一、什么是泛型
1.泛型类和泛型方法兼复用性、类型安全和高效率于一身,是与之对应的非泛型的类和方法所不及。泛型广泛用于容器(collections)和对容器操作的方法中。.NET框架2.0的类库提供一个新的命名空间System.Collections.Generic,其中包含了一些新的基于泛型的容器类。要查找新的泛型容器类(collection classes)的示例代码,请参见基础类库中的泛型。当然,你也可以创建自己的泛型类和方法,以提供你自己的泛化的方案和设计模式,这是类型安全且高效的。
二、泛性优点
1.在我们.net 1.0刚刚推出的时候,我们有不同的类型调用同一个方法的时候,要么给每一个类型写一个专门的方法,还有一种处理方案就是,利用了我们继承的特点,因为Object是所有类型的基类,我们就可以定义一个Object参数的方法,但是这样会有一个缺点,我们都知道Object是引用类型,当我们实际的参数是值类型的时候需要拆箱、装箱操作这里就是没必要的消耗了。

/// <summary> /// 我们可以做一个测试,将三种方法进行一亿次操作对比时间消耗 /// </summary> public void Show() { Console.WriteLine("****************Monitor******************"); { //我们先创建几个计数的变量 int iValue = 12345; long commonSecond = 0; long objectSecond = 0; long genericSecond = 0; //这个是普通类型的方法 { Stopwatch watch = new Stopwatch(); watch.Start(); for (int i = 0; i < 100000000; i++) { ShowInt(iValue); } watch.Stop(); commonSecond = watch.ElapsedMilliseconds; } //这个是Object类型的方法 { Stopwatch watch = new Stopwatch(); watch.Start(); for (int i = 0; i < 100000000; i++) { ShowObject(iValue); } watch.Stop(); objectSecond = watch.ElapsedMilliseconds; } //这个是泛型类型的方法 { Stopwatch watch = new Stopwatch(); watch.Start(); for (int i = 0; i < 100000000; i++) { ShowT<int>(iValue); } watch.Stop(); genericSecond = watch.ElapsedMilliseconds; } Console.WriteLine("commonSecond={0},objectSecond={1},genericSecond={2}" , commonSecond, objectSecond, genericSecond); } } #region 实例一 /// <summary> /// 打印个int值 /// </summary> /// <param name="iParameter"></param> public static void ShowInt(int iParameter) { //Console.WriteLine(iParameter); } /// <summary> /// 打印个string值 /// </summary> /// <param name="sParameter"></param> public static void ShowString(string sParameter) { //Console.WriteLine(sParameter); } /// <summary> /// 打印个DateTime值 /// </summary> /// <param name="oParameter"></param> public static void ShowDateTime(DateTime dtParameter) { //Console.WriteLine(dtParameter); } /// <summary> /// 当我们的方法需要给多个类型调用的时候,在没有泛型之前我们 /// 就只能使用object 基类来做这样的事情,但是确定就是object是引用 /// 类型或造成没必要的拆箱装箱操作 /// </summary> /// <param name="oParameter"></param> public static void ShowObject(object oParameter) { //Console.WriteLine(oParameter); } /// <summary> /// .Net 2.0出现来,我们可以使用T作为一个展位的类型, /// T只有会在编译的时候才会获取我们的类型,达到一种延迟 /// 效果。 /// </summary> /// <typeparam name="T"></typeparam> /// <param name="num"></param> public void ShowT<T>(T oParameter) { //Console.WriteLine(oParameter); } #endregion
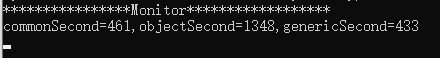
2.上面我针对几种方法测试的时候,可以明显发现使用Object方法慢于普通方法,和泛型方法,我们有可以看到泛型方法会比普通方法快那么一点点,不过可以忽略不计。因为泛型方法的类型不会立即编译出来,会生成一个占位符的东西。
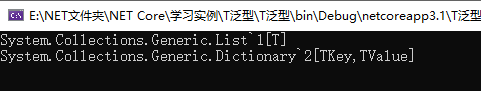
3.我们定义一个泛型,它不会立即获取我们的类型,会生成一个占位符,只有我们在运行中的时候才获取类型。一切延迟的思想。
//我们可以打印出来,可以看到会生成一个展位符 Console.WriteLine(typeof(List<>)); Console.WriteLine(typeof(Dictionary<,>));
三、泛型约束
1.虽然我们的泛型可以放置任何类型,但是如果我们想要限制我们的方法不能胡乱使用,就可以使用我们的泛型约束
|
约束
|
描述
|
|
where T: struct
|
类型参数必须为值类型。
|
|
where T : class
|
类型参数必须为类型。
|
|
where T : new()
|
类型参数必须有一个公有、无参的构造函数。当于其它约束联合使用时,new()约束必须放在最后。
|
|
where T : <base class name>
|
类型参数必须是指定的基类型或是派生自指定的基类型。
|
|
where T : <interface name>
|
类型参数必须是指定的接口或是指定接口的实现。可以指定多个接口约束。接口约束也可以是泛型的。
|
/// <summary> /// 在方法或者类上面我们可以约束T 的类型 /// 在方法后面我们可以使用Where 约束 /// </summary> /// <typeparam name="T"></typeparam> /// <param name="t"></param> public void Show<T>() where T : BaseEntity, IBaseEntity, new() { //仅当T是引用类型时,t = null语句才是合法的; t = 0只对数值的有效 T tNew = default(T); T tNew1 = new T(); Console.WriteLine(tNew); Console.WriteLine(tNew1); Console.WriteLine(typeof(T)); } public static T Get<T>(T t) //where T : ISports//接口约束 //where T : class//引用类型约束 //where T : struct//值类型约束 //where T : BaseEntity //约束基类 where T : new()//无参数构造函数约束 { //T tNew = null; //T tNew = default(T);//会根据T的不同 赋予默认值 T tNew = new T(); return t; }
四、泛型进阶
1.协变、逆变(不过我在项目中还没有遇到过这样的需求,但是思想还是可以的)

/// <summary> /// 协变 ,逆变 /// </summary> public class CCTest { public void Show() { //在我们正常的编码 is a 子类实例化可以等于父类 Bird bird = new Bird(); Bird sparrow = new Sparrow(); //但是我们的泛型就不可以,就有点不科学了 //List<Bird> birds = new List<Sparrow>(); //虽然这样是可以,但是其实是最后面我们遍历了List<Sparrow>()转化为了Bird List<Bird> birds = new List<Sparrow>().Select(x => (Bird)x).ToList(); //我们微软也出了对应的方法,就是我们的协变、逆变 //协变:只能将泛型类型当成返回值 out T //逆变:只能将泛型类型当场参数 in T //协变 IEnumerable<Bird> birdsOut = new List<Bird>(); IEnumerable<Bird> birdsOut1 = new List<Sparrow>(); ICustomerListOut<Bird> customerListOut = new CustomerListOut<Bird>(); ICustomerListOut<Bird> customerListOut1 = new CustomerListOut<Sparrow>(); //逆变 ICustomerListIn<Sparrow> customerListIn = new CustomerListIn<Sparrow>(); ICustomerListIn<Sparrow> customerListIn1 = new CustomerListIn<Bird>(); //协变、逆变 IMyList<Sparrow, Bird> myList1 = new MyList<Sparrow, Bird>(); IMyList<Sparrow, Bird> myList2 = new MyList<Sparrow, Sparrow>();//协变 IMyList<Sparrow, Bird> myList3 = new MyList<Bird, Bird>();//逆变 IMyList<Sparrow, Bird> myList4 = new MyList<Bird, Sparrow>();//逆变+协变 } } #region 类型 /// <summary> /// 鸟类 /// </summary> public class Bird { public int Id { get; set; } } /// <summary> /// 麻雀继承鸟类 /// </summary> public class Sparrow : Bird { public string Name { get; set; } } #endregion #region 接口和类 #region 协变 public interface ICustomerListOut<out T> { //如果我们将T 改成参数,马上报错 T Get(); } public class CustomerListOut<T> : ICustomerListOut<T> { public T Get() { throw new NotImplementedException(); } } #endregion #region 逆变 public interface ICustomerListIn<in T> { //如果我们将T 改成返回值,马上报错 void Get(T t); } public class CustomerListIn<T> : ICustomerListIn<T> { public void Get(T t) { throw new NotImplementedException(); } } #endregion #region 协变,逆变 public interface IMyList<in inT, out outT> { void Show(inT t); outT Get(); outT Do(inT t); } public class MyList<T1, T2> : IMyList<T1, T2> { public void Show(T1 t) { Console.WriteLine(t.GetType().Name); } public T2 Get() { Console.WriteLine(typeof(T2).Name); return default(T2); } public T2 Do(T1 t) { Console.WriteLine(t.GetType().Name); Console.WriteLine(typeof(T2).Name); return default(T2); } } #endregion #endregion
2.泛型缓存,当我们执行一个类之前都会先执行我们的静态构造函数,和初始化我们的静态字段。然后将执行的信息保存到内存中,直到我们的程序重启之后,才会失效。主要是利用了我们静态容器一旦执行完之后会一直保存在程序内存中,然后配合我们的泛型类,就可以根据不同的泛型产生不同的静态容器,分别存储了不同信息(我在项目中经常会使用这个技术比较方便,性能也很奈斯。)
public class GenericCacheTest { public static void Show() { for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++) { Console.WriteLine(GenericCache<int>.GetCache()); Thread.Sleep(10); Console.WriteLine(GenericCache<long>.GetCache()); Thread.Sleep(10); Console.WriteLine(GenericCache<DateTime>.GetCache()); Thread.Sleep(10); Console.WriteLine(GenericCache<string>.GetCache()); Thread.Sleep(10); Console.WriteLine(GenericCache<GenericCacheTest>.GetCache()); Thread.Sleep(10); } } } /// <summary> /// 字典缓存:静态属性常驻内存 /// 但是字典缓存每次都需要运行寻址算法,去算地址 /// </summary> public class DictionaryCache { private static Dictionary<Type, string> _TypeTimeDictionary = null; static DictionaryCache() { Console.WriteLine("This is DictionaryCache 静态构造函数"); _TypeTimeDictionary = new Dictionary<Type, string>(); } public static string GetCache<T>() { Type type = typeof(Type); if (!_TypeTimeDictionary.ContainsKey(type)) { _TypeTimeDictionary[type] = string.Format("{0}_{1}", typeof(T).FullName, DateTime.Now.ToString("yyyyMMddHHmmss.fff")); } return _TypeTimeDictionary[type]; } } /// <summary> /// 每个不同的T,都会生成一份不同的副本 /// 适合不同类型,需要缓存一份数据的场景,效率高 /// 不能主动释放 /// /// 相比上面字典缓存,这种缓存相比要好很多,因为不需要查找地址 /// </summary> /// <typeparam name="T"></typeparam> public class GenericCache<T> { static GenericCache() { Console.WriteLine("This is GenericCache 静态构造函数"); _TypeTime = string.Format("{0}_{1}", typeof(T).FullName, DateTime.Now.ToString("yyyyMMddHHmmss.fff")); } private static string _TypeTime = ""; public static string GetCache() { return _TypeTime; } }
