Using Database Resource Manager
Objectives
After completing this lesson, you should be able to do the following:
• Configure the Database Resource Manager
• Access and create resource plans
• Create consumer groups
• Specify directives for allocating resources to consumer groups
• Map consumer groups to plans
• Activate a resource plan
• Monitor the Resource Manager
目标
完成本课程后,您应该能够执行以下操作:
•配置数据库资源管理器
•访问和创建资源计划
•创建消费者群体
•指定将资源分配给消费者群体的指令
•将消费者群体映射到计划
•启动资源计划
•监控资源管理器
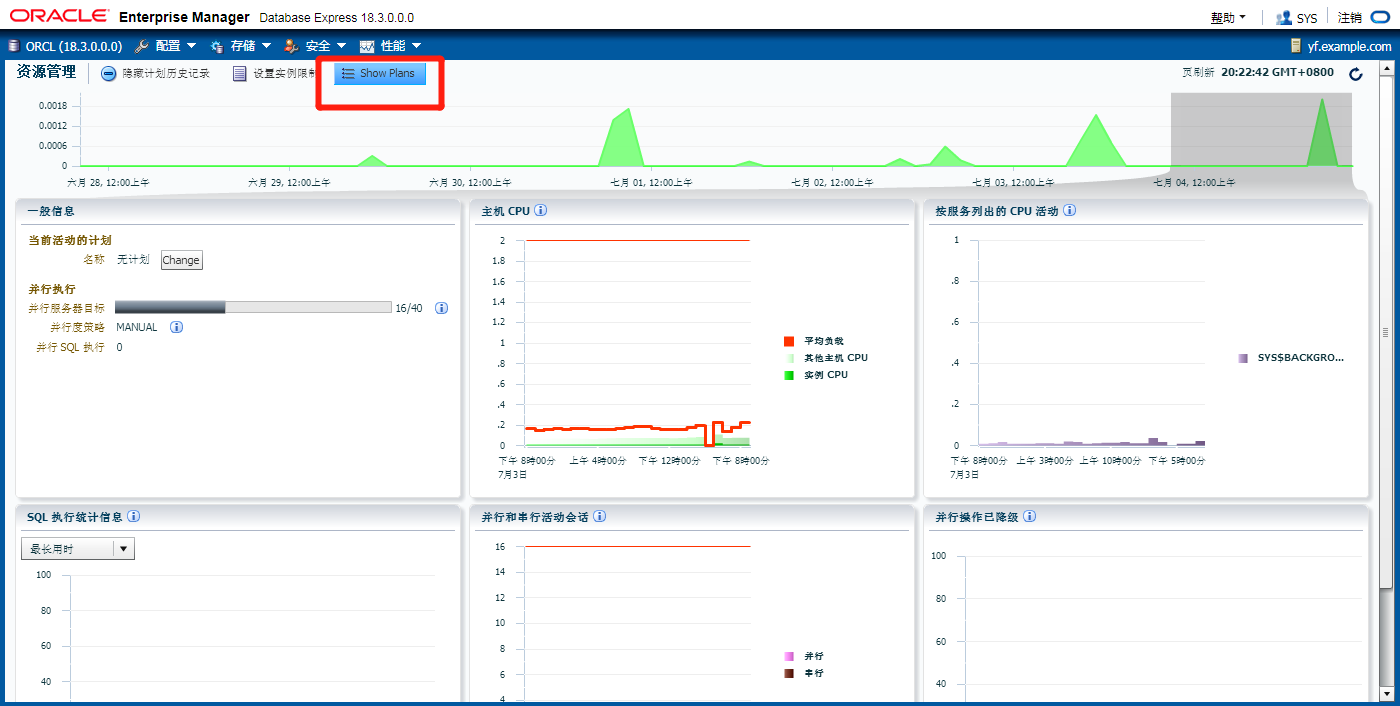
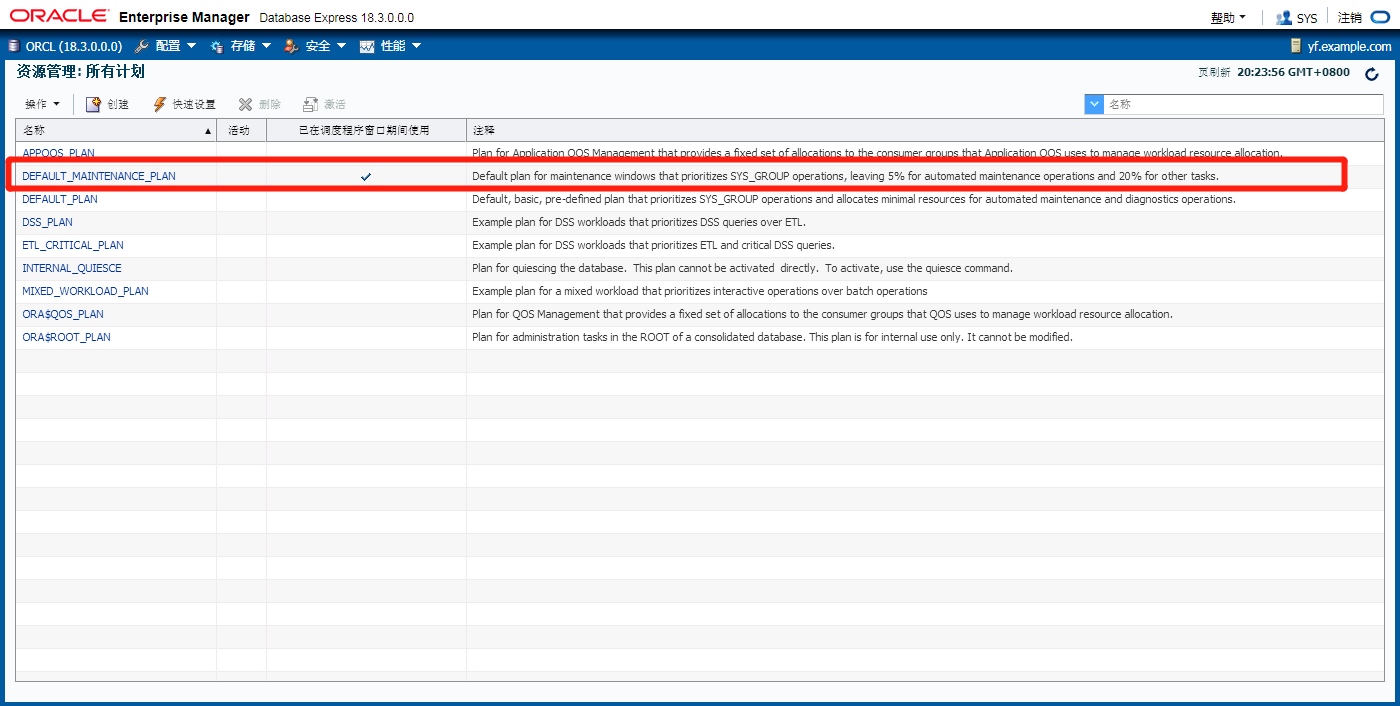
默认维护计划
QL> show parameter plan
NAME TYPE VALUE
------------------------------------ ----------- ------------------------------
cell_offload_plan_display string AUTO
optimizer_adaptive_plans boolean TRUE
optimizer_capture_sql_plan_baselines boolean FALSE
optimizer_use_sql_plan_baselines boolean TRUE
resource_manager_plan string
SQL>
创建一个计划

begin
sys.dbms_resource_manager.clear_pending_area();
sys.dbms_resource_manager.create_pending_area();
sys.dbms_resource_manager.create_plan(
plan => 'apps_plan',
comment => 'test for resource manager',
mgmt_mth => 'RATIO');
sys.dbms_resource_manager.create_plan_directive(
plan => 'apps_plan',
GROUP_OR_SUBPLAN => 'OTHER_GROUPS');
sys.dbms_resource_manager.validate_pending_area();
sys.dbms_resource_manager.submit_pending_area();
sys.dbms_resource_manager.clear_pending_area();
exception
when others then
sys.dbms_resource_manager.clear_pending_area();
raise;
end;
;
QL> show parameter plan
NAME TYPE VALUE
------------------------------------ ----------- ------------------------------
cell_offload_plan_display string AUTO
optimizer_adaptive_plans boolean TRUE
optimizer_capture_sql_plan_baselines boolean FALSE
optimizer_use_sql_plan_baselines boolean TRUE
resource_manager_plan string APPS_PLAN
双击新建的计划
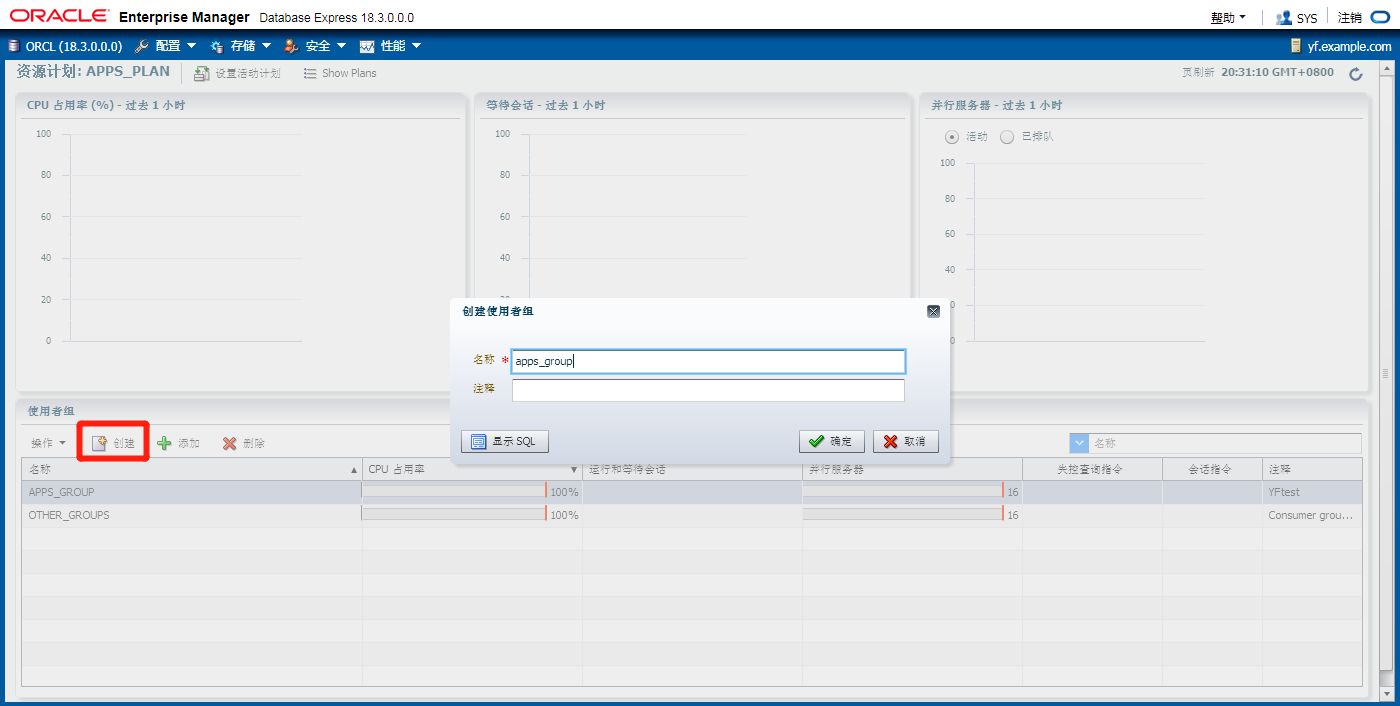

Database Resource Manager: Overview
Use the Resource Manager to:
• Manage mixed workload
• Control system performance
数据库管理器概述
使用资源管理器可以:
•管理混合工作负载
•控制系统性能
Database Resource Manager: Concepts
User groups or sessions with similar resource needs
A blueprint for resource allocation among resource consumer groups (one active plan)
Specifies how a resource is divided among the resource consumer groups (within the scope of allocation methods)
数据库资源管理器:概念
具有类似资源需求的用户组或会话
资源消费群体间资源分配蓝图(一个活动计划)
指定如何在资源使用者组之间分配资源(在分配方法的范围内)
Using the Resource Manager
• You can manage database and operating system resources, such as:
– CPU usage
– Degree of parallelism
– Number of active sessions
– Undo generation
– Operation execution time
– Idle time
– Database consolidation
– Server consolidation
• You can also specify criteria that, if met, cause the automatic switching of sessions to another consumer group.
使用资源管理器
•您可以管理数据库和操作系统资源,例如:
–CPU使用率
–平行度
–活动会话数
–撤消生成
–操作执行时间
–空闲时间
–数据库整合
–服务器整合
•您还可以指定条件,如果满足这些条件,则会自动将会话切换到另一个用户组。
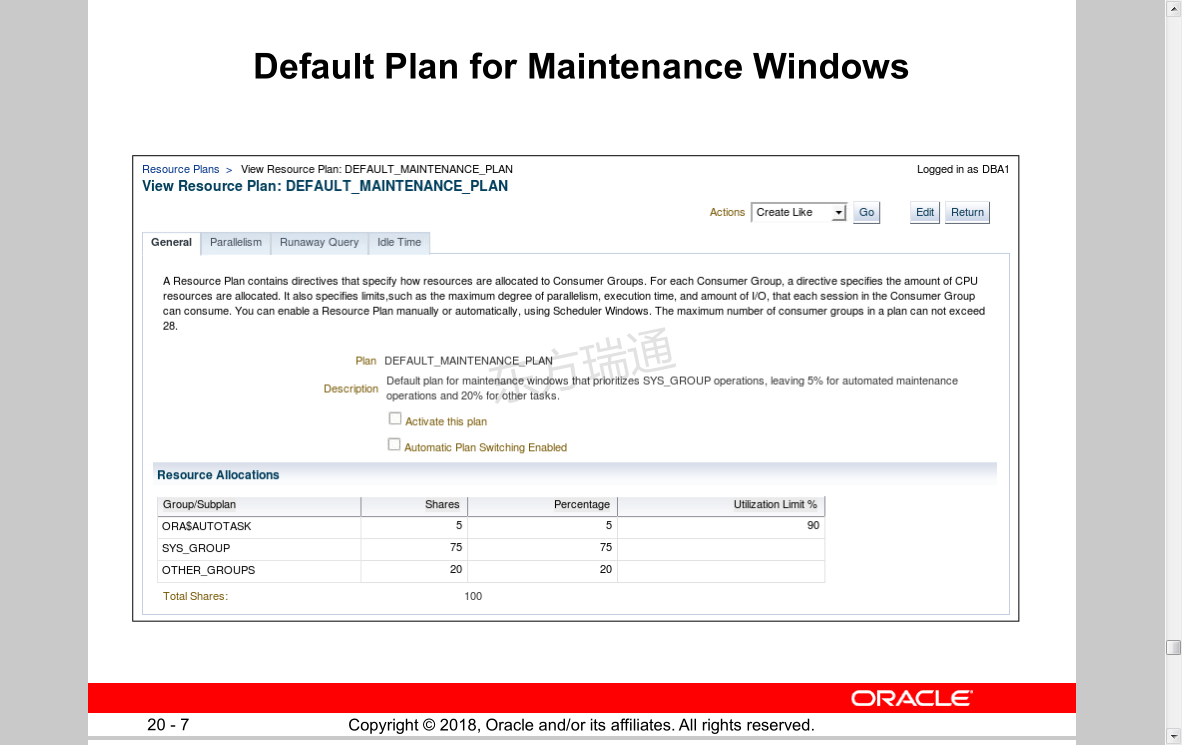
Default Plan for Maintenance Windows 维护窗口的默认计划
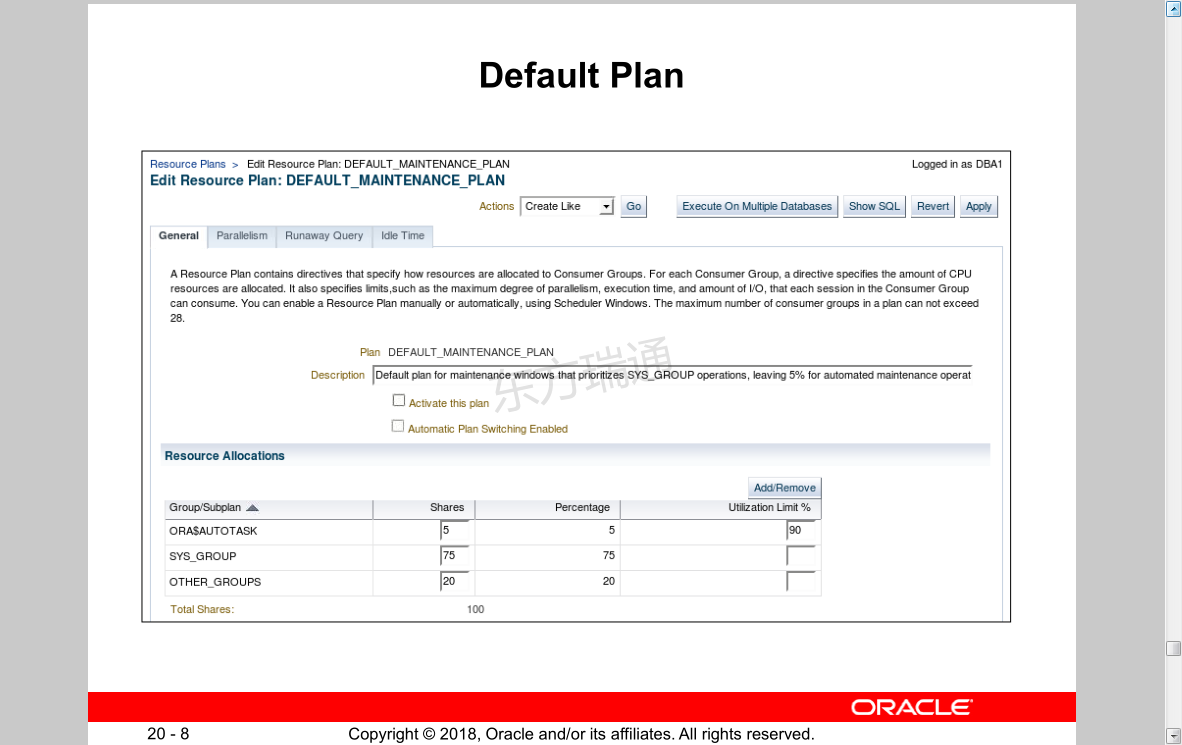
Default Plan 默认计划
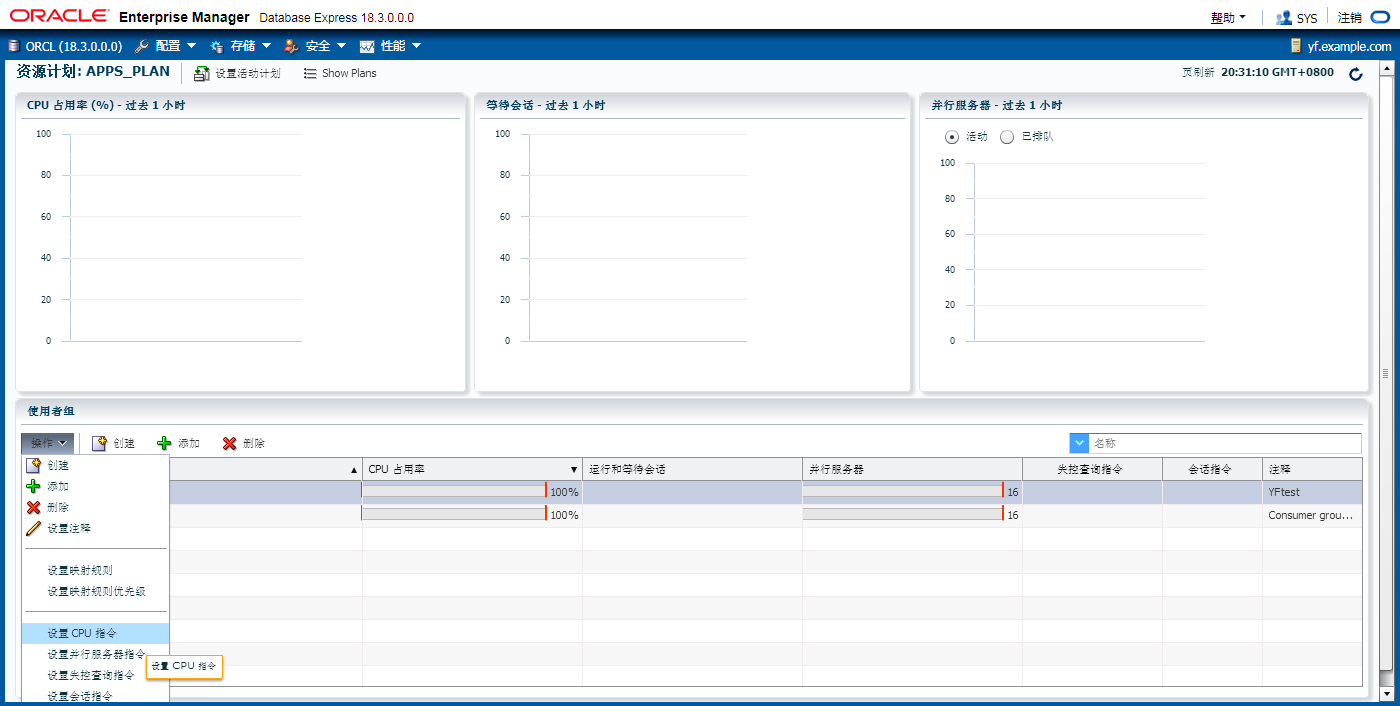
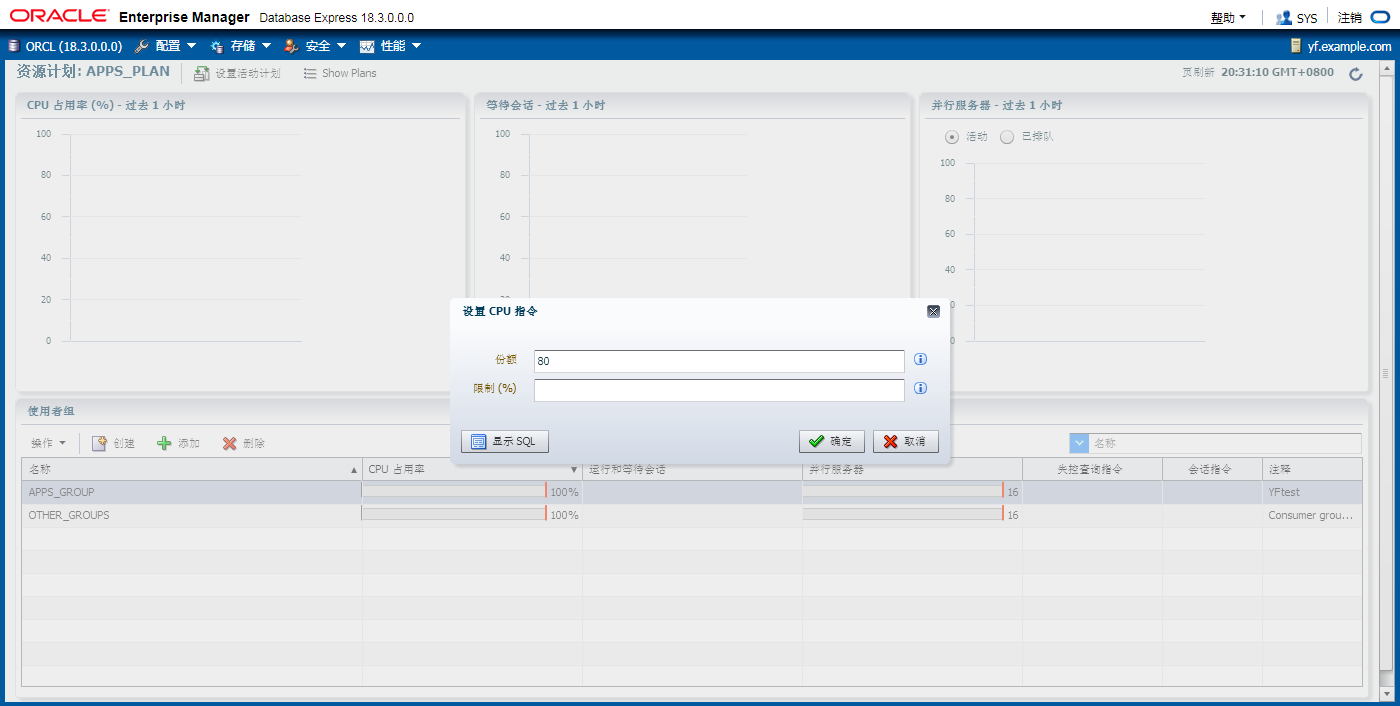
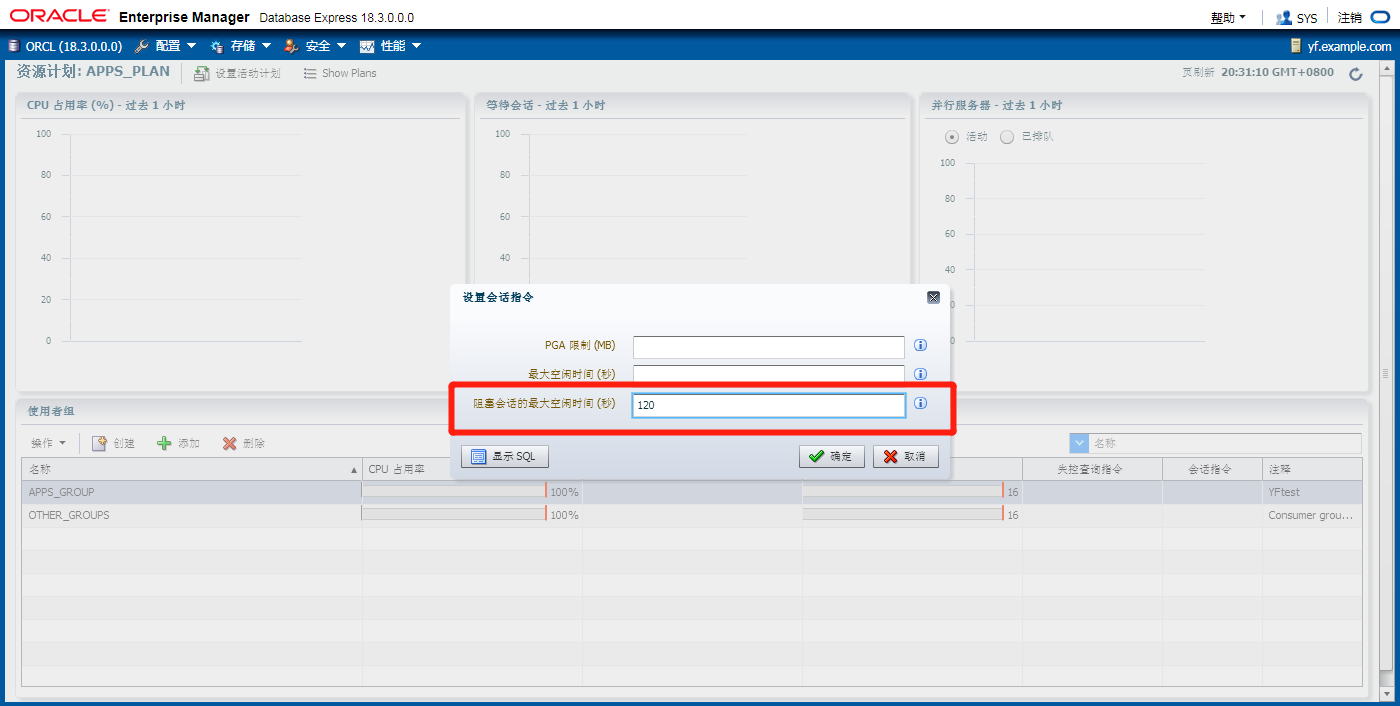
将用户阻塞的最大时间设置成120秒
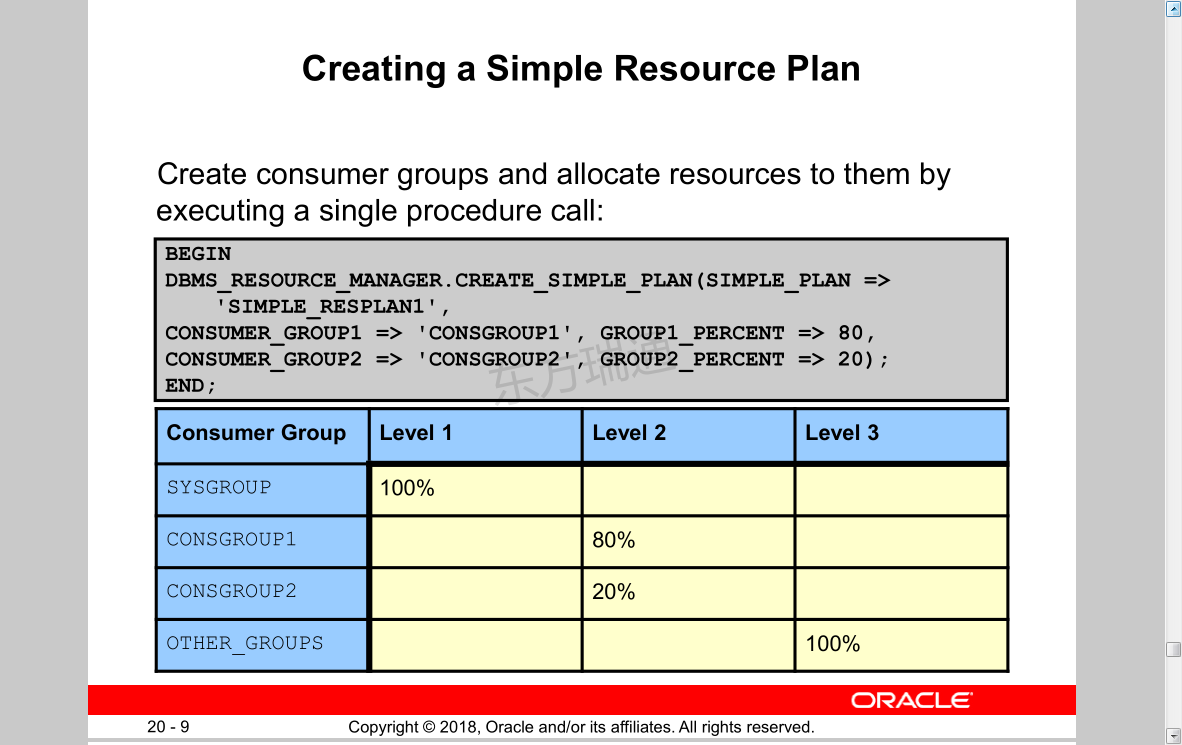
Creating a Simple Resource Plan
Create consumer groups and allocate resources to them by executing a single procedure call:
创建简单的资源计划
创建使用者组并通过执行单个过程调用为其分配资源:
Creating a Complex Resource Plan
1. Create a pending area.
2. Create, modify, or delete consumer groups.
3. Map sessions to consumer groups.
4. Create the resource plan.
5. Create resource plan directives.
6. Validate the pending area.
7. Submit the pending area.
创建复杂的资源计划
1创建挂起区域。
2创建、修改或删除消费者组。
3将会话映射到消费者组。
4创建资源计划。
5创建资源计划指令。
6验证挂起区域。
7提交待处理区域。

Specifying Resource Plan Directives 指定资源计划指令
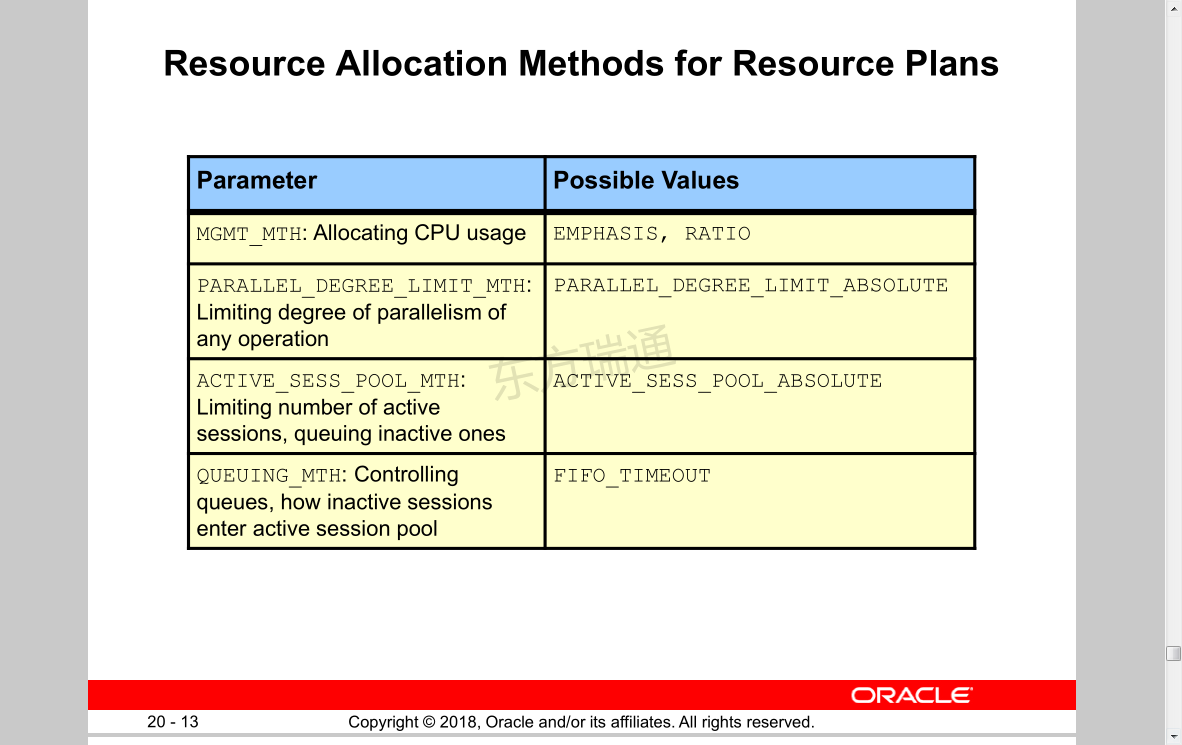
Resource Allocation Methods for Resource Plans 资源计划的资源分配方法
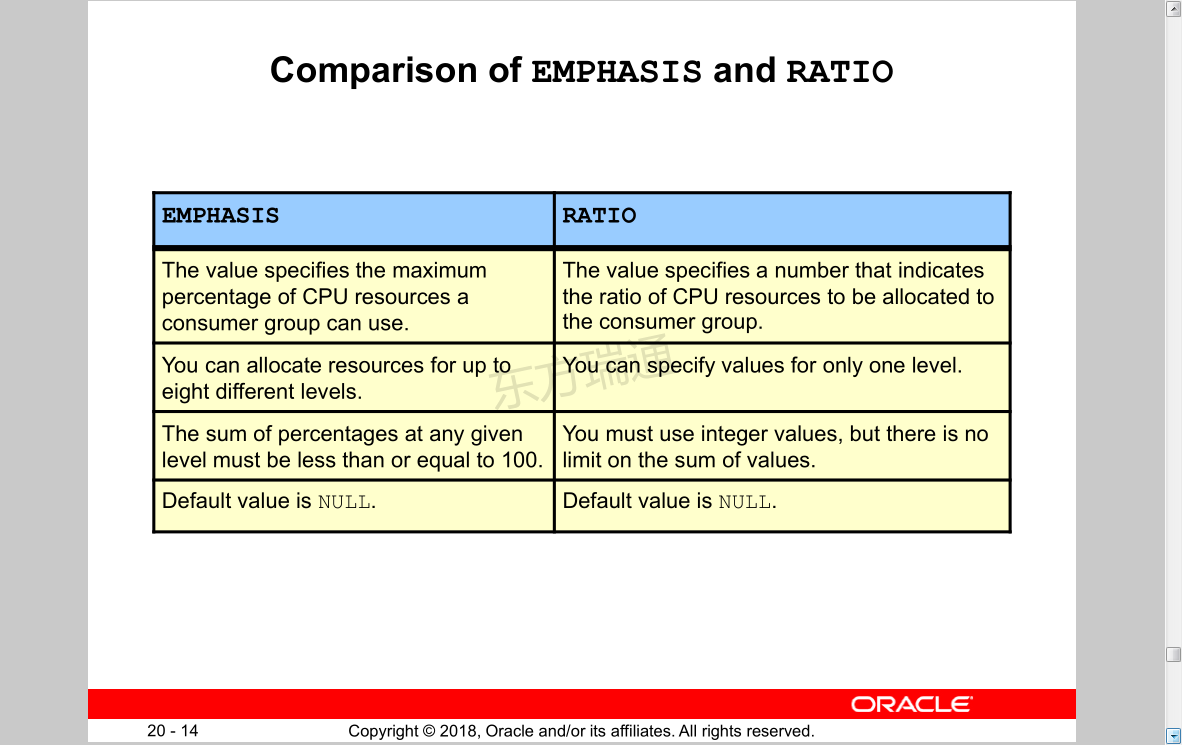
Comparison of EMPHASIS and RATIO 重点与比例比较

Active Session Pool Mechanism 活动会话池机制
Specifying Thresholds
Specifying execution time limit:
• Proactive estimation of the execution time for an operation (via cost-based optimizer statistics), default: UNLIMITED
• Specifying maximum estimated execution time at the resource consumer group level
• Huge jobs will not be allowed to start if the estimate is longer than MAX_EST_EXEC_TIME:(ORA-07455)
Specifying other thresholds:
• Limiting session I/O with SWITCH_IO_MEGABYTES (in MB)
• Limiting session I/O requests with SWITCH_IO_REQS
Returning to original consumer group with SWITCH_FOR_CALL (Default: FALSE, consumer group is not restored)
指定阈值
指定执行时间限制:
•主动估计操作的执行时间(通过基于成本的优化器统计),默认值:无限制
•指定资源使用者组级别的最大估计执行时间
•如果估计时间超过最长执行时间(ORA-07455),则不允许开始大量工作
指定其他阈值:
•使用交换机限制会话I/O,兆字节(MB)
•使用交换机请求限制会话I/O请求
使用开关_FOR_CALL返回原始用户组(默认值:FALSE,不恢复用户组)
Setting Idle Timeouts 设置空闲超时
DBMS_RESOURCE_MANAGER.UPDATE_PLAN_DIRECTIVE
(PLAN => 'DAY_PLAN',
GROUP_OR_SUBPLAN => 'APPUSER',
COMMENT => 'Limit Idle Time Example',
NEW_MAX_IDLE_TIME => 600,
NEW_MAX_IDLE_BLOCKER_TIME => 300);
Limiting CPU Utilization at the Database Level
• Database consolidation requirements:
– Applications isolated from each other
– Consistent performance
• CPU directives can be used to:
– Specify a minimum CPU allocation for each application
– Designate how unused allocations should be redistributed
– Specify the MAX_UTILIZATION_LIMIT attribute to impose an absolute upper limit on CPU utilization (which overrides any redistribution of CPU within a plan)
– Good candidate: Auto-maintenance tasks
在数据库级别限制CPU利用率
•数据库整合要求:
–应用程序彼此隔离
–始终如一的表现
•CPU指令可用于:
–为每个应用程序指定最小CPU分配
–指定如何重新分配未使用的分配
–指定MAX_UTILIZATION_LIMIT属性以对CPU利用率施加绝对上限(覆盖计划内CPU的任何重新分配)
–优秀候选人:汽车维修任务
练习
创建新的用户,并与使用者租绑定
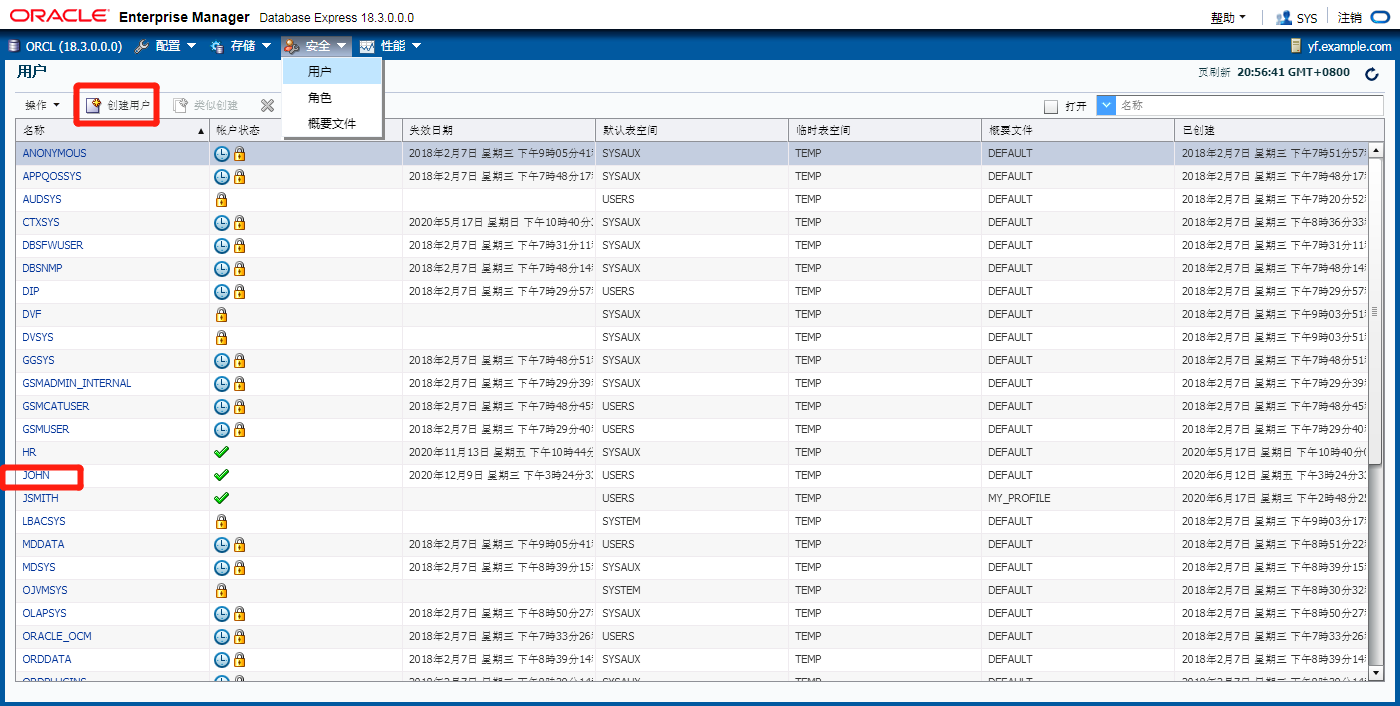
SQL> grant connect,resource to john; 给john用户授权
SQL> grant unlimited tablespace to john;
SQL> create table john.departments as select * from hr.departments;
SQL> exec dbms_resource_manager_privs.grant_switch_consumer_group(grantee_name=>'JOHN',consumer_group=>'APPS_GROUP',grant_option=>false); 链接用户john与刚才建立的使用者组apps_group
PL/SQL procedure successfully completed.
SQL> exec dbms_resource_manager.set_initial_consumer_group(user=>'JOHN',consumer_group=>'APPS_GROUP'); 绑定用户与使用者组
PL/SQL procedure successfully completed.
重新激活APPS_PLAN

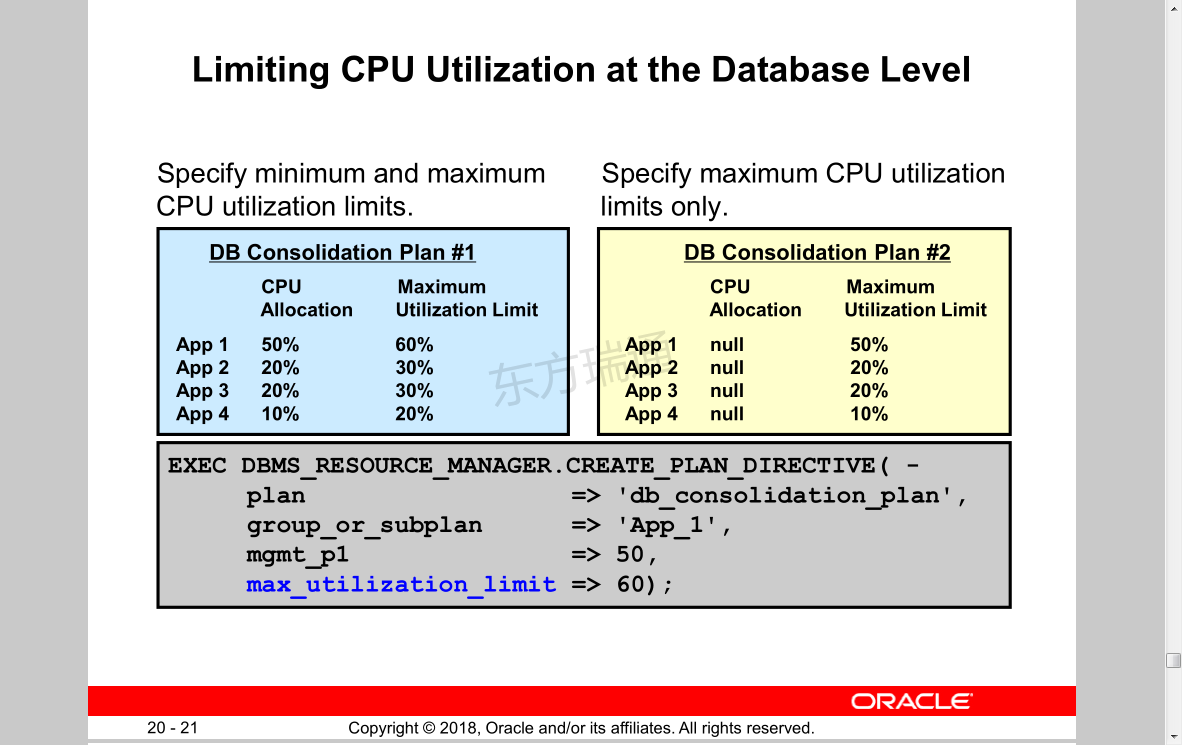
Limiting CPU Utilization at the Database Level
Specify minimum and maximumCPU utilization limits.
Specify maximum CPU utilizationlimits only.
在数据库级别限制CPU利用率
指定最小和最大CPU利用率限制。
仅指定最大CPU利用率限制
Limiting CPU Utilization at the Server Level:
Instance Caging
• Managing CPU allocations on a multi-CPU server with multiple database instances
• Enabling instance caging:
– Enable any CPU resource plan.
ALTER SYSTEM SET resource_manager_plan = 'default_plan';
– Specify the maximum number of CPUs that the instance can use at any time.
ALTER SYSTEM SET cpu_count=4;
• Two approaches:
– Over-provisioning: The sum of the CPU limit for each instance exceeds the actual number of CPUs.
– Partitioning: The sum of the CPU limit for each instance equals the actual number of CPUs.
限制服务器级别的CPU利用率:
实例限制
•在具有多个数据库实例的多CPU服务器上管理CPU分配
•启用实例缓存:
–启用任何CPU资源计划。
–指定实例在任何时候可以使用的最大CPU数。
•两种方法:
–过度配置:每个实例的CPU限制总和超过实际CPU数量。
–分区:每个实例的CPU限制之和等于实际的CPU数量。
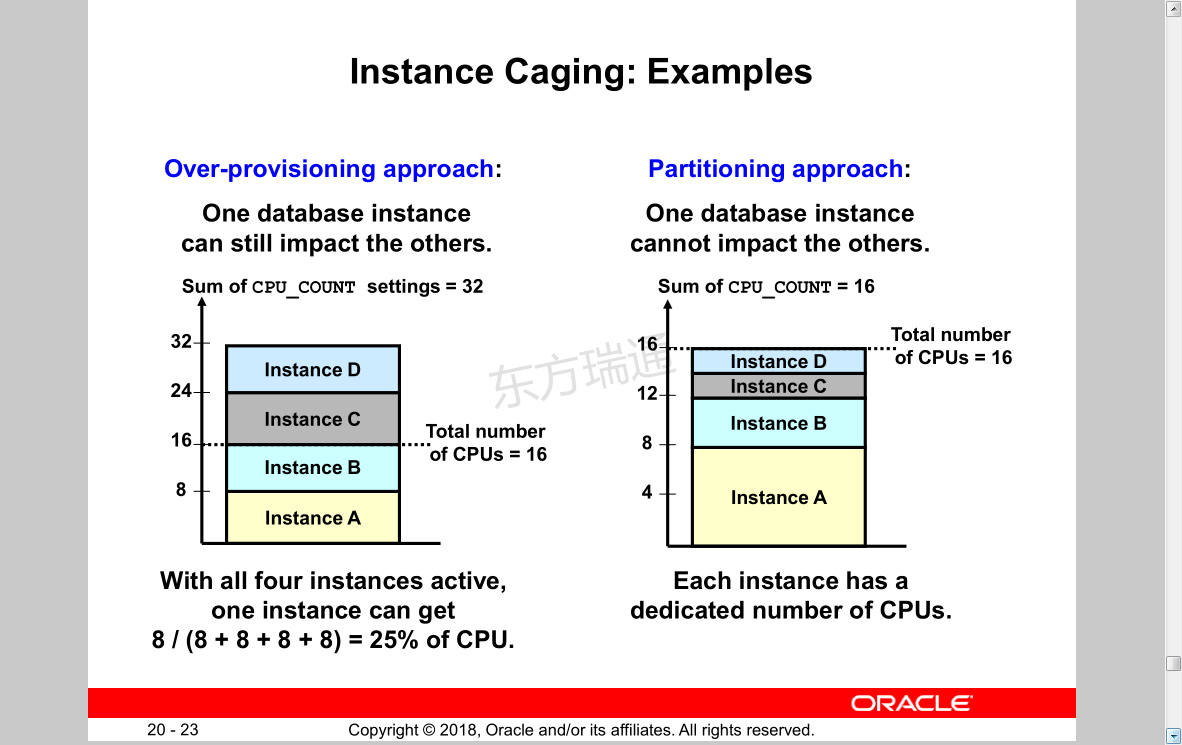
Instance Caging: Examples 实例限制:示例
Monitoring Instance Caging
View value of the CPU_COUNT parameter:
SELECT value FROM v$parameter WHERE name = 'cpu_count'
AND (isdefault = 'FALSE' OR ismodified != 'FALSE');
Determine the Resource Manager status:
SELECT name FROM v$rsrc_plan
WHERE is_top_plan = 'TRUE' AND cpu_managed = 'ON';
Manage throttling:
SELECT begin_time, consumer_group_name,
cpu_consumed_time, cpu_wait_time
FROM v$rsrcmgrmetric_history
ORDER BY begin_time;
SELECT name, consumed_cpu_time, cpu_wait_time
FROM v$rsrc_consumer_group;
监控实例缓存
CPU_COUNT参数的查看值:
确定资源管理器状态:
管理限制:
Runaway Queries and Resource Manager
• Parameters used to trigger consumer group switching:
– SWITCH_IO_LOGICAL
– SWITCH_ELAPSED_TIME
• Meta consumer group called LOG_ONLY
• Columns in V$SQL_MONITOR:
– RM_LAST_ACTION
– RM_LAST_ACTION_REASON
– RM_LAST_ACTION_TIME
– RM_CONSUMER_GROUP
• V$RSRCMGRMETRIC and V$RSRCMGRMETRIC_HISTORY always populated
失控查询和资源管理器
•用于触发用户组切换的参数:
–逻辑开关
–开关运行时间
•仅名为LOG帴的元消费者群体
•V$SQL_监视器中的列:
–RM_最后一次行动
–最后一次行动原因
–RM上次动作时间
–RM_消费者集团
•始终填充V$RSRCMGRMETRIC和V$RSRCMGRMETRICu历史记录
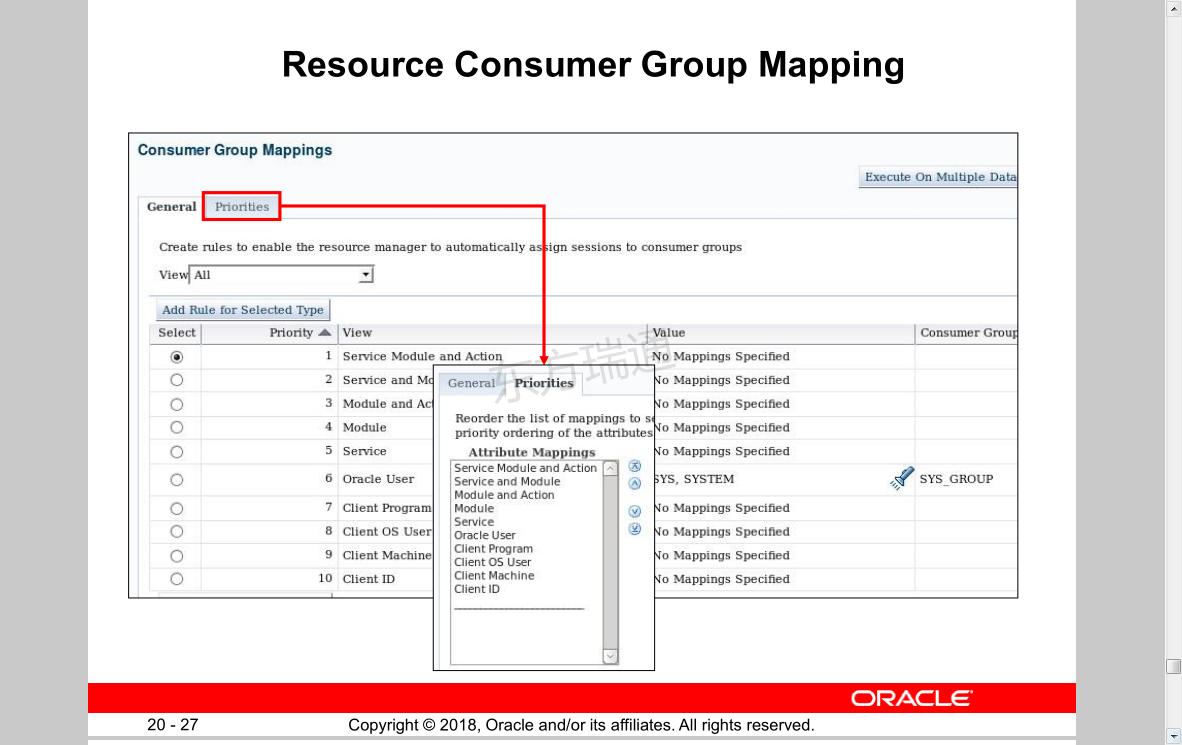
Resource Consumer Group Mapping 资源使用者组映射
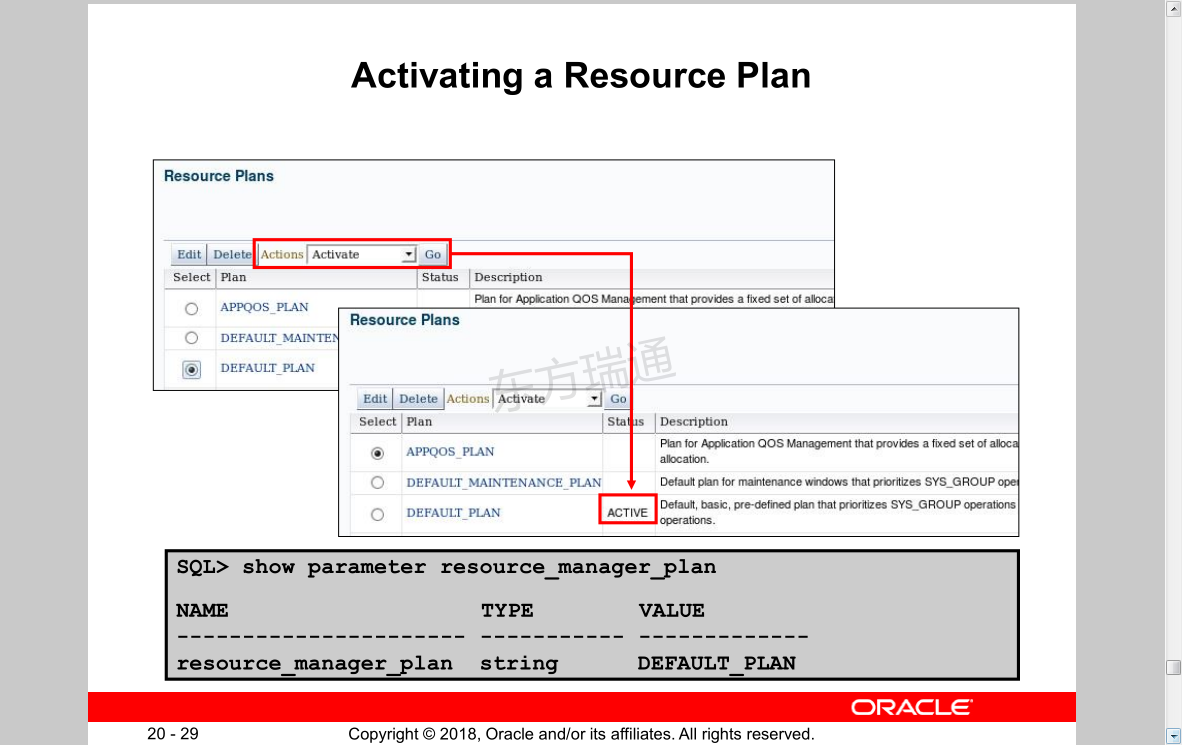
Activating a Resource Plan 激活资源计划
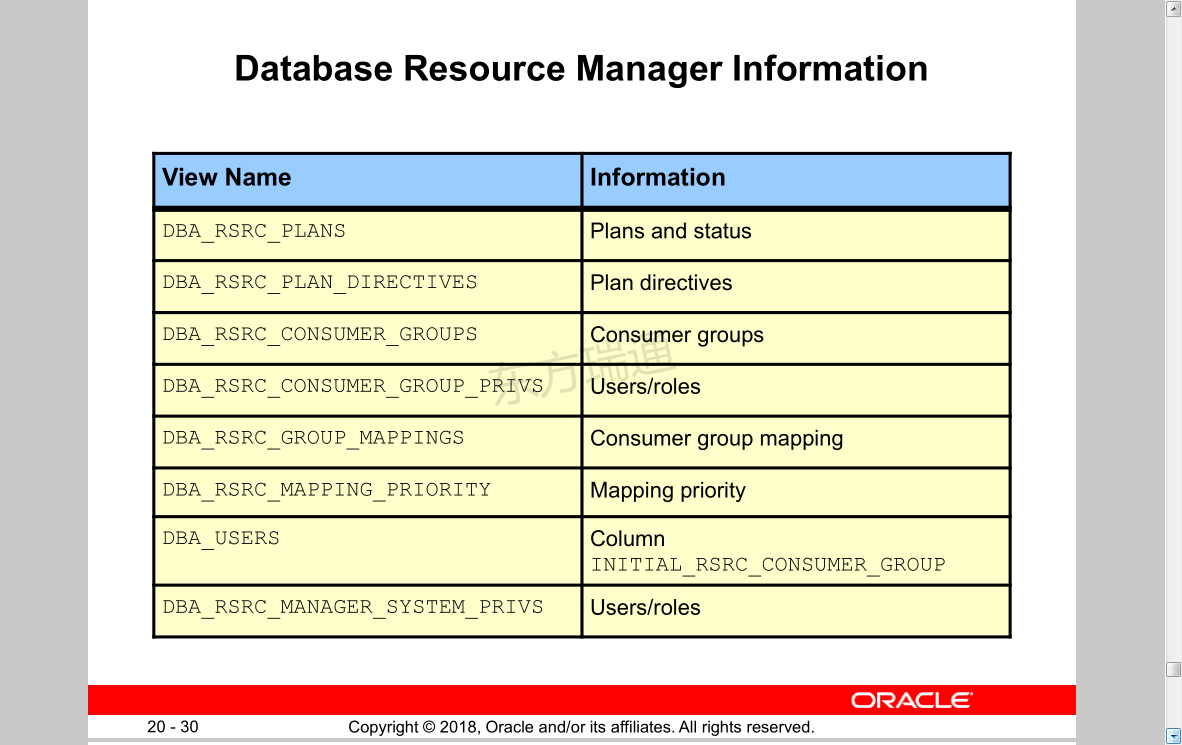
Database Resource Manager Information 数据库资源管理器信息
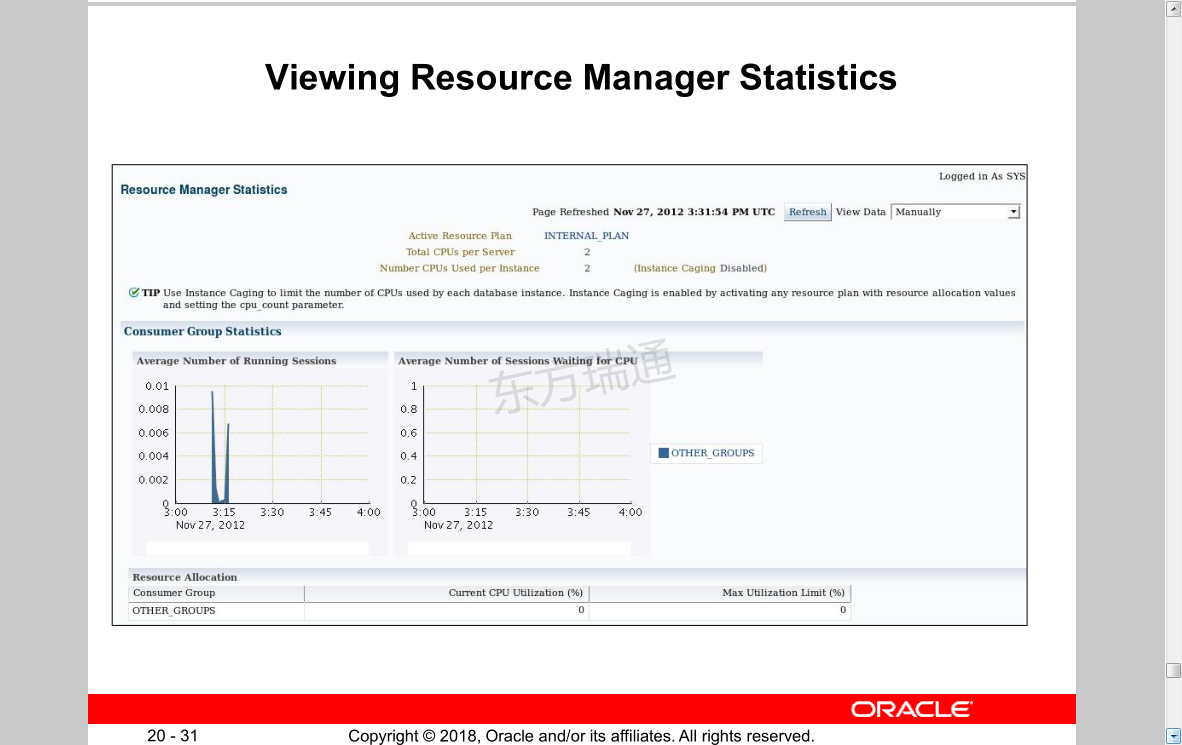
Viewing Resource Manager Statistics 查看资源管理器统计信息
Monitoring the Resource Manager
• V$SESSION: Contains the RESOURCE_CONSUMER_GROUP column that shows the current group for a session
• V$RSRC_PLAN: A view that shows the active resource plan
• V$RSRC_CONSUMER_GROUP: A view that contains statistics for all active groups
监视资源管理器
•V$SESSION:包含RESOURCE_CONSUMER_GROUP列,显示会话的当前组
•V$RSRC_PLAN:显示活动资源计划的视图
•V$RSRC_CONSUMER_GROUP:包含所有活动组的统计信息的视图
Quiz
Select the statements that are true about the Resource Manager and its functionality.
a. You can set threshold values only for execution time, not for session I/O.
b. You can limit CPU utilization at the database level to isolate applications for each other.
c. On a multi-CPU server with multiples database instances, you can limit each server’s CPU utilization by enabling instance caging.
d. When the SWITCH_TIME, SWITCH_IO_MEGABYTES, or SWITCH_IO_REQS parameters cause a switch in consumer groups, you can never return to the original consumer groups
测验
选择对资源管理器及其功能正确的语句。
a、 您只能为执行时间设置阈值,而不能为会话I/O设置阈值。
b、 您可以在数据库级别限制CPU利用率,以将应用程序彼此隔离。
c、 在具有多个数据库实例的多CPU服务器上,可以通过启用实例缓存来限制每台服务器的CPU利用率。
d、 当交换机时间、交换机兆字节或交换机请求参数导致用户组中的交换机时,您永远无法返回到原始的用户组
Summary
In this lesson, you should have learned how to do the following:
• Configure the Database Resource Manager
• Access and create resource plans
• Create consumer groups
• Specify directives for allocating resources to consumer groups
• Map consumer groups to plans
• Activate a resource plan
• Monitor the Resource Manager
摘要
在本课中,您应该学习如何执行以下操作:
•配置数据库资源管理器
•访问和创建资源计划
•创建消费者群体
•指定将资源分配给消费者群体的指令
•将消费者群体映射到计划
•启动资源计划
•监控资源管理器
Practice: Overview
This practice covers the following topics:
• Creating a resource consumer group
• Specifying CPU resource allocation directives for consumer groups
• Associating users with a resource consumer group
• Activating a resource plan
• Testing in SQL*Plus
• Deactivating a resource plan
实践:概述
本实践包括以下主题:
•创建资源消费群体
•为用户组指定CPU资源分配指令
•将用户与资源使用者组关联
•启动资源计划
•使用SQL*Plus进行测试
•停用资源计划