一杯敬朝阳,一杯敬月光。
算法分析
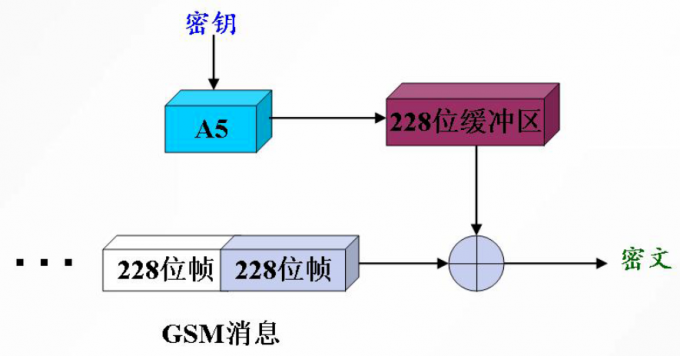
- A5算法已被应用于GSM通信系统中,用于加密从手机到基站的连接,以保护语音通信。一个GSM语言消息被转换成一系列的帧,每帧长
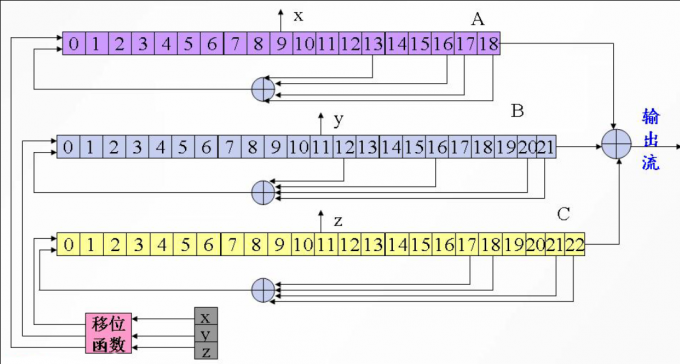
228位,每帧用A5进行加密。 - A5算法主要由三个长度不同的线性移位寄存器组成,即A, B, C。其中A有19位,B有22位,C有23位。
- 移位由时钟控制的,且遵循“择多”的原则。即从每个寄存器中取出一个中间位,三个数中占多数的寄存器参加移位,其余的不移位。
可以参考:A5算法理解
算法实现
import re
def createkey(key,Fn):
tem = strtobin(key)
# 线性反馈移位寄存器LFSR A,B,C
A = list(tem[:19])
B = list(tem[19:41])
C = list(tem[41:])
res = []
for i in range(114):
resa = int(A[13]) ^ int(A[16]) ^ int(A[17]) ^ int(A[18])
resb = int(B[12]) ^ int(A[16]) ^ int(B[20]) ^ int(B[21])
resc = int(C[17]) ^ int(C[18]) ^ int(C[21]) ^ int(C[22])
if int(A[9]) ^ int(B[11]) ^ int(C[11]) == 1:
if A[9] == '1' and B[11] == '1':
A[1: 18] = A[0: 17]
A[0] = str(resa)
B[1: 21] = B[0: 20]
B[0] = str(resb)
elif A[9] == '1' and C[11] == '1':
A[1: 18] = A[0: 17]
A[0] = str(resa)
C[1: 22] = C[0: 21]
C[0] = str(resc)
else:
B[1: 21] = B[0: 20]
B[0] = str(resb)
C[1: 22] = C[0: 21]
C[0] = str(resc)
else:
if A[9] == '0' and B[11] == '0':
A[1: 18] = A[0: 17]
A[0] = str(resa)
B[1: 21] = B[0: 20]
B[0] = str(resb)
elif A[9] == '0' and C[11] == '0':
A[1: 18] = A[0: 17]
A[0] = str(resa)
C[1: 22] = C[0: 21]
C[0] = str(resc)
else:
B[1: 21] = B[0: 20]
B[0] = str(resb)
C[1: 22] = C[0: 21]
C[0] = str(resc)
res.append(int(A[18]) ^ int(B[21]) ^ int(C[22]))
Fn = list(Fn)
for i in range(22):
B[i] = int(B[i]) ^ int(Fn[i])
for i in range(114):
resa = int(A[13]) ^ int(A[16]) ^ int(A[17]) ^ int(A[18])
resb = int(B[12]) ^ int(A[16]) ^ int(B[20]) ^ int(B[21])
resc = int(C[17]) ^ int(C[18]) ^ int(C[21]) ^ int(C[22])
if int(A[9]) ^ int(B[11]) ^ int(C[11]) == 1:
if A[9] == '1' and B[11] == '1':
A[1: 18] = A[0: 17]
A[0] = str(resa)
B[1: 21] = B[0: 20]
B[0] = str(resb)
elif A[9] == '1' and C[11] == '1':
A[1: 18] = A[0: 17]
A[0] = str(resa)
C[1: 22] = C[0: 21]
C[0] = str(resc)
else:
B[1: 21] = B[0: 20]
B[0] = str(resb)
C[1: 22] = C[0: 21]
C[0] = str(resc)
else:
if A[9] == '0' and B[11] == '0':
A[1: 18] = A[0: 17]
A[0] = str(resa)
B[1: 21] = B[0: 20]
B[0] = str(resb)
elif A[9] == '0' and C[11] == '0':
A[1: 18] = A[0: 17]
A[0] = str(resa)
C[1: 22] = C[0: 21]
C[0] = str(resc)
else:
B[1: 21] = B[0: 20]
B[0] = str(resb)
C[1: 22] = C[0: 21]
C[0] = str(resc)
res.append(int(A[18]) ^ int(B[21]) ^ int(C[22]))
return res
# 字符串转换为二进制字符串
def strtobin(s):
res = []
for c in s:
tem = bin(ord(c)).replace('b', '')
# 转为字符串时,后7位中,如果存在前面为0,会自动去掉,需要加回来,使之满足8位
if len(tem) < 8:
tem = "0" + tem
res.append(tem)
return ''.join(res)
# 二进制转字符串
def bintostr(s):
tem = ""
for i in s:
tem += str(chr(int(i, base=2)))
return tem
# 将明文字符串分割为指定长度字符串并存于列表中
def cut_text(text, lenth):
tem = re.findall('.{' + str(lenth) + '}', text)
tem.append(text[(len(tem) * lenth):])
# 由于分割后,末尾出现一个空字符,故去掉
result = [i for i in tem if i != '']
return result
if __name__ == "__main__":
# 明文
plaintext = "ifnottothesunforsmilingwarmisstillinthesuntherebutwewilllaughmoreconfidentcalmifturnedtofoundhisownshadowappropriateescapethesunwillbethroughtheheartwarmeachplacebehindthecornerifanoutstretchedpalmcannotfallbutterflythenclenchedwavingarmsgivenpowerificanthavebrightsmileitwillfacetothesunshineandsunshinesmiletogetherinfullbloom"
# 秘钥
key = "asdfghjk"
# 转换成二进制
mtext = strtobin(plaintext)
key = strtobin(key)
# 帧号码Fn 22位
Fn = "0101101000110101010101"
# 生成密钥流
keystream = createkey(key, Fn)
# 加密
mlist = cut_text(mtext, 228)
ciphertext = ""
for t in mlist:
# 对每组明文分别加密
for i in range(len(t)):
ciphertext += str(int(keystream[i]) ^ int(t[i]))
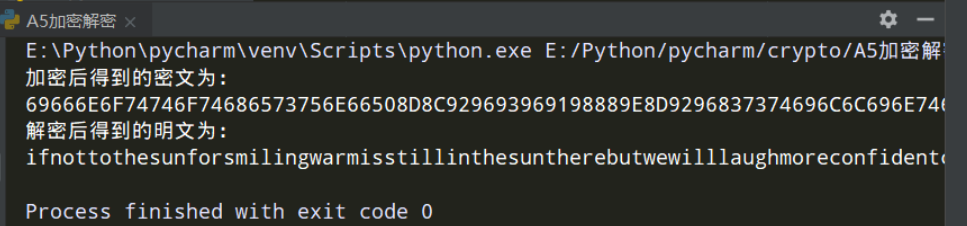
print("加密后得到的密文为: \n" + hex(int(ciphertext,2)).upper()[2:])
# 解密
clist = cut_text(ciphertext, 228)
res = ""
for t in clist:
for i in range(len(t)):
res += str(int(keystream[i]) ^ int(t[i]))
result = cut_text(res, 8)
end = bintostr(result)
print("解密后得到的明文为: \n" + end)
加解密