1.Libpcap简介
Libpcap是Packet Capture Libray的英文缩写,即数据包捕获函数库。该库提供的C函数接口用于捕捉经过指定网络接口的数据包,该接口应该是被设为混杂模式。这个在原始套接子中有提到。
著名的软件TCPDUMP就是在Libpcap的基础上开发而成的。Libpcap提供的接口函数实现和封装了与数据包截获有关的过程。
Libpcap提供了用户级别的网络数据包捕获接口,并充分考虑到应用程序的可移植性。Libpcap可以在绝大多数Linux平台上运行。在Windows平台上,也有一款与其功能类似的开发库:Wincap。
它的工作在上层应用程序与网络接口之间。
主要功能:
- 数据包捕获:捕获流经网卡的原始数据包
- 自定义数据包发送:构造任何格式的原始数据包
- 流量采集与统计:采集网络中的流量信息
- 规则过滤:提供自带规则过滤功能,按需要选择过滤规则
它的应用范围非常广泛,典型应用包括玩罗协议分析器,网络流量发生器,网络入侵检测系统,网络扫描器和其他安全工具。
2.Libpcap的安装
Libpcap的下载地址:点击
切换到下载目录,解压压缩文件,配置,编译,安装
cd ****
tar zxvf ****
./configure
make
make install
配置中如果出现错误,请查看你是否安装了所有的依赖包bison, m4, GNU, flex以及libpcap-dev(安装方法 sudo apt-get ****)
注意运行时候,是需要root权限的 sudo ./***
测试程序:
 View Code
View Code
#include <pcap.h>
#include <stdio.h>
int main()
{
char errBuf[PCAP_ERRBUF_SIZE], * device;
device = pcap_lookupdev(errBuf);
if(device)
{
printf("success: device: %s\n", device);
}
else
{
printf("error: %s\n", errBuf);
}
return 0;
}
makefile文件:
test: test.c
gcc -Wall -o test test.c -lpcap
clean:
rm -rf *.o test
3.Libpcap的工作原理
作为捕捉网络数据包的库,它是一个独立于系统的用户级的API接口,为底层网络检测提供了一个可移植的框架。
一个包的捕捉分为三个主要部分,包括面向底层包捕获、面向中间层的数据包过滤和面向应用层的用户接口。这与Linux操作系统对数据包的处理流程是相同的(网卡->网卡驱动->数据链路层->IP层->传输层->应用程序)。包捕获机制是在数据链路层增加一个旁路处理(并不干扰系统自身的网络协议栈的处理),对发送和接收的数据包通过Linux内核做过滤和缓冲处理,最后直接传递给上层应用程序。
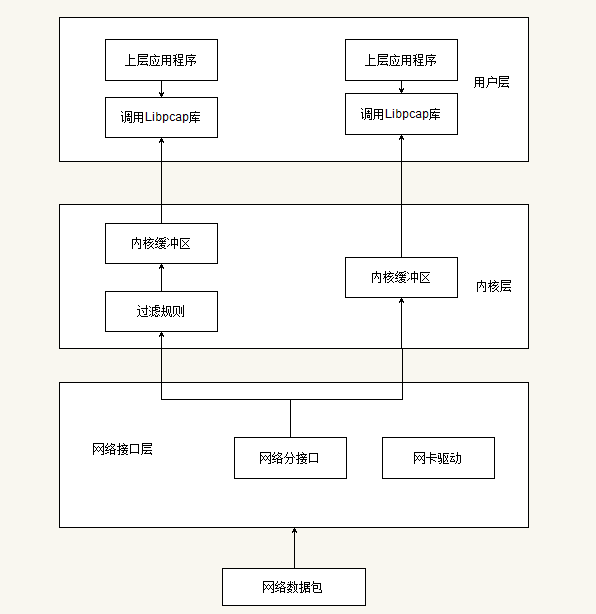
下面介绍Libpcap的抓包流程:
- 查找网络设备:目的是发现可用的网卡,实现的函数为pcap_lookupdev(),如果当前有多个网卡,函数就会返回一个网络设备名的指针列表。
- 打开网络设备:利用上一步中的返回值,可以决定使用哪个网卡,通过函数pcap_open_live()打开网卡,返回用于捕捉网络数据包的秒数字。
- 获得网络参数:这里是利用函数pcap_lookupnet(),可以获得指定网络设备的IP地址和子网掩码。
- 编译过滤策略:Lipcap的主要功能就是提供数据包的过滤,函数pcap_compile()来实现。
- 设置过滤器:在上一步的基础上利用pcap_setfilter()函数来设置。
- 利用回调函数,捕获数据包:函数pcap_loop()和pcap_dispatch()来抓去数据包,也可以利用函数pcap_next()和pcap_next_ex()来完成同样的工作。
- 关闭网络设备:pcap_close()函数关系设备,释放资源。
4.函数功能具体介绍与分析
1.获取网络接口
char * pcap_lookupdev(char * errbuf)
//上面这个函数返回第一个合适的网络接口的字符串指针,如果出错,则errbuf存放出错信息字符串,errbuf至少应该是PCAP_ERRBUF_SIZE个字节长度的
int pcap_lookupnet(const char * device, bpf_u_int32 * netp, bpf_u_int32 * maskp, char * errbuf) //可以获取指定设备的ip地址,子网掩码等信息 //netp:传出参数,指定网络接口的ip地址 //maskp:传出参数,指定网络接口的子网掩码 //pcap_lookupnet()失败返回-1
//net,mask的转换方式,inet_ntoa可以把他转换成10机制字符串 头文件 arpa/inet.h addr.s_addr=netp; net=inet_ntoa(addr); addr.s_addr=maskp; mask=inet_ntoa(addr);
举例:
 View Code
View Code
#include <stdio.h> #include <pcap.h> #include <time.h> #include <netinet/in.h> #include <arpa/inet.h> void show_ip_mask(char* dev) { char errbuf[1024]; struct in_addr addr; char *net,*mask; bpf_u_int32 netp,maskp; int err=pcap_lookupnet(dev,&netp,&maskp,errbuf); if(err==-1){ printf("couldn't detect the ip and maskp: %s\n",errbuf); return; } addr.s_addr=netp; net=inet_ntoa(addr); if(net==NULL){ printf("ip error\n"); return; } printf("ip: %s\n",net); addr.s_addr=maskp; mask=inet_ntoa(addr); if(mask==NULL){ printf("mask errorn"); return; } printf("mask: %s\n",mask); } int main() { char *dev, errbuf[1024]; char select='a'; printf("select(dispaly the packet in detail)/n:( Y/N ?))"); scanf("%c",&select); while(select!='Y'&&select!='y'&&select!='n'&&select!='N'){ printf("input the error!\nplease input the Y/N/y/n:"); scanf("%c",&select); } //look for the net device dev=pcap_lookupdev(errbuf); if(dev==NULL){ printf("couldn't find default device: %s\n",errbuf); return 1; } else{ printf("fidn success: device :%s\n",dev); } //ip mask display show_ip_mask(dev); return 0; }
2.释放网络接口
void pcap_close(pcap_t * p)
//该函数用于关闭pcap_open_live()获取的pcap_t的网络接口对象并释放相关资源。
3.打开网络接口
pcap_t * pcap_open_live(const char * device, int snaplen, int promisc, int to_ms, char * errbuf)
//上面这个函数会返回指定接口的pcap_t类型指针,后面的所有操作都要使用这个指针。
//第一个参数是第一步获取的网络接口字符串,可以直接使用硬编码。
//第二个参数是对于每个数据包,从开头要抓多少个字节,我们可以设置这个值来只抓每个数据包的头部,而不关心具体的内容。典型的以太网帧长度是1518字节,但其他的某些协议的数据包会更长一点,但任何一个协议的一个数据包长度都必然小于65535个字节。
//第三个参数指定是否打开混杂模式(Promiscuous Mode),0表示非混杂模式,任何其他值表示混合模式。如果要打开混杂模式,那么网卡必须也要打开混杂模式,可以使用如下的命令打开eth0混杂模式:ifconfig eth0 promisc
//第四个参数指定需要等待的毫秒数,超过这个数值后,第3步获取数据包的这几个函数就会立即返回。0表示一直等待直到有数据包到来。
//第五个参数是存放出错信息的数组。
4.获取数据包
u_char * pcap_next(pcap_t * p, struct pcap_pkthdr * h)
//如果返回值为NULL,表示没有抓到包
//第一个参数是第2步返回的pcap_t类型的指针
//第二个参数是保存收到的第一个数据包的pcap_pkthdr类型的指针
pcap_pkthdr类型的定义如下:
struct pcap_pkthdr
{
struct timeval ts; /* time stamp */
bpf_u_int32 caplen; /* length of portion present */
bpf_u_int32 len; /* length this packet (off wire) */
};
int pcap_loop(pcap_t * p, int cnt, pcap_handler callback, u_char * user)
//第一个参数是第2步返回的pcap_t类型的指针
//第二个参数是需要抓的数据包的个数,一旦抓到了cnt个数据包,pcap_loop立即返回。负数的cnt表示pcap_loop永远循环抓包,直到出现错误。
//第三个参数是一个回调函数指针,它必须是如下的形式:
void callback(u_char * userarg, const struct pcap_pkthdr * pkthdr, const u_char * packet)
//第一个参数是pcap_loop的最后一个参数,当收到足够数量的包后pcap_loop会调用callback回调函数,同时将pcap_loop()的user参数传递给它
//第二个参数是收到的数据包的pcap_pkthdr类型的指针
//第三个参数是收到的数据包数据
int pcap_dispatch(pcap_t * p, int cnt, pcap_handler callback, u_char * user)
//这个函数和pcap_loop()非常类似,只是在超过to_ms毫秒后就会返回(to_ms是pcap_open_live()的第4个参数)
来试试这几个函数,一个简单的例子:
#include <stdio.h>
#include <pcap.h>
#include <time.h>
void capture_packet1(pcap_t* device)
{
struct pcap_pkthdr packet;
char errbuf[1024];
//capture the packet
const u_char* pkt=pcap_next(device,&packet);
if(!pkt){
printf("couldn't capture packet: %s\n",errbuf);
return;
}
//output the pacaket length byte and time
printf("Packet length: %d\n", packet.len);
printf("Number of bytes: %d\n", packet.caplen);
printf("Recieved time: %s\n", ctime((const time_t*)&packet.ts.tv_sec));
}
void getPacket(u_char * arg, const struct pcap_pkthdr * pkthdr, const u_char * packet)
{
int * id = (int *)arg;
printf("id: %d\n", ++(*id));
printf("Packet length: %d\n", pkthdr->len);
printf("Number of bytes: %d\n", pkthdr->caplen);
printf("Recieved time: %s\n", ctime((const time_t *)&pkthdr->ts.tv_sec));
//print packet
int i;
for(i=0; i<pkthdr->len; ++i) {
printf(" %02x", packet[i]);
if( (i + 1) % 16 == 0 )
printf("\n");
}
printf("\n\n");
}
void capture_packet2(pcap_t* device)
{
struct pcap_pkthdr packet;
int id = 0;
//capture the packet
pcap_loop(device,-1,getPacket,(u_char*)&id);
}
int main()
{
char *dev, errbuf[1024];
char select='a';
printf("select(dispaly the packet in detail)/n:( Y/N ?))");
scanf("%c",&select);
while(select!='Y'&&select!='y'&&select!='n'&&select!='N'){
printf("input the error!\nplease input the Y/N/y/n:");
scanf("%c",&select);
}
//look for the net device
dev=pcap_lookupdev(errbuf);
if(dev==NULL){
printf("couldn't find default device: %s\n",errbuf);
return 1;
}
else{
printf("fidn success: device :%s\n",dev);
}
//open the finded device(must set :ifconfig eth0 promisc)
pcap_t* device=pcap_open_live(dev,65535,1,0,errbuf);
if(!device){
printf("couldn't open the net device: %s\n",errbuf);
return 1;
}
if(select=='Y')
capture_packet2(device);
else
while(1)//由于pcap_next()函数只返回下一个数据包的指针
capture_packet1(device);
return 0;
}
5.分析数据包
根据不同的网络协议,来设计不同的数据包分析方法,具体参考相关协议的说明。
6.过滤数据包(这部分是非常重要的)
libpcap利用BPF来过滤数据包。
过滤数据包需要完成3件事:
a) 构造一个过滤表达式
b) 编译这个表达式
c) 应用这个过滤器
a)Lipcap已经把BPF语言封装成为了更高级更容易的语法了。
举例:
src host 127.0.0.1 //选择只接受某个IP地址的数据包 dst port 8000 //选择只接受TCP/UDP的目的端口是80的数据包 not tcp //不接受TCP数据包 tcp[13]==0x02 and (dst port ** or dst port **) //只接受SYN标志位置(TCP首部开始的第13个字节)且目标端口号是22或23的数据包 icmp[icmptype]==icmp-echoreply or icmp[icmptype]==icmp-echo //只接受icmp的ping请求和ping响应的数据包 ehter dst 00:00:00:00:00:00 //只接受以太网MAC地址为00:00:00:00:00:00的数据包 ip[8]==5 //只接受ip的ttl=5的数据包(ip首位第八的字节为ttl)
b)构造完过滤表达式后,就可以使用pcap_compile()函数来编译。
int pcap_compile(pcap_t * p, struct bpf_program * fp, char * str, int optimize, bpf_u_int32 netmask) //fp:这是一个传出参数,存放编译后的bpf //str:过滤表达式 //optimize:是否需要优化过滤表达式 //metmask:简单设置为0即可
c)最后通过函数pcap_setfilter()来设置这个规则
int pcap_setfilter(pcap_t * p, struct bpf_program * fp) //参数fp就是pcap_compile()的第二个参数,存放编译后的bpf
举例:
可以在抓包前,也就是pcap_next()或pcap_loop之前,加入下面的代码:
//design filter struct bpf_program filter; pcap_compile(device, &filter, "dst port 80", 1, 0); //只接受80端口的TCP/UDP数据包 pcap_setfilter(device, &filter);
5.基于Libpcap实现一个网络数据包嗅探器
基本功能就是来捕获所有流经本网卡的数据包。
实现流程:
- 查找网络设备
- 打开网络设备
- 查找设备信息
- 输入过滤规则
- 编译输入规则
- 设置输入规则
- 开始捕获数据包
- 调用数据包分析模块
- 输出MAC,IP,协议以及数据帧
- 结束
具体实现代码:
#include <stdio.h> #include <pcap.h> #include <time.h> #include <netinet/in.h> #include <arpa/inet.h> #include <errno.h> #include <string.h> //链路层数据包格式 typedef struct { u_char DestMac[6]; u_char SrcMac[6]; u_char Etype[2]; }ETHHEADER; //IP层数据包格式 typedef struct { int header_len:4; int version:4; u_char tos:8; int total_len:16; int ident:16; int flags:16; u_char ttl:8; u_char proto:8; int checksum:16; u_char sourceIP[4]; u_char destIP[4]; }IPHEADER; //协议映射表 char *Proto[]={ "Reserved","ICMP","IGMP","GGP","IP","ST","TCP" }; //回调函数 void pcap_handle(u_char* user,const struct pcap_pkthdr* header,const u_char* pkt_data) { ETHHEADER *eth_header=(ETHHEADER*)pkt_data; printf("---------------Begin Analysis-----------------\n"); printf("----------------------------------------------\n"); printf("Packet length: %d \n",header->len); //解析数据包IP头部 if(header->len>=14){ IPHEADER *ip_header=(IPHEADER*)(pkt_data+14); //解析协议类型 char strType[100]; if(ip_header->proto>7) strcpy(strType,"IP/UNKNWN"); else strcpy(strType,Proto[ip_header->proto]); printf("Source MAC : %02X-%02X-%02X-%02X-%02X-%02X==>",eth_header->SrcMac[0],eth_header->SrcMac[1],eth_header->SrcMac[2],eth_header->SrcMac[3],eth_header->SrcMac[4],eth_header->SrcMac[5]); printf("Dest MAC : %02X-%02X-%02X-%02X-%02X-%02X\n",eth_header->DestMac[0],eth_header->DestMac[1],eth_header->DestMac[2],eth_header->DestMac[3],eth_header->DestMac[4],eth_header->DestMac[5]); printf("Source IP : %d.%d.%d.%d==>",ip_header->sourceIP[0],ip_header->sourceIP[1],ip_header->sourceIP[2],ip_header->sourceIP[3]); printf("Dest IP : %d.%d.%d.%d\n",ip_header->destIP[0],ip_header->destIP[1],ip_header->destIP[2],ip_header->destIP[3]); printf("Protocol : %s\n",strType); //显示数据帧内容 int i; for(i=0; i<(int)header->len; ++i) { printf(" %02x", pkt_data[i]); if( (i + 1) % 16 == 0 ) printf("\n"); } printf("\n\n"); } } int main(int argc, char **argv) { char *device="eth0"; char errbuf[1024]; pcap_t *phandle; bpf_u_int32 ipaddress,ipmask; struct bpf_program fcode; int datalink; if((device=pcap_lookupdev(errbuf))==NULL){ perror(errbuf); return 1; } else printf("device: %s\n",device); phandle=pcap_open_live(device,200,0,500,errbuf); if(phandle==NULL){ perror(errbuf); return 1; } if(pcap_lookupnet(device,&ipaddress,&ipmask,errbuf)==-1){ perror(errbuf); return 1; } else{ char ip[INET_ADDRSTRLEN],mask[INET_ADDRSTRLEN]; if(inet_ntop(AF_INET,&ipaddress,ip,sizeof(ip))==NULL) perror("inet_ntop error"); else if(inet_ntop(AF_INET,&ipmask,mask,sizeof(mask))==NULL) perror("inet_ntop error"); printf("IP address: %s, Network Mask: %s\n",ip,mask); } int flag=1; while(flag){ //input the design filter printf("Input packet Filter: "); char filterString[1024]; scanf("%s",filterString); if(pcap_compile(phandle,&fcode,filterString,0,ipmask)==-1) fprintf(stderr,"pcap_compile: %s,please input again....\n",pcap_geterr(phandle)); else flag=0; } if(pcap_setfilter(phandle,&fcode)==-1){ fprintf(stderr,"pcap_setfilter: %s\n",pcap_geterr(phandle)); return 1; } if((datalink=pcap_datalink(phandle))==-1){ fprintf(stderr,"pcap_datalink: %s\n",pcap_geterr(phandle)); return 1; } printf("datalink= %d\n",datalink); pcap_loop(phandle,-1,pcap_handle,NULL); return 0; }
参考资料:Linux c程序基础与实例讲解
http://blog.csdn.net/htttw/article/details/7521053
网络数据包捕获函数库Libpcap安装与使用(非常强大) 由 cococo点点 创作,采用 知识共享 署名-非商业性使用-相同方式共享 3.0 中国大陆 许可协议进行许可。欢迎转载,请注明出处:
转载自:cococo点点 http://www.cnblogs.com/coder2012

