写在前面
上周,同事写了一段ConcurrentHashMap的测试代码,说往map里放了32个元素就内存溢出了,我大致看了一下他的代码及运行的jvm参数,觉得很奇怪,于是就自己捣鼓了一下。首先上一段代码:
public class MapTest { public static void main(String[] args) { System.out.println("Before allocate map, free memory is " + Runtime.getRuntime().freeMemory()/(1024*1024) + "M"); Map<String, String> map = new ConcurrentHashMap<String, String>(2000000000); System.out.println("After allocate map, free memory is " + Runtime.getRuntime().freeMemory()/(1024*1024) + "M"); int i = 0; try { while (i < 1000000) { System.out.println("Before put the " + (i + 1) + " element, free memory is " + Runtime.getRuntime().freeMemory()/(1024*1024) + "M"); map.put(String.valueOf(i), String.valueOf(i)); System.out.println("After put the " + (i + 1) + " element, free memory is " + Runtime.getRuntime().freeMemory()/(1024*1024) + "M"); i++; } } catch (Exception e) { e.printStackTrace(); } catch (Throwable t) { t.printStackTrace(); } finally { System.out.println("map size is " + map.size()); } } }
执行时加上jvm执行参数 -Xms512m -Xmx512m ,执行结果:
Before allocate map, free memory is 120M After allocate map, free memory is 121M Before put the 1 element, free memory is 121M After put the 1 element, free memory is 121M Before put the 2 element, free memory is 121M After put the 2 element, free memory is 122M Before put the 3 element, free memory is 122M After put the 3 element, free memory is 122M Before put the 4 element, free memory is 122M After put the 4 element, free memory is 122M Before put the 5 element, free memory is 122M After put the 5 element, free memory is 114M Before put the 6 element, free memory is 114M java.lang.OutOfMemoryError: Java heap space map size is 5 at java.util.concurrent.ConcurrentHashMap.ensureSegment(Unknown Source) at java.util.concurrent.ConcurrentHashMap.put(Unknown Source) at com.j.u.c.tj.MapTest.main(MapTest.java:17)
最开始的代码是没有加入一些日志打印的,当时就很奇怪,为什么只往map里放一个元素就报了OutOfMemoryError了。
于是就加了上述打印日志,发现在创建map的时候已经占用了二百多兆的空间,然后往里面put一个元素,put前都还有二百多兆,put时就报了OutOfMemoryError, 那就更奇怪了,初始化map的时候会占用一定空间,可以理解,但是只是往里面put一个很小的元素,为什么就会OutOfMemoryError呢?
排查过程
1、第一步,将第一段代码中的Map<String, String> map = new ConcurrentHashMap<String, String>(2000000000);修改为Map<String, String> map = new ConcurrentHashMap<String, String>();,这次运行正常。(没有找到问题根因,但是以后使用ConcurrentHashMap得注意:1、尽量不初始化;2、如果需要初始化,尽量给一个比较合适的值)
2、第二步,执行时加上jvm参数-Xms20124m -Xmx1024m 。发现还是同样出现问题。
3、第三步,分析ConcurrentHashMap源代码,首先,了解一下ConcurrentHashMap的结构,它是由多个Segment组成(每个Segment拥有一把锁,也是ConcurrentHashMap线程安全的保证,不是本文讨论的重点),每个Segment由一个HashEntry数组组成,出问题就在这个HashEntry上面
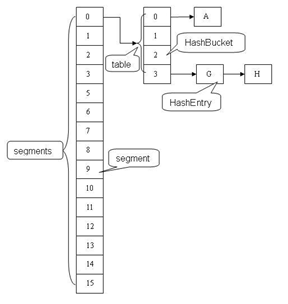
4、第四步,查看ConcurrentHashMap的初始化方法,可以看出,初始化了Segment[0]的HashEntry数组,数组的长度为cap值,这个值为67108864
cap的计算过程(可以针对于初始化过程进行调试)
1)initialCapacity为2,000,000,000,而MAXIMUM_CAPACITY的默认值(也即ConcurrentHashMap支持的最大值是1<<30,即230=1,073,741,824),initialCapacity的值大于MAXIMUM_CAPACITY,即initialCapacity=1,073,741,824
2)c的值计算为 initialCapacity/ssize=67108864
3)cap为 大于等于c的第一个2的n次方数 也即67108864
public ConcurrentHashMap(int initialCapacity, float loadFactor, int concurrencyLevel) { if (!(loadFactor > 0) || initialCapacity < 0 || concurrencyLevel <= 0) throw new IllegalArgumentException(); if (concurrencyLevel > MAX_SEGMENTS) concurrencyLevel = MAX_SEGMENTS; // Find power-of-two sizes best matching arguments int sshift = 0; int ssize = 1; while (ssize < concurrencyLevel) { ++sshift; ssize <<= 1; } this.segmentShift = 32 - sshift; this.segmentMask = ssize - 1; if (initialCapacity > MAXIMUM_CAPACITY) initialCapacity = MAXIMUM_CAPACITY; int c = initialCapacity / ssize; if (c * ssize < initialCapacity) ++c; int cap = MIN_SEGMENT_TABLE_CAPACITY; while (cap < c) cap <<= 1; // create segments and segments[0] Segment<K,V> s0 = new Segment<K,V>(loadFactor, (int)(cap * loadFactor), (HashEntry<K,V>[])new HashEntry[cap]); Segment<K,V>[] ss = (Segment<K,V>[])new Segment[ssize]; UNSAFE.putOrderedObject(ss, SBASE, s0); // ordered write of segments[0] this.segments = ss; }
5、第五步,查看ConcurrentHashMap的put方法,可以看出在put一个元素的时候,
1)计算当前key的hash值,查看当前key所在的semgment有没有初始化,若果有,则执行后续的put操作。
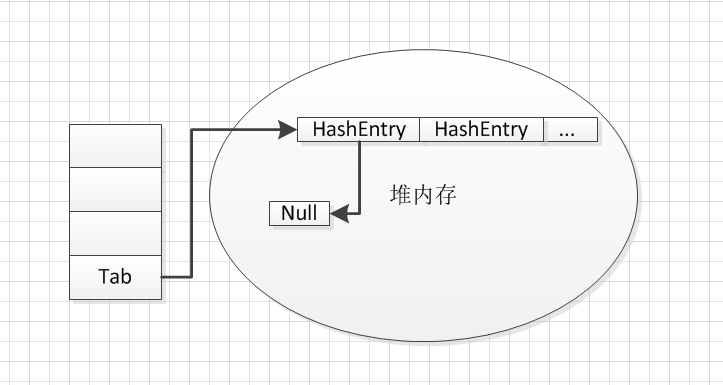
2)如果没有去执行ensureSement()方法,而在ensureSement()方法中又会初始化了一个HashEntry数组,数组的长度和第一个初始化的Segment的HashEntry的长度一致。
public V put(K key, V value) { Segment<K,V> s; if (value == null) throw new NullPointerException(); int hash = hash(key); int j = (hash >>> segmentShift) & segmentMask; if ((s = (Segment<K,V>)UNSAFE.getObject // nonvolatile; recheck (segments, (j << SSHIFT) + SBASE)) == null) // in ensureSegment s = ensureSegment(j); return s.put(key, hash, value, false); } private Segment<K,V> ensureSegment(int k) { final Segment<K,V>[] ss = this.segments; long u = (k << SSHIFT) + SBASE; // raw offset Segment<K,V> seg; if ((seg = (Segment<K,V>)UNSAFE.getObjectVolatile(ss, u)) == null) { Segment<K,V> proto = ss[0]; // use segment 0 as prototype int cap = proto.table.length; float lf = proto.loadFactor; int threshold = (int)(cap * lf); HashEntry<K,V>[] tab = (HashEntry<K,V>[])new HashEntry[cap]; if ((seg = (Segment<K,V>)UNSAFE.getObjectVolatile(ss, u)) == null) { // recheck Segment<K,V> s = new Segment<K,V>(lf, threshold, tab); while ((seg = (Segment<K,V>)UNSAFE.getObjectVolatile(ss, u)) == null) { if (UNSAFE.compareAndSwapObject(ss, u, null, seg = s)) break; } } } return seg; }
6、这个时候能定位到是因为put一个元素的时候创建了一个长度为67103684的HashEntry数组,而这个HashEntry数组会占用67108864*4byte=256M,和上面的测试结果能对应起来。为什么数组会占用这么大的空间,很多同学可能会有疑问,那来看一下数组的初始化 而数组初始化会在堆内存创建一个HashEntry引用的数组,且长度为67103684,而每个HashEntry引用(所引用的对象都为null)都占用4个字节。
问题总结
1、ConcurrentHashMap初始化时要指定合理的初始化参数(当然本人做了一个小测试,指定初始化参数暂时没有发现性能上的提升)