ADO.NET Data Service是基于WCF的一套REST风格的服务,但是它在很多方面又与WCF很不一样,典型的情况就是在身份验证方面。这篇文章专门来说一说如何为其实现身份验证。
1. 采用Windows验证方式。
这种方式总是最简单也是最安全的。基本上我们也无需做太多事情。
web.config中配置
<authentication mode="Windows"/> <authorization> <allow users="Chenxizhang-pc\chenxizhang"/> <deny users="*"/> </authorization>
Data Service里面,我们要通过所谓的QueryInterceptor进行拦截
[QueryInterceptor("Customers")] public Expression<Func<Customers, bool>> OnQueryCustomers() { if (!HttpContext.Current.User.Identity.IsAuthenticated) throw new AuthenticationException(); else return (c) => true; }
这样,我们就实现了目的:该服务(或者说其他的网站资源),只允许Chenxizhang-pc\chenxizhang这个账号能访问到。
接下来,客户端中应该怎么做呢?
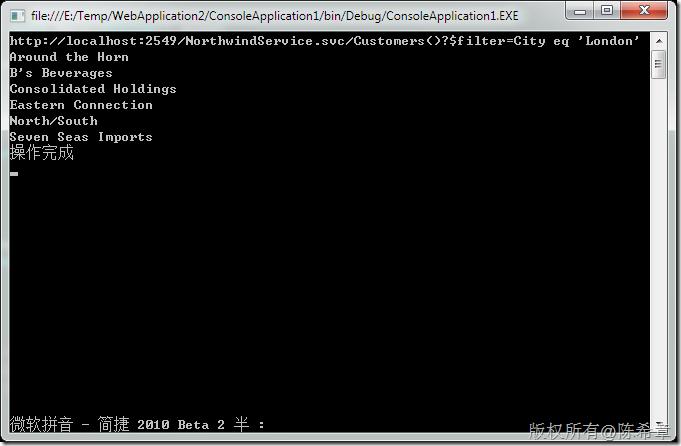
localhost.NorthwindEntities context = new localhost.NorthwindEntities( new Uri("http://localhost:2549/NorthwindService.svc/")); context.Credentials = System.Net.CredentialCache.DefaultNetworkCredentials; ////查询 var query = from c in context.Customers where c.City.Equals("London") select c; Console.WriteLine(query.ToString()); foreach (var item in query) { Console.WriteLine(item.CompanyName); }
现在我的身份是合法的,所以能看到结果
但是如果我把下面这一句去除掉
<allow users="Chenxizhang-pc\chenxizhang"/>
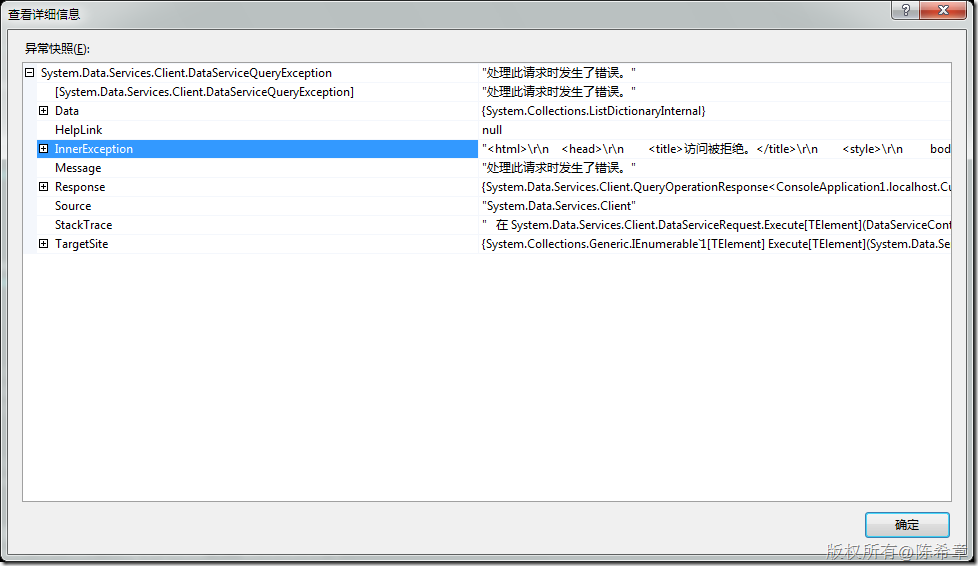
就会发生一个错误
很好,我们这样就实现了身份验证了。
等一下,这样是否就真的万事大吉了呢?大家要知道,不是任何场合都有机会使用Windows验证的,例如在internet上,可能就无法使用Windows验证方式。
那么,是不是可以使用传统的Forms验证呢?如果在一个网站内部,那么看起来确实可以:先让用户去一个页面(Login.aspx)进行登录,此时它的凭据会保存起来,然后再访问服务的话就拥有了身份。
但是,问题是,如果仅仅在网站内部使用,那么有什么必要用Data Service呢?为什么不直接用EDM去存取数据库呢?
好吧,那么,如果我们既希望在外部能访问到这个Data Service,又不想用Windows 验证,并且我们也无法使用Forms验证,那么该怎么办呢?答案是自定义验证。
首先,我们编写一个HttpModule
using System; using System.Collections.Generic; using System.Linq; using System.Text; using System.Web; using System.Security.Principal; namespace DataServiceAuthenticationModule { public class AuthenticationModule : IHttpModule { const string accessDeniedStatus = "拒绝访问"; const string accessDeniedHtml = "<html><body>401 您的请求被拒绝,因为没有通过身份验证</body></html>"; const string realmFormatString = "Basic realm=\"{0}\""; const string authServerHeader = "WWW-Authenticate"; const string authClientHeader = "Authorization"; const string basicAuth = "Basic"; #region IHttpModule 成员 public void Dispose() { } public void Init(HttpApplication context) { context.AuthenticateRequest += new EventHandler(context_AuthenticateRequest); } void context_AuthenticateRequest(object sender, EventArgs e) { HttpApplication context = (HttpApplication)sender; if (context.Request.Headers["Authorization"] == null) { context.Response.StatusCode = 401; context.Response.StatusDescription = accessDeniedStatus; context.Response.Write(accessDeniedHtml); // TODO: not sure this is quite right wrt realm. context.Response.AddHeader(authServerHeader,string.Format(realmFormatString,context.Request.Url.GetLeftPart(UriPartial.Authority))); } else { string credential = ASCIIEncoding.ASCII.GetString(Convert.FromBase64String(GetBase64CredentialsFromHeader())); string[] usernameandpassword = credential.Split(':'); context.Context.User= new MyPrinciple( new MyIdentity(usernameandpassword[0], Authenticate(usernameandpassword[0], usernameandpassword[1]))); } } bool Authenticate(string username, string password) { //your code logic here to authenticate user if (username !="chenxizhang" || password!="password") return false; else return true; } string GetBase64CredentialsFromHeader() { string credsHeader =HttpContext.Current.Request.Headers[authClientHeader]; string creds = null; int credsPosition = credsHeader.IndexOf(basicAuth, StringComparison.OrdinalIgnoreCase); if (credsPosition != -1) { credsPosition += basicAuth.Length + 1; creds = credsHeader.Substring(credsPosition, credsHeader.Length - credsPosition); } return (creds); } #endregion } public class MyPrinciple : IPrincipal { private IIdentity _id; public MyPrinciple(IIdentity id) { _id = id; } public IIdentity Identity { get { return _id; } } public bool IsInRole(string role) { throw new NotImplementedException(); } } public class MyIdentity : IIdentity { private bool _isAuthenticated = false; private string _name; public MyIdentity(string name, bool isAuthenticated) { _isAuthenticated = isAuthenticated; _name = name; } public string AuthenticationType { get { throw new NotImplementedException(); } } public bool IsAuthenticated { get { return _isAuthenticated; } } public string Name { get { return _name; } } } }
然后,我们将web.config中的身份验证模式改为不验证(也就是说由我们自定义验证)
<authentication mode="None"/>
然后,我们将上面这个模块注册到配置文件中
<add name="DataServiceAuthentication" type="DataServiceAuthenticationModule.AuthenticationModule,DataServiceAuthenticationModule"/>
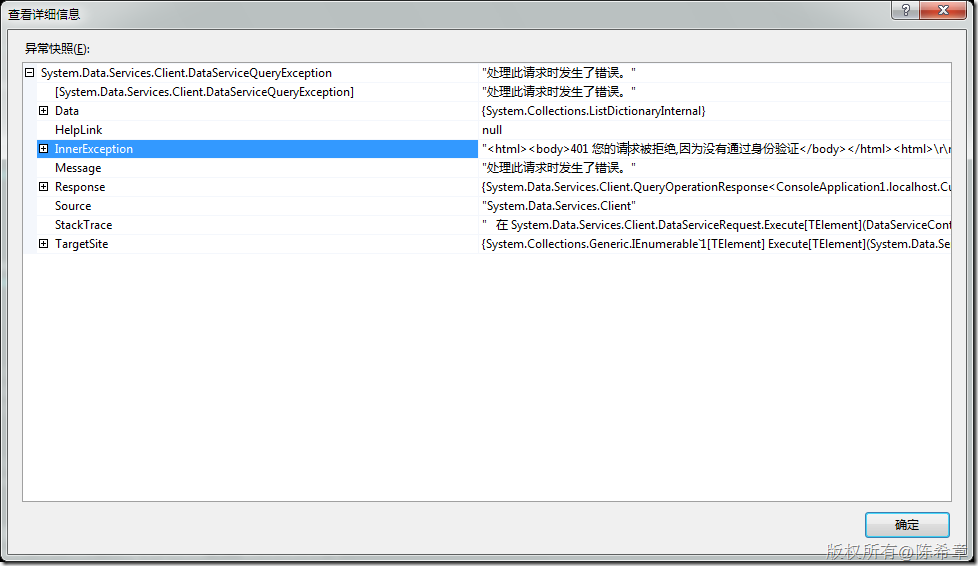
配置好之后,我们再次运行一下客户端,收到了如下的错误。这一点都不奇怪,因为我们并没有传递身份过来。
那么客户端应该如何传递身份呢
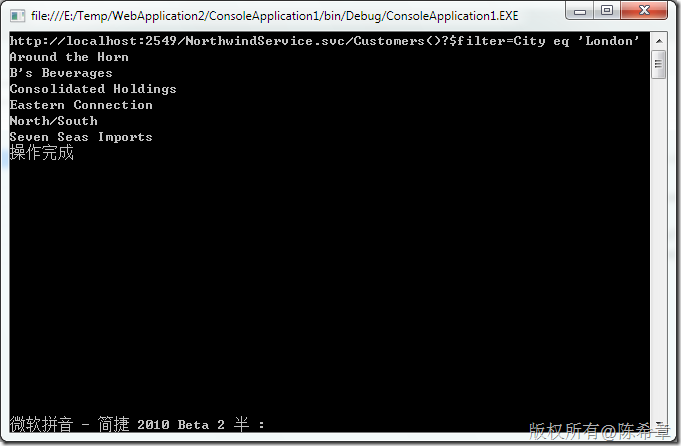
context.Credentials = new System.Net.NetworkCredential("chenxizhang", "password");
这样的话,我们就能如愿看到结果了
写到这里,我想很多朋友就看明白了,我们做了一个自定义的HttpModule,接管了请求的身份验证过程。那么现在的做法是直接比较用户名和密码,是不是很不合理呢?
当然,正式的环境下我们不能这么做,但是你既然拿到了username,和password,其实你要怎么验证都不重要了。