原文:SpringAOP联盟(2)— Cglib代理流程分析 - 简书 (jianshu.com)
1. 在resources目录下加入logback-test.xml的配置文件
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <configuration> <springProperty scope="context" name="logPath" source="log.out.path" defalutValue="/app/test.log"/> <!-- %m输出的信息,%p日志级别,%t线程名,%d日期,%c类的全名,%i索引【从数字0开始递增】,,, --> <!-- appender是configuration的子节点,是负责写日志的组件。 --> <!-- ConsoleAppender:把日志输出到控制台 --> <appender name="STDOUT" class="ch.qos.logback.core.ConsoleAppender"> <encoder> <pattern>%d %p [%r] [%t] [%X{traceRootId}] (%file:%line\): %m%n</pattern> <!-- 控制台也要使用UTF-8,不要使用GBK,否则会中文乱码 --> <charset>UTF-8</charset> </encoder> </appender> <!-- 控制台输出日志级别 --> <root level="TRACE"> <appender-ref ref="STDOUT"/> </root> <!-- 指定项目中某个包,当有日志操作行为时的日志记录级别 --> <!-- 级别依次为【从高到低】:FATAL > ERROR > WARN > INFO > DEBUG > TRACE --> </configuration>
@Slf4j public class Person { public void run1() { log.info("我在跑步1..."); } public void run2() { log.info("我在跑步2..."); } }
2. 测试源码:
@Test public void testProxyFactory() { Person person = new Person(); //被建议的类,即面向目标类生成代理类 ProxyFactory proxyFactory = new ProxyFactory(person); NameMatchMethodPointcut nameMatchMethodPointcut = new NameMatchMethodPointcut(); nameMatchMethodPointcut.addMethodName("run1"); //通知+切点=advisor DefaultPointcutAdvisor advisor = new DefaultPointcutAdvisor(); advisor.setPointcut(nameMatchMethodPointcut); advisor.setAdvice(new MethodBeforeAdvice() { @Override public void before(Method method, Object[] args, Object target) throws Throwable { System.out.println("before Advice..."); } }); //加入第二个adsivor NameMatchMethodPointcutAdvisor nameMatchMethodPointcutAdvisor= new NameMatchMethodPointcutAdvisor(); nameMatchMethodPointcutAdvisor.addMethodName("run1"); nameMatchMethodPointcutAdvisor.setAdvice(new SimpleTraceInterceptor()); //第三个advisor NameMatchMethodPointcutAdvisor advisor3= new NameMatchMethodPointcutAdvisor(); advisor3.addMethodName("run2"); advisor3.setAdvice(new DebugInterceptor()); //advisor放入到adviced proxyFactory.addAdvisor(advisor); proxyFactory.addAdvisor(advisor3); proxyFactory.addAdvisor(nameMatchMethodPointcutAdvisor); //最后经过代理生成代理对象 Person proxy = (Person) proxyFactory.getProxy(); //执行方法 proxy.run1(); }
3. 测试结果
before Advice...
2021-11-16 11:34:59.859 [main] TRACE o.s.aop.interceptor.SimpleTraceInterceptor - Entering method 'run1' of class [cn.lemon.spring.demo.pojo.Person]
2021-11-16 11:34:59.865 [main] INFO cn.lemon.spring.demo.pojo.Person - 我在跑步1...
2021-11-16 11:34:59.865 [main] TRACE o.s.aop.interceptor.SimpleTraceInterceptor - Exiting method 'run1' of class [cn.lemon.spring.demo.pojo.Person]
流程解析
1. 将advisor交由advised管理
- advisor:增强器(由advice和pointcut组成)
- advised:代理对象配置类(代理对象的配置以及所有的advisor)
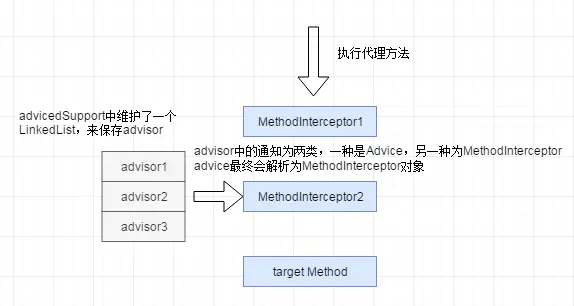
继承AdvisedSupport的ProxyFactory负责创建代理对象,创建出来的代理对象不仅保存了target对象,也保存了Advised(所有Advisor)对象、ProxyConfig(代理对象的配置)对象。
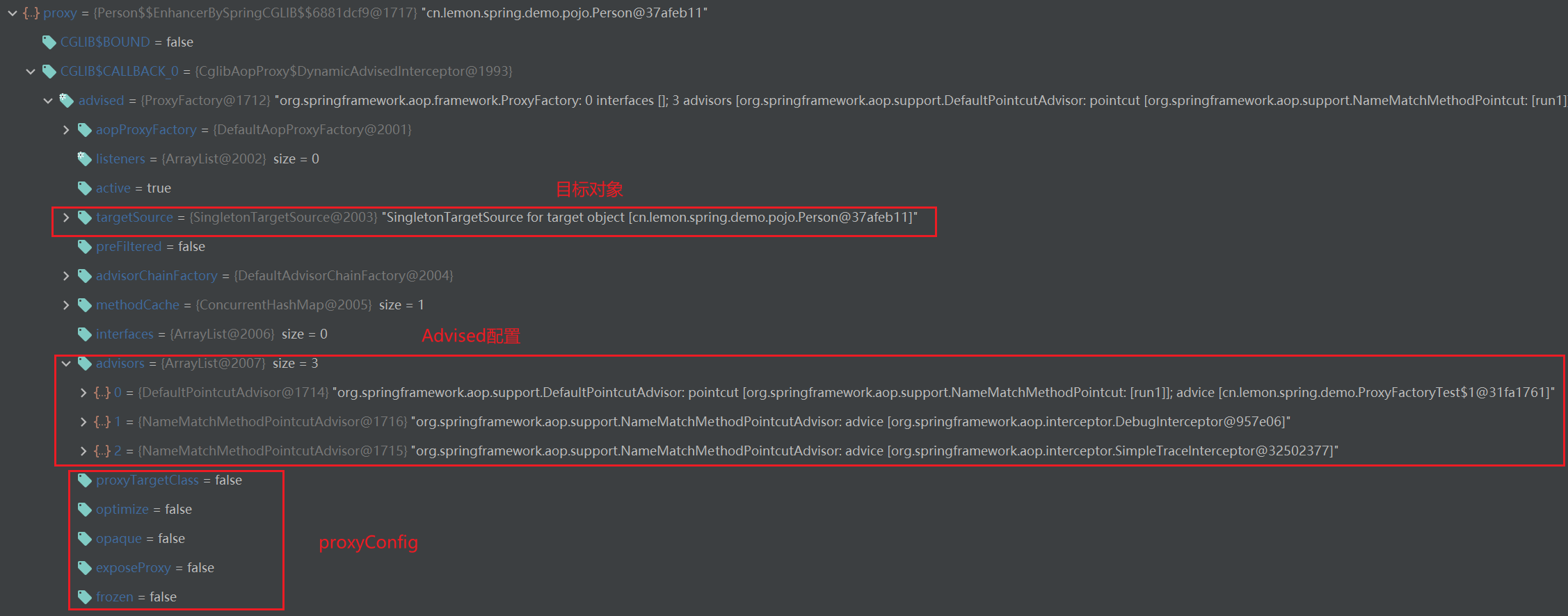
AdvisedSupport实现了Advised接口大部分的方法。
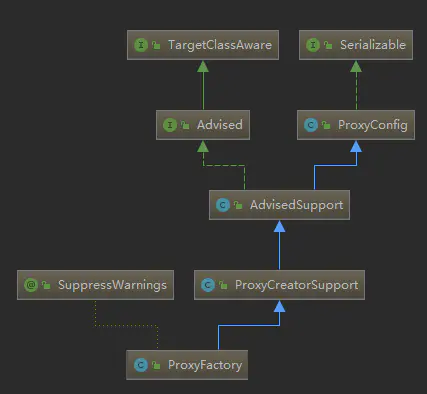
Advisor由Advice+Pointcut组成(通知 + 切入点),可以称为一个增强器,而ProxyFactory管理着所有的Advisor,根据Pointcut(切入点)配置决定为目标对象的方法增加拦截。
调用ProxyFactory的addAdvisor实际上的是AdvisedSupport实现的addAdvisor。
使用List存储所有Advisor
public class AdvisedSupport extends ProxyConfig implements Advised { // 实现的 Advised 接口的方法, 添加一个 Advisor @Override public void addAdvice(Advice advice) throws AopConfigException { int pos = this.advisors.size(); addAdvice(pos, advice); } // ? public void addAdvice(int pos, Advice advice) throws AopConfigException { if (advice instanceof IntroductionInfo) { // We don't need an IntroductionAdvisor for this kind of introduction: // It's fully self-describing. addAdvisor(pos, new DefaultIntroductionAdvisor(advice, (IntroductionInfo) advice)); } else if (advice instanceof DynamicIntroductionAdvice) { // We need an IntroductionAdvisor for this kind of introduction. throw new AopConfigException("DynamicIntroductionAdvice may only be added as part of IntroductionAdvisor"); } else { addAdvisor(pos, new DefaultPointcutAdvisor(advice)); } } /** * 添加一个 Advisor * @param pos 在 chain 中的位置, 0 为头部 head position in chain (0 is head). Must be valid. */ @Override public void addAdvisor(int pos, Advisor advisor) throws AopConfigException { if (advisor instanceof IntroductionAdvisor) { validateIntroductionAdvisor((IntroductionAdvisor) advisor); } addAdvisorInternal(pos, advisor); } private void addAdvisorInternal(int pos, Advisor advisor) throws AopConfigException { Assert.notNull(advisor, "Advisor must not be null"); // 配置不能再改变了 if (isFrozen()) { throw new AopConfigException("Cannot add advisor: Configuration is frozen."); } if (pos > this.advisors.size()) { throw new IllegalArgumentException( "Illegal position " + pos + " in advisor list with size " + this.advisors.size()); } // List<Advisor> advisors, 链表 this.advisors.add(pos, advisor); // this.methodCache.clear() 缓存清空 adviceChanged(); } }
2. 创建出代理对象
源码位置:org.springframework.aop.framework.CglibAopProxy#getProxy

由上图所知,即使不存在advisor,getProxy()依旧生成了一个代理对象。
ProxyFactory的作用是将target与adviced中的所有advisors整合在一起,生成proxy对象。待执行具体方法进行拦截。
3. 拦截方法
当调用代理对象的
run1()方法后,实际上执行的是DynamicAdvisedInterceptor接口(CglibAopProxy内部类)的intercept()方法。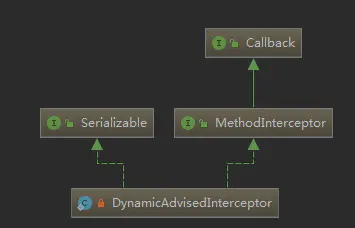
(1)首先获取到对应Method方法上的chain(拦截器链)。
(2)递归执行拦截方法+目标方法。
代理对象的运行:
public Object intercept(Object proxy, Method method, Object[] args, MethodProxy methodProxy) throws Throwable { Object oldProxy = null; boolean setProxyContext = false; Object target = null; TargetSource targetSource = this.advised.getTargetSource(); try { //若是设置了exposeProxy=true属性,便可以在同一线程中获取代理对象 if (this.advised.exposeProxy) { oldProxy = AopContext.setCurrentProxy(proxy); setProxyContext = true; } //获取到目标对象 target = targetSource.getTarget(); Class<?> targetClass = (target != null ? target.getClass() : null); //(重点关注)1. 获取advised的该方法上的过滤器链 List<Object> chain = this.advised.getInterceptorsAndDynamicInterceptionAdvice(method, targetClass); Object retVal; if (chain.isEmpty() && Modifier.isPublic(method.getModifiers())) { Object[] argsToUse = AopProxyUtils.adaptArgumentsIfNecessary(method, args); retVal = methodProxy.invoke(target, argsToUse); } else { //(重点关注)2. 开始执行方法的回调 retVal = new CglibMethodInvocation(proxy, target, method, args, targetClass, chain, methodProxy).proceed(); } retVal = processReturnType(proxy, target, method, retVal); return retVal; } finally { if (target != null && !targetSource.isStatic()) { targetSource.releaseTarget(target); } if (setProxyContext) { // Restore old proxy. AopContext.setCurrentProxy(oldProxy); } } }
3.1 获取过滤器链
依旧是AdvicedSupport,代理对象配置类的方法,作用是获取方法上的拦截器链。
在addAdvisorInternal方法中,最后执行的adviceChanged()方法,实际上是调用methodCache.clear()方法,即清空拦截器缓存List。
注意:MethodCacheKey是由Method实例 + method.hashCode()组成,确保key的唯一性。
public List<Object> getInterceptorsAndDynamicInterceptionAdvice(Method method, @Nullable Class<?> targetClass) { MethodCacheKey cacheKey = new MethodCacheKey(method); //每次加入advisor后均清空methodCache,于是需要重新的生成cached List<Object> cached = this.methodCache.get(cacheKey); if (cached == null) { cached = this.advisorChainFactory.getInterceptorsAndDynamicInterceptionAdvice( this, method, targetClass); this.methodCache.put(cacheKey, cached); } return cached; }
而实际上获取AdvisorChain的方法是AdvisorChainFactory接口实现的。
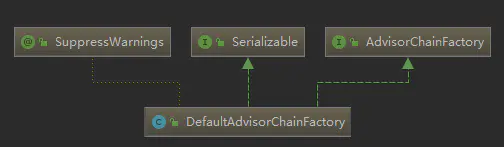
该方法作用有两个,
- 遍历所有的
Advisor,若可以切入该方法(根据Pointcut配置决定),执行步骤2; - 将
Advisor解析为MethodInterceptor[]对象,并加入到List<Object> interceptorList中
注:MethodInterceptor 接口就一个 invoke 方法,入参类型 MethodInvocation,MethodInvocation 接口则有getMethod 、 getArguments 、getThis、procced 等方法
public class DefaultAdvisorChainFactory implements AdvisorChainFactory, Serializable { @Override public List<Object> getInterceptorsAndDynamicInterceptionAdvice( Advised config, Method method, @Nullable Class<?> targetClass) { // This is somewhat tricky... We have to process introductions first, // but we need to preserve order in the ultimate list. // 饿汉式单例,最终生成DefaultAdvisorAdapterRegistry对象 AdvisorAdapterRegistry registry = GlobalAdvisorAdapterRegistry.getInstance(); // 入参配置中获取所有 Advisor Advisor[] advisors = config.getAdvisors(); List<Object> interceptorList = new ArrayList<>(advisors.length); // 获取声明 method 的实际类型, 也就是目标对象的类型 Class<?> actualClass = (targetClass != null ? targetClass : method.getDeclaringClass()); Boolean hasIntroductions = null; for (Advisor advisor : advisors) { // 两种 Advisor, PointcutAdvisor 和 IntroductionAdvisor // PointcutAdvisor#getPointcut 直接能获得切入点[AspectJPointcutAdvisor] // IntroductionAdvisor#getClassFilter[DefaultIntroductionAdvisor] if (advisor instanceof PointcutAdvisor) { PointcutAdvisor pointcutAdvisor = (PointcutAdvisor) advisor; // ? || Class是否满足被拦截条件 if (config.isPreFiltered() || pointcutAdvisor.getPointcut().getClassFilter().matches(actualClass)) { MethodMatcher mm = pointcutAdvisor.getPointcut().getMethodMatcher(); boolean match; if (mm instanceof IntroductionAwareMethodMatcher) { if (hasIntroductions == null) { hasIntroductions = hasMatchingIntroductions(advisors, actualClass); } match = ((IntroductionAwareMethodMatcher) mm).matches(method, actualClass, hasIntroductions); } else { match = mm.matches(method, actualClass); } // 方法拦截匹配了 if (match) { // 将advisor中的内容转化为MethodInterceptor MethodInterceptor[] interceptors = registry.getInterceptors(advisor); // MethodMatcher 是否为动态的, 也就是在运行期间是否匹配可能改变, 那么就需要每次invoke运行时再判断一次是否匹配 if (mm.isRuntime()) { for (MethodInterceptor interceptor : interceptors) { // MethodInterceptors 和 MethodMatcher 的封装, DynamicMethodMatcher - 动态方法匹配 interceptorList.add(new InterceptorAndDynamicMethodMatcher(interceptor, mm)); } } else { // 直接添加 interceptorList.addAll(Arrays.asList(interceptors)); } } } } else if (advisor instanceof IntroductionAdvisor) { IntroductionAdvisor ia = (IntroductionAdvisor) advisor; // Class 匹配即可? if (config.isPreFiltered() || ia.getClassFilter().matches(actualClass)) { // 将advisor中的内容转化为MethodInterceptor Interceptor[] interceptors = registry.getInterceptors(advisor); // 直接添加, 没有动态的判断 interceptorList.addAll(Arrays.asList(interceptors)); } } else { Interceptor[] interceptors = registry.getInterceptors(advisor); interceptorList.addAll(Arrays.asList(interceptors)); } } return interceptorList; } }
AdvisorAdapterRegistry registry = GlobalAdvisorAdapterRegistry.getInstance();生成的注册器。该类的主要作用是将通知Advice解析为MethodInterceptor对象。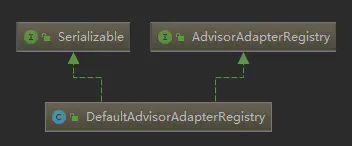
public class DefaultAdvisorAdapterRegistry implements AdvisorAdapterRegistry, Serializable { private final List<AdvisorAdapter> adapters = new ArrayList<>(3); /** * Create a new DefaultAdvisorAdapterRegistry, registering well-known adapters. */ public DefaultAdvisorAdapterRegistry() { // 支持 MethodBeforeAdvice 类型的通知(Advice) registerAdvisorAdapter(new MethodBeforeAdviceAdapter()); // 支持 AfterReturningAdvice 类型通知, 封装为 AfterReturningAdviceInterceptor registerAdvisorAdapter(new AfterReturningAdviceAdapter()); // 支持 ThrowsAdvice 类型通知 registerAdvisorAdapter(new ThrowsAdviceAdapter()); } @Override public MethodInterceptor[] getInterceptors(Advisor advisor) throws UnknownAdviceTypeException { List<MethodInterceptor> interceptors = new ArrayList<>(3); Advice advice = advisor.getAdvice(); //若是Advice实现了MethodInterceptor接口,直接加入到List中 if (advice instanceof MethodInterceptor) { interceptors.add((MethodInterceptor) advice); } for (AdvisorAdapter adapter : this.adapters) { //若是advice实现了MethodBeforeAdvice等类型,则转换为MethodInterceptor,注意这些方法由子类实现。 if (adapter.supportsAdvice(advice)) { interceptors.add(adapter.getInterceptor(advisor)); } } if (interceptors.isEmpty()) { throw new UnknownAdviceTypeException(advisor.getAdvice()); } return interceptors.toArray(new MethodInterceptor[0]); } }
3.2 递归执行方法
retVal = new CglibMethodInvocation(proxy, target, method, args, targetClass, chain, methodProxy).proceed();
注意在这里每次调用都new,意味着下面的 ReflectiveMethodInvocation 每次状态都是重置的(currentInterceptorIndex)
也要注意到 ReflectiveMethodInvocation 类就是 ProxyMethodInvocation(MethodInvocation),而通知封装为 MethodInterceptor 的 invoke 参数类型就是 MethodInvocation,这里传入了 this,
那么 MethodInterceptor 实现只要调用参数 MethodInvocation#procced 就能够回调 ReflectionMethodInvocation 的方法实现下一个拦截器的调用
class CglibAopProxy implements AopProxy, Serializable { private static class CglibMethodInvocation extends ReflectiveMethodInvocation { public Object proceed() throws Throwable { try { return super.proceed(); } } } } public class ReflectiveMethodInvocation implements ProxyMethodInvocation, Cloneable { // Joinpoint 接口实现, 连接点 @Override @Nullable public Object proceed() throws Throwable { // We start with an index of -1 and increment early. // 默认-1, 后者实际是 List<Object>, 不要被名称迷惑了 if (this.currentInterceptorIndex == this.interceptorsAndDynamicMethodMatchers.size() - 1) { // 所有拦截器已经调用完毕了, 则反射调用其 target 的方法 return invokeJoinpoint(); } // 获取第一个拦截器 Object interceptorOrInterceptionAdvice = this.interceptorsAndDynamicMethodMatchers.get(++this.currentInterceptorIndex); // 动态 Matcher 则再次判断是否匹配 if (interceptorOrInterceptionAdvice instanceof InterceptorAndDynamicMethodMatcher) { // Evaluate dynamic method matcher here: static part will already have // been evaluated and found to match. InterceptorAndDynamicMethodMatcher dm = (InterceptorAndDynamicMethodMatcher) interceptorOrInterceptionAdvice; Class<?> targetClass = (this.targetClass != null ? this.targetClass : this.method.getDeclaringClass()); if (dm.methodMatcher.matches(this.method, targetClass, this.arguments)) { // 匹配则调用拦截, 注意传入了this(参数声明类型 MethodInvocation) // this 也是一个 ProxyMethodInvocation(MethodInvocation), 每个 interceptor 都会调用 MethodInvocation#proceed, 类似递归调用 return dm.interceptor.invoke(this); } else { // Dynamic matching failed. // Skip this interceptor and invoke the next in the chain. // 不匹配则递归调用, 执行下一个拦截点 return proceed(); } } else { // It's an interceptor, so we just invoke it: The pointcut will have // been evaluated statically before this object was constructed. // 其他的直接调用, 注意传入了this(参数声明类型 MethodInvocation) return ((MethodInterceptor) interceptorOrInterceptionAdvice).invoke(this); } } }
拦截器回调方法:org.springframework.aop.framework.adapter.MethodBeforeAdviceInterceptor#invoke
如何实现前置通知:下一个拦截器/target方法执行前执行增强逻辑
如何实现后置通知:下一个拦截器/target方法执行后执行增强逻辑
这也是对不同 Advice 封装为 MethodInvocation 的具体 MethodInvocation 的实现逻辑
@Override public Object invoke(MethodInvocation mi) throws Throwable { //因为Advice被转换成为了MethodInterceptor对象,包装了invoke方法 this.advice.before(mi.getMethod(), mi.getArguments(), mi.getThis()); //继续执行(JoinPoint)后续的方法,即递归调用。 return mi.proceed(); }
org.springframework.aop.framework.CglibAopProxy.CglibMethodInvocation#invokeJoinpoint@Override protected Object invokeJoinpoint() throws Throwable { if (this.methodProxy != null) { //回调方法 return this.methodProxy.invoke(this.target, this.arguments); } else { return super.invokeJoinpoint(); } }
实际上执行的是:org.springframework.cglib.proxy.MethodProxy#invoke
class CglibAopProxy implements AopProxy, Serializable { private static class CglibMethodInvocation extends ReflectiveMethodInvocation { @Override protected Object invokeJoinpoint() throws Throwable { if (this.methodProxy != null) { // 一般是这个 return this.methodProxy.invoke(this.target, this.arguments); } else { // 父类就是直接反射调用 target 的方法 return super.invokeJoinpoint(); } } } } public class MethodProxy { public Object invoke(Object obj, Object[] args) throws Throwable { try { // 初始化 FastClass 封装便于快速调用 init(); FastClassInfo fci = fastClassInfo; // 上面init初始化的, f1是target类, f2是proxy类型, i1是target的方法, i2是proxy代理后方法, obj 为 target 实例 // 这里的 Cglib 有一个 FastClass 的概念, 就是将要调用的方法映射为int型值, 然后invoke传入int型值, 内部switch-case, 每个case直接target.method调用指定的方法, 避免了使用 method.invoke(target)反射调用 return fci.f1.invoke(fci.i1, obj, args); } } }
Cglib详解...指出了生成一个Cglib的Proxy对象,实际上会生成3个文件,在Java代码中表示:
f1表示的是代理类的FastClass对象;f2表示目标类的FastClass对象i1表示run1()方法的下标(代理对象run1()会经过拦截)。i2表示CGLIB$run1$0方法的下标(代理对象中该方法是super.run1())。
super.run1()执行的是目标对象的run1()方法。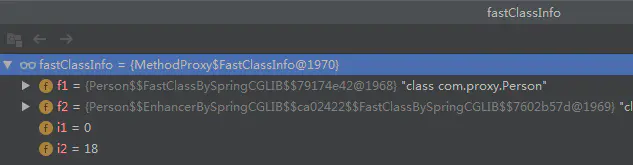
fci.f1.invoke(fci.i1, obj, args)含义是,在代理类的FastClass对象中执行run1()方法,而参数obj对象去执行run1()方法。而此处obj对象是target对象。
即递归出口中最终执行的是target的run1(),且结束调用。