http://acm.hust.edu.cn/vjudge/contest/view.action?cid=25019#problem/E
Description
Prof. Tigris is the head of an archaeological team who is currently in charge of an excavation in a site of ancient relics.
This site contains relics of a village where civilization once flourished. One night, examining a writing record, you find some text meaningful to you. It reads as follows.
“Our village is of glory and harmony. Our relationships are constructed in such a way that everyone except the village headman has exactly one direct boss and nobody will be the boss of himself, the boss of boss of himself, etc. Everyone expect the headman is considered as his boss’s subordinate. We call it relationship configuration. The village headman is at level 0, his subordinates are at level 1, and his subordinates’ subordinates are at level 2, etc. Our relationship configuration is harmonious because all people at same level have the same number of subordinates. Therefore our relationship is …”
The record ends here. Prof. Tigris now wonder how many different harmonious relationship configurations can exist. He only cares about the holistic shape of configuration, so two configurations are considered identical if and only if there’s a bijection of n people that transforms one configuration into another one.
Please see the illustrations below for explanation when n = 2 and n = 4.
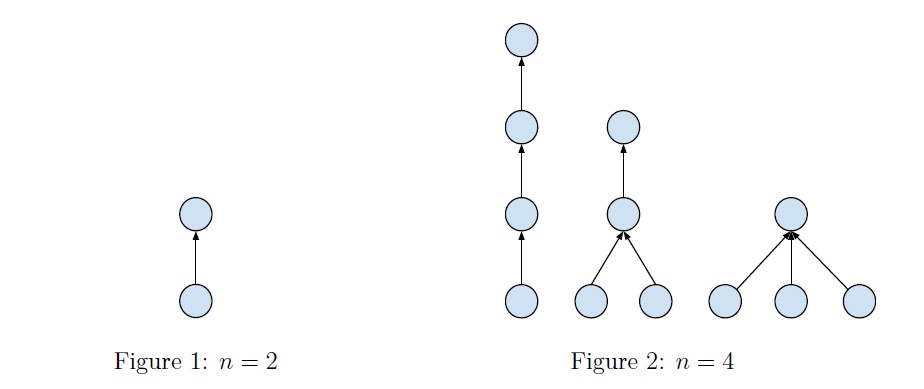
The result might be very large, so you should take module operation with modules 109 +7 before print your answer.
This site contains relics of a village where civilization once flourished. One night, examining a writing record, you find some text meaningful to you. It reads as follows.
“Our village is of glory and harmony. Our relationships are constructed in such a way that everyone except the village headman has exactly one direct boss and nobody will be the boss of himself, the boss of boss of himself, etc. Everyone expect the headman is considered as his boss’s subordinate. We call it relationship configuration. The village headman is at level 0, his subordinates are at level 1, and his subordinates’ subordinates are at level 2, etc. Our relationship configuration is harmonious because all people at same level have the same number of subordinates. Therefore our relationship is …”
The record ends here. Prof. Tigris now wonder how many different harmonious relationship configurations can exist. He only cares about the holistic shape of configuration, so two configurations are considered identical if and only if there’s a bijection of n people that transforms one configuration into another one.
Please see the illustrations below for explanation when n = 2 and n = 4.

The result might be very large, so you should take module operation with modules 109 +7 before print your answer.
Input
There are several test cases.
For each test case there is a single line containing only one integer n (1 ≤ n ≤ 1000).
Input is terminated by EOF.
For each test case there is a single line containing only one integer n (1 ≤ n ≤ 1000).
Input is terminated by EOF.
Output
For each test case, output one line “Case X: Y” where X is the test case number (starting from 1) and Y is the desired answer.
Sample Input
1
2
3
40
50
600
700
Sample Output
Case 1: 1
Case 2: 1
Case 3: 2
Case 4: 924
Case 5: 1998
Case 6: 315478277
Case 7: 825219749

/* n个点,去掉头部,剩下n-1个点。 因为要求每一层的每个节点的子节点数相同,所以可以将n-1个点等分。 对于一颗符合要求n个节点的树,去掉头部后,剩下的点要么连在一起(n-1),要么等分成几部分, 连在一起的可看成是等分为1份。所以将所有等分情况加起来即为所求。 dp[i] = sum(dp[j]) j可整除i-1 画画图(n=1,2,3,4,5,6)就懂了 */ #include <iostream> using namespace std; #define Mod 1000000007 #define Max 1002 long long dp[Max]; void init() { dp[1] = dp[2] = 1; for (int i = 3; i < Max; ++i) { for (int j = 1; j <= i; ++j) { if ((i-1)%j == 0) { dp[i] += dp[j]; dp[i] %= Mod; } } } } int main() { init(); int n, cases = 1; while (cin >> n) { cout << "Case " << cases++ << ": " << dp[n] << endl; } }
