云中树莓派(5):利用 AWS IoT Greengrass 进行 IoT 边缘计算
云中树莓派(2):将传感器数据上传到AWS IoT 并利用Kibana进行展示
云中树莓派(3):通过 AWS IoT 控制树莓派上的Led
云中树莓派(5):利用 AWS IoT Greengrass 进行 IoT 边缘计算
IoT 的诸多场景中,边缘计算有很多需求。比如,不是每个物联网设备都能连接到互联网,从而连接云上物联网服务。还比如有一些数据安全考虑,不允许将某些数据发到云上。因此,AWS 发布了 Greengrass 服务,用于支持物联网场景中的边缘计算。
1. AWS IoT Greengrass 服务概述
- Greengrass 是一个软件,可以安装在多种设备上,比如树莓派、AWS EC2 实例、Ubuntu 虚拟机,以及多种专用设备。 具体参加AWS 官网。
- Lambda 运行时:可以将云上创建的 Lambda 函数部署到 Greengrass Core 上并使其运行。Lambda 函数可以和边缘物联网设备,以及云服务进行交互。
- 影子设备:为边缘物联网设备提供 Device Shadow 服务,类似云上 Device Shadow 服务。可以通过更新和查询设备的影子,来获取和修改设备的状态。
- 消息管理器:支持 Greengrass 组中的物联网设备之间的通信,以及与 Lambda 函数、设备影子服务之间通信。影子数据可以只保存在本地(Local Shadow),也可以同步到云上。
- 组管理: 管理 Greengrass Group,一个 group 为一个独立的边缘物联网环境。
- 发现服务:物联网设备可以通过连接到IoT云服务,然后通过 Discovery 功能来发现 Greengrass Core,从而与之通信。
- 无线更新代理:可以远程更新 Greengrass Core 软件。
- 本地资源访问:支持 Greengrass Core 上的 Lambda 函数访问本地资源,比如树莓派的GPIO,本地视频摄像头等。
- 机器学习推理:支持将云上 ML 机器学习推理功能部署到Greengrass Core。
架构:

关于架构的部分说明:
-
- 若干本地设备和一个Greengrass Core (GGC)组成一个 Greengrass 组。与 AWS Greengrass 核心通信的所有设备都必须是 Greengrass 组的成员。每个组都必须包含 AWS Greengrass 核心(似乎一个组只能有一个 GGC)。Discovery API 使设备能够检索连接到 AWS Greengrass 核心 (与设备位于同一 Greengrass 组中) 所需的信息。
- 本地设备和 Greengrass Core 通过本地网络通信,无法访问云(有看到 Discovery Service 需要设备在启动时连接到云上获取到 GG Core 的连接信息)。设备上必须安装 AWS IoT Device SDK。
- Greengrass 可以和云通信,需要有互联网访问能力。
- 可以在 Greengrass Core 上运行 Lambda 函数,这些函数可以和设备之间通信,也可以和云通信。
- 云上的配置、Lambda 函数以及机器学习模版通过 『Deploy』 被安装到 Greengrass Core 上。Greengrass Core 上有一个部署代理,它在接到通知后,从云上获取待部署材料,然后在 Greengrass Core 上进行部署。
- 组中设备连接到GGC 的过程:
- AWS IoT 设备使用其设备证书、私有密钥和 AWS IoT 根 CA 连接到 Greengrass 云服务。
- 连接后,AWS IoT 设备将使用 Greengrass Discovery Service 查找其 AWS Greengrass 核心设备的 IP 地址。该设备还可下载组的根 CA 证书,该证书可用于对 Greengrass 核心设备进行身份验证。
- AWS IoT 设备尝试连接到 AWS Greengrass 核心,并传递其设备证书和客户端 ID。如果客户端 ID 与设备的事物名称匹配并且证书有效,则将进行连接。否则,将终止连接。
2. 部署 AWS IoT Greengrass Core
2.1 操作系统准备
我在本地创建了一台 ubuntu 16.04 虚机,用于 Greengrass Core 部署。根据 Greengrass 文档做一些操作系统配置,具体参见Greengrass文档。在配置完成后,可运行检查工具来验证环境是否可用:
cd /home/pi/Downloads git clone https://github.com/aws-samples/aws-greengrass-samples.git cd aws-greengrass-samples cd greengrass-dependency-checker-GGCv1.5.0 sudo modprobe configs sudo ./check_ggc_dependencies | more
遇到两个小问题,提示未发现 java8 和 nodejs610。此时,需要创建三个软链接:
ln -s /usr/bin/node /usr/bin/nodejs6.10 ln -s /usr/bin/node /usr/bin/nodejs ln -s /usr/bin/java /usr/bin/java8
2.2 在 AWS IoT 上配置 Greengrass 服务
目前全球只有5个region 提供了 Greengrass 服务。在选择使用哪个region时候,一定要注意本地到这个region的网络情况。一开始,我想当然地认为国内到亚洲比如东京或者悉尼因为地理距离较近因此网络会较好,但实际上却发现到美国弗吉尼亚的网络比到东京的网络要好得多。
(1)创建 Greengrass Group

创建后,需下载两个压缩包:
- 一个是证书包:
- 一个是 Greengrass Core 软件安装包:根据系统平台选择。

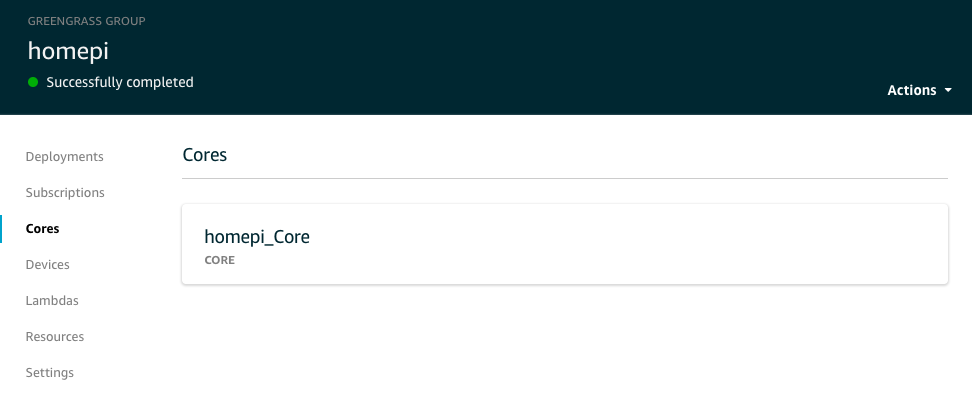
一个 Greengrass Group 包含的资源如下图所示,具体有:
- 部署(Deployments)
- 订阅表(Subscriptions)
- 核心(Cores)
- 本地设备(Devices)
- Lambda函数
- 本地资源(Resources)
(2)在设备上启动 Greengrass Core
- 将上面两个 zip 文件传到待安装 Greengrass Core 的环境中
- 将软件安装包解压到 /greengrass 中
- 将证书zip文件解压到 /greengrass/certs
- 下载 AWS IoT ROOT 证书到 /greengrass/certs 中
- 修改 config/config.json 文件如下所示
- 运行 /greengrass/ggc/core/greengrassd start 启动 Greengrass Core 服务
{
"coreThing": {
"caPath": "root.ca.pem",
"certPath": "022829d5c4.cert.pem",
"keyPath": "022829d5c4.private.key",
"thingArn": "arn:aws:iot:us-east-1:*******:thing/homepi_Core",
"iotHost": "*********.iot.us-east-1.amazonaws.com",
"ggHost": "greengrass.iot.us-east-1.amazonaws.com",
"keepAlive": 2000
},
"runtime": {
"cgroup": {
"useSystemd": "yes"
}
},
"managedRespawn": false
}
(3)问题排查
可以在 /greengrass/ggc/var/log/system 中查看 Greengrass Core 的日志文件。如果有错误,则定向排查。
2.3 测试
2.3.1 创建第一个 Lambda 函数
运行在 GGC 中的 Lambda 函数需要把 Greengrass SDK 打包进去。它的SDK 中提供了 HelloWorld 示例函数代码。函数代码如下,很简单,它每隔5秒钟向 hello/world MQTT 主题发送『Hello World』消息。
import greengrasssdk
import platform
from threading import Timer
import time
# Creating a greengrass core sdk client
client = greengrasssdk.client('iot-data')
# Retrieving platform information to send from Greengrass Core
my_platform = platform.platform()
def greengrass_hello_world_run():
if not my_platform:
client.publish(topic='hello/world', payload='Hello world! Sent from Greengrass Core.')
else:
client.publish(topic='hello/world', payload='Hello world! Sent from Greengrass Core running on platform: {}'.format(my_platform))
# Asynchronously schedule this function to be run again in 5 seconds
Timer(5, greengrass_hello_world_run).start()
# Start executing the function above
greengrass_hello_world_run()
def function_handler(event, context):
return
参考GG文档,完成所需步骤后,完成该函数的创建。发布它的的一个版本,并创建别名 GG_HelloWorld。
2.3.2 将该函数添加到 Greengrass Group 中
在 Greengrass 服务中添加上面创建的函数:

2.3.3 创建订阅 (subscription)
订阅表用于定义 Greengrass 组内 (AWS Greengrass 核心设备、AWS IoT 设备和 Lambda 函数之间) 如何交换消息。订阅表中的每个条目指定源、目标和发送/接收消息时使用的 MQTT 主题。仅当订阅表中存在指定源 (消息发件人)、目标 (消息收件人) 和 MQTT 主题的条目时才能交换消息。订阅表条目指定从源到目标的单向消息传递。如果您需要双向消息传递,请创建两个订阅表条目,每个条目针对一个方向。
为了测试该函数是否按设计发出了消息,创建一个从该函数到 IoT Service 的订阅,这样从 IoT 服务上就可以收到它发出的消息了。

2.3.4 部署(Deploy)
云上的所有操作都必须通过『部署』应用到 Greengrass Core 上。因此,对 Greengroup 做了任何变化后,都必须通过部署操作将其应用到Core 上。
点击 Actions -> Deploy,开始部署。可以从 Core 的 runtime.log 文件中看到其大致过程:
- 在Group 上有部署请求后,部署代理收到消息,消息中有 deploymentId
- 部署代理从云上获取待部署的素材
- 部署代理在Core上进行实际部署
[2018-08-13T15:56:55.622+08:00][INFO]-Received deploymentId 613dc2ec-8877-41b2-a217-8f939a7782fc of type NewDeployment for group f7a0bc8f-4527-481d-9301-1545b86fcf68 [2018-08-13T15:56:55.622+08:00][INFO]-Updating status to InProgress of deployment 613dc2ec-8877-41b2-a217-8f939a7782fc for group f7a0bc8f-4527-481d-9301-1545b86fcf68 [2018-08-13T15:56:56.611+08:00][INFO]-Executing the group Downloading step
然后查询其状态:
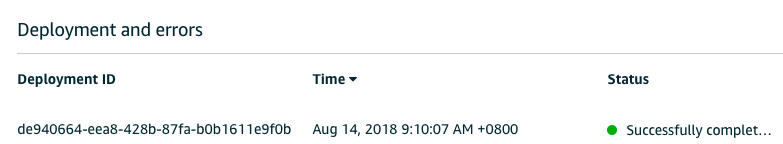
2.3.5 测试消息接收
在界面上的Test 功能中,可以收到 Lambda 函数发出的消息:

2.3.6 Core 上的变化
在 Lambda 函数被部署到 Core 上之后,在 Core 上起了一个新的进程:
ggc_user 21106 0.3 0.7 189616 15148 ? Ssl 16:33 0:12 python2.7 -u /runtime/python2.7/lambda_runtime.py --handler=greengrassHelloWorld.function_handler
该进程利用了 cgroup 来限制资源:
root@greengrass:/home/ubuntu# cat /proc/21106/cgroup 11:freezer:/system.slice/83db5d89-d650-4f65-542a-f6669153d4e6 10:blkio:/user.slice/system.slice/83db5d89-d650-4f65-542a-f6669153d4e6 9:memory:/user.slice/system.slice/83db5d89-d650-4f65-542a-f6669153d4e6 8:net_cls,net_prio:/system.slice/83db5d89-d650-4f65-542a-f6669153d4e6 7:pids:/user.slice/user-1000.slice/system.slice/83db5d89-d650-4f65-542a-f6669153d4e6 6:hugetlb:/system.slice/83db5d89-d650-4f65-542a-f6669153d4e6 5:perf_event:/system.slice/83db5d89-d650-4f65-542a-f6669153d4e6 4:devices:/user.slice/system.slice/83db5d89-d650-4f65-542a-f6669153d4e6 3:cpuset:/system.slice/83db5d89-d650-4f65-542a-f6669153d4e6 2:cpu,cpuacct:/user.slice/system.slice/83db5d89-d650-4f65-542a-f6669153d4e6 1:name=systemd:/user.slice/user-1000.slice/session-63.scope/system.slice/83db5d89-d650-4f65-542a-f6669153d4e6
目前只支持指定函数的内存限制:

3. 边缘物联网设备通过 Greengrass Core 进行消息交互
示意图:
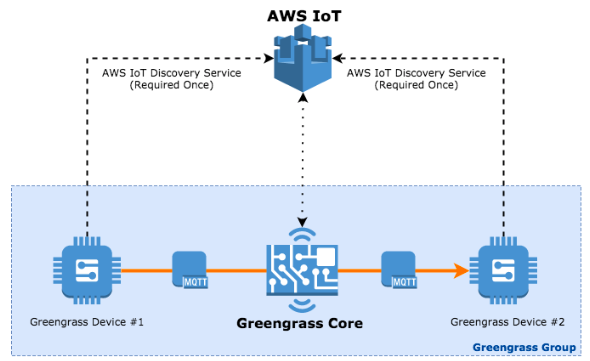
3.1 云上配置
(1)在 IoT Greengrass 服务中创建两个设备,分别是 HelloWorld_Publisher (模拟上图中的设备 #1)和 HelloWorld_Subscriber(模拟上图中的设备 #2)。将获取到各自的证书文件。
创建设备:
创建结果:
(2)配置订阅,从 Publisher 到 Subscriber:

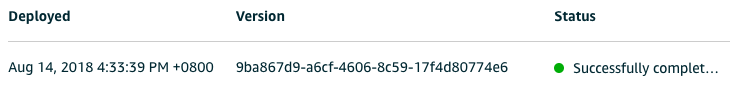
(3)通过 部署,把应用同步到 Greengrass Core 上。
3.2 树莓派中的配置和操作
以树莓派为平台,在上面运行两个程序,来模拟上面的两个物联网设备。
(1)首先需要在树莓派上安装 AWS IoT Device SDK
git clone https://github.com/aws/aws-iot-device-sdk-python.git cd aws-iot-device-sdk-python python setup.py install
(2)SDK 中有个示例文件 /aws-iot-device-sdk-python/samples/greengrass/basicDiscovery.py 可用于本测试
(3)运行脚本模拟 publlisher:
python basicDiscovery.py -e *****.iot.us-east-1.amazonaws.com -r pubcerts/root-ca.pem -c pubcerts/3ed88f606a.cert.pem -k pubcerts/3ed88f606a.private.key -n HelloWorld_Publisher -m publish -t hello/world/pubsub -M "Hellow, I am Publisher"
它会不停地向 hello/world/pubsub 发送消息:
2018-08-14 16:44:14,143 - AWSIoTPythonSDK.core.protocol.internal.workers - DEBUG - Produced [puback] event
2018-08-14 16:44:14,145 - AWSIoTPythonSDK.core.protocol.internal.workers - DEBUG - Dispatching [puback] event
2018-08-14 16:44:15,144 - AWSIoTPythonSDK.core.protocol.mqtt_core - INFO - Performing sync publish...
Published topic hello/world/pubsub: {"message": "Hellow, I am Publisher", "sequence"
(4)运行另一个脚本模拟 subscriber:
python basicDiscovery.py -e *******.iot.us-east-1.amazonaws.com -r subcerts/root-ca.pem -k subcerts/7d8fefa9d3.private.key -c subcerts/7d8fefa9d3.cert.pem -n HelloWorld_Subscriber -t hello/world/pubsub -m subscribe
它会不断收到消息:
2018-08-14 16:44:15,194 - AWSIoTPythonSDK.core.protocol.internal.workers - DEBUG - Produced [message] event
2018-08-14 16:44:15,196 - AWSIoTPythonSDK.core.protocol.internal.workers - DEBUG - Dispatching [message] event
2018-08-14 16:44:15,197 - AWSIoTPythonSDK.core.protocol.internal.clients - DEBUG - Invoking custom event callback...
Received message on topic hello/world/pubsub: {"message": "Hellow, I am Publisher", "sequence": 6}
3.3 过程说明
(1)订阅者一开始,会向 IoT Service Endpoint 发送一个 Discovery 消息:
Sending discover request: GET /greengrass/discover/thing/HelloWorld_Subscriber HTTP/1.1 Host: a1upjpa864lewg.iot.us-east-1.amazonaws.com:8443
说明:这里说明边缘的物联网设备还是需要连接到云上的IoT端点,这说明它们仍然需要互联网访问能力。
(2)它收到返回消息
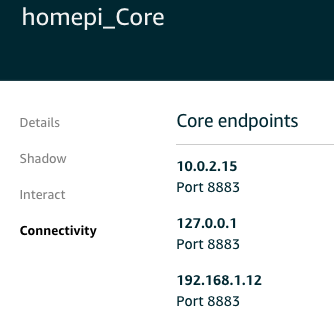
Receiving discover response body... Discovered GGC: arn:aws:iot:us-east-1:*******:thing/homepi_Core from Group: 669d91fc-0690-48ab-a36d-90816b2332b4 Now we persist the connectivity/identity information...
(3)它连接到 Greengrass Core
Trying to connect to core at 192.168.1.12:8883
(4)它订阅到指定 topic
Adding a new subscription record: hello/world/pubsub qos: 0
(5)它开始接收消息
2018-08-14 16:44:09,381 - AWSIoTPythonSDK.core.protocol.internal.workers - DEBUG - Produced [message] event
2018-08-14 16:44:09,382 - AWSIoTPythonSDK.core.protocol.internal.workers - DEBUG - Dispatching [message] event
2018-08-14 16:44:09,384 - AWSIoTPythonSDK.core.protocol.internal.clients - DEBUG - Invoking custom event callback...
Received message on topic hello/world/pubsub: {"message": "Hellow, I am Publisher", "sequence": 0}
可见这过程里面,处于边缘的物联网设备还是需要连接到云上IoT 服务一次,去获取Core 的信息。Core 的 Connectivity 信息可以收入输入,也可以由Core 自动推送到云上。
4. 与本地设备影子进行交互
示意图:
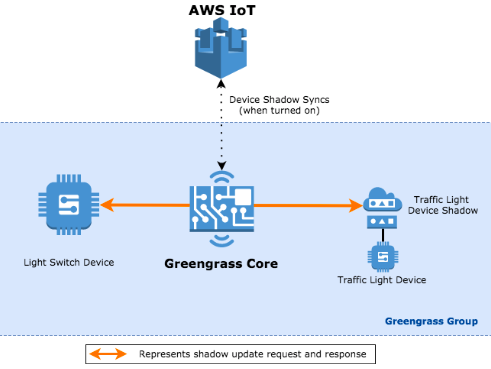
4.1 云上配置
(1)在IoT 服务中,在 Greengrass 组内,创建两个设备,GG_Switch 和 GG_TrafficLight。
(2)创建订阅
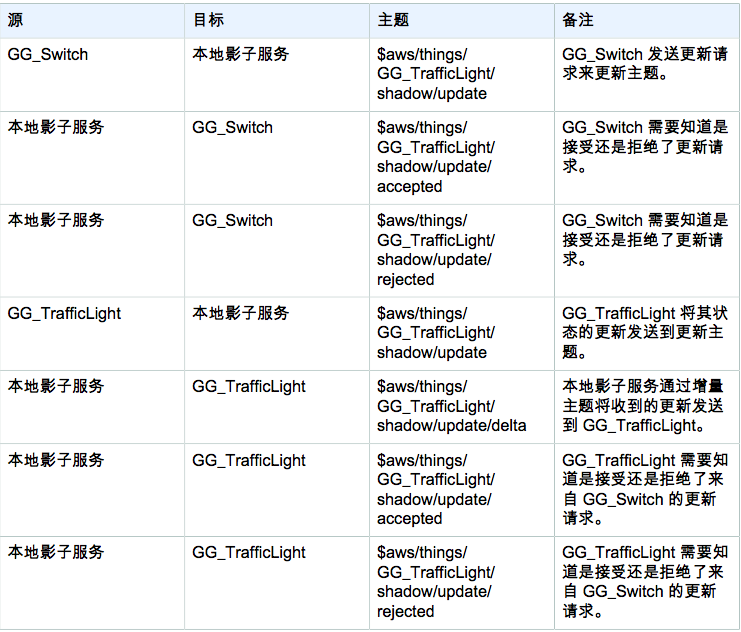
(3)部署
4.2 树莓派上的配置和操作
从 https://github.com/aws-samples/aws-greengrass-samples/tree/master/traffic-light-example-python 下载 lightController.py 和 trafficLight.py 文件。前者模拟一个Led 灯的控制器,后者模拟Led 灯。
(1)运行Controller
python lightController.py -e ****.iot.us-east-1.amazonaws.com -r switchcerts/root-ca.pem -c switchcerts/8bb0278c01.cert.pem -k switchcerts/8bb0278c01.private.key -n GG_TrafficLight --clientId GG_Switch
它会定时向设备影子发出更新请求:
{"state":{"desired":{"property":"Y"}}}
2018-08-14 17:00:28,915 - AWSIoTPythonSDK.core.protocol.mqtt_core - INFO - Performing sync publish...
~~~~~~~~~~Shadow Update Accepted~~~~~~~~~~~~~
Update request with token: 1827378e-9b0b-4b03-a7df-2c1af119510f accepted!
property: Y
(2)运行 Light
python trafficLight.py -e ****.iot.us-east-1.amazonaws.com -r lightcerts/root-ca.pem -c lightcerts/eae63a2ee2.cert.pem -k lightcerts/eae63a2ee2.private.key -n GG_TrafficLight --clientId GG_TrafficLight
它会收到 Delta 请求,变更Led 的状态:
Light changed to: Y
{"state":{"reported":{"property":"Y"}}}
2018-08-14 17:02:29,111 - AWSIoTPythonSDK.core.protocol.mqtt_core - INFO - Performing sync subscribe...
2018-08-14 17:02:29,120 - AWSIoTPythonSDK.core.protocol.mqtt_core - INFO - Performing sync subscribe...
2018-08-14 17:02:31,132 - AWSIoTPythonSDK.core.shadow.deviceShadow - INFO - Subscribed to update accepted/rejected topics for deviceShadow: GG_TrafficLight
2018-08-14 17:02:31,133 - AWSIoTPythonSDK.core.protocol.mqtt_core - INFO - Performing sync publish...
~~~~~~~~~~ Shadow Update Accepted ~~~~~~~~~~~~~
Update request with token: ec5f0cdb-0558-44b7-a685-02d2df8a31cb accepted!
property: Y
5. 从 Lambda 函数中访问云服务
示意图:

5.1 云上配置
(1)创建 IAM Role Greengrass_DynamoDB_Role,将其赋予给 Greengrass,用于访问 DynamoDB。
(2)创建 IAM Role Lambda_DynamoDB_Role,它会被赋予给 Lambda 函数,用于访问 DynamoDB。
(3)从 https://github.com/aws-samples/aws-greengrass-samples/tree/master/traffic-light-example-python 下载 carAggregator.py,打包成 Lambda 函数包,创建 Lambda 函数。函数名为 GG_Car_Aggregator。看下它的代码:
import logging
import boto3
from datetime import datetime
from random import *
from botocore.exceptions import ClientError
dynamodb = boto3.resource('dynamodb', region_name='us-east-1')
tableName = "CarStats"
# Create the dynamo db table if needed
try:
table = dynamodb.create_table(
TableName=tableName,
KeySchema=[
{
'AttributeName': 'Time',
'KeyType': 'HASH' #Partition key
}
],
AttributeDefinitions=[
{
'AttributeName': 'Time',
'AttributeType': 'S'
}
],
ProvisionedThroughput={
'ReadCapacityUnits': 5,
'WriteCapacityUnits': 5
}
)
# Wait until the table exists.
table.meta.client.get_waiter('table_exists').wait(TableName=tableName)
except ClientError as e:
if e.response['Error']['Code'] == 'ResourceInUseException':
print("Table already created")
else:
raise e
# initialize the logger
logger = logging.getLogger()
logger.setLevel(logging.INFO)
# This is a long lived lambda so we can keep state as below
totalTraffic = 0
totalGreenlights = 0
minCars = -1
maxCars = -1
def function_handler(event, context):
global totalTraffic
global totalGreenlights
global minCars
global maxCars
# grab the light status from the event
# Shadow JSON schema:
# { "state": { "desired": { "property":<R,G,Y> } } }
logger.info(event)
lightValue = event["current"]["state"]["reported"]["property"]
logger.info("reported light state: " + lightValue)
if lightValue == 'G':
logger.info("Green light")
# generate a random number of cars passing during this green light
cars = randint(1, 20)
# update stats
totalTraffic += cars
totalGreenlights+=1
if cars < minCars or minCars == -1:
minCars = cars
if cars > maxCars:
maxCars = cars
logger.info("Cars passed during green light: " + str(cars))
logger.info("Total Traffic: " + str(totalTraffic))
logger.info("Total Greenlights: " + str(totalGreenlights))
logger.info("Minimum Cars passing: " + str(minCars))
logger.info("Maximum Cars passing: " + str(maxCars))
# update car stats to dynamodb every 3 green lights
if totalGreenlights % 3 == 0:
global tableName
table = dynamodb.Table(tableName)
table.put_item(
Item={
'Time':str(datetime.utcnow()),
'TotalTraffic':totalTraffic,
'TotalGreenlights':totalGreenlights,
'MinCarsPassing':minCars,
'MaxCarsPassing':maxCars,
}
)
return
代码也很简单。它首先会尝试创建一个 Dynamo table。然后在每次收到 documents 后,检查 reported 状态。如果为 「G」,表示为绿灯,它会向Dynamo 表中写入一条数据。
(4)将该函数添加到 Greengrass 组中。
(5)配置订阅。本地影子服务会将设备的 documents 发给 Aggregator Lambda 函数。

5.2 树莓派上的配置
保持 4.2 中的 Controller 和 Light 持续运行。几分钟后,Dynamo 中将会有数据产生:
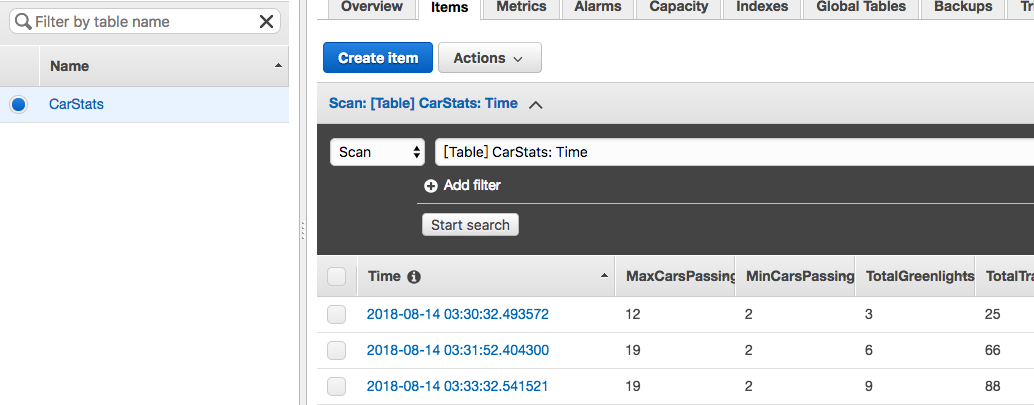
6. 一点感受
感觉AWS IoT Greengrass 服务还有一些不太完善,主要有以下几个原因:
- 目前全球只有5个区域内可以使用 Greengrass 服务
- 似乎无法做到边缘物联网设备完全不需访问云而只需要能访问 Greengrass Core,因为至少 Discovery Serivce 需要访问 IoT Service Endpoint来获取 Core 的连接信息。
- 利用订阅来控制消息的发送很繁琐。如果有很多的设备,很多的topic,那这个配置将成为一个苦力活。
- Greengrass 服务应该需要高可用,但是没看到相关的文档和方案。
参考链接:
- AWS 官方的 《AWS Greengrass 开发人员指南》
- https://medium.com/tensoriot/aws-greengrass-on-raspberry-pi-creating-core-and-node-devices-707a38452293
