JDBC简介
JDBC即Java Database Connectivity,java数据库连接,是一套用于执行sql语句的Java API。
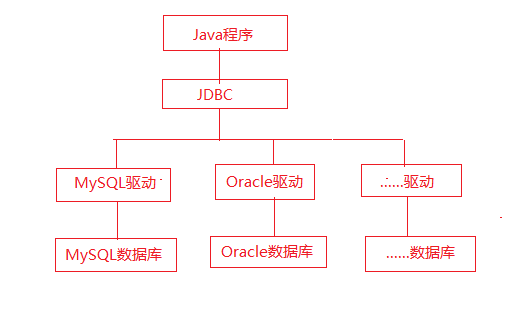
原本操作mysql数据库要使用mysql的语句,操作oracle数据库要使用oracle的语句,如果原来使用mysql,现在要换为oracle,就需要将mysql语句换为oracle语句,很麻烦。
当然,也可以使用通用的sql语句,但这样就不能使用数据库的特性。
jdbc是一套数据库编程接口,由各数据库厂商提供实现(数据库驱动),实现了跨数据库编程。原本使用mysql,现在要换为oracle,把数据库驱动换了就ok,不必重写sql语句。
使用时需要导入对应的数据库驱动(jar包)。
使用Statement接口
1 //注册驱动 2 Class.forName("com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver"); 3 /* 4 如果使用的是mysql5及之前版本的mysql,不加cj;如果使用的是mysql5之后的mysql,要加cj。 5 不加cj的是老版本的mysql驱动,加了cj的是新版本的mysql驱动 6 7 也可以这样来注册驱动: 8 Driver driver=new com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver(); 9 DriverManager.registerDriver(driver); 10 因为要创建Driver对象,在多个操作中可能会创建多个Driver对象,重复注册驱动。不推荐。 11 12 Class.forName("com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver");是使用静态方法来注册驱动,只注册一次,不会重复注册,也更简便,推荐。 13 */ 14 15 16 17 //获取数据库连接 18 String url = "jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/my_db?serverTimezone=GMT"; 19 /* 20 jdbc下有mysql、oracle等多种驱动,最大的肯定是jdbc 21 然后指定是jdbc下的哪种数据库(哪种驱动),mysql 22 数据库地址:端口号 23 要使用的数据库名称 24 使用?传递参数,mysql的时区 25 */ 26 String user = "chy"; 27 String pwd = "abcd"; 28 Connection connection = DriverManager.getConnection(url, user, pwd); //使用DriverManager的静态方法获取数据库连接 29 30 31 //通过数据库连接获取Statement对象 32 Statement statement = connection.createStatement(); 33 34 35 //通过Statement对象执行sql语句 36 String sql = "select * from student_tb"; 37 ResultSet resultSet = statement.executeQuery(sql); //executeQuery(sql)是执行查询,返回结果集 38 39 40 //遍历结果集 41 while (resultSet.next()){ 42 int id = resultSet.getInt("id"); //参数可以是String类型的列名,也可使int型的列索引,注意列索引是从1开始,1表示结果集中当前记录的的第一列的值。 43 String name = resultSet.getString("name"); //建议使用列名,见名知义,不容易出错 44 int age = resultSet.getInt("age"); 45 int score = resultSet.getInt("score"); 46 System.out.println(id+" "+name+" "+age+" "+score); 47 } 48 49 //关闭资源 50 resultSet.close(); 51 connection.close();
设置结果集中的记录数:
1 String sql = "select * from student_tb"; 2 statement.setMaxRows(10); //设置结果集中最多可以装多少条记录,在执行sql语句之前设置 3 ResultSet resultSet = statement.executeQuery(sql);
执行sql语句的方式:
1 ResultSet resultSet = statement.executeQuery(sql) //executeQuery(sql)是执行查询,返回结果集 2 3 int count = statement.executeUpdate(sql); //执行增删改,返回int,受影响的记录数 4 //long count=statement.executeLargeUpdate(sql); //如果受影响的记录数很多(超过21亿),则使用此句 5 6 statement.execute(sql); //可执行所有的sql语句,返回boolean,操作是否成功 7 int count1 = statement.getUpdateCount(); //获取受影响的记录数 8 ResultSet resultSet1 = statement.getResultSet(); //获取结果集
批量操作:
Class.forName("com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver");
String url = "jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/my_db?serverTimezone=GMT";
String user = "chy";
String pwd = "abcd";
Connection connection = DriverManager.getConnection(url, user, pwd);
Statement statement = connection.createStatement();
//批量操作
String[] names=new String[]{"张三","李四","王五"};
int[] ages = new int[]{19, 18, 20};
int[] scores = new int[]{99, 100, 98};
for(int i=0;i<names.length;i++){
String sql = "insert into student_tb (name,age,score) values ('"+names[i]+"',"+ages[i]+","+scores[i]+")";
statement.addBatch(sql);
}
int[] result = statement.executeBatch(); //返回值是int[],对应每条sql语句操作受影响的记录数
// long[] result = statement.executeLargeBatch(); //如果单条sql语句操作受影响的记录数很多(超过21亿),使用这个
connection.close();
Statement接口并没有提供设置sql语句参数的方法,要设置sql语句的参数,需使用字符串的连接:
1 //使用传来的参数 2 int id=1; 3 String name="张三"; 4 String sql = "select * from student_tb where id="+id+" and name='"+name+"'";
如果要设置的参数较多,比如插入记录的时候就需要设置很多参数,sql语句会很长,看得眼花缭乱,还容易写错,尤其是参数中有String类型的时候,引号容易出问题。老是报错:你的sql语句有错。
Statement接口不好设置sql语句的参数,且每次都要重新编译sql语句,浪费时间。Statement接口是直接执行sql语句,而sql语句是使用+号拼接起来的,容易被sql注入攻击。
Statement的子接口PreparedStatement可解决上述问题。
使用PreparedStatement接口
PreparedStatement是Statement的子接口,继承了Statement的所有功能,除此之外,PreparedStatement还具有自身的一些功能:
- 预编译sql语句 prepared ,意为准备,即预编译
- 具有一系列设置参数的方法
使用示例:
Class.forName("com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver");
String url = "jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/my_db?serverTimezone=GMT";
String user = "chy";
String pwd = "abcd";
Connection connection = DriverManager.getConnection(url, user, pwd);
//既然可以对sql进行预编译,那sql语句自然要写在获取PreparedStatement对象之前。使用?作为占位符。
String sql = "select * from student_tb where id=? and name=?";
PreparedStatement preparedStatement = connection.prepareStatement(sql);
//设置参数,第一个参数指定设置的是第几个?(从1开始),第二个参数指定参数值
preparedStatement.setInt(1,1);
preparedStatement.setString(2,"张三");
//执行sql语句,括号中不写sql
ResultSet resultSet = preparedStatement.executeQuery();
while (resultSet.next()){
System.out.println(resultSet.getInt("id")+" "+resultSet.getString("name")+" "+resultSet.getInt("age")+" "+resultSet.getInt("score"));
}
resultSet.close();
connection.close();
预编译:
如果我们要多次执行相似的sql语句,比如:
String sql1="insert into student_tb (name,age,score) values(?,?,?)"; //设置参数 //执行 String sql2="insert into student_tb (name,age,score) values(?,?,?)"; //设置参数 //执行
执行的时候这些语句只有?部分的值不同,其余均相同。
Statement是每次都要重新编译整个sql语句,PreparedStatement是第一次执行这种sql语句(只有?部分不同,其余均相同)时,对整个sql语句进行预编译,预编译结果驻留内存,之后再执行这种sql语句时,只编译?部分的值,不再重新编译整个sql语句,节约了时间,速度更快,尤其是大批量操作的时候。
对整个语句进行编译,叫做编译;只编译语句的一部分,叫做预编译。
PreparedStatement的预编译是编译sql语句?以外的部分。
Statement每次都要重新编译sql语句,所以每次都要传入sql语句:
ResultSet resultSet = statement.executeQuery(sql);
PreparedStatement使用的预编译的sql语句,传入?部分的值即可,不必再传入sql语句:
String sql = "select * from student_tb where id=? and name=?"; //预编译 PreparedStatement preparedStatement = connection.prepareStatement(sql); //设置?部分参数的值 preparedStatement.setInt(1,1); preparedStatement.setString(2,"张三"); //执行sql语句,不必再传入sql语句 ResultSet resultSet = preparedStatement.executeQuery();
批量操作:
1 Class.forName("com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver"); 2 3 String url = "jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/my_db?serverTimezone=GMT"; 4 String user = "chy"; 5 String pwd = "abcd"; 6 Connection connection = DriverManager.getConnection(url, user, pwd); 7 8 //批量操作 9 String[] names=new String[]{"张三","李四","王五"}; 10 int[] ages = new int[]{19, 18, 20}; 11 int[] scores = new int[]{99, 100, 98}; 12 13 String sql = "insert into student_tb (name,age,score) values (?,?,?)"; 14 PreparedStatement preparedStatement = connection.prepareStatement(sql); 15 16 for(int i=0;i<names.length;i++){ 17 preparedStatement.setString(1,names[i]); 18 preparedStatement.setInt(2,ages[i]); 19 preparedStatement.setInt(3,scores[i]); 20 preparedStatement.addBatch(); //不必传入sql语句 21 } 22 23 int[] result = preparedStatement.executeBatch(); 24 // long[] result = preparedStatement.executeLargeBatch(); 25 26 connection.close();