Springboot的jar启动方式,是通过IOC容器启动 带动了Web容器的启动
而Springboot的war启动方式,是通过Web容器(如Tomcat)的启动 带动了IOC容器相关的启动
一、不可不说的Web容器(如Tomcat)
不管是jar启动还是war包启动,都绕不开web容器相关。先了解这个怎么工作的,以Tomcat为例,
看看Springboot 怎么来自动装配tomcat 相关的组件?
1.1 相关类
相关包org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.web,在springboot的自动配置包的web下(自动配置功能都在这个autoconfigure包下)。
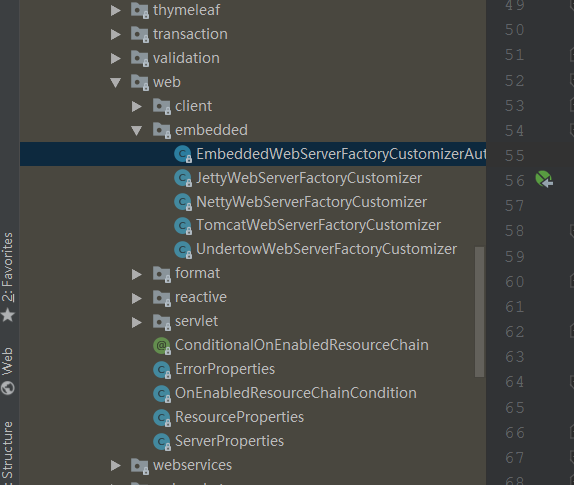
embedded(内嵌)里面四个类一个A四B,一个:
EmbeddedWebServerFactoryCustomizerAutoConfiguration(内嵌web容器工厂自定义定制器装配类)
四个具体容器相关:
JettyWebServerFactoryCustomizer、NettyWebServerFactoryCustomizer、TomcatWebServerFactoryCustomizer、UndertowWebServerFactoryCustomizer
一个自动配置类+四个常用web容器定制器
1.2.工作流程
以Tomcat定制器切入,断点落在构造器上,启动。
总结出它的工作流程:
1.启动=》2.createWebServer=》
3.拿TomcatServletWebServerFactory(tomcatWeb容器工厂)=》
4.拿WebServerFactoryCustomizer(工厂定制器)
也就是拿工厂定制器获取工厂,再拿工厂获取web容器,这么个流程
1.3.具体工作
可以仔细看下相关工厂是如何配置创建容器运行的
TomcatServletWebServerFactory的创建Tomcat方法
public WebServer getWebServer(ServletContextInitializer... initializers) {
Tomcat tomcat = new Tomcat();
File baseDir = (this.baseDirectory != null) ? this.baseDirectory
: createTempDir("tomcat");
tomcat.setBaseDir(baseDir.getAbsolutePath());
Connector connector = new Connector(this.protocol);
tomcat.getService().addConnector(connector);
customizeConnector(connector);
tomcat.setConnector(connector);
tomcat.getHost().setAutoDeploy(false);
configureEngine(tomcat.getEngine());
for (Connector additionalConnector : this.additionalTomcatConnectors) {
tomcat.getService().addConnector(additionalConnector);
}
prepareContext(tomcat.getHost(), initializers);
return getTomcatWebServer(tomcat);
}
创建Tocmat类并设置相关这些组件,应该很熟悉(以后出Tomcat源码分析)。
TomcatWebServerFactoryCustomizer的customize定制方法,通过类serverProperties配置文件设置工厂的属性
二、SpringBoot的jar启动方式
来自:
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(StudySpringbootApplication.class, args);
}
打开源码:
public static ConfigurableApplicationContext run(Class<?>[] primarySources,
String[] args) {
return new SpringApplication(primarySources).run(args);
}
其实两步,一步创建SpringApplication ,一步run运行。
创建类做的事情比较简单,主要包括判断web应用类型、用SpringFactories技术从 spring.factories 文件里获取ApplicationContextInitializer 对应类和ApplicationListener,最后获取当前应用的启动类的类对象。
2.1 run方法
public ConfigurableApplicationContext run(String... args) {
//StopWatch是记录时间的工具,为了打印那句SpringBoot启动耗时的
StopWatch stopWatch = new StopWatch();
stopWatch.start();
ConfigurableApplicationContext context = null;
Collection<SpringBootExceptionReporter> exceptionReporters = new ArrayList<>();
//系统设置,在缺失显示屏、鼠标或者键盘时也让这个java应用相关正常工作
configureHeadlessProperty();
//去meta-info/spring.factories中获取SpringApplicationRunListener 监听器(事件发布监听器)
SpringApplicationRunListeners listeners = getRunListeners(args);
//发布容器 starting事件(for循环一个个调用,通过spring的事件多播器)
listeners.starting();
try {
//封装命令行参数
ApplicationArguments applicationArguments = new DefaultApplicationArguments(
args);
//准备容器环境
//1:获取或者创建环境
//2:把命令行参数设置到环境中
//3:通过监听器发布环境准备事件
ConfigurableEnvironment environment = prepareEnvironment(listeners,
applicationArguments);
//配置是否跳过搜索BeanInfo类,默认忽略跳过
configureIgnoreBeanInfo(environment);
//打印控制台那个SpringBoot图标
Banner printedBanner = printBanner(environment);
//根据类型(servlet或者reactive?)创建应用上下文ApplicationContext
context = createApplicationContext();
//到spring.factoris文件里拿springboot异常报告类的集合
exceptionReporters = getSpringFactoriesInstances(
SpringBootExceptionReporter.class,
new Class[] { ConfigurableApplicationContext.class }, context);
//准备环境
//1:把应用上下文ApplicationContext环境设置到容器中
//2:循环调用AppplicationInitnazlier 进行容器初始化工作
//3:发布 容器上下文准备 完成事件
//4:注册关于springboot特定特性的相关单例Bean
//5:BeanDefinitionLoader加载资源源码,将启动类注入容器
//6:发布 容器上下文加载 完毕事件
prepareContext(context, environment, listeners, applicationArguments,
printedBanner);
//IOC容器refresh,见以前IOC源码分析
refreshContext(context);
//springboot2.x已经改成空方法,以前里面是后面的callRunners
afterRefresh(context, applicationArguments);
//计时(耗时统计)停止
stopWatch.stop();
//打印那句springboot在多少秒内启动了
if (this.logStartupInfo) {
new StartupInfoLogger(this.mainApplicationClass)
.logStarted(getApplicationLog(), stopWatch);
}
//发布容器启动事件
listeners.started(context);
//运行 ApplicationRunner 和CommandLineRunner
callRunners(context, applicationArguments);
}
catch (Throwable ex) {
handleRunFailure(context, ex, exceptionReporters, listeners);
throw new IllegalStateException(ex);
}
try {
//发布容器运行事件
listeners.running(context);
}
catch (Throwable ex) {
handleRunFailure(context, ex, exceptionReporters, null);
throw new IllegalStateException(ex);
}
return context;
}
其实大多是准备、工具、事件等,最核心的还是里面的refreshContext(context);带动了IOC容器启动
2.2 refreshContext(context)
其实大部分内容在之前IOC容器源码写过,唯一的区别在于:
SpringIOC的refresh方法里的onRefresh方法是空的,而SpringBoot继承重写了这个方法!
SpringBoot的onRefresh:
@Override
protected void onRefresh() {
super.onRefresh();
try {
createWebServer();
}
catch (Throwable ex) {
throw new ApplicationContextException("Unable to start web server", ex);
}
}
SpringBoot里应用上下文是用的新的ServletWebServerApplicationContext类(更具体实现之一是AnnotationConfigServletWebServerApplicationContext)
这里就开始和上面说过的Web容器相关知识衔接上了,这里进行的Web容器(Tomcat)的创建运行!
createWebServer:
private void createWebServer() {
WebServer webServer = this.webServer;
ServletContext servletContext = getServletContext();
if (webServer == null && servletContext == null) {
ServletWebServerFactory factory = getWebServerFactory();
this.webServer = factory.getWebServer(getSelfInitializer());
}
else if (servletContext != null) {
try {
getSelfInitializer().onStartup(servletContext);
}
catch (ServletException ex) {
//...
}
}
initPropertySources();
}
这里就是判断有没有Server以及环境,没有的话就获取web容器制造工厂,最后通过工厂获取Tomcat赋值。
实际上获取Tomcat创建的时候,此时构造器最后的代码就是启动,TomcatWebServer类构造器如下:
public TomcatWebServer(Tomcat tomcat, boolean autoStart) {
Assert.notNull(tomcat, "Tomcat Server must not be null");
this.tomcat = tomcat;
this.autoStart = autoStart;
initialize();
}
TomcatWebServer的initialize:
private void initialize() throws WebServerException {
logger.info("Tomcat initialized with port(s): " + getPortsDescription(false));
synchronized (this.monitor) {
try {
addInstanceIdToEngineName();
Context context = findContext();
context.addLifecycleListener((event) -> {
if (context.equals(event.getSource())
&& Lifecycle.START_EVENT.equals(event.getType())) {
removeServiceConnectors();
}
});
this.tomcat.start();
rethrowDeferredStartupExceptions();
try {
ContextBindings.bindClassLoader(context, context.getNamingToken(),
getClass().getClassLoader());
}
catch (NamingException ex) {
}
startDaemonAwaitThread();
}
catch (Exception ex) {
stopSilently();
throw new WebServerException("Unable to start embedded Tomcat", ex);
}
}
}
最终在IOC 容器中的 org.springframework.context.support.AbstractApplicationContext的refresh 的
onReFresh方法带动了Tomcat启动
三、SpringBoot的war包启动方式
@SpringBootApplication
public class StudySpringbootApplication extends SpringBootServletInitializer {
@Override
protected SpringApplicationBuilder configure(SpringApplicationBuilder builder) {
return builder.sources(StudySpringbootApplication.class);
}
}
Springboot的war启动方式,是通过Web容器(如Tomcat)的启动 带动了IOC容器相关的启动
3.1 Tomcat加载war
要说Tomcat怎么加载war包就不得不从servlet3.0的特性说起:
1.web应用启动,会创建当前Web应用导入jar包中的 ServletContainerInitializer类的实例
2.ServletContainerInitializer 类必须放在jar包的 META-INF/services目录下,文件名称为javax.servlet.ServletContainerInitializer
3.文件的内容指向ServletContainerInitializer实现类的全路径
4.ServletContainerInitializer实现类使用@HandlesTypes注解, 在我们应用启动的时候,加载注解指定的的类
3.2 Spring中的ServletContainerInitializer
Spring中实现ServletContainerInitializer的类是SpringServletContainerInitializer
@HandlesTypes(WebApplicationInitializer.class)
public class SpringServletContainerInitializer implements ServletContainerInitializer {
@Override
public void onStartup(@Nullable Set<Class<?>> webAppInitializerClasses, ServletContext servletContext) {
//创建保存需要加载的类的集合
List<WebApplicationInitializer> initializers = new LinkedList<>();
if (webAppInitializerClasses != null) {
for (Class<?> waiClass : webAppInitializerClasses) {
//判断需要加载的类不是接口不是抽象类
if (!waiClass.isInterface() && !Modifier.isAbstract(waiClass.getModifiers()) &&
WebApplicationInitializer.class.isAssignableFrom(waiClass)) {
try {
//通过反射创建实例并且加入到集合中
initializers.add((WebApplicationInitializer)
ReflectionUtils.accessibleConstructor(waiClass).newInstance());
}
catch (Throwable ex) {
//...
}
}
}
}
if (initializers.isEmpty()) {
return;
}
AnnotationAwareOrderComparator.sort(initializers);
//循环调用集合中的感兴趣类对象的onstartup的方法
for (WebApplicationInitializer initializer : initializers) {
initializer.onStartup(servletContext);
}
}
}
总结:HandlesTypes指定了WebApplicationInitializer类,并在onStartup方法中,创建这些需要加载的类的实例,并且循环调用他们的onStartup方法。
3.2 工作过程
1.Tomcat启动,war包应用的jar包里找ServletContainerInitializer 文件,然后找到spring-web-5.1.2.RELEASE.jar这个jar包里的META-INFservicesjavax.servlet.ServletContainerInitializer 文件指向自己实现的SpringServletContainerInitializer并执行它
2.将@HandlesTypes标注的类(WebApplicationInitializer)都传入到 onStartup()的方法中Set<Class<?>>参数中
,通过 ReflectionUtils.accessibleConstructor(waiClass).newInstance());,为这些类创建实例
3.调用WebApplicationInitializer的onStartup方法
4.而Springboot启动类继承了SpringBootServletInitializer(实现了接口WebApplicationInitializer)
5.而我们的启动类StudySpringbootApplication没有重写onStartup,调的SpringBootServletInitializer的onStartup
6.而SpringBootServletInitializer的onStartup方法调了我们重写的configure方法,加载启动。
4.1 实战调试细节
@SpringBootApplication
public class StudySpringbootApplication extends SpringBootServletInitializer {
@Override
protected SpringApplicationBuilder configure(SpringApplicationBuilder builder) {
return builder.sources(StudySpringbootApplication.class);
}
}
可以把断点打到第六行里builder.sources,通过断点一看调用栈和代码,逻辑就全出来了:
StudySpringbootApplication.configure <<==== 父类SpringBootServletInitializer(主类继继承的这个类).createRootApplicationContext
父类SpringBootServletInitializer.createRootApplicationContext:
protected WebApplicationContext createRootApplicationContext(
ServletContext servletContext) {
//创建spring应用的构建器
SpringApplicationBuilder builder = createSpringApplicationBuilder();
builder.main(getClass());
//设置环境
ApplicationContext parent = getExistingRootWebApplicationContext(servletContext);
if (parent != null) {
servletContext.setAttribute(
WebApplicationContext.ROOT_WEB_APPLICATION_CONTEXT_ATTRIBUTE, null);
builder.initializers(new ParentContextApplicationContextInitializer(parent));
}
builder.initializers(
new ServletContextApplicationContextInitializer(servletContext));
builder.contextClass(AnnotationConfigServletWebServerApplicationContext.class);
//调用我们自己启动类上的confiure方法 传入我们自己的主启动类
builder = configure(builder);
builder.listeners(new WebEnvironmentPropertySourceInitializer(servletContext));
SpringApplication application = builder.build();
if (application.getAllSources().isEmpty() && AnnotationUtils
.findAnnotation(getClass(), Configuration.class) != null) {
application.addPrimarySources(Collections.singleton(getClass()));
}
if (this.registerErrorPageFilter) {
application.addPrimarySources(
Collections.singleton(ErrorPageFilterConfiguration.class));
}
//调用我们类上的run方法
return run(application);
}
注意重点是 调用了自己的方法(传入主类)和 run方法
run源码:
protected WebApplicationContext run(SpringApplication application) {
return (WebApplicationContext) application.run();
}
继续打开run源码:
public ConfigurableApplicationContext run(String... args) {
StopWatch stopWatch = new StopWatch();
stopWatch.start();
ConfigurableApplicationContext context = null;
Collection<SpringBootExceptionReporter> exceptionReporters = new ArrayList<>();
configureHeadlessProperty();
SpringApplicationRunListeners listeners = getRunListeners(args);
listeners.starting();
try {
ApplicationArguments applicationArguments = new DefaultApplicationArguments(
args);
ConfigurableEnvironment environment = prepareEnvironment(listeners,
applicationArguments);
configureIgnoreBeanInfo(environment);
Banner printedBanner = printBanner(environment);
context = createApplicationContext();
exceptionReporters = getSpringFactoriesInstances(
SpringBootExceptionReporter.class,
new Class[] { ConfigurableApplicationContext.class }, context);
prepareContext(context, environment, listeners, applicationArguments,
printedBanner);
refreshContext(context);
afterRefresh(context, applicationArguments);
stopWatch.stop();
if (this.logStartupInfo) {
new StartupInfoLogger(this.mainApplicationClass)
.logStarted(getApplicationLog(), stopWatch);
}
listeners.started(context);
callRunners(context, applicationArguments);
}
catch (Throwable ex) {
handleRunFailure(context, ex, exceptionReporters, listeners);
throw new IllegalStateException(ex);
}
try {
listeners.running(context);
}
catch (Throwable ex) {
handleRunFailure(context, ex, exceptionReporters, null);
throw new IllegalStateException(ex);
}
return context;
}
是不是很熟悉,和jar启动的run IOC一样!所以最终还是殊途同归,还是走了application.run()方法,走了IOC容器启动Refresh!