ES6中class的继承
父类(基类)
子类
extends 关键字
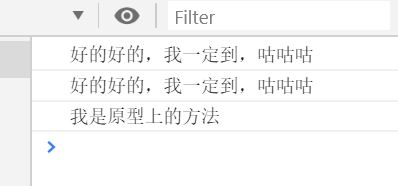
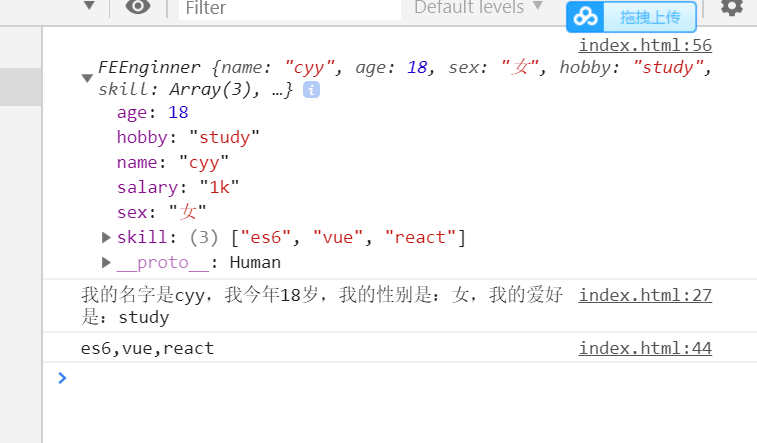
//父类 class Human{ //父类的构造函数 constructor(name,age,sex,hobby){ this.name=name this.age=age this.sex=sex this.hobby=hobby } desc(){ const {name,age,sex,hobby}=this console.log(`我的名字是${ name },我今年${ age }岁,我的性别是:${ sex },我的爱好是:${ hobby }`) } eat(){ console.log("吧唧吧唧") } } //子类 前端工程师类 class FEEnginner extends Human{ constructor(name,age,sex,hobby,skill,salary){ super(name,age,sex,hobby)//在this之前调用super,实际上就是调用父类的构造函数 this.skill=skill this.salary=salary } say(){ console.log(this.skill.join(",")) } } const feer=new FEEnginner( "cyy", 18, "女", "study", ["es6","vue","react"], "1k" ) console.log(feer) //调用父类的方法 feer.desc() //调用子类自己的方法 feer.say()
模拟网游的职业系统
父类:代表一个角色
子类:代表一个具有职业的角色
class Character{ //父类的构造函数 constructor(name,sex){ this.name=name this.sex=sex this.skill=[]//技能 } } //子类 巫师类 class Wizard extends Character{ constructor(name,sex){ super(name,sex)//在this之前调用super,实际上就是调用父类的构造函数 this.initSkill() } //初始化技能 initSkill(){ this.skill=[ { name:"阿瓦达索命", mp:666, level:999 }, { name:"守护神咒", mp:333, level:888 } ] } }
super关键字的其他内容
super
1、作为父类构造函数调用
2、作为对象的方式调用
第一种方式,上面已经演示过了
第二种方式,又可以分为两种:
1、非静态方法中访问super -> 父类原型
2.静态方法中访问super -> 父类
在调用super时,父类的this始终是子类的this
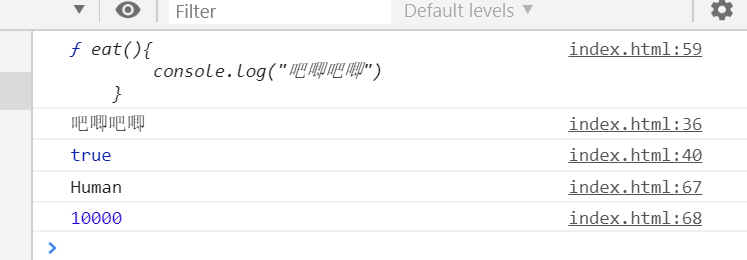
//super 作为对象的方式调用 //父类 class Human{ //父类的构造函数 constructor(name,age,sex,hobby){ this.name=name this.age=age this.sex=sex this.hobby=hobby } desc(){ const {name,age,sex,hobby}=this console.log(`我的名字是${ name },我今年${ age }岁,我的性别是:${ sex },我的爱好是:${ hobby }`) } eat(){ console.log("吧唧吧唧") } checkThis(_this){ console.log(_this===this)//this是父类的this,_this是子类传递过来的子类的this } } //静态属性 Human.total=10000 //子类 前端工程师类 class FEEnginner extends Human{ constructor(name,age,sex,hobby,skill,salary){ super(name,age,sex,hobby)//在this之前调用super,实际上就是调用父类的构造函数 this.skill=skill this.salary=salary } say(){ //非静态方法中访问super -> 父类原型 //console.log(super)//这样会报错 console.log(super.eat)//这样会报错 super.eat() // true 在调用super时,父类的this始终是子类的this super.checkThis(this)//将子类的this传递过去 } static test(){ //静态方法中访问super -> 父类 console.log(super.name)//Human console.log(super.total)//10000 } } const feer=new FEEnginner( "cyy", 18, "女", "study", ["es6","vue","react"], "1k" ) //调用子类自己的方法 feer.say() FEEnginner.test()//调用静态方法
简单的多态
同一个接口,在不同情况下做不一样的事情
相同的接口,不同的表现
在js中,接口可以理解为,需要子类去实现的方法
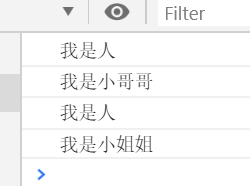
//多态 //子类如果有父类的同名方法,则会执行子类自己的方法,不会去走父类的 class Human{ say(){ console.log("我是人") } } class Man extends Human{ say(){ super.say()//调用父类的同名方法 console.log("我是小哥哥") } } class Woman extends Human{ say(){ super.say()//调用父类的同名方法 console.log("我是小姐姐") } } new Man().say() new Woman().say()
重载演示:三个案例
//重载演示1 class simpleCalc{ add(...args){ if(args.length===0) return this.zero() if(args.length===1) return this.one(args) return this.sum(args) } zero(){ return 0 } one(args){ return args[0] } sum(args){ //累加 return reduce((a,b)=>a+b,0) } }
//重载演示2 function post(url,header,params){ //如果没有第三个参数,则传入的第二个参数赋值给params,header默认为null if(!params){ params=header header=null //undefind也可以 } } post("https://baidu.com",{ a:1, b:2 })
//重载演示3 //有方法必须通过子类去实现,不然就会报错 //映射表 const ModelMap={ "红眼僵尸":1, "南瓜精":2, "独眼蝠":3, "绿眼僵尸":4, } //基类 怪物类 class Monster{ constructor(name,level,model){ this.name=name this.level=level this.model=model } attack(){ throw Error("必须由子类来实现`attack`攻击方法") } } //子类 红眼僵尸类 class RedEyeZombie extends Monster{ constructor(name,level,model){ super("红眼僵尸",10,ModelMap["红眼僵尸"]) } } //子类 绿眼僵尸类 class GreenEyeZombie extends Monster{ constructor(name,level,model){ super("绿眼僵尸",20,ModelMap["绿眼僵尸"]) } attack(){ console.log("绿眼僵尸发动了攻击") } } const gez=new GreenEyeZombie() gez.attack() const rez=new RedEyeZombie() rez.attack()
ES5中的继承
//ES5中继承的实现 //不是真正意义上的继承,而是在原型链上操作 //1、利用构造函数(不能继承原型上的方法) //父类 function P(){ this.name="parent"; this.gender=2; this.say=function(){ console.log("好的好的,我一定到,咕咕咕"); } } P.prototype.test=function(){ console.log("我是原型上的方法"); } //子类 function C(){ P.call(this);//实现继承的一种方式 this.name="child"; this.age=18; } var c=new C(); c.say(); //c.test();//不能继承原型上的方法 //解决方法,把子类的原型变成父类的实例 function P2(){ this.name="parent"; this.gender=2; this.say=function(){ console.log("好的好的,我一定到,咕咕咕"); } } P2.prototype.test=function(){ console.log("我是原型上的方法"); } //子类 function C2(){ P2.call(this);//实现继承的一种方式 this.name="child"; this.age=18; } C2.prototype=new P2();//把C2的原型变成P2的实例(因为P2的实例能够访问到P2原型上的方法) var c2=new C2(); c2.say(); c2.test();//成功继承原型上的方法