1.条件判断语句
Python中条件选择语句的关键字为:if 、elif 、else这三个。其基本形式如下:
age_of_cc = 27
age = int(input("guessage:"))
if age == age_of_cc:
print("Yes,you got it!")
elif age > age_of_cc:
print("猜大啦!")
else:
print("猜小啦!")
if语句执行的特点是从上往下判断;
其中elif和else语句块是可选的。对于if和elif只有判断为True时,该分支语句才执行,只有当if和所有的elif的判断都为False时,才执行else分支。注意Python中条件选择语句中判断后面有个冒号。
2.循环语句
2.1 while循环
他的原理是:当条件为真的时候运行,当条件为假的时候停止!
没有一个规定次数,不设置条件永远循环下去。
用法:
while 条件:
xxxxxx
while循环判断语句代码示例:
age_of_cc = 27
count =0
while count < 3:
age = int(input("guessage:"))
if age == age_of_cc:
print("Yes,you got it!")
break
elif age > age_of_cc:
print("猜大啦!")
else:
print("猜小啦!")
count += 1
else:
if count == 3:
print("错误太多次啦!")
2.1.1 break跳出整个循环
代码示例
age_of_cc = 27
count =0
while count < 3:
age = int(input("guessage:"))
if age == age_of_cc:
print("Yes,you got it!")
break
elif age > age_of_cc:
print("猜大啦!")
else:
print("猜小啦!")
count += 1
else:
if count == 3:
print("错误太多次啦!")
2.1.2 continue跳过当前循环
代码示例:
i = 1
while i < 10:
i += 1
if i%2 > 0: # 非双数时跳过输出
continue
print(i) # 输出双数2、4、6、8、10
2.2 for循环
for循环需要预先设定好循环的次数(n),然后执行隶属于for的语句n次。
代码示例:
for i in range(10):
print(i) #输出0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9
for条件判断代码示例:
age_of_cc = 27
count = 0
for i in range(3):
age = int(input("guessage:"))
if age == age_of_cc:
print("Yes,you got it!")
break
elif age > age_of_cc:
print("猜大啦!")
else:
print("猜小啦!")
count += 1
else:
if count == 3:
print("错误太多次啦!")
3 其他
3.1 input
input是输入函数,用户可以输入字符串保存到变量中
代码示例:
name = input("Please input your name")
3.2 print
用print()在括号中加上字符串,就可以向屏幕上输出指定的文字
代码示例:
print("Hello!")
3.3 类型转换
通过上文可以看出,input输入的在python中都会被认为是字符串(见下图),所以我们需要对input的内容进行类型转换:
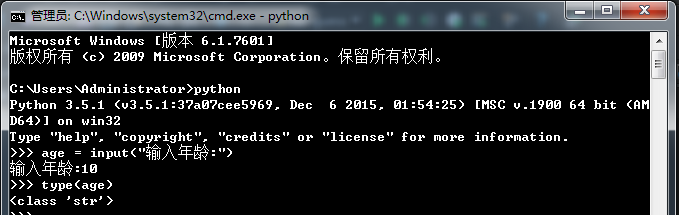
转换成int示例:
age = int(input("age is:"))
转换回字符串:str()
4.练习
登录接口开发:
1.输入用户名密码
2.错误三次即锁定用户
3.登陆成功则显示欢迎信息
# author:cc
import sys, os, getpass
count = 0# 计数器
if os.path.exists('user.txt'):# 判断用户文件是否存在
pass
else:
print("Sorry!")
while count < 3:#登录异常不超过三次就不断循环
username = input("请输入用户名:")#输入用户名
with open('lockuser.txt','r+') as f:#输入用户名后检查是否在锁定文件中
lock_file = f.readlines()#读取文件内容
for lock_line in lock_file:#遍历锁定文件
lock_line = lock_line.strip('
')#使用strip函数分割文件
if username in lock_line:#判断用户名是否在锁定文件中,若被锁定则直接退出程序
sys.exit("用户%s已被锁定,请联系管理员解锁" % username)
else:
pass
with open('user.txt','r+') as u:
user_file = u.readlines()#读取用户文件
for user_line in user_file:#遍历用户文件
(user,password)= user_line.strip('
').split()#获取用户名和密码
if username == user:
pwd = 0 #密码计数
while pwd < 3:#只要用户密码异常不超过三次就一直循环
passwd = getpass.getpass("请输入密码:") #输入暗文显示密码
if passwd == password:#如果用户名密码匹配,则提示登录成功
print("欢迎用户%s进入管理平台..." % username)
sys.exit(0)
else:#用户名密码不匹配提示密码错误,剩余几次机会;密码错误次数+1
print("%s密码错误,您仅剩%s次机会,请注意!" % (username,2-pwd))
pwd += 1
else:#错误三次后写入lock_file文件
with open('lockuser.txt', 'r+') as fw:
fw.write(username + "
")
print("用户%s登录达到最大次数,已被锁定,请联系管理员处理。。。" % username)
break
else:
pass
else:#用户名不存在时计入错误次数
print("用户%s不存在,请重新输入,您还有%s次机会" % (username,2-count))
count += 1
if count == 3:#错误三次时提示没有机会了
print("没有机会啦~!")
else:
print("用户%s不存在,退出。。。" % username)