工具类:java开发者写好的类
1.包装相关类
2.数字相关类
3.日期类
4.字符串
5.集合相关类
6.异常相关类
7.输入输出相关 IO(input/output)
8.线程
9.网络
10.注解
11.GUI
1.包装类:
为了将基本类型也面向对象,所以将他们分装进包装类中
1.byte -- Byte,short --Short,int -- Integer,long -- Long
2.float -- Float,double -- Double
3.char -- Character
4.boolean -- Boolean
6个数字相关的类都继承Number类
除了Character都有用String类型作为参数的构造方法, 也可以用 类名.valueOf();
package number_test; public class NumberTest { public static void main(String[] args){ //构造方法和valueOf //注意这类变量是包装类的类型,不是基本类型,基本类型是小写。 Integer i1 = 111; Integer i2 = 111; Integer i3 = new Integer("111"); Integer i4 = new Integer("111"); Integer i5 = i3; //使用起来和 基本类型int 基本没区别,可以加减乘除打印等,但是储存方法不同, // == 比较基本类型比较的是值,比较引用类型则比较的是地址, equals比较的是值(所以也用来比较String这种引用类型) // Integer直接赋值时,值存在方法区的静态元素区,值一样时地址也一样。 java底层有一个静态数组,里面存了-127 - 128,直接赋值会把变量指向这个数组对应位置。 //因为静态数组是-127 - 128,所以如果Integer的值大于这个范围,则会自动给他new一个对象存在堆内存中 System.out.println("i1 == i2: " + (i1 == i2)); //定义时两个存在了方法区的静态元素区中 i1 = 1111; i2 = 1111; System.out.println("i1 == i2: " + (i1 == i2)); //定义时两个存在了堆内存中 System.out.println("i3 == i4: " + (i3 == i4)); //两个定义时用了new,存在了堆内存,所以地址不同 System.out.println("i3 == i5: " + (i3 == i5)); System.out.println("i1 .equals( i2 ): " + (i1.equals(i2))); System.out.println("i3 .equals( i4 ): " + (i3.equals(i4))); // i1 == i2: true // i1 == i2: false // i3 == i4: false // i3 == i5: true // i1 .equals( i2 ): true // i3 .equals( i4 ): true //String String s1 = i1.toString(); String s2 = i2.toString(); System.out.println("s1 == s2: " + (s1 == s2)); //值通过计算获得,两者地址不同 System.out.println("s1.equali3;s(s2): " + (s1.equals(s2))); s1 = "abc"; s2 = "abc"; System.out.println("改为直接赋值:s1 == s2: " + (s1 == s2)); //如果是直接赋值,他们的值会相同 - -这里我有点没明白 //查资料,说是java对String进行了优化,对象是存在常量区的- -,然后直接赋相同的值,变量会指向常量区的同一个地址。 //所以测试一下: String s3 = "bcd"; String s4 = "bc"; s4 = s4 + "d"; //s4 = s4 + "d";是false,如果直接 s4 = "bc" + "d";则下面s3 == s4依旧为true,稍微有点不太明白- - System.out.println("直接赋值测试:s1 == s2: " + (s1 == s2)); System.out.println("直接赋值测试:s3 == s4: " + (s3 == s4)); // s1 == s2: false // s1.equali3;s(s2): true // 改为直接赋值:s1 == s2: true // 直接赋值测试:s1 == s2: true // 直接赋值测试:s3 == s4: false Byte b = Byte.valueOf("111"); int i = Integer.valueOf("111"); Long l = Long.valueOf("222"); Float f = new Float("1.1"); Double d = Double.valueOf("2.2"); boolean bt = new Boolean("true"); Boolean bf = Boolean.valueOf("false"); //可以直接使用 System.out.println(i * 10); System.out.println(l * 10); System.out.println(f * 10); System.out.println(d * 10); if(bt){ System.out.println(bt); } if(!bf){ System.out.println(bf); } // 1110 // 2220 // 11.0 // 22.0 // true // false //intValue int intTest = i1.intValue(); //把包装类变成基本类型 int doubleTest = d.intValue();//取整数部分 int charTest = 'a';//asc码转成数字,char和int可以直接转换 int stringTest = Integer.parseInt("111");//直接把字符串转为int System.out.println(intTest); System.out.println(doubleTest); System.out.println(charTest); System.out.println(stringTest); // 111 // 2 // 97 // 111 //于是想测试一下。。。 System.out.println("i3 == i4: " + (i3 == i4)); //两个定义时用了new所以地址不同 int ii3 = i3.intValue(); int ii4 = i4.intValue(); System.out.println("ii3 == ii4: " + (ii3 == ii4)); //两个是int型的所以地址相同 //i3 == i4: false //ii3 == ii4: true //int值存在常量区,所以只要值一样地址就一样, // Integer不是直接赋值时,如new赋值时,和引用类型一样 // intValue()是把Integer对象类型变成int的基础数据类型; // parseInt()是把String 变成int的基础数据类型; // Valueof()是把给定的String参数转化成Integer对象类型; //不过现在java支持自动转换了,所以其实可以混着用。。。 } }
2.数学相关的类:
Math用来进行基本类型的运算相关
Random
BigInteger
BigDecimal
package Math_test; import java.math.BigDecimal; import java.math.BigInteger; import java.util.Random; public class MathTest { public static void main(String[] args){ //Math构造方法为私有,方法都是static,所以可以直接调用(单例模式),Math有很多方法,只挑部分常用的 //Math.random(),返回一个0-1之间的double类型的数字 for(int i = 0; i < 5; i++){ System.out.println(Math.random());//返回一个0-1之间的double类型的数字 } // 0.30222893423699926 // 0.37739767545532177 // 0.13927359803309325 // 0.9123839746760073 // 0.9768944004877123 //Random,专门用来生成随机数的类 for(int i = 0; i < 5; i++){ System.out.println( new Random().nextInt(10) );//返回一个0-9之间的int类型的数字 ,还可以nextFloat,nextBoolean等 } // 8 // 5 // 3 // 3 // 0 //Math.abs(); 变为正数 int i = -111; System.out.println( Math.abs(i) ); //取最近值 System.out.println( Math.ceil(1.4) ); //向上取 System.out.println( Math.ceil(1.5) ); //向上取 // 2.0 // 2.0 System.out.println( Math.floor(1.8) );//向下取 System.out.println( Math.floor(1.5) );//向下取 // 1.0 // 1.0 System.out.println( Math.rint(1.4) ); //最近的整数,一样的话返回偶数 System.out.println( Math.rint(1.5) ); //最近的整数,一样的话返回偶数 System.out.println( Math.rint(2.5) ); //最近的整数,一样的话返回偶数 // 1.0 // 2.0 // 2.0 System.out.println( Math.round(1.4) );//四舍五入返回int System.out.println( Math.round(1.5) );//四舍五入返回int System.out.println( Math.round(2.5) );//四舍五入返回int // 1 // 2 // 3 //负数测试: System.out.println( Math.ceil(-1.4) ); //向上取 System.out.println( Math.ceil(-1.5) ); //向上取 // -1.0 // -1.0 System.out.println( Math.floor(-1.8) );//向下取 System.out.println( Math.floor(-1.5) );//向下取 // -2.0 // -2.0 System.out.println( Math.rint(-1.4) ); //最近的整数,一样的话返回偶数 System.out.println( Math.rint(-1.5) ); //最近的整数,一样的话返回偶数 System.out.println( Math.rint(-2.5) ); //最近的整数,一样的话返回偶数 // -1.0 // -2.0 // -2.0 System.out.println( Math.round(-1.4) );//四舍五入返回int System.out.println( Math.round(-1.5) );//四舍五入返回int System.out.println( Math.round(-2.5) );//四舍五入返回int // -1 // -1 // -2 //Math.max, Math.min System.out.println( Math.max(111,222) );//取最大值 System.out.println( Math.min(111,222L) );//取最小值 // 222 // 111 //Math.sqrt() 平方根 System.out.println( Math.sqrt(1.21) ); //double类型返回 System.out.println( Math.sqrt(9) ); //double类型返回 // 1.1 // 3.0 //BigInteger,用来储存超大整数 BigInteger bi = new BigInteger( "5555555555555555555555555555555555555555555555555555555555555555"); System.out.println(bi); // 111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111 System.out.println(bi.add(new BigInteger( "1111111122222222222222222233333333333333333333333333333444444444")));//加 System.out.println(bi.subtract(new BigInteger("1111111122222222222222222233333333333333333333333333333444444444")));//减 System.out.println(bi.multiply(new BigInteger("11111111")));//乘 System.out.println(bi.divide(new BigInteger( "1111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111")));//除 //BigInteger的运算只能是BigInteger之间 // 5555555555555555555555555555555555555555555555555555555555555555 // 6666666677777777777777777788888888888888888888888888888999999999 // 4444444433333333333333333322222222222222222222222222222111111111 // 61728394444444444444444444444444444444444444444444444444444444438271605 // 5 //BigDecimal,用来储存超大小数,加减乘除运算和NigInteger一致 BigDecimal bd = new BigDecimal("55555555555555555555555555555555.555555555555555555555555555555555555555555555555555555"); System.out.println(bd.add(new BigDecimal("55555555555555555555555555555555.555555555555555555555555555555555555555555555555555555"))); System.out.println(bd.setScale(2,BigDecimal.ROUND_UP)); //setScale(int newScale, RoundingMode roundingMode) System.out.println(bd.setScale(2,BigDecimal.ROUND_DOWN)); // 111111111111111111111111111111111.111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111110 // 55555555555555555555555555555555.56 // 55555555555555555555555555555555.55 } }
3.日期:
Date
Date.before(Date)判断是否在给定的date之前
Date.after(Date)判断是否在给定的date之后
Calendar
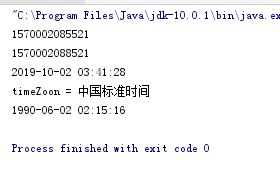
import java.text.SimpleDateFormat; import java.util.Calendar; import java.util.Date; public class TimeTest { public static void main(String[] args){ System.out.println(System.currentTimeMillis());//计算机元年1970.1.1到现在的毫秒差 try { Thread.sleep(3000); //尝试让这个线程睡眠3000毫秒 } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } System.out.println(System.currentTimeMillis()); //正好过了3000毫秒 // 1570000718473 // 1570000721473 //这个方法也可以用来测试电脑或者程序运算性能 //Date Date d = new Date(System.currentTimeMillis()); //构造方法中添加的是计算机元年1970.1.1到现在的毫秒差 d = new Date();//直接new默认当前时间 SimpleDateFormat simpleDateFormat = new SimpleDateFormat("yyyy-MM-dd KK:mm:ss"); //kk可以用HH输出1-24点的值 System.out.println(simpleDateFormat.format(d)); //2019-10-02 03:23:22 //Date现在很少使用了,日期处理采用calendar Calendar cal = Calendar.getInstance(); //创建当前时间的时间对象 //public void set(int year,int month,int date,int hourofday,int minute,int second) cal.set(1990,5,26,2,15,16); cal.set(Calendar.DATE, 2); // 获取年 int year = cal.get(Calendar.YEAR); // 获取月 int month = cal.get(Calendar.MONTH); // 获取日 int date = cal.get(Calendar.DATE); // 获取时 int hour = cal.get(Calendar.HOUR); //会自动 %12,所以上面就算hourOfDay设成25也是能存入 1 的= = //getTimeZoon(); System.out.println("timeZoon = " + cal.getTimeZone().getDisplayName()); System.out.println(simpleDateFormat.format(cal.getTime()));//simpleDateFormat一样可以处理cal,需要把calendar先转为date } }