地区开发模式校准控制器 */ public class DevelopmentModelAreaAction extends DJActionSupport{ private long id; private String name; private long parent; private long firstRankId; private long secondRankId; private long code; /** * letao_DevelopmentModelArea_listArea * @return * @throws Exception */ @NoNeedLogin public String listArea() throws Exception { return executePage(() -> { AreaDao aDao = new AreaDao(); if(firstRankId == 0 && secondRankId == 0){ List<Area> rank1 = aDao.findByParent(0); List<Area> rank2 = null; List<Area> rank3 = null; if(rank1.size() > 0){ rank2 = aDao.findByParent(rank1.get(0).getId()); ActionContext.getContext().put("current1", rank1.get(0)); } if(rank2.size() > 0){ rank3 = aDao.findByParent(rank2.get(0).getId()); ActionContext.getContext().put("current2", rank2.get(0)); } ActionContext.getContext().put("rank1", rank1); ActionContext.getContext().put("rank2", rank2); ActionContext.getContext().put("rank3", rank3); return DJAction.SHOW; }else if(firstRankId != 0 && secondRankId == 0){ List<Area> rank1 = aDao.findByParent(0); List<Area> rank2 = null; List<Area> rank3 = null; if(rank1.size() > 0){ rank2 = aDao.findByParent(rank1.get(0).getId()); ActionContext.getContext().put("current1", aDao.findByById(firstRankId)); } if(rank2.size() > 0){ rank3 = aDao.findByParent(rank2.get(0).getId()); ActionContext.getContext().put("current2", rank2.get(0)); } ActionContext.getContext().put("rank1", rank1); ActionContext.getContext().put("rank2", rank2); ActionContext.getContext().put("rank3", rank3); return DJAction.SHOW; }else if(firstRankId != 0 && secondRankId != 0){ System.out.println("==================="); List<Area> rank1 = aDao.findByParent(0); List<Area> rank2 = null; List<Area> rank3 = null; if(rank1.size() > 0){ rank2 = aDao.findByParent(rank1.get(0).getId()); ActionContext.getContext().put("current1", aDao.findByById(firstRankId)); } if(rank2.size() > 0){ rank3 = aDao.findByParent(aDao.findByById(secondRankId).getId()); ActionContext.getContext().put("current2", aDao.findByById(secondRankId)); } ActionContext.getContext().put("rank1", rank1); ActionContext.getContext().put("rank2", rank2); ActionContext.getContext().put("rank3", rank3); return DJAction.SHOW; }else return DJAction.FAILURE; }); } /** * letao_DevelopmentModelArea_updateInfo * @return * @throws Exception */ @NoNeedLogin public String updateInfo() throws Exception { return execute(() -> { if(name == null || code == 0 || id == 0) return ok(JsonResult.jsonResultError("请求为空")); AreaDao aDao = new AreaDao(); Area a = aDao.findByById(id); a.setName(name); a.setCode(code); if(a.update()) return ok(JsonResult.jsonResultSuccess("更新成功:")); else return ok(JsonResult.jsonResultError("更新失败")); }); } /** * letao_DevelopmentModelArea_deleteInfo * @return * @throws Exception */ @NoNeedLogin public String deleteInfo() throws Exception { if(id == 0) return ok(JsonResult.jsonResultError("请求为空")); AreaDao aDao = new AreaDao(); Area a = aDao.findByById(id); if(a == null) return ok(JsonResult.jsonResultError("条目不存在")); List<Area> son1 = aDao.findByParent(a.getId()); if(son1.size() >0){ List<Area> son2 = aDao.findByParentList(son1); for(Area s:son2) s.delete(); } for(Area s:son1) s.delete(); a.delete(); return ok(JsonResult.jsonResultSuccess("删除成功")); } /** * letao_DevelopmentModelArea_addArea * @return * @throws Exception */ @NoNeedLogin public String addArea() throws Exception { return execute(() -> { if(name == null) return ok(JsonResult.jsonResultError("请求为空")); if(parent >0){ AreaDao aDao = new AreaDao(); if(aDao.findByParent(parent) == null) ok(JsonResult.jsonResultError("父级不存在 添加不合法")); } Area a = new Area(); a.setName(name); a.setCode(code); a.setParent(parent); if(a.save()) return ok(JsonResult.jsonResultSuccess("添加成功:")); else return ok(JsonResult.jsonResultError("添加失败,已存在")); }); } public long getId() { return id; } public void setId(long id) { this.id = id; } public String getName() { return name; } public void setName(String name) { this.name = name; } public long getParent() { return parent; } public void setParent(long parent) { this.parent = parent; } public long getFirstRankId() { return firstRankId; } public void setFirstRankId(long firstRankId) { this.firstRankId = firstRankId; } public long getSecondRankId() { return secondRankId; } public void setSecondRankId(long secondRankId) { this.secondRankId = secondRankId; } public long getCode() { return code; } public void setCode(long code) { this.code = code; } }
dao层查询的方法,也是很简单的单表查询。
public List<Area> findByParent(long parent) { return mysql.queryListSql(model, " where parent="+parent); } public List<Area> findByParentList(List<Area> list){ StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder(); sb.append("where parent in ("); sb.append(list.get(0).getId()); for(int i=1;i<list.size();i++){ sb.append(","); sb.append(list.get(i).getId()); } sb.append(")"); return mysql.queryListSql(model, sb.toString()); }