本次总结适合初次接触委托事件,或者对委托事件了解但是不能熟练运用的学习者。
再次学习总结委托、事件,上一篇《委托与事件》http://www.cnblogs.com/chenyongblog/archive/2013/03/04/2942924.html
01委托
 View Code
View Code
using System; using System.Collections.Generic; using System.Linq; using System.Text; namespace _01委托 { //第一步声明委托 delegate int MyDelegate(); delegate int MyDelegateNumber(int a,int b); class MyClass { public int M1() { Console.WriteLine("调用实例方法"); return 0; } public static int M2() { Console.WriteLine("调用静态方法"); return 0; } } class Add { public int NumberAdd(int num1,int num2) { return(num1+num2); } } class Program { static void Main(string[] args) { MyClass myClss = new MyClass(); //实例化委托。非静态方法的调用需要先实例化该类 MyDelegate myDelete1 = new MyDelegate(myClss.M1); Console.WriteLine("委托一"); myDelete1(); //静态方法的调用直接用 类名.方法名 MyDelegate myDelete2; myDelete2 = MyClass.M2;//给委托类型的变量赋值 Console.WriteLine("委托二"); myDelete2(); MyDelegate myDelete3 = myDelete1 + myDelete2; Console.WriteLine("委托三"); myDelete3(); Add myAdd = new Add(); MyDelegateNumber p = new MyDelegateNumber(myAdd.NumberAdd); Console.WriteLine(p(1,2)); Console.ReadLine(); #region /* * 1、委托类似C++中的函数指针,用于通过对方法特征(方法签名)和返回类型的声明,封装了 * 具有相同特征和返回类型的方法,与指针不同的是委托实例独立于它所封装的方法的类。 * 2、委托类型隐含为sealed(密封类),是一个引用类型。 */ #endregion } } }
02事件
 View Code
View Code
using System; using System.Collections.Generic; using System.Linq; using System.Text; namespace 事件 { delegate void MyEventHandler(int m,int n); class MyEvent { //声明事件 事件名:active public event MyEventHandler active; //触发事件的方法 public void OnEvent(int m,int n) { //判断是否有事件被绑定 if(active!=null) { active(m,n);//事件发生。格式:事件名(参数); } } } class Program { static void Handler(int m,int n) { Console.WriteLine("事件发生"+(m+n)); } static void Main(string[] args) { MyEvent evt = new MyEvent(); //将封装Handler方法的委托添加到active事件的列表中 evt.active += new MyEventHandler(Handler); //事件的预定就是向委托的调用列表中添加方法。 事件名 += new 委托名(方法名); //只要事件被触发,委托列表中所预定的方法就会被调用 //调用触发事件的方法 evt.OnEvent(3,4); Console.ReadLine(); #region//总结一下 /* * 1、首先声明一个委托,委托的后缀名是EventHandler * 2、然后在声明一个事件,事件名就是委托名去掉EventHandler的部分。可以在另一个类中声明 * 3、写一个触发事件的方法。首先要判断是否有事件被绑定,然后再触发事件 * 4、写一个方法,用于封装到委托中。 * 5、将封装方法的委托添加到事件的列表中 * 6、最后在Main()方法中调用触发事件的方法。事件名.触发事件的方法名() * 7、本程序执行的过程:实例化MyEvent类->注册事件->触发事件的方法OnEvent->判断事件是否为空,否:触发事件->执行委托列表中对应的方法 */ #endregion } } }
03多播委托
 View Code
View Code
using System; using System.Collections.Generic; using System.Linq; using System.Text; namespace _03多重委托 { //第一步声明一个委托 delegate void AddEventHandler(int m,int n); class AddNum { public void Test1(int m,int n) { Console.WriteLine("非静态方法"+(m+n)); } public static void Test2(int m,int n) { Console.WriteLine("静态方法"+(m+n)); } } class Program { static void Main(string[] args) { AddNum myNum = new AddNum(); //第二步实例化委托 AddEventHandler myAdd1 = new AddEventHandler(myNum.Test1); AddEventHandler myAdd2 = new AddEventHandler(AddNum.Test2); //调用委托myAdd2 myAdd1 myAdd2(1,1);//封装了myNum.Test1()方法 myAdd1(2,2);//封装了AddNum.Test2() //多重委托 AddEventHandler myAdd3 = myAdd1 + myAdd2;//(1)封装了 myNum.Test1()和AddNum.Test2()方法 myAdd3(3,3); AddEventHandler myAdd4 = myAdd3 - myAdd1;//(2)封装了AddNum.Test2() myAdd4(4,4); myAdd1 += myAdd2;//(3)封装了 myNum.Test1()和AddNum.Test2()方法 myAdd1(5,5); myAdd3 -= myAdd2;//(4)封装了myNum.Test1()方法 myAdd3(6,6); Console.ReadLine(); #region//总结一下-委托的调用与运算 /* *1、委托实例一旦被创建,将始终引用同一目标对象和方法。这样myAdd1实现了对静态方法 AddNum.Test2()和类的实例化方法myNum.Test1()的封装。 *2、当主程序中调用委托的实例时,实际会调用myNum.Test1()和AddNum.Test2()方法,这样 就实现了对方法的回调。 *3、委托实例所封装的方法的集合称为调用列表 *4、多重委托实质上相当于一个委托实例指向多个方法地址,调用多重委托就会按照调用列表中 的顺序调用多个方法。----实现了C#中的多态 *5、注意在调用委托的时候还应该传入与委托声明时的参数列表匹配的识记参数,当然这些参数 实际传入了被封装的方法,这也就要求我们在声明委托和添加方法的时候格式要对应 *6、委托运算符 * +:将两个委托实例的调用列表组合起来,产生一个新的委托。如(1) * -:从一个委托的调用列表中移除另一个委托的列表项,产生一个新的委托。如(2) * +=:将一个委托的调用列表合并到另一个委托的调用列表中,不产生新的委托。如:(3) * -=:从一个委托的调用列表中删除另一个委托的调用列表,不产生新的委托。如:(4) * 初始化一个委托后不能第一次就是用+=,将会出现“使用了未赋值的局部变量” */ #endregion } } }
04委托实现回调
 View Code
View Code
using System; using System.Collections.Generic; using System.Linq; using System.Text; namespace _04委托实现回调 { /* * 问题描述:对于任意的一组数据,进行选择排序和冒泡排序 *问题解析:给被封装的排序方法提供一个整型数组,通过输出方法将排好序的整型数组输出,至于如何 * 实现排序,委托并不关心。通俗的说就是:给你材料,交给你做,我只要结果。 */ public delegate int[] sortEventHandler(int [] arr); //建立一个排序类 public class Sort { //选择排序 public int[] xuanzeSort(int[] arr) { if(arr.Length==0) { Console.WriteLine("空数组"); } else { for(int i=0;i<arr.Length;i++) { for (int j = i+1; j < arr.Length ;j++ ) { int temp; if (arr[i] > arr[j]) { temp=arr[i]; arr[i]=arr[j]; arr[j] = temp; } } } } return arr; } //冒泡排序 public int[] maopaoSort(int [] arr) { if (arr.Length == 0) { Console.WriteLine("空数组"); } else { for(int i=0;i<arr.Length;i++) { for (int j = 0; j < arr.Length - 1 - i;j++ ) { if (arr[j] > arr[j + 1]) { int temp=arr[j]; arr[j] = arr[j+1]; arr[j+1] = temp; } } } } return arr; } } class Program { static void Main(string[] args) { int[] myarr = { 12,5,40,8,45,3,1,25,18,10,2}; Console.WriteLine("原数组为"); foreach (int item in myarr) { Console.Write(item+" "); } Console.WriteLine(); Sort st = new Sort(); sortEventHandler mySort1 = new sortEventHandler(st.xuanzeSort); sortEventHandler mySort2 = new sortEventHandler(st.maopaoSort); Console.WriteLine("选择排序"); if (mySort1!= null) { int[] resultArr = mySort1(myarr); foreach (int item in resultArr) { Console.Write(item + " "); } Console.WriteLine(); } else { Console.WriteLine("mySort1的调用列表为空"); } Console.WriteLine("冒泡排序"); if(mySort2!=null) { int[] resultArr = mySort2(myarr); foreach (int item in resultArr) { Console.Write(item+" "); } Console.WriteLine(); } else { Console.WriteLine("mySort2的调用列表为空"); } Console.ReadLine(); } } }
04委托实现回调-改进版
 View Code
View Code
1 using System; 2 using System.Collections.Generic; 3 using System.Linq; 4 using System.Text; 5 6 namespace _04委托实现回调_改进版 7 { 8 /* 9 * 问题描述:对于任意的一组数据,进行选择排序和冒泡排序 10 *问题解析:给被封装的排序方法提供一个整型数组,通过输出方法将排好序的整型数组输出,至于如何 11 * 实现排序,委托并不关心。通俗的说就是:给你材料,交给你做,我只要结果。 12 */ 13 14 public delegate int[] sortEventHandler(int[] arr); 15 //建立一个排序类 16 public class Sort 17 { 18 //选择排序-直接选择排序 19 #region//直接选择排序思想 20 /* 21 * 选择排序思想:每次遍历数组将剩余数组中的最小值排到本次遍历数组的最前面 22 * 1、两层for循环,第一层用于控制循环遍历的次数,第二层循环用于找到本次循环中的最小值,并将 其排到本次循环体的最前面(每一次第一层循环体中的值在第二层循环体中是保持不变的) 23 * 2、时间复杂度:(arr.Length-1)*arr.Length/2 24 */ 25 #endregion 26 public int[] xuanzeSort(int[] arr) 27 { 28 if (arr.Length == 0) 29 { 30 Console.WriteLine("空数组"); 31 } 32 else 33 { 34 for (int i = 0; i < arr.Length - 1; i++) 35 { 36 for (int j = i + 1; j < arr.Length; j++) 37 { 38 int temp; 39 //不断的将最小的送到arr[i]的面前,直到循环结束。 40 if (arr[i] > arr[j]) 41 { 42 temp = arr[i]; 43 arr[i] = arr[j]; 44 arr[j] = temp; 45 } 46 } 47 } 48 49 } 50 return arr; 51 } 52 //交换排序-冒泡排序 53 #region//冒泡排序思想 54 /* 55 * 冒泡排序思想:每遍历数组一次将数组中剩下的最大的排到本次遍历数组的最后。 56 * 1、每次遍历均是从数组的第一个元素开始的 57 * 2、两层for循环,第一层用来控制遍历的次数,为数组的长度-1;第二层用来找到本次循环中元素的 最大值,并将其排到本次数组的最后。(每一次第一层循环体中的值在第二层循环体中是保持不 变的) 58 * 3、时间复杂度:1+2+...+arr.Length-1=(1+arr.Lngth-1)*(arr.Lngth-1)/2=arr.Length*(arr.Length-1)/2 59 */ 60 #endregion 61 public int[] maopaoSort(int[] arr) 62 { 63 if (arr.Length == 0) 64 { 65 Console.WriteLine("空数组"); 66 } 67 else 68 { 69 for (int i = 0; i < arr.Length - 1; i++) 70 { 71 for (int j = 0; j < arr.Length - 1 - i; j++) 72 { 73 if (arr[j] > arr[j + 1]) 74 { 75 int temp = arr[j]; 76 arr[j] = arr[j + 1]; 77 arr[j + 1] = temp; 78 } 79 } 80 } 81 } 82 return arr; 83 } 84 //插入排序-直接插入排序 85 #region//插入排序思想 86 /* 87 * 插入排序思想:假设数组中前n-1个都排好序了,现在将数组中的第n个放到前面已排好序的数组中, 88 * 使得这n个数任然是一个排好序的数组。 89 * 1、有一个for循环,先将数组中的前两个数排序,然后再将前三个数排序,...... 90 * 2、每次都是从后向前排序,直到找到合适的位置 91 * 3、时间复杂度:在O(n)到O(n2) 92 */ 93 #endregion 94 public int[] charuSort(int[] arr) 95 { 96 if (arr.Length == 0) 97 { 98 Console.WriteLine("空数组"); 99 } 100 else 101 { 102 for (int i = 1; i < arr.Length; i++) 103 { 104 int temp; 105 int j=i; 106 while(j>0&&arr[j-1]>arr[j]) 107 { 108 temp=arr[j]; 109 arr[j] = arr[j - 1]; 110 arr[j - 1] = temp; 111 --j; 112 } 113 } 114 } 115 return arr; 116 } 117 #region//希尔排序思想 118 /* 119 * 希尔排序思想:先取一个小于n的整数d1作为第一个增量,把文件的全部记录分成d1个组。所有距离为dl的倍数的记录放在同一个组中。 120 * 先在各组内进行直接插人排序;然后,取第二个增量d2<d1重复上述的分组和排序,直至所取的增量dt=1(dt<dt-l<…<d2<d1), 121 * 即所有记录放在同一组中进行直接插入排序为止。 122 */ 123 #endregion 124 public int[] shellSort(int[]arr) 125 { 126 int k = arr.Length / 2;//设置步长 127 128 while (k > 0) 129 { 130 for (int i = k; i < arr.Length; i++) 131 { 132 int t = arr[i]; 133 int j = i - k; 134 while (j >= 0 && t < arr[j]) 135 { 136 arr[j + k] = arr[j]; 137 j = j - k; 138 } 139 arr[j + k] = t; 140 } 141 k /= 2; 142 } 143 return arr; 144 } 145 //显示排序后的数组 146 public void ShowResult(sortEventHandler se, int[] arr) 147 { 148 if (se != null) 149 { 150 int[] resultArr = se(arr); 151 foreach (int item in resultArr) 152 { 153 Console.Write(item + " "); 154 } 155 Console.WriteLine(); 156 } 157 else 158 { 159 Console.WriteLine(se + "调用列表为空"); 160 } 161 } 162 163 } 164 165 class Program 166 { 167 static void Main(string[] args) 168 { 169 int[] myarr = { 12, 5, 40, 8, 45, 3, 1, 25, 18, 10, 2 }; 170 Console.WriteLine("原数组为"); 171 foreach (int item in myarr) 172 { 173 Console.Write(item + " "); 174 } 175 Console.WriteLine(); 176 177 Sort st = new Sort(); 178 sortEventHandler mySort1 = new sortEventHandler(st.xuanzeSort); 179 sortEventHandler mySort2 = new sortEventHandler(st.maopaoSort); 180 sortEventHandler mySort3 = new sortEventHandler(st.charuSort); 181 sortEventHandler mySort4 = new sortEventHandler(st.shellSort); 182 Console.WriteLine("选择排序"); 183 st.ShowResult(mySort1, myarr); 184 185 Console.WriteLine("冒泡排序"); 186 st.ShowResult(mySort2, myarr); 187 188 Console.WriteLine("快速排序"); 189 st.ShowResult(mySort3, myarr); 190 191 Console.WriteLine("希尔排序"); 192 st.ShowResult(mySort4,myarr); 193 194 Console.ReadLine(); 195 } 196 } 197 }
05委托、事件与Observer模式
 View Code
View Code
1 using System; 2 using System.Collections.Generic; 3 using System.Linq; 4 using System.Text; 5 using System.Threading; 6 7 namespace _05委托_事件与Observer设计模式 8 { 9 public delegate void HeateEventHandler(int temp); 10 public class Heater 11 { 12 //定义一个私有字段 13 private int temperature; 14 public event HeateEventHandler heate; 15 public void HeateOnEvent() 16 { 17 for (int i = 0; i <= 100;i++ ) 18 { 19 temperature = i; 20 if(i>96) 21 { 22 if(heate!=null) 23 { 24 heate(temperature); 25 Thread.Sleep(5000); 26 } 27 } 28 } 29 } 30 31 } 32 public class Alarm 33 { 34 public void MakeAlarm(int temp) 35 { 36 Console.WriteLine("警报:当前水温{0}度",temp); 37 } 38 } 39 public class Display 40 { 41 public static void ShowDisplay(int temp) 42 { 43 Console.WriteLine("显示:水快烧开了,当前温度为{0}",temp); 44 } 45 } 46 class Program 47 { 48 static void Main(string[] args) 49 { 50 Heater he = new Heater(); 51 Alarm al = new Alarm(); 52 he.heate += al.MakeAlarm; 53 //给匿名对象注册方法 54 //he.heate+=(new Alarm).MakeAlarm; 55 he.heate += Display.ShowDisplay; 56 he.HeateOnEvent(); 57 Console.ReadLine(); 58 } 59 #region//总结一下-Observer设计模式 60 /*概念:Observer设计模式是为了定义对象间的一种一对多的依赖关系,以便于当一个对象的状态改变 时,其他依赖于它的对象会被自动告知并更新。Observer模式是一种松耦合的设计模式。 61 * 1、什么是耦合?什么是松耦合?什么是紧耦合? 62 解释:耦合就是依赖的程度。松耦合就是依赖程度不强,紧耦合就是依赖程度很强。网上找了个 63 形象的解释:假如你去麦当劳前台买可乐, 你可以把你和麦当劳工作人员想象为软件的两层或两 个模块.那么你给服务员5块钱,然后他帮你打一杯可乐,你们之间是松耦合的,你们的接口就是5块 钱,你只要给他钱,就不用管他是怎么拿杯子,从哪打的可乐.但是如果你给他5块钱,然后你要自己 去取杯子,去找可乐机,自己排队, 那么你跟麦当劳就是紧密耦合的. 64 * 2、Observer设计模式中主要包括两类对象:Subject(监视对象,包含监视者感兴趣的东西)和 Observer(监视者,当监视的对象中某个事件发生时,监视者就采取行动)。本例中Heate是监视对 象,Alarm和Dispaly是监视者,感兴趣的东西就是温度,当温度超过某一临界值的时候,监视对 象将监视者感兴趣的东西传给监视者,监视者采取行动。 65 * 3、匿名对象:一个临时的对象。没有明确给出名字的对象,只在堆内存中开辟空间,在棧内存中没 有引用地址。 66 */ 67 #endregion 68 } 69 }
06为什么要使用事件呢?
 View Code
View Code
1 using System; 2 using System.Collections.Generic; 3 using System.Linq; 4 using System.Text; 5 6 namespace _06为什么使用事件 7 { 8 //定义委托 9 public delegate void NumberChangedEventHandler(int count); 10 //定义事件的发布者 11 public class Publisher 12 { 13 //声明一个事件 14 public event NumberChangedEventHandler NumberChanged; 15 //声明一个委托变量 16 //(1)public NumberChangedEventHandler NumberChanged; 17 //声明触发事件的方法 18 public void DoSomething() 19 { 20 for (int i = 0; i < 23; i++) 21 { 22 if (i == 8) 23 { 24 if (NumberChanged != null) 25 { 26 NumberChanged(i); 27 } 28 } 29 } 30 } 31 } 32 //定义事件的订阅者 33 public class Subscriber 34 { 35 public void OnNumberChanged(int count) 36 { 37 Console.WriteLine("事件订阅者:{0}", count); 38 } 39 } 40 class Program 41 { 42 static void Main(string[] args) 43 { 44 Subscriber sb = new Subscriber(); 45 Publisher pb = new Publisher(); 46 pb.NumberChanged += new NumberChangedEventHandler(sb.OnNumberChanged); 47 pb.DoSomething();//事件的本意是当事件发布类中的某个行为触发时,引发事件,也就是说当触发事件的方法满足某个条件时触发事件。事件不应该由客户端触发,而是由事件的发布类的内部触发。这样写使事件的发布类的封装性更好。 48 //(1)pb.NumberChanged(100);//定义一个委托变量,这里的NumberChanged不是事件 49 Console.ReadLine(); 50 } 51 } 52 }
07让事件只允许一个客户端订阅
 View Code
View Code
1 using System; 2 using System.Collections.Generic; 3 using System.Linq; 4 using System.Text; 5 6 namespace _07让事件只允许一个客户端订阅 7 { 8 public delegate string GenneralEventHandler(); 9 public class Publisher 10 { 11 public event GenneralEventHandler NumberChanged; 12 public void Register(GenneralEventHandler method) 13 { 14 //注意这里:此处注册事件采用的是方法,而不再用+=了 15 NumberChanged=method; 16 } 17 public void UnRegister(GenneralEventHandler method) 18 { 19 NumberChanged-=method; 20 } 21 public void DoSomething() 22 { 23 if(NumberChanged!=null) 24 { 25 string rtn=NumberChanged(); 26 Console.WriteLine(rtn); 27 } 28 } 29 } 30 public class Subscriber1 31 { 32 public string OnNumberChanged() 33 { 34 Console.WriteLine("subscriber1 invoke"); 35 return "subscriber1"; 36 } 37 } 38 public class Subscriber2 39 { 40 public string OnNumberChanged() 41 { 42 Console.WriteLine("subscriber2 invoke"); 43 return "subscriber2"; 44 } 45 } 46 class Program 47 { 48 static void Main(string[] args) 49 { 50 Publisher pub = new Publisher(); 51 Subscriber1 sub1 = new Subscriber1(); 52 Subscriber2 sub2 = new Subscriber2(); 53 pub.Register(sub1.OnNumberChanged); 54 pub.Register(sub2.OnNumberChanged);//输出的是subscriber2 55 //pub.UnRegister(sub2.OnNumberChanged);//将其注释去掉,输出为空 56 pub.DoSomething(); 57 Console.ReadLine(); 58 } 59 } 60 }
08用事件访问器来实现只让一个用户端订阅
 View Code
View Code
1 using System; 2 using System.Collections.Generic; 3 using System.Linq; 4 using System.Text; 5 6 namespace _08用事件访问器来实现只让一个用户端订阅 7 { 8 public delegate string GeneralEventHandler(); 9 public class Publisher 10 { 11 private event GeneralEventHandler numberChanged; 12 public event GeneralEventHandler Numberchanged 13 { 14 add 15 { 16 numberChanged = value; 17 } 18 remove 19 { 20 numberChanged -= value; 21 } 22 } 23 public void DoSomething() 24 { 25 if(numberChanged!=null) 26 { 27 string str = numberChanged(); 28 Console.WriteLine(str); 29 } 30 } 31 } 32 public class Subscriber1 33 { 34 public string OnNumberChanged() 35 { 36 Console.WriteLine("subscriber1 invoke"); 37 return "subscriber1"; 38 } 39 } 40 public class Subscriber2 41 { 42 public string OnNumberChanged() 43 { 44 Console.WriteLine("subscriber2 invoke"); 45 return "subscriber2"; 46 } 47 } 48 class Program 49 { 50 static void Main(string[] args) 51 { 52 Publisher pub = new Publisher(); 53 Subscriber1 sub1 = new Subscriber1(); 54 Subscriber2 sub2 = new Subscriber2(); 55 pub.Numberchanged += sub1.OnNumberChanged; 56 pub.Numberchanged += sub2.OnNumberChanged; 57 // pub.Numberchanged -= sub2.OnNumberChanged; 58 pub.DoSomething(); 59 Console.ReadLine(); 60 } 61 } 62 }
09获得多个返回值与异常处理
 View Code
View Code
1 using System; 2 using System.Collections.Generic; 3 using System.Linq; 4 using System.Text; 5 6 namespace _09获得多个返回值与异常处理 7 { 8 public delegate string DemoEventHandler(int num); 9 public class Publisher 10 { 11 public event DemoEventHandler NumberChanged; 12 public List<string> DoSomething() 13 { 14 List<string> strList = new List<string>(); 15 if(NumberChanged==null) 16 { 17 return strList; 18 } 19 Delegate[] delArray = NumberChanged.GetInvocationList(); 20 foreach(Delegate del in delArray) 21 { 22 DemoEventHandler method = (DemoEventHandler)del;//强制向下转换 23 strList.Add(method(100)); 24 } 25 return strList; 26 } 27 } 28 public class Subscriber1 29 { 30 public string OnNumberChanged(int num) 31 { 32 Console.WriteLine("subscriber1 invoke,number:{0}",num); 33 return "[Subscriber1 returned]"; 34 } 35 } 36 public class Subscriber2 37 { 38 public string OnNumberChanged(int num) 39 { 40 Console.WriteLine("subscriber2 invoke,number:{0}", num); 41 return "[Subscriber2 returned]"; 42 } 43 } 44 public class Subscriber3 45 { 46 public string OnNumberChanged(int num) 47 { 48 Console.WriteLine("subscriber3 invoke,number:{0}", num); 49 return "[Subscriber3 returned]"; 50 } 51 } 52 class Program 53 { 54 static void Main(string[] args) 55 { 56 Publisher pub = new Publisher(); 57 Subscriber1 sub1 = new Subscriber1(); 58 Subscriber2 sub2 = new Subscriber2(); 59 Subscriber3 sub3 = new Subscriber3(); 60 pub.NumberChanged += new DemoEventHandler(sub1.OnNumberChanged); 61 pub.NumberChanged += new DemoEventHandler(sub2.OnNumberChanged); 62 pub.NumberChanged += new DemoEventHandler(sub3.OnNumberChanged); 63 List<string> list = pub.DoSomething(); 64 foreach (string item in list) 65 { 66 Console.WriteLine(item); 67 } 68 Console.ReadLine(); 69 } 70 } 71 }
10异常处理
 View Code
View Code
1 using System; 2 using System.Collections.Generic; 3 using System.Linq; 4 using System.Text; 5 6 namespace _10异常处理 7 { 8 public delegate void MyEventHandler(object sender,EventArgs e); 9 public class Publisher 10 { 11 public event MyEventHandler MyEvent; 12 public void DoSomething() 13 { 14 if (MyEvent != null) 15 { 16 try 17 { 18 MyEvent(this,EventArgs.Empty); 19 } 20 catch(Exception e) 21 { 22 Console.WriteLine("Exception:{0}",e.Message); 23 } 24 } 25 } 26 } 27 public class Subscriber1 28 { 29 public void OnEvent(object sender,EventArgs e) 30 { 31 Console.WriteLine("Subscriber1 Invoked !"); 32 } 33 } 34 public class Subscriber2 35 { 36 public void OnEvent(object sender,EventArgs e) 37 { 38 throw new Exception("Exception2 Failed"); 39 //捕获异常,使得程序没有异常结束,但是却影响到了后面的订阅者的执行 40 } 41 } 42 public class Subscriber3 43 { 44 public void OnEvent(object sender,EventArgs e) 45 { 46 Console.WriteLine("Subscriber3 Invoked!"); 47 } 48 } 49 class Program 50 { 51 static void Main(string [] args) 52 { 53 Publisher pub = new Publisher(); 54 Subscriber1 sub1 = new Subscriber1(); 55 Subscriber2 sub2 = new Subscriber2(); 56 Subscriber3 sub3 = new Subscriber3(); 57 pub.MyEvent += new MyEventHandler(sub1.OnEvent); 58 pub.MyEvent += new MyEventHandler(sub2.OnEvent); 59 pub.MyEvent += new MyEventHandler(sub3.OnEvent); 60 pub.DoSomething(); 61 Console.ReadKey(); 62 } 63 } 64 65 }
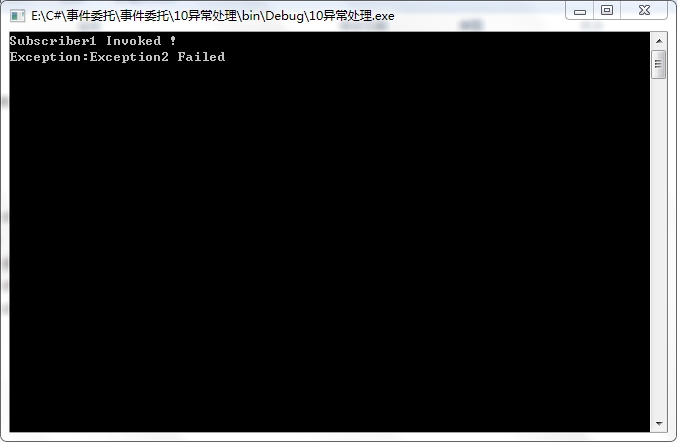
10异常处理02
 View Code
View Code
1 using System; 2 using System.Collections.Generic; 3 using System.Linq; 4 using System.Text; 5 6 namespace _10异常处理02 7 { 8 public delegate void MyEventHandler(object sender, EventArgs e); 9 public class Publisher 10 { 11 public event MyEventHandler MyEvent; 12 public void DoSomething() 13 { 14 if (MyEvent != null) 15 { 16 Delegate[] delArray = MyEvent.GetInvocationList(); 17 foreach (Delegate del in delArray) 18 { 19 try 20 { 21 del.DynamicInvoke(this,EventArgs.Empty); 22 } 23 catch(Exception e) 24 { 25 Console.WriteLine("Exception:{0}",e.Message); 26 } 27 } 28 } 29 } 30 } 31 public class Subscriber1 32 { 33 public void OnEvent(object sender, EventArgs e) 34 { 35 Console.WriteLine("Subscriber1 Invoked !"); 36 } 37 } 38 public class Subscriber2 39 { 40 public void OnEvent(object sender, EventArgs e) 41 { 42 throw new Exception("Exception2 Failed"); 43 //捕获异常,使得程序没有异常结束,但是却影响到了后面的订阅者的执行 44 } 45 } 46 public class Subscriber3 47 { 48 public void OnEvent(object sender, EventArgs e) 49 { 50 Console.WriteLine("Subscriber3 Invoked!"); 51 } 52 } 53 class Program 54 { 55 static void Main(string[] args) 56 { 57 Publisher pub = new Publisher(); 58 Subscriber1 sub1 = new Subscriber1(); 59 Subscriber2 sub2 = new Subscriber2(); 60 Subscriber3 sub3 = new Subscriber3(); 61 pub.MyEvent += new MyEventHandler(sub1.OnEvent); 62 pub.MyEvent += new MyEventHandler(sub2.OnEvent); 63 pub.MyEvent += new MyEventHandler(sub3.OnEvent); 64 pub.DoSomething(); 65 Console.ReadKey(); 66 } 67 } 68 }
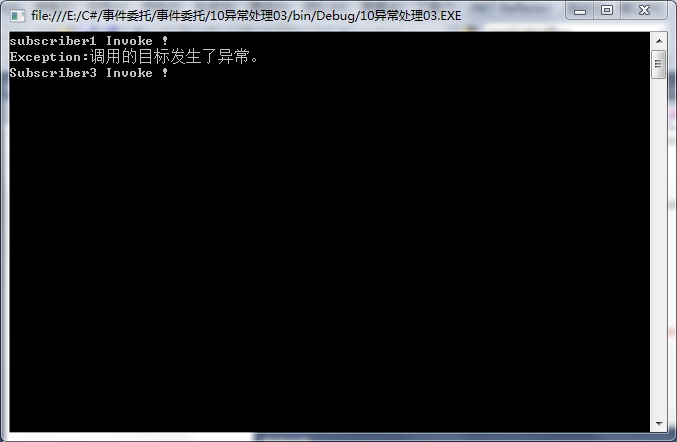
10异常处理03
 View Code
View Code
1 using System; 2 using System.Collections.Generic; 3 using System.Linq; 4 using System.Text; 5 6 namespace _10异常处理03 7 { 8 public delegate void MyEventHandler(object sender,EventArgs e); 9 public class Publisher 10 { 11 public event MyEventHandler MyEvent; 12 public void DoSomething() 13 { 14 Publisher.FireEvent(MyEvent,this,EventArgs.Empty); 15 } 16 public static object[]FireEvent(Delegate del,params object[]args) 17 { 18 List<object>objList=new List<object>(); 19 if(del!=null) 20 { 21 Delegate[]delArray=del.GetInvocationList(); 22 foreach(Delegate method in delArray) 23 { 24 try 25 { 26 object obj=method.DynamicInvoke(args); 27 if(obj!=null) 28 { 29 objList.Add(obj); 30 } 31 } 32 catch(Exception e) 33 { 34 Console.WriteLine("Exception:{0}",e.Message); 35 //此处修改写法 36 } 37 } 38 39 } 40 return objList.ToArray(); 41 } 42 } 43 public class Subscriber1 44 { 45 public void OnEvent(object sender,EventArgs e) 46 { 47 Console.WriteLine("subscriber1 Invoke !"); 48 } 49 } 50 public class Subscriber2 51 { 52 public static void OnEvent(object sender,EventArgs e) 53 { 54 throw new Exception("Subscriber2 failed !"); 55 } 56 } 57 public class Subscriber3 58 { 59 public void OnEvent(object sender,EventArgs e) 60 { 61 Console.WriteLine("Subscriber3 Invoke !"); 62 } 63 } 64 65 class Program 66 { 67 static void Main(string[] args) 68 { 69 Publisher pub = new Publisher(); 70 Subscriber1 sub1 = new Subscriber1(); 71 Subscriber3 sub3 = new Subscriber3(); 72 73 pub.MyEvent += new MyEventHandler(sub1.OnEvent); 74 pub.MyEvent += new MyEventHandler(Subscriber2.OnEvent); 75 pub.MyEvent += new MyEventHandler(sub3.OnEvent); 76 77 pub.DoSomething(); 78 79 Console.ReadLine(); 80 } 81 } 82 83 }
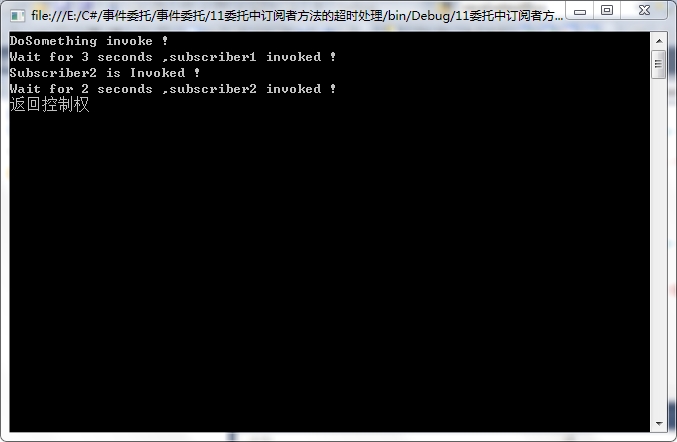
11委托中订阅者方法的超时处理
 View Code
View Code
1 using System; 2 using System.Collections.Generic; 3 using System.Linq; 4 using System.Text; 5 using System.Threading; 6 7 namespace _11委托中订阅者方法的超时处理 8 { 9 public delegate void MyEventHandler(object sender,EventArgs e); 10 public class Publisher 11 { 12 public event MyEventHandler MyEvent; 13 public void DoSomething() 14 { 15 Console.WriteLine("DoSomething invoke !"); 16 Program.FireEvent(MyEvent,this,EventArgs.Empty); 17 } 18 } 19 public class Subscriber1 20 { 21 public void OnEvent(object sender,EventArgs e) 22 { 23 Thread.Sleep(TimeSpan.FromSeconds(3)); 24 Console.WriteLine("Wait for 3 seconds ,subscriber1 invoked !"); 25 } 26 27 } 28 public class Subscriber2 29 { 30 public void OnEvent(object sender,EventArgs e) 31 { 32 Console.WriteLine("Subscriber2 is Invoked !"); 33 } 34 } 35 public class Subscriber3 36 { 37 public void OnEvent(object sender,EventArgs e) 38 { 39 Thread.Sleep(TimeSpan.FromSeconds(2)); 40 Console.WriteLine("Wait for 2 seconds ,subscriber2 invoked !"); 41 } 42 } 43 class Program 44 { 45 static void Main(string[] args) 46 { 47 //初始化对象 48 Publisher pub = new Publisher(); 49 Subscriber1 sub1 = new Subscriber1(); 50 Subscriber2 sub2 = new Subscriber2(); 51 Subscriber3 sub3 = new Subscriber3(); 52 //初始化事件 53 pub.MyEvent += new MyEventHandler(sub1.OnEvent); 54 pub.MyEvent += new MyEventHandler(sub2.OnEvent); 55 pub.MyEvent += new MyEventHandler(sub3.OnEvent); 56 //调用触发事件的方法 57 pub.DoSomething(); 58 Console.WriteLine("返回控制权"); 59 Console.ReadLine(); 60 } 61 public static object[] FireEvent(Delegate del,params object[]args) 62 { 63 List<object> objList = new List<object>(); 64 if(del!=null) 65 { 66 Delegate[] delArray = del.GetInvocationList(); 67 foreach(Delegate method in delArray) 68 { 69 try 70 { 71 object obj = method.DynamicInvoke(args); 72 if (obj != null) 73 { 74 objList.Add(obj); 75 } 76 } 77 catch { } 78 } 79 } 80 return objList.ToArray(); 81 } 82 } 83 #region//总结一下 84 /* 85 * 1、在依次执行订阅者方法时,当前线程会转去执行方法中的代码,调用方法的客户端会被中断, 86 * 只有当方法全部执行完毕之后,控制权才回到客户端手里。 87 * 2、事件的发布者并不关心谁订阅了事件,也不关心订阅者的方法有没有返回值,它只需要在事件 88 * 发生的瞬间告知订阅者事件已经发生并将相关的参数传给订阅者就可以了,然后继续执行它后 89 * 面的代码,而不是等待订阅者完成后再执行后面的代码。 90 */ 91 #endregion 92 }
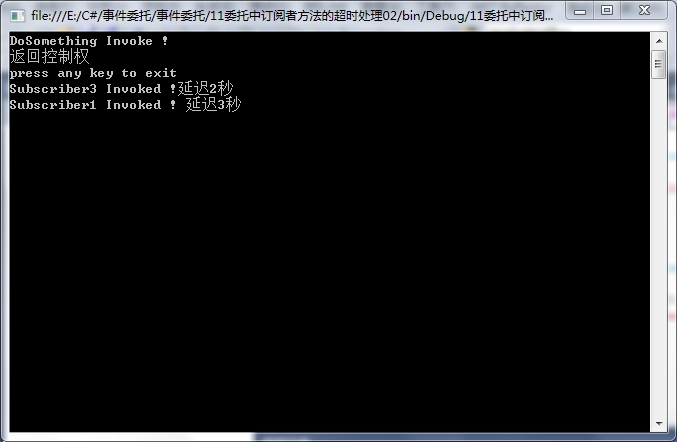
11委托中订阅者方法的超时处理02
 View Code
View Code
1 using System; 2 using System.Collections.Generic; 3 using System.Linq; 4 using System.Text; 5 using System.Threading; 6 7 namespace _11委托中订阅者方法的超时处理02 8 { 9 //public delegate void MyEventHandler(object sender,EventArgs e); 10 public class Publisher 11 { 12 public event EventHandler MyEvent; 13 public void DoSomething() 14 { 15 Console.WriteLine("DoSomething Invoke !"); 16 if (MyEvent != null) 17 { 18 Delegate[] delArray = MyEvent.GetInvocationList(); 19 foreach (Delegate del in delArray) 20 { 21 try 22 { 23 EventHandler method = (EventHandler)del; 24 method.BeginInvoke(null, EventArgs.Empty, null, null); 25 //对于多个订阅者注册的情况,必须使用GetInvocationList()获得所有委托对象, 26 ///然后遍历它们,分别在其上调用BeginInvoke()方法 27 } 28 catch(Exception e) 29 { 30 Console.WriteLine(e.Message); 31 } 32 33 } 34 } 35 } 36 } 37 public class Subscriber1 38 { 39 public void OnEvent(object sender, EventArgs e) 40 { 41 Thread.Sleep(TimeSpan.FromSeconds(3)); 42 Console.WriteLine("Subscriber1 Invoked ! 延迟3秒"); 43 } 44 } 45 public class Subscriber2 46 { 47 public void OnEvent(object sender, EventArgs e) 48 { 49 throw new Exception("Subscriber2 failed !"); 50 } 51 } 52 public class Subscriber3 53 { 54 public void OnEvent(object sender, EventArgs e) 55 { 56 Thread.Sleep(TimeSpan.FromSeconds(2)); 57 Console.WriteLine("Subscriber3 Invoked !延迟2秒"); 58 } 59 } 60 class Program 61 { 62 static void Main(string[] args) 63 { 64 //初始化对象 65 Publisher pub = new Publisher(); 66 Subscriber1 sub1 = new Subscriber1(); 67 Subscriber2 sub2 = new Subscriber2(); 68 Subscriber3 sub3 = new Subscriber3(); 69 //初始化事件 70 pub.MyEvent += new EventHandler(sub1.OnEvent); 71 pub.MyEvent += new EventHandler(sub2.OnEvent); 72 pub.MyEvent += new EventHandler(sub3.OnEvent); 73 //调用触发事件的方法 74 pub.DoSomething(); 75 Console.WriteLine("返回控制权"); 76 Console.WriteLine("press any key to exit"); 77 Console.ReadLine(); 78 79 #region 80 /* 81 * 1、当我们直接调用委托时,实际上是调用了Invoke()方法,它会中断调用它的客户端,然后在 82 * 客户端程序上执行所有订阅者的方法,最后将控制权返回客户端 83 * 2、客户端所在的线程通常是主线程,而执行订阅者方法的线程来自线程池,属于后台线程,当 84 * 主线程结束时,不论后台线程有没有结束,都会退出程序。 85 * 3、本次订阅者中一个停留3秒,一个停留两秒,实际上这两个方法是并行执行的,也就是说最长 86 * 的是3秒。 87 */ 88 #endregion 89 } 90 } 91 }
12委托和方法的异步调用
 View Code
View Code
1 using System; 2 using System.Collections.Generic; 3 using System.Linq; 4 using System.Text; 5 using System.Threading; 6 7 namespace _12委托和方法的异步调用 8 { 9 class Program 10 { 11 static void Main(string[] args) 12 { 13 Console.WriteLine("Client application started !"); 14 Thread.CurrentThread.Name = "Main Thread"; 15 16 Calculator cal = new Calculator(); 17 int result = cal.Add(2,5); 18 Console.WriteLine("Result:{0}",result); 19 for (int i = 1; i <= 3;i++ ) 20 { 21 Thread.Sleep(TimeSpan.FromSeconds(i)); 22 Console.WriteLine("{0}:Client executed{1}seconds",Thread.CurrentThread.Name,i); 23 } 24 Console.ReadLine(); 25 } 26 } 27 public class Calculator 28 { 29 public int Add(int x,int y) 30 { 31 if(Thread.CurrentThread.IsThreadPoolThread==true) 32 { 33 Thread.CurrentThread.Name = "Pool Thread"; 34 } 35 Console.WriteLine("Method invoked!"); 36 for (int i = 1; i <= 2;i++ ) 37 { 38 Thread.Sleep(TimeSpan.FromSeconds(i)); 39 Console.WriteLine("{0}:Add executed{1}seconds.",Thread.CurrentThread.Name,i); 40 } 41 Console.WriteLine("Method complete !"); 42 return x + y; 43 } 44 } 45 }

12委托和方法的异步调用02
 View Code
View Code
1 using System; 2 using System.Collections.Generic; 3 using System.Linq; 4 using System.Text; 5 using System.Threading; 6 7 namespace _12委托和方法的异步调用02 8 { 9 public delegate int AddDelegate(int x,int y); 10 public class Calculator 11 { 12 public int Add(int x,int y) 13 { 14 if(Thread.CurrentThread.IsThreadPoolThread==true) 15 { 16 Thread.CurrentThread.Name = "线程池"; 17 } 18 //延缓两秒钟 19 for (int i = 1; i <= 2;i++ ) 20 { 21 Thread.Sleep(TimeSpan.FromSeconds(i)); 22 Console.WriteLine("{0}:延缓{1}秒",Thread.CurrentThread.Name,i); 23 } 24 Console.WriteLine("方法执行完毕"); 25 return x + y; 26 } 27 } 28 class Program 29 { 30 static void Main(string[] args) 31 { 32 Console.WriteLine("客户端应用程序开始执行"); 33 Thread.CurrentThread.Name = "主线程"; 34 35 Calculator cal = new Calculator(); 36 AddDelegate del = new AddDelegate(cal.Add); 37 IAsyncResult asr=del.BeginInvoke(2,3,null,null); 38 //模拟3秒钟 39 for (int i = 1; i <= 3;i++ ) 40 { 41 Thread.Sleep(TimeSpan.FromSeconds(i)); 42 Console.WriteLine("{0}:客户端线程停留{1}",Thread.CurrentThread.Name,i); 43 } 44 int result = del.EndInvoke(asr); 45 Console.WriteLine("结果:{0}",result); 46 Console.WriteLine("结束"); 47 48 Console.ReadLine(); 49 } 50 } 51 }

委托的分析:
参考文章地址:http://www.cnblogs.com/Alpha-Fly/archive/2012/04/04/2431880.html
委托的定义: public delegate 返回类型 FuncDelegate(参数列表);
这里是一个类型,可以定义一个FuncDelegate类型的变量
而定义的这个变量就可以存放与这个委托具有相同返回值类型、相同参数类型的方法名
委托是一种类型安全的函数回调机制,它不仅能够调用实例方法,也能够调用静态方法,并且具备按顺序执行多个方法的能力。
委托与函数指针的区别:
函数指针是面向过程的,它指向内存空间的一片地址,再由地址找到函数的代码块,去执行代码。
委托是面向对象的,是一个类(用Reflector查看,是new出来的),实际上是将方法名作为参数传递进来进行了封装,在调用的时候直接调用这个方法。
委托本质是一个类。委托内部(在其父类MulticastDelegate)有一个集合(invocationList)来维护方法列表,执行的时候是调用方法列表中的方法,即用委托名.Invoke();同时有一个invocationCount变量记录方法列表中方法的个数,而对于实例,是将其存放在基类Delegate的Target中的。(如下例的name字段)
下图是对委托原理的大致总结:

要想了解具体的实现步骤,请结合Reflector查看!
异步委托:说白了就是另外开启一个线程来执行操作
实现方式一:没有回调函数
using System; using System.Collections.Generic; using System.Linq; using System.Text; using System.Threading; namespace 异步委托 { //声明一个委托 public delegate int DelAdd(int x,int y); class Program { static void Main(string[] args) { //打印当前主线程 Console.WriteLine("当前主线程是:{0}",Thread.CurrentThread.ManagedThreadId); //实例化委托 DelAdd delAdd = new DelAdd(MyAdd); var asResult = delAdd.BeginInvoke(1, 2, null, null); int num = 1; //询问异步委托执行完了没有 while (!asResult.IsCompleted) { //主线程可以执行其他操作 Console.WriteLine("主线程还在执行"+num); num++; } int result = delAdd.EndInvoke(asResult); Console.WriteLine("我执行完了"); Console.ReadKey(); } //定义满足委托定义的方法 static int MyAdd(int x,int y) { //打印当前线程 Console.WriteLine("当前线程标识符是:"+Thread.CurrentThread.ManagedThreadId); return x+y; } } }
实现方式二:有回调函数
using System; using System.Collections.Generic; using System.Linq; using System.Runtime.Remoting.Messaging; using System.Text; using System.Threading; namespace 异步委托02 { public delegate int DelAdd(int x,int y); class Program { static void Main(string[] args) { //这个程序中采用回调函数来帮助实现异步委托 //打印当前线程的标识符 Console.WriteLine("当前线程的标识符"+Thread.CurrentThread.ManagedThreadId); DelAdd delAdd = new DelAdd(MyAdd); delAdd.BeginInvoke(1, 2, new AsyncCallback(MyAsyncCallback), 12); Console.WriteLine("我结束了"); Console.ReadKey(); } //编写一个符合委托的方法 static int MyAdd(int x, int y) { Console.WriteLine("1当前线程标识符是"+Thread.CurrentThread.ManagedThreadId); return x + y; } static void MyAsyncCallback(IAsyncResult result) { Console.WriteLine("2当前线程标识符是" + Thread.CurrentThread.ManagedThreadId); //将接口类型转换成实例类型 AsyncResult aResult = (AsyncResult)result; //将实例类型转换成委托类型 DelAdd del=(DelAdd)aResult.AsyncDelegate; //获取执行结果 int addResult = del.EndInvoke(result); //获取随BeginInvoke传入的参数 int state = (int)aResult.AsyncState; Console.WriteLine("异步完成回调方法执行的结果"+state); } } }
