对象的遍历
对象可以当做数组处理,使用for in
var person={}; person.name="cyy"; person.age=25; person.infos=function(){ alert(this.name+" "+this.age); } for(var i in person){ console.log(i);//属性名或方法名 console.log(person[i]);//属性值或方法值 }
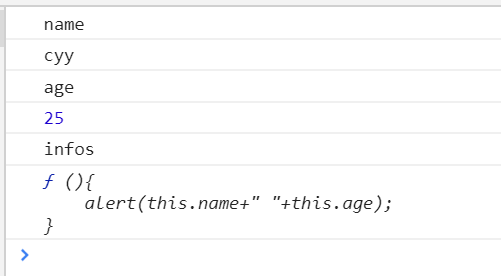
使用构造函数声明的对象,需要实例化之后再进行遍历
function Person(){ this.name="cyy"; this.age=25; } var p=new Person(); for(var i in p){ console.log(i+":"+p[i]); }
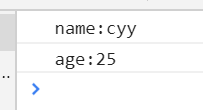
对象在内存中的分布
参考以下神图
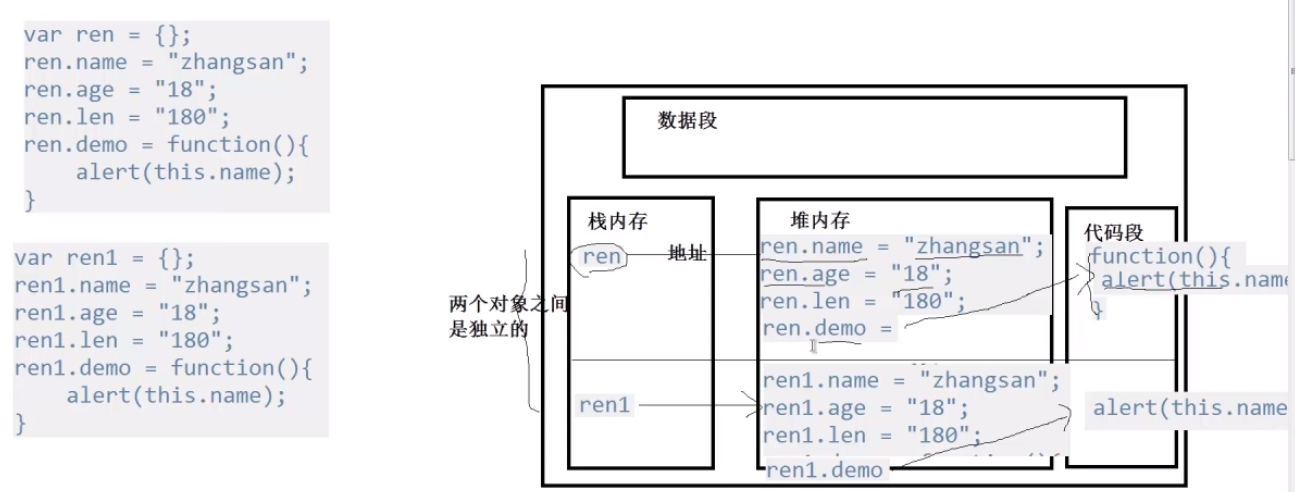
封装:把对象的内部数据和操作细节进行隐藏
提供private关键词隐藏某些属性和方法,限制被封装的数据或者内容的访问,只对外提供一个对象的专门访问的接口
接口一般为调用方法
不过js没有提供这样的关键词,但可以通过闭包来实现
函数内部声明的变量,外部是访问不到的
function fn(){ var n=1; function fn2(){//特权方法 alert(++n); } return fn2; } fn()();//2
//封装 function Person(){ var name="cyy"; function _name(){ alert(name); } this.name=function(){//这是给外部的接口 return _name; } } var p=new Person(); var fn=p.name(); fn();//cyy
封装的缺点:1、占用内存 2、不利于继承
利用闭包特性来封装一个对象student,运用对象student存储一个学生的信息,信息包括姓名,性别和年龄,这些信息不可被外部直接访问,只能通过对象的方法获取
student的数据结构如下:
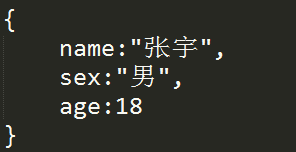
//封装 function Student(){ var obj={}; function _set(name,sex,age){ obj.name=name; obj.sex=sex; obj.age=age; } function _get(){ return obj.name+" "+obj.sex+" "+obj.age; } obj.get=function(){//对外接口 return _get; } obj.set=function(){//对外接口 return _set; } return obj; } var stu=new Student; stu.set()("小明", "男", 23); console.log(stu.get()());//小明 男 23
原型和原型链
原型:利用 prototype 添加属性和方法,prototype对象
原型链:JS在创建对象时,有一个 __proto__ 的内置属性,指向它的原型对象 prototype
var Person=function(){} var p=new Person(); Person.prototype.say=function(){ alert("老娘超美"); } p.say(); /* p没有say方法,所以会去p.__proto__里找 p.__proto__是一个对象,指向Person.prototype Person.prototype中有say方法 */ /* 创建对象的过程 1、创建对象 var p={} 2、将Person的原型对象赋值给p p.__proto__=Person.prototype 3、初始化对象p Person.call(p) */ alert(p.__proto__==Person.prototype);//true
原型和原型链,实现原型继承
var Person=function(){}//Person是一个对象 Person.prototype.say=function(){ alert("陈莺莺超美"); } var Cyy=function(){};//Cyy也是一个对象 Cyy.prototype=new Person();//将Cyy的原型指向Person,实现Cyy继承自Person Cyy.prototype.sing=function(){ alert("陈莺莺会唱歌"); } var me=new Cyy(); me.say();//陈莺莺超美 me.sing();// 陈莺莺会唱歌 /* 分析:me.__proto__ -> Cyy.ptototype -> Person.prototype Person是父 Cyy是子 继承:如果子类中没有的,会继承自父类;如果子类和父类中都有,那么子类的会覆盖掉父类的 */
__proto__ 实现原型继承
function Person(name,age){ this.name=name; this.age=age; } Person.prototype.say=function(){ alert(this.name+" "+this.age); } function Student(){}; Student.prototype=new Person("cyy",25); //Person是Student的父类 //子类必须继承自父类的实例 Student.prototype.grade=3; Student.prototype.test=function(){ alert(this.grade); } var s=new Student(); s.say();//cyy 25 s.test();//3 //s.__proto__ -> Student.prototype -> Person.prototype
原型的值可以是一个对象,也可以是null
原型链的最终指向null
alert(Object.prototype.__proto__);//null
// 情况一 function Parent(){ this.name="parent"; this.age=45; } function Child(){ this.age=25; } Child.prototype.name="child"; Child.prototype=new Parent(); var c=new Child(); console.log(c.name);//parent // 情况二 function Parent(){ this.name="parent"; this.age=45; } function Child(){ this.age=25; } Child.prototype=new Parent(); Child.prototype.name="child"; var c=new Child(); console.log(c.name);//child
情况一中,Child.prototype=new Parent(); 这一句覆盖掉了前面的 Child.prototype.name="child";
属性的值与代码执行顺序有关,后继承的父级的,会覆盖住先定义的自己的
创建一个动物类的对象 ,对象中有动物名称和数量的属性 。创建一个猫的对象并继承动物类对象 ,并为猫对象定义一个方法 。实例化一个猫对象 ,调用其方法 ,弹出动物名称和数量
function Animal(name,number){ this.name=name; this.number=number; } function Cat(){}; Cat.prototype=new Animal("cat",30); Cat.prototype.info=function(){ alert(this.name+" "+this.number); } var c=new Cat(); c.info();//cat 30
构造函数的继承
在子类内部构造父类的对象来实现继承
父对象被子对象继承后,所有的属性和方法,都会传递到子对象中
function Parent(name){ this.name=name; this.pSay=function(){ alert(this.name); } } function Child(name,age){ this.obj=Parent; this.obj(name);//继承了父元素中的两句代码 this.age=age; this.cSay=function(){ alert(this.name+" "+this.age); } } var p=new Parent("爸爸"); p.pSay();//爸爸 var c=new Child("女儿",25); c.cSay();//女儿 25 c.pSay();//女儿
对象内置方法中的apply和call都可用于继承,两者的区别在于传参方式不同
obj.call( 方法, var1, var2...)
obj.apply( 方法, [var1, var2...])
function Parent(name,age,sex){ this.name=name; this.age=age; this.sex=sex; this.say=function(){ alert(this.name+" "+this.age+" "+this.sex); } } function Child(name,age){ //实现继承 Parent.call(this,name,age);//this是指Child } function Child2(name,age){ //实现继承 Parent.apply(this,[name,age]);//this是指Child } var c=new Child("cyy",25); c.say(); //cyy 25 undefined //Child也拥有了Parent的属性和方法 var c2=new Child2("cyy2",25); c2.say();//cyy2 25 undefined
使用构造方法创建一个动物类对象Animal, 对象中定义属性有动物名称和数量 ,并且定义一个方法。再创建两个动物的对象(如猫和狗),一个动物使用call方法实现继承Animal, 一个动物使用apply方法实现继承Animal。分别实例化两个动物并弹出动物的名称和数量
function Animal(name,num){ this.name=name; this.num=num; this.getInfo=function(){ alert(this.name+" "+this.num); } } function Cat(name,num){ Animal.call(this,name,num); } function Dog(name,num){ Animal.apply(this,[name,num]); } var c=new Cat("cat",20); c.getInfo();//cat 20 var d=new Dog("dog",30); d.getInfo();//dog 30
JS面向对象的关键词
instanceof 变量是否是对象的实例
var arr=new Array(); console.log(arr instanceof Array);//true console.log(arr instanceof Object);//true function Person(){}; var p=new Person(); console.log(p instanceof Person);//true console.log(p instanceof Object);//true
delete 删除对象属性(不能删除原型链中的属性和方法)
function Person(){ this.name="cyy"; this.eat=function(){ alert("吃饭"); } } var p=new Person(); console.log(p.name);//cyy delete p.name;//删除对象的属性 console.log(p.name);//undefined p.eat();//吃饭 delete p.eat();//吃饭 删除对象的方法,失败 p.eat();//吃饭 var name="cyy"; console.log(name);//cyy delete name; console.log(name);//name is not defined
call 参数逐个实现继承
apply 参数以数组方式实现继承
function add(a,b){ alert(a+b); } function sub(a,b){ alert(a-b); } add.call(sub,4,8); //12 调用的是add这个方法 add.call(sub2,4,8); //sub2 is not defined 只能引用一个已经存在的对象 add.apply(sub,[3,2]);
function Animal(){ this.name="animal"; this.show=function(){ alert(this.name); } } function Cat(){ this.name="cat"; } var a=new Animal(); var c=new Cat(); a.show.call(c);//cat c拥有了a所拥有的show方法 a.show.apply(c,[]);//cat c拥有了a所拥有的show方法
创建两个数组 ,并运用apply实现两个数组的拼接
var arr1=[2,3]; var arr2=[4,5]; arr1.push.apply(arr1,arr2); //调用的是apply前面的方法:arr1.push console.log(arr1);
arguments 实参的类数组对象
callee 返回正在执行的function对象,返回的是function的内容
arguments.callee
function fn(){ console.log(arguments.callee); /*ƒ fn(){ console.log(arguments.callee); } */ //console.log(arguments.callee());不停调用自身,陷入死循环 } fn();
常用于递归函数调用函数自身
var sum=function(n){ if(n<=1) return 1; return n+sum(n-1); } console.log(sum(4));//10
var sum=function(n){ if(n<=1) return 1; return n+arguments.callee(n-1); } console.log(sum(4));//10
this 指向当前对象
1、this函数调用
var x=1; function fn(){ this.x=2;//this改变的是全局变量的x的值 } fn(); console.log(x);//2
2、this作为方法调用
构造函数内指代当前对象
function Person(){ this.name="cyy"; this.show=function(){ alert(this.name); } } var p=new Person(); p.show();//cyy
3、在call和apply中,this作为第一个参数
var name="cyy"; function show(){ alert(this.name); } var obj={}; obj.name="cyy2"; obj.showName=show; obj.showName.apply();//调用show(),this指向全局 obj.showName.apply(window);//同上 obj.showName.apply(obj);//调用show(),this指向obj
用arguments计算参数总和
function sum(){ var sum=0; for(var i=0;i<arguments.length;i++){ sum+=arguments[i]; } return sum; } console.log(sum(2,5,7));//14
对象冒充:将父类的属性和方法传给子类,作为特权属性和特权方法
function Parent(name,age){ this.name=name;//特权属性 this.age=age; this.show=function(){//特权方法 alert(this.name+" "+this.age); } } Parent.prototype.walk=function(){//非特权方法 alert("walking..."); } function Child(name,age,sex){ this.obj=Parent;//对象冒充,可以使用父类的特权属性和特权方法 this.obj(name,age); this.sex=sex; } var c=new Child("cyy",25,"女"); c.show();//cyy 25 c.walk();// c.walk is not a function