接上文 多线程编程学习笔记——线程同步(一)
四、使用AutoResetEvent
1. 使用AutoResetEvent类来实现从一个线程向另一个线程发出通知。
2.代码如下
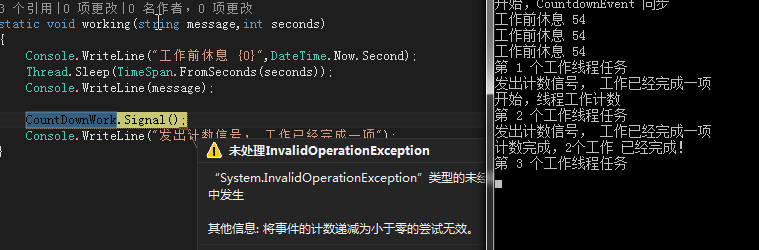
using System; using System.Collections.Generic; using System.Linq; using System.Text; using System.Threading; //引入线程 using System.Diagnostics; namespace ThreadSynchronousDemo { class Program { static AutoResetEvent autoResetWork = new AutoResetEvent(false); static AutoResetEvent autoResetMain = new AutoResetEvent(false); static void Main(string[] args) { Console.WriteLine("开始,AutoResetEvent 同步"); string threadName = "线程 1"; var t = new Thread((() => working(threadName, 10))); t.Start(); Console.WriteLine("开始,第一次工作"); autoResetWork.WaitOne();//万事俱备只欠东风,事情卡在这里了, Console.WriteLine("第一次工作完成"); Console.WriteLine("主线程操作,准备发信号"); Thread.Sleep(TimeSpan.FromSeconds(5)); //发信号,说明值已经被写进去了。这里的意思是说Set是一个发信号的方法。 autoResetMain.Set(); Console.WriteLine("现在运行第二次工作。"); autoResetWork.WaitOne(); Console.WriteLine("第二次工作完成"); Console.Read(); } static void working(string name,int seconds) { Console.WriteLine("{0} 开始运行工作", name); Thread.Sleep(TimeSpan.FromSeconds(seconds)); Console.WriteLine("{0} 正在工作。。。。。。", name); //发信号,说明值已经被写进去了。这里的意思是说Set是一个发信号的方法。 autoResetWork.Set(); Console.WriteLine("等待主线程完成工作,并发出信号"); autoResetMain.WaitOne(); Console.WriteLine("主线程发来信号,开始第二次工作"); Thread.Sleep(TimeSpan.FromSeconds(seconds)); Console.WriteLine("{0} 第二次工作正在进行中。。。。。", name); autoResetWork.Set(); } } }
3.程序运行结果,如下图。
以上程序中,我们定义了两个AutoResetEvent实例。其中一个是从子线程往主线程发信号 ,另一个是主线程往子线程发信号。我们在构造AutoResetEvent时,传入了false,定义了这两个实例的初始状态unsignaled。这个状态下,任何线程调用这两个实例的WaitOne方法将会被阻塞,直到我们调用了Set方法。如果我们在构造的时候传入了true,则这两个实例的初始状态是singnaled,则线程调用WaitOne则会被立即处理。
五、使用ManualResetEventSlim类
1. 使用ManualResetEventSlim在线程间传递信号。
2.代码如下
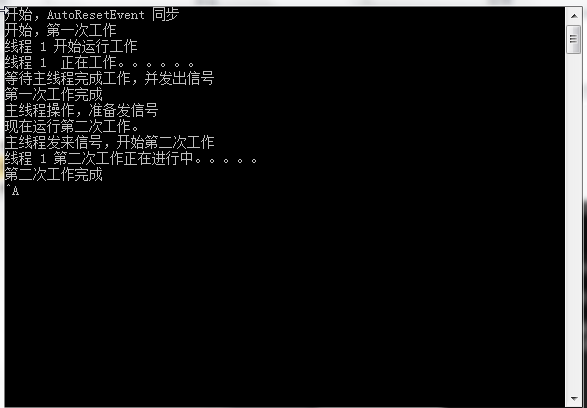
using System; using System.Collections.Generic; using System.Linq; using System.Text; using System.Threading; //引入线程 using System.Diagnostics; namespace ThreadSynchronousDemo { class Program { static ManualResetEventSlim manuResetWork = new ManualResetEventSlim(false); static void Main(string[] args) { Console.WriteLine("开始,ManualResetEventSlim 同步"); string threadName = "线程 1"; string threadName2 = "线程 2"; string threadName3 = "线程 3"; var t = new Thread((() => working(threadName, 3))); var t2 = new Thread((() => working(threadName2, 6))); var t3 = new Thread((() => working(threadName3, 12))); t.Start(); t2.Start(); t3.Start(); Thread.Sleep(TimeSpan.FromSeconds(5)); Console.WriteLine("开始,打开 线程工作大门"); manuResetWork.Set(); //发信号 Thread.Sleep(TimeSpan.FromSeconds(3)); manuResetWork.Reset(); Console.WriteLine("线程工作大门,关闭"); Thread.Sleep(TimeSpan.FromSeconds(10)); Console.WriteLine("打开线程工作大门第二次打开了"); manuResetWork.Set(); //发信号 Thread.Sleep(TimeSpan.FromSeconds(3)); manuResetWork.Reset(); Console.WriteLine("线程工作大门,又关闭了"); Console.Read(); } static void working(string name,int seconds) { Console.WriteLine("{0} 休息", name); Thread.Sleep(TimeSpan.FromSeconds(seconds)); Console.WriteLine("{0} 等待打开线程运行的大门", name); manuResetWork.Wait(); Console.WriteLine("线程运行的大门打开了,{0} 进行工作", name); } } }
3.程序运行结果,如下图。

当主程序启动时,首先创建ManualResetEvenSlim类的一个实例,然后启动了三个线程,等待事件信号通知它们继续工作。
ManualResetEvenSlim的工作方式有点像人群通过大门,而AutoResetEvent事件像一个旋转门,一次只能通过一人。
ManualResetEvenSlim打开了大门,一直保持打开,直到调用了Reset方法。直到再次调用Set方法打开 大门。
六、使用CountDownEvent类
1. 使用CountDownEvent信号类来等待直到一定数量的操作完成。
2.代码如下
using System; using System.Collections.Generic; using System.Linq; using System.Text; using System.Threading; //引入线程 using System.Diagnostics; namespace ThreadSynchronousDemo { class Program { static CountdownEvent CountDownWork = new CountdownEvent(2); static void Main(string[] args) { Console.WriteLine("开始,CountdownEvent 同步"); var t = new Thread((() => working("第 1 个工作线程任务", 3))); var t2 = new Thread((() => working("第 2 个工作线程任务", 6))); //var t3 = new Thread((() => working("第 3 个工作线程任务", 12))); t.Start(); t2.Start(); //t3.Start(); Thread.Sleep(TimeSpan.FromSeconds(5)); Console.WriteLine("开始,线程工作计数"); CountDownWork.Wait(); Console.WriteLine("计数完成,2个工作 已经完成!"); //如果把上面代码注释的第三个线程还原,释放对象,可以造成第三个线程的抛出错误 CountDownWork.Dispose(); Console.Read(); } static void working(string message,int seconds) { Console.WriteLine("工作前休息 {0}",DateTime.Now.Second); Thread.Sleep(TimeSpan.FromSeconds(seconds)); Console.WriteLine(message); CountDownWork.Signal(); Console.WriteLine("发出计数信号, 工作已经完成一项"); } } }
3.程序运行结果如下图。
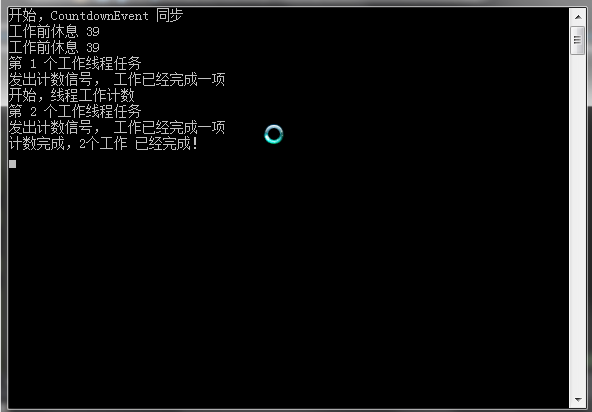
程序启动时,创建了一个CountDownEven实例,在构造中指定了,当两个操作完成时给出信号。然后我们启动了两个线程进行工作,当第二个线程完成操作时,主线程从等待CountDownEvent的状态中返回并继续工作。这个类使用场景是,主线程需要等待多个线程完成工作之后,才能继续的情形。
缺点:必须要等待指定数量的线程全部完成工作,否则就一直会等待,请确保使用CountDownEvent时,所有线程完成工作后,都要调用Signal方法。
说明:
1) 把上面代码中注释的第三个线程的代码,还原则会出现以下错误。
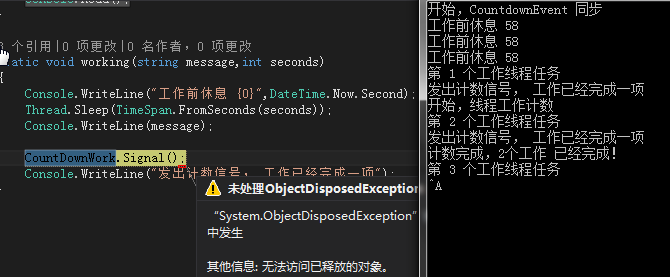
2) 如果把 第三个线程启用,同时把 CountDownWork.Dispose();注释,则会出现以下错误信息。