javascript相对于其它语言来说是一种弱类型的语言,在其它如java语言中,程序的执行需要有编译的阶段,而在javascript中也有类似的“预编译阶段”(javascript的预编译是以代码块为范围<script></script>,即每遇到一个代码块都会进行 预编译>执行),了解javascript引擎的执行机理,将有助于在写js代码过程中的思路总结。
首先javascript是解释型语言,自然就是编译一行,执行一行。
js运行过程分为三步: 1、语法分析 2、预编译 3、解释执行
语法分析就是指js引擎去判断检查你的代码是否存在语法错误,解释执行更不用多说,自然就是执行你的代码,然而重中之重的是预编译,预编译简单理解就是在内存中开辟一些空间,存放一些变量与函数 。
理解预编译首先要明白函数声明和变量赋值:
javascript中的两种声明方式,var和function,前者声明的是变量,后者声明的是方法。
在预编译中,javascript对这两种声明做出了两种处理方案:
<script>
var a = "1"; //声明变量a
function b() { //声明方法b
alert();
}
var c = function () { //声明变量c
alert();
}
</script>
以上代码块中,a、c为变量赋值,b为函数声明,当执行以上的代码时,首先会进入预编译阶段,对与变量赋值a、c会在内存中开辟一块内存空间并指向变量名,且赋值为undefined
预编译(函数执行前)
1. 创建AO对象(Active Object) 2. 查找函数形参及函数内变量声明,形参名及变量名作为AO对象的属性,值为undefined 3. 实参形参相统一,实参值赋给形参 4. 查找函数声明,函数名作为AO对象的属性,值为函数引用
题目1:
<script>
function fn(a) {
console.log(a)
var a = 123
console.log(a)
function a() {
}
console.log(a)
var b = function () {
}
console.log(b)
function d() {
}
console.log(d)
}
fn(1)
</script>
分析:
1)、创建AO对象
AO{
}
2)、查找函数形参及函数内变量声明,形参名及变量名作为AO对象的属性,值为undefined
AO{
a:undefined,
b:undefined,
}
3)、实参形参相统一,实参值赋给形参
AO{
a:1,
b:undefined,
}
4)、查找函数声明,函数名作为AO对象的属性,值为函数引用
AO{
a:function a() {
},
b:undefined,
d:function d() {
}
}
变量、函数声明后代码顺序
function fn(a) {
var a
var b
function a() {
}
function d() {
}
console.log(a)
a = 123
console.log(a)
console.log(a)
b = function () {
}
console.log(b)
console.log(d)
}
</script>
解释执行
当执行到a=123之前时: 此时 console.log(a)打印的值为: function a() {}
AO{
a:function a() {
},
b:undefined,
d:function d() {
}
}
当执行到a=123时: 此时 console.log(a)打印的值为: 123 123
AO{
a:123,
b:undefined,
d:function d() {
}
}
当执行到b = function () {}时:
此时 console.log(b)打印的值为: function () {} console.log(d)打印的值为: function d() {}
AO{
a:123,
b:function () {
},
d:function d() {
}
}
浏览器执行结果:

题目2:
<script>
function test(a, b) {
console.log(a);
c = 0;
var c;
a = 3;
b = 2;
console.log(b);
function b() {
}
function d() {
}
console.log(b)
}
test(1)
</script>
分析:
1)、创建AO对象
AO{
}
2)、查找函数形参及函数内变量声明,形参名及变量名作为AO对象的属性,值为undefined
AO{
a:undefined,
b:undefined,
c:undefined
}
3)、实参形参相统一,实参值赋给形参
AO{
a:1,
b:undefined,
c:undefined
}
4)、查找函数声明,函数名作为AO对象的属性,值为函数引用
AO{
a:1,
b:function b() {
},
c:undefined,
d:function d() {
}
}
变量、函数声明后代码顺序
function test(a, b) {
var a
var b
var c
function b() {
}
function d() {
}
console.log(a);
c = 0;
a = 3;
b = 2;
console.log(b);
console.log(b)
}
解释执行
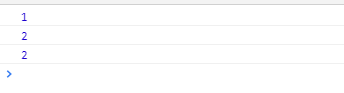
当执行到function d() {}之前时: 此时 console.log(a)打印的值为: 1
AO{
a:1,
b:function b() {
},
c:undefined,
d:function d() {
}
}
当执行到b=2之前时: 此时 console.log(b)打印的值为: 2 2
AO{
a:1,
b:2,
c:0,
d:function d() {
}
}
浏览器执行结果:
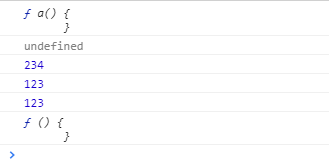
题目3:
<script>
function test(a, b) {
console.log(a);
console.log(b);
var b = 234;
console.log(b);
a = 123;
console.log(a);
function a() {
}
var a;
b = 456;
var b = function () {
}
console.log(a);
console.log(b);
}
test(1)
</script>
分析:
1)、创建AO对象
AO{
}
2)、查找函数形参及函数内变量声明,形参名及变量名作为AO对象的属性,值为undefined
AO{
a:undefined,
b:undefined
}
3)、实参形参相统一,实参值赋给形参
AO{
a:1,
b:undefined
}
4)、查找函数声明,函数名作为AO对象的属性,值为函数引用
AO{
a:function a() {
},
b:undefined
}
变量、函数声明后代码顺序
function test(a, b) {
var a;
var b;
function a() {
}
console.log(a);
console.log(b);
b = 234;
console.log(b);
a = 123;
console.log(a);
b = 456;
b = function () {
}
console.log(a);
console.log(b);
}
解释执行
当执行到function a() {}时:
此时 console.log(a)打印的值为: function a() {} console.log(b)打印的值为: undefined
AO{
a:function a() {
},
b:undefined
}
当执行到 b=234时: 此时 console.log(b)打印的值为: 234
AO{
a:function a() {
},
b:234
}
当执行到 a=123时: 此时 console.log(a)打印的值为: 123
AO{
a:123,
b:234
}
当执行到 b=456 时
AO{
a:123,
b:456
}
当执行到 b = function () {}时:
此时 console.log(a)打印的值为: 123 console.log(b)打印的值为: function () {}
AO{
a:123,
b:function () {
}
}
浏览器执行结果: