线性表 顺序存储实现
(1)如何存储
//如何存储
typedef struct
{
ElementType Data[MAXSIZE];
int Last;
}List;
List L, *PtrL;
访问下标为i的元素:L.Data[i] 或 PtrL->Data[i]
线性表的长度:L.Last+1 或者 PtrL->Last+1

(2)初始化(建立空的顺序表)
List *MakeEmpty()
{
List *PtrL;
PtrL = (List *)malloc(sizeof(List));
PtrL->Last = -1;
return PtrL;
}
(3)查找
int Find(ElementType X, List *PtrL)
{
int i = 0;
while(i<=PtrL->Last && PtrL->Data[i]!=X)
i++;
if (i > PtrL->Last)
return -1;
else
return i;
}
查找成功的平均比较次数为(n+1)/ 2(第一次比较就找到或者最后一次比较才找到),平均时间性能为O(n)。
(4)插入
插入到第 i 个位置(即下标+1:1<=i<=n+1)上插入一个值为X的新元素)
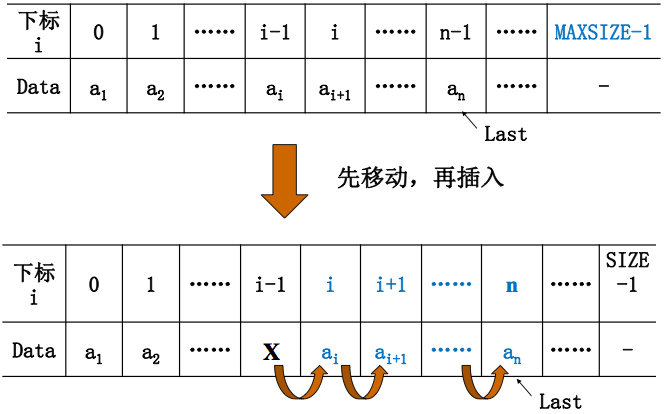
//插入
void Insert(ElementType X, int i, List *PtrL){
if (PtrL->Last == MAXSIZE-1){
printf("表满");
return;
}
if (i < 1 || PtrL->Last+2){
printf("位置不合法");
return;
}
for (int j = PtrL->Last; j >= i-1; --j){
PtrL->Data[j+1] = PtrL->Data[j]; //将 an~a1 依次向后移动一位
}
PtrL->Data[i-1] = X;//插入新元素
PtrL->Last++; //Last仍指向最后元素
return;
}
平均移动次数为n/2,平均时间性能为O(n)。
(5)删除
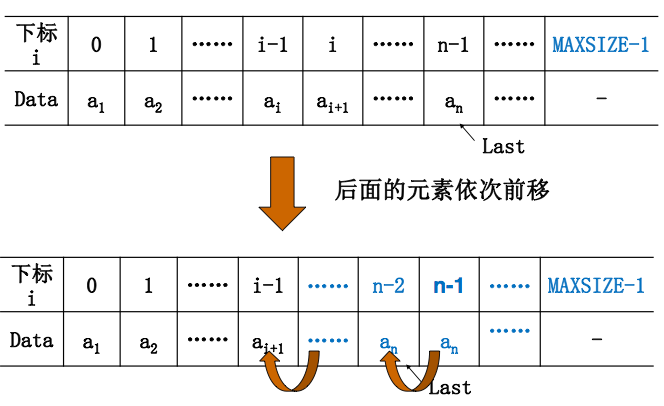
//删除
void Delete(int i, List *PtrL){
if (i < 1 || i > PtrL->Last+1){
printf("不存在第 %d 个元素", i );
return;
}
for (j = i; j <= PtrL->Last; ++j){
PtrL->Data[j-1] = PtrL->Data[j]; //将ai+1~an顺序向前移动
}
PtrL->Last--;
return;
}
平均移动次数为(n-1)/2,平均时间性能为O(n)。
线性表 链式存储实现
基本操作
Node* applyNode(); //分配节点
Node* addNodeH(Node* Head,Node* InsertNode); //在头部添加节点
Node* addNodeT(Node* Head,Node* InsertNode); //在尾部添加节点
Node* addNodeSort(Node* Head, Node* InsertNode); //以升序方式添加节点
Node* createList(int n,int choose); //构造链表
void printList(Node*Head); //打印链表
void freeList(Node*& Head); //释放链表
int numOfNodes(Node* Head); //求表长(节点数)
Node* locateNodeI(Node*Head,int i); //定位
int SearchList(Node*Head,int value); //查找
bool insertNodeI(Node* Head, int i); //插入
bool deleteNodeI(Node*&Head,int i); //删除
void sortList(Node*& Head); //排序
1、构造节点
//定义节点类型
struct Node{
int value;
Node*next;
};
2、分配节点
//将分配内存和初始化该节点放在一个函数中
Node* applyNode(){
Node* newNode;
if( ( newNode = (Node*)malloc(sizeof(Node)) )==NULL ){
cout << "分配内存失败!" << endl;
exit(0);
}
cin >> newNode->value;
newNode->next = NULL;
return newNode;
}
3、在头部添加节点
Node* addNodeH(Node* Head){
Node* InsertNode = applyNode();
if(Head==NULL)
Head = InsertNode;
else{
InsertNode->next = NULL;
Head->next = InsertNode;
}
return Head;
}
4、在尾部添加节点
Node* addNodeT(Node* Head){
Node* InsertNode = applyNode();
if(Head==NULL)
Head=InsertNode;
else{
Node* p=Head;
while(p->next!=NULL)
p=p->next;
p->next = InsertNode;
}
return Head;
}
5、以升序方式添加节点
Node* addNodeSort(Node* Head){
Node* InsertNode = applyNode(); //分配节点
if(Head==NULL){
Head=InsertNode;
}
else{
Node* p=Head;
while( (p->value)<(InsertNode->value) && p->next!=NULL )
p=p->next;
if( (p->value)>=(InsertNode->value)){
InsertNode->next = p->next; //先在p后增加节点
p->next = InsertNode;
swap(p->value, InsertNode->value); //再交换p和InsertNode的value值
}
else{ //因为(p->next==NULL)而退出循环!表示在尾部增加节点
p->next = InsertNode;
}
}
return Head;
}
6、构造链表
//建立n个节点的链表
//choose=0:在表头加入; choose=1:在表尾加入; choose=2:按value值升序加入
Node* createList(int n, int choose){
Node *Head=NULL, *p=NULL;
for(int i=0; i<n; i++){
p = applyNode(); //分配节点
cin >> choose;
switch(choose){
case 0:
Head = addNodeH(Head, p); //头插
break;
case 1:
Head = addNodeT(Head, p); //尾插
break;
case 2:
Head = addNodeSort(Head, p); //升序插
break;
default:
printf("default");
break;
}
return Head;
}
7、打印链表
//遍历链表并输出
void printList(Node* Head){
Node* p=Head;
while(p!=NULL){
cout << p->value << "->";
p=p->next;
}
cout << "NULL" << endl;
}
8、释放链表
void freeList(Node* Head){
Node* tmp=Head;
while(tmp!=NULL){
Head = Head->next;
free(tmp);
tmp = Head;
}
Head=NULL;
}
9、求表长(节点数)
//求节点个数
int numOfNodes(Node* Head){
Node* temp = Head;
int count=0;
while(temp!=NULL){
count++;
temp=temp->next;
}
return count;
}
10、定位
//定位(指向)第i个节点,i从1开始
Node* locateNodeI(Node* Head, int i){
Node* pos=NULL;
int count = numOfNodes(Head);
if(i<=0 || i>count){
cout << "定位越界!" << endl;
}
else {
pos=Head;
for(int j=1; j<i; j++)
pos=pos->next;
}
return pos;
}
11、查找
1)按照序号查找:FindKth
List *FindKth(int K, List *PtrL){
List *p = PtrL;
int i = 1;
while(p!=NULL && i< k){
p = p->Next;
i++;
}
if (i==k)
return p; //找到第K个,返回指针
else
return NULL;
}
2)按照值查找:Find
List *Find(ElementType X, List *PtrL){
List *p = PtrL;
while(p!=NULL && p->Data!=X)
p = p->Next;
return p;
}
3)按照值查找,返回其序号:SearchList
//查找值value并返回第一个出现该值的位置
//如果需要引用其指针,可以再locate该位置
int SearchList(Node* Head, int value){
Node* p=Head;
int pos=0;
bool find=false;
while(p!=NULL){
pos++;
if(p->value==value){
find=true;
break;
}
p=p->next;
}
if(find)
return pos;
else
return -1;
}
12、插入
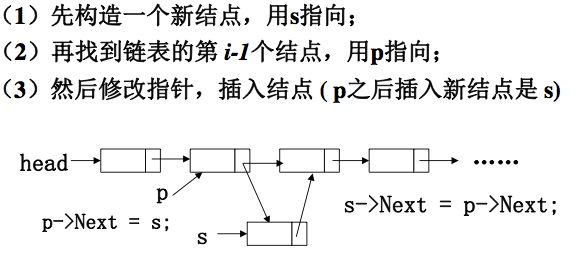
//新节点插入到某位置i
bool insertNodeI(Node* Head, int i){
Node* s = applyNode();
if(i==1){ //新节点插入在表头
s->next = Head;
Head = s;
return true;
}
Node* p = locateNodeI(Head, i-1);
if(p==NULL){
return false;
}
else{
s->next = p->next;
p->next = s;
return true;
}
}
13、删 除
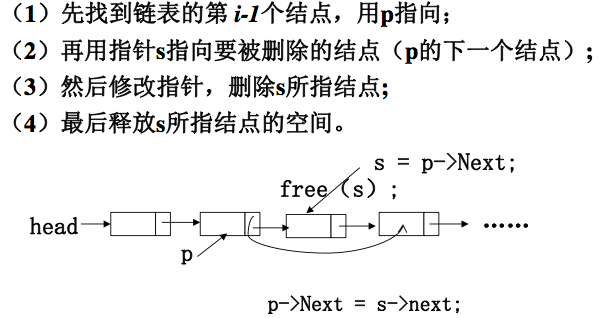
//删除某位置i的节点
bool deleteNodeI(Node* Head, int i){
Node* s = locateNodeI(Head, i);
if(s==NULL){
return false;
}
else{
if(s==Head){ //要删除的是头节点
Head = s->next;
free(s);
}
else{
Node* p = locateNodeI(Head, i-1); //定位前一个节点,必定存在
p->next = s->next;
free(s);
}
return true;
}
}
14、排序
//链表排序
//方法:只进行value的交换,不破坏链表结构
void sortList(Node* Head){
int count = numOfNodes(Head);
if(count==0 || count==1)
return ;
//冒泡排序
bool exchange;
for(int i=2; i<=count; i++){
exchange=false;
for(int j=count;j>=i; j--){
Node* p1 = locateNodeI(Head, j);
Node* p2 = locateNodeI(Head, j-1);
if(p1->value < p2->value){
exchange=true;
swap(p1->value, p2->value); //交换数据
}
}
if(!exchange)
break;
}
}