一.Spring 简史
- Spring 1.x 时代:在 Spring1.x 时代,都是通过 xml 文件配置 bean,随着项目的不断扩大,需要将 xml 配置分放到不同的配置文件中,需要频繁的在 java 类和 xml 配置文件中切换。
-
Spring 2.x 时代:随着 JDK 1.5 带来的注解支持,Spring2.x 可以使用注解对 Bean 进行申明和注入,大大的减少了 xml 配置文件,同时也大大简化了项目的开发。
那么,问题来了,究竟是应该使用 xml 还是注解呢?最佳实践:- 应用的基本配置用 xml,比如:数据源、资源文件等
- 业务开发用注解,比如:Service 中注入 bean 等
- Spring 3.x 时代:从 Spring3.x 开始提供了 Java 配置方式,使用 Java 配置方式可以更好的理解你配置的 Bean,现在我们就处于这个时代,并且 Spring4.x 和 Spring boot 都推荐使用 java 配置的方式。
二.Spring Boot 简介
- 随着动态语言的流行 (Ruby、Groovy、Scala、Node.js),Java 的开发显得格外的笨重:繁多的配置、低下的开发效率、复杂的部署流程以及第三方技术集成难度大。
-
在上述环境下,Spring Boot 应运而生。它使用“习惯优于配置”(项目中存在大量的配置,此外还内置了一个习惯性的配置,让你无需手动进行配置)的理念让你的项目快速的运行起来。使用 Spring Boot 很容易创建一个独立运行(运行 Jar,内嵌 Servlet 容器)准生产级别的基于 Spring 框架的项目,使用 Spring Boot 你可以不用或者只需很少的 Spring 配置。(减少了配置文件)
三.Spring Boot 的优点
- 快速构建项目
- 对主流开发框架的无配置集成
- 项目可独立运行,无需外部依赖 Servlet 容器
- 提供运行时的应用监控
- 极大地提高了开发、部署效率
- 与云计算的天然集成
四.Spring Boot 的缺点
- 坑多文档少
- 版本迭代速度很快,一些模块改动很大
- 由于不用自己做配置,报错时很难定位
- 网上现成的解决方案比较少
五.第一个 Spring Boot 应用程序
- 这里我们使用 Intellij IDEA 来新建一个 Spring Boot 项目。
-
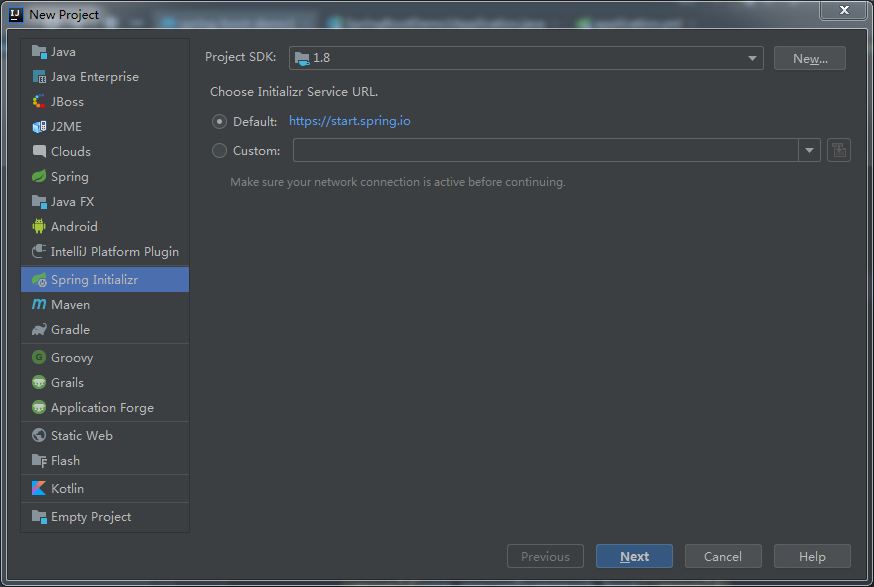 新建 Spring Initializr 项
新建 Spring Initializr 项 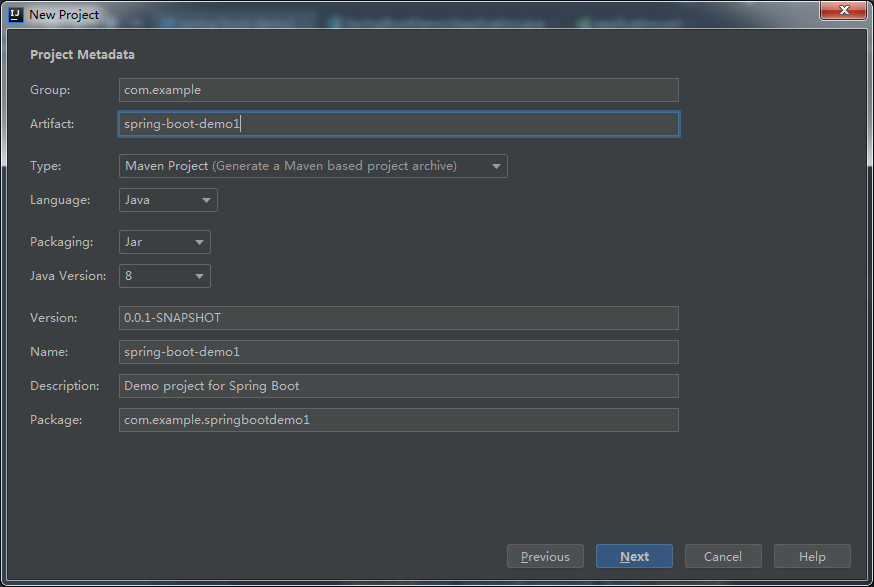 填写项目信息
填写项目信息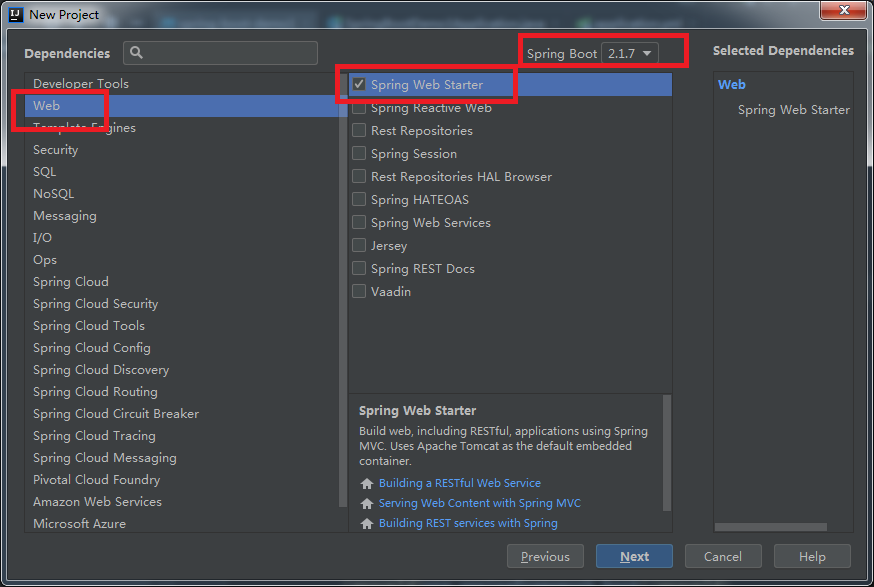 选择项目使用技术,SpringBot版本可以到pom.xml文件中修改,后来我改成了1.5.8
选择项目使用技术,SpringBot版本可以到pom.xml文件中修改,后来我改成了1.5.8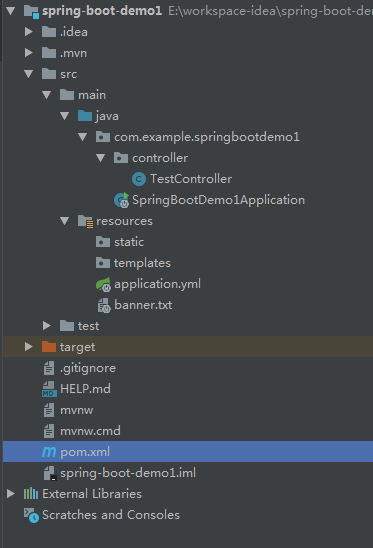 创建好项目后进行测试。整个测试项目的目录结构
创建好项目后进行测试。整个测试项目的目录结构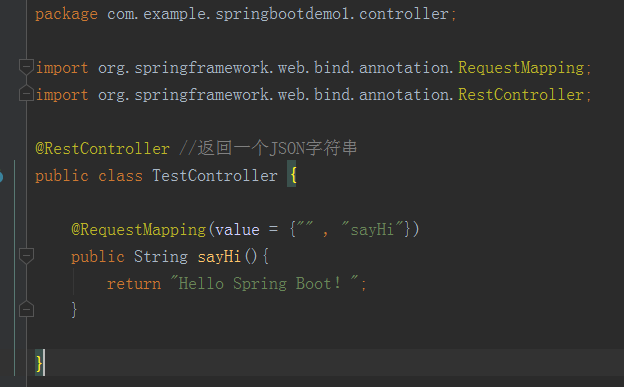 添加控制器
添加控制器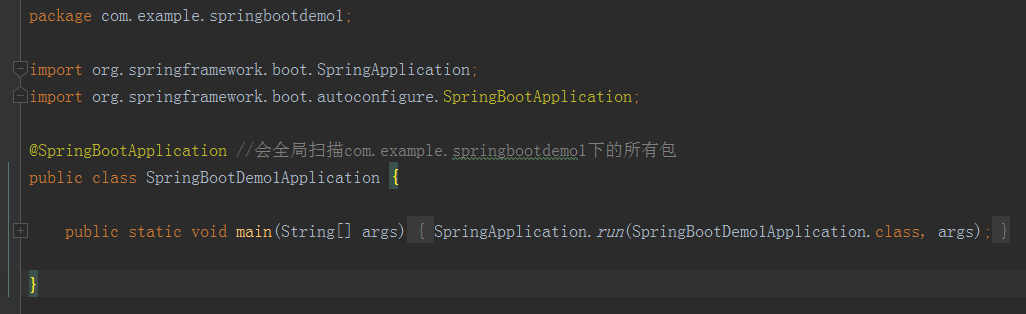 新建 Spring Boot 项目后,会在根包目录下有一个 artifactId + Application 命名规则的入口类,如上图。
新建 Spring Boot 项目后,会在根包目录下有一个 artifactId + Application 命名规则的入口类,如上图。main()方法:是一个标准的 Java 应用的 main 方法,主要作用是作为项目启动的入口。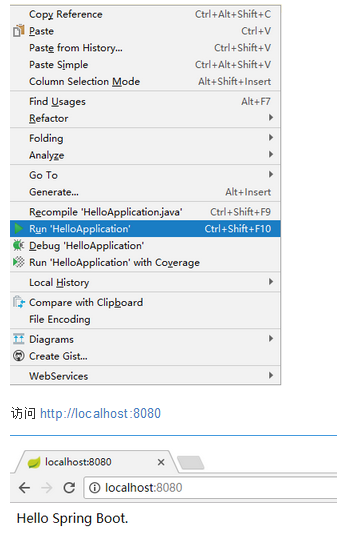 运行效果:HelloApplication 文件中单击右键,在右键菜单中选择 Run "HelloApplication" 运行项目
运行效果:HelloApplication 文件中单击右键,在右键菜单中选择 Run "HelloApplication" 运行项目
六.Spring Boot 基本配置
-
 自定义 Banner,
自定义 Banner,
我们在
通过 http://patorjk.com/software/taag 网站生成字符串,将网站生成的字符复制到 banner.txt 中。再次运行这个程序src/main/resources目录下新建一个 banner.txt_ooOoo_
o8888888o
88" . "88
(| -_- |)
O = /O
____/`---'\____
.' \| |// `.
/ \||| : |||//
/ _||||| -:- |||||-
| | \ - /// | |
| \_| ''---/'' | |
.-\__ `-` ___/-. /
___`. .' /--.-- `. . __
."" '< `.___\_<|>_/___.' >'"".
| | : `- \`.;` _ /`;.`/ - ` : | |
`-. \_ __ /__ _/ .-` / /
======`-.____`-.___\_____/___.-`____.-'======
`=---='
^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^
佛祖保佑 永无BUG
再次启动springboot项目后图案就会变成上面的图案
- Spring Boot 配置文件
Spring Boot项目使用一个全局的配置文件
application.properties或者是application.yml,在resources目录下或者类路径下的/config下,一般我们放到resources下。修改 tomcat 的端口为 9090,并将默认的访问路径 "/" 修改为 "boot",可以在
application.properties中添加:server.port=9090 server.context-path=/boot或在 application.yml 中添加:
server:
port: 9090
context-path: /boot #虚拟目录也就是我们学过的自定义的命名空间只不过这里是全局的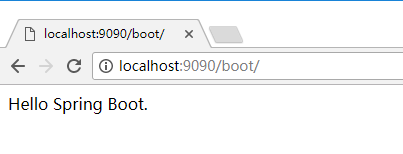 测试效果
测试效果修改 DispatcherServlet 的规则为:*.html
server: port: 9090 context-path: /boot #虚拟目录也就是我们学过的自定义的命名空间只不过这里是全局的 servlet-path: "*.html" #后缀必须以.html结尾 测试效果
测试效果 -
starter pom(就是pom.xml文件)
Spring Boot 为我们提供了简化企业级开发绝大多数场景的 starter pom ,只要使用了应用场景所需要的 starter pom ,相关的技术配置将会消除,就可以得到 Spring Boot 为我们提供的自动配置的 Bean。
-
官方提供的 starter pom
Name
Description
Pom
spring-boot-starterCore starter, including auto-configuration support, logging and YAML
spring-boot-starter-activemqStarter for JMS messaging using Apache ActiveMQ
spring-boot-starter-amqpStarter for using Spring AMQP and Rabbit MQ
spring-boot-starter-aopStarter for aspect-oriented programming with Spring AOP and AspectJ
spring-boot-starter-artemisStarter for JMS messaging using Apache Artemis
spring-boot-starter-batchStarter for using Spring Batch
spring-boot-starter-cacheStarter for using Spring Framework’s caching support
spring-boot-starter-cloud-connectorsStarter for using Spring Cloud Connectors which simplifies connecting to services in cloud platforms like Cloud Foundry and Heroku
spring-boot-starter-data-cassandraStarter for using Cassandra distributed database and Spring Data Cassandra
spring-boot-starter-data-couchbaseStarter for using Couchbase document-oriented database and Spring Data Couchbase
spring-boot-starter-data-elasticsearchStarter for using Elasticsearch search and analytics engine and Spring Data Elasticsearch
spring-boot-starter-data-gemfireStarter for using GemFire distributed data store and Spring Data GemFire
spring-boot-starter-data-jpaStarter for using Spring Data JPA with Hibernate
spring-boot-starter-data-ldapStarter for using Spring Data LDAP
spring-boot-starter-data-mongodbStarter for using MongoDB document-oriented database and Spring Data MongoDB
spring-boot-starter-data-neo4jStarter for using Neo4j graph database and Spring Data Neo4j
spring-boot-starter-data-redisStarter for using Redis key-value data store with Spring Data Redis and the Jedis client
spring-boot-starter-data-restStarter for exposing Spring Data repositories over REST using Spring Data REST
spring-boot-starter-data-solrStarter for using the Apache Solr search platform with Spring Data Solr
spring-boot-starter-freemarkerStarter for building MVC web applications using FreeMarker views
spring-boot-starter-groovy-templatesStarter for building MVC web applications using Groovy Templates views
spring-boot-starter-hateoasStarter for building hypermedia-based RESTful web application with Spring MVC and Spring HATEOAS
spring-boot-starter-integrationStarter for using Spring Integration
spring-boot-starter-jdbcStarter for using JDBC with the Tomcat JDBC connection pool
spring-boot-starter-jerseyStarter for building RESTful web applications using JAX-RS and Jersey. An alternative to
spring-boot-starter-webspring-boot-starter-jooqStarter for using jOOQ to access SQL databases. An alternative to
spring-boot-starter-data-jpaorspring-boot-starter-jdbcspring-boot-starter-jta-atomikosStarter for JTA transactions using Atomikos
spring-boot-starter-jta-bitronixStarter for JTA transactions using Bitronix
spring-boot-starter-jta-narayanaSpring Boot Narayana JTA Starter
spring-boot-starter-mailStarter for using Java Mail and Spring Framework’s email sending support
spring-boot-starter-mobileStarter for building web applications using Spring Mobile
spring-boot-starter-mustacheStarter for building MVC web applications using Mustache views
spring-boot-starter-securityStarter for using Spring Security
spring-boot-starter-social-facebookStarter for using Spring Social Facebook
spring-boot-starter-social-linkedinStater for using Spring Social LinkedIn
spring-boot-starter-social-twitterStarter for using Spring Social Twitter
spring-boot-starter-testStarter for testing Spring Boot applications with libraries including JUnit, Hamcrest and Mockito
spring-boot-starter-thymeleafStarter for building MVC web applications using Thymeleaf views
spring-boot-starter-validationStarter for using Java Bean Validation with Hibernate Validator
spring-boot-starter-webStarter for building web, including RESTful, applications using Spring MVC. Uses Tomcat as the default embedded container
spring-boot-starter-web-servicesStarter for using Spring Web Services
spring-boot-starter-websocketStarter for building WebSocket applications using Spring Framework’s WebSocket support
Name
Description
Pom
spring-boot-starter-actuatorStarter for using Spring Boot’s Actuator which provides production ready features to help you monitor and manage your application
spring-boot-starter-remote-shellStarter for using the CRaSH remote shell to monitor and manage your application over SSH. Deprecated since 1.5
Name
Description
Pom
spring-boot-starter-jettyStarter for using Jetty as the embedded servlet container. An alternative to
spring-boot-starter-tomcatspring-boot-starter-log4j2Starter for using Log4j2 for logging. An alternative to
spring-boot-starter-loggingspring-boot-starter-loggingStarter for logging using Logback. Default logging starter
spring-boot-starter-tomcatStarter for using Tomcat as the embedded servlet container. Default servlet container starter used by
spring-boot-starter-webspring-boot-starter-undertowStarter for using Undertow as the embedded servlet container. An alternative to
spring-boot-starter-tomcat - Spring Boot 日志配置
Spring Boot 对各种日志框架都做了支持,我们可以通过配置来修改默认的日志的配置
默认情况下,Spring Boot 使用 Logback 作为日志框架
-
配置日志文件
logging: file: ../logs/spring-boot-hello.log level.org.springframework.web: DEBUG -
关闭特定的自动配置
关闭特定的自动配置使用 @SpringBootApplication 注解的 exclude 参数
@SpringBootApplication(exclude = {DataSourceAutoConfiguration.class})说明:这里是关闭数据源的自动配置