Alice’s Cube
Time Limit: 2000/1000 MS (Java/Others) Memory Limit: 32768/32768 K (Java/Others)
Total Submission(s): 1866 Accepted Submission(s): 591
Problem Description
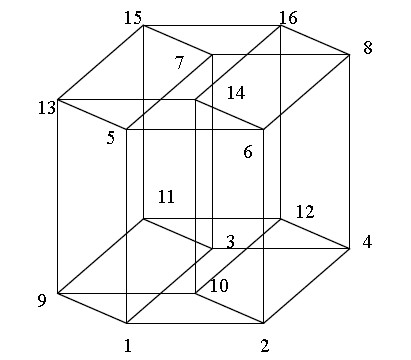
Alice has received a hypercube toy as her birthday present. This hypercube has 16 vertices, numbered from 1 to 16, as illustrated below. On every vertex, there is a light bulb that can be turned on or off. Initially, eight of the light bulbs are turned on and the other eight are turned off. You are allowed to switch the states of two adjacent light bulbs with different states (“on” to “off”, and “off” to “on”; specifically, swap their states) in one operation.
Given the initial state of the lights, your task is to calculate the minimum number of steps needed to achieve the target state, in which the light bulbs on the sub cube (1,2,3,4)-(5,6,7,8) are turned off, and the rest of them are turned on.
Input
There are multiple test cases. The first line of the input contains an integer T, meaning the number of the test cases. There are about 13000 test cases in total.
For each test case there are 16 numbers in a single line, the i-th number is 1 meaning the light of the i-th vertex on the picture is on, and otherwise it’s off.
For each test case there are 16 numbers in a single line, the i-th number is 1 meaning the light of the i-th vertex on the picture is on, and otherwise it’s off.
Output
For every test cases output a number with case number meaning the minimum steps needed to achieve the goal. If the number is larger than 3, you should output “more”.
Sample Input
3
0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1
0 1 0 0 0 0 0 0 1 0 1 1 1 1 1 1
0 0 0 0 0 0 1 0 1 0 1 1 1 1 1 1
Sample Output
Case #1: 0
Case #2: 1
Case #3: more
Source
/** 题意:现在给出16盏灯的状态 然后每盏灯都有4个相连的灯 如果要改变当前灯的状态必须是它和它相邻的灯的状态不一样 要求最后转变的结果是1~8灭 9~16亮 并且操作步数<=3 如果满足要求 输出最小的步数,否则输出-1 做法:bfs() + 剪枝 **/ #include <iostream> #include <cmath> #include <algorithm> #include <stdio.h> #include <string.h> #include <queue> using namespace std; #define INF 100000000 int step[(1 << 16) + 20]; int num[17][4] = { {0}, {2, 3, 5, 9}, {1, 4, 6, 10}, {1, 4, 7, 11}, {2, 3, 8, 12}, {1, 6, 7, 13}, {2, 5, 8, 14}, {3, 5, 8, 15}, {4, 6, 7, 16}, {1, 10, 11, 13}, {2, 9, 12, 14}, {3, 9, 12, 15}, {4, 10, 11, 16}, {5, 9, 14, 15}, {6, 10, 13, 16}, {7, 11, 13, 16}, {8, 12, 14, 15} }; struct Node { int step; int flag[17]; }; void init() { for(int i = 1; i <= (1 << 16) + 5; i++) { step[i] = INF; } } int eed = (1 << 16) - (1 << 8); int getnum(int aa[17]) { int sum = 0; for(int i = 16; i >= 1; i--) { sum = sum * 2 + aa[i]; } return sum; } Node Begin; void bfs() { queue<Node>que; Node now, tmp; Begin.step = 0; que.push(Begin); while(!que.empty()) { now = que.front(); que.pop(); if(now.step >= 3) { continue; } int tt = getnum(now.flag); if(tt == eed) { break; } int numm = 0; for(int i = 1; i <= 8; i++) { if(now.flag[i] == 1) { numm++; } } if(now.step + numm > 3) { continue; } for(int i = 1; i <= 16; i++) { for(int j = 0; j < 4; j++) { if(num[i][j] > i && now.flag[i] != now.flag[num[i][j]]) { int ttt = now.flag[num[i][j]]; now.flag[num[i][j]] = now.flag[i]; now.flag[i] = ttt; now.step ++; int res = getnum(now.flag); if(step[res] > now.step) { step[res] = now.step; que.push(now); } now.step --; ttt = now.flag[num[i][j]]; now.flag[num[i][j]] = now.flag[i] ; now.flag[i] = ttt; } } } } } int main() { int T; scanf("%d", &T); int Case = 1; while(T--) { int tmp = 0; init(); for(int i = 1; i <= 16; i++) { scanf("%d", &Begin.flag[i]); if(i <= 8 && Begin.flag[i] == 1) { tmp++; } } printf("Case #%d: ", Case++); if(tmp > 3) { printf("more "); continue; } int st; st = getnum(Begin.flag); step[st] = 0; bfs(); if(step[eed] <= 3) { printf("%d ", step[eed]); } else { printf("more "); } } return 0; }