A move consists of taking a point (x, y) and transforming it to either (x, x+y) or (x+y, y).
Given a starting point (sx, sy) and a target point (tx, ty), return True if and only if a sequence of moves exists to transform the point (sx, sy) to (tx, ty). Otherwise, return False.
Examples: Input: sx = 1, sy = 1, tx = 3, ty = 5 Output: True Explanation: One series of moves that transforms the starting point to the target is: (1, 1) -> (1, 2) (1, 2) -> (3, 2) (3, 2) -> (3, 5) Input: sx = 1, sy = 1, tx = 2, ty = 2 Output: False Input: sx = 1, sy = 1, tx = 1, ty = 1 Output: True
Note:
sx, sy, tx, tywill all be integers in the range[1, 10^9].
到达终点。
从点 (x, y) 可以转换到 (x, x+y) 或者 (x+y, y)。
给定一个起点 (sx, sy) 和一个终点 (tx, ty),如果通过一系列的转换可以从起点到达终点,则返回 True ,否则返回 False。
来源:力扣(LeetCode)
链接:https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/reaching-points
著作权归领扣网络所有。商业转载请联系官方授权,非商业转载请注明出处。
题意是给一个起点的坐标(sx, sy)和一个终点的坐标(tx, ty),以及坐标的转换规则,问你是否能按规则转换起点坐标从而得到终点坐标。
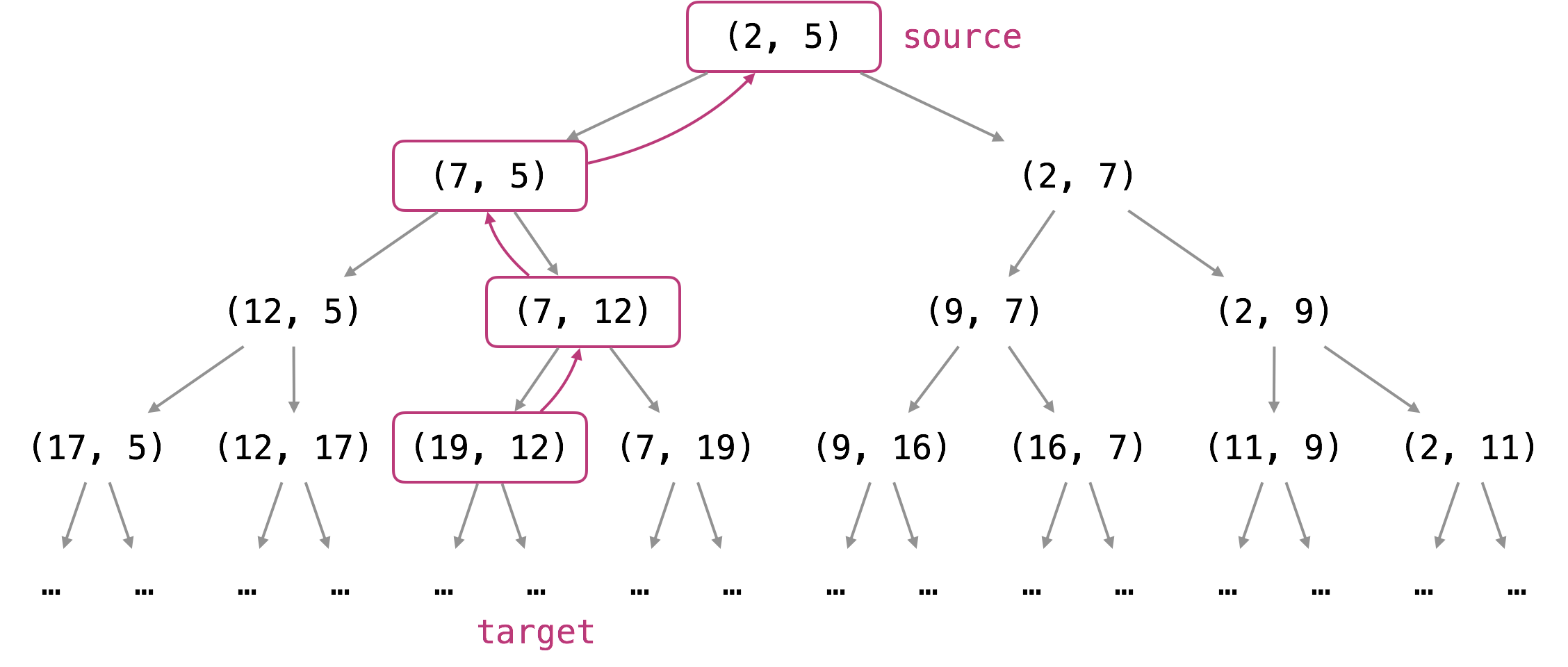
这道题的思路不难,但是需要优化才能通过所有的test case。如果从起点开始往终点硬刚,你会发现情况很多,既可以改变纵坐标,也可以改变横坐标,这样是很容易超时的。但是如果你从终点开始往起点找,会容易很多。因为根据规则,每一个父亲节点(x, y)有可能有两个孩子节点(x + y, y)和(x, x + y),但是对于每个孩子节点来说,他只会有一个父亲节点。比如这两个孩子节点,无论怎么算,都是用较大的坐标 - 较小的坐标,得到父节点(x, y)。同时注意题目是需要满足x和y都需要 >= 1的所以不需要考虑负数的情况,只要有一个坐标小于1即知道肯定不对了,可以排除这种case,考虑别的case了。下图帮助理解(引用)。
既然知道了是需要做减法操作,也还是需要优化的。一个比较恶心的case是(1, 99999999)。如果你只是一点点做减法,最后是会超时的。优化的方法是做模运算。一开始我们肯定是需要用一个while循环控制终点的横纵坐标都分别大于起点的横纵坐标,然后根据终点的横纵坐标谁比较大,来判断到底怎么做这个模运算。当跳出这个while循环的时候,也就意味着终点的横纵坐标起码有一个在做了多次运算之后已经小于等于起点的横纵坐标了,此时我们需要判断的是
- 如果起点和终点的横坐标相同,判断纵坐标是否也相同,或者起点的纵坐标能经过若干次变换得到终点的纵坐标
- 如果起点和终点的纵坐标相同,判断横坐标是否也相同,或者起点的横坐标能经过若干次变换得到终点的横坐标
注意加粗的这两个条件,既然是要变换,那么肯定是要满足起终点的纵坐标的差要大于横坐标或者是起终点的横坐标的差要大于纵坐标
时间O(log(max(tx, ty)))
空间O(1)
Java实现
1 class Solution { 2 public boolean reachingPoints(int sx, int sy, int tx, int ty) { 3 while (tx > sx && ty > sy) { //调整坐标到x方向或y方向之一与初始坐标相同 4 if (tx > ty) { 5 tx = tx % ty; 6 } else { 7 ty = ty % tx; 8 } 9 } 10 if (tx == sx) { //在与初始坐标x相同的情况下,要么与初始坐标完全相同,要么另一方向经过有限次变换 11 return ty == sy || (ty - sy >= sx && (ty - sy) % sx == 0); 12 } 13 if (ty == sy) { //在与初始坐标y相同的情况下,另一方向经过有限次变换 14 return tx - sx >= sy && (tx - sx) % sy == 0; 15 } 16 return false; 17 } 18 }