跳表基于单链表实现,链表查找、插入、删除绝大部分时间花在遍历链表上,跳表使用索引来优化链表遍历的过程,使得跳表具有非常优秀的查找、插入、删除性能,并且是天然的动态数据结构
-
查找、插入、删除时间复杂度都是O(logn)
-
跳表原理的理解
-
二叉搜索通过计算mid的值,使得每一次要遍历的数据量减半,那么链表可不可以实现类似的功能呢
-
如果有一个指针指向链表中点,那么在搜索时先与中点比较,根据比较结果决定是从链表头开始遍历还是从中点开始遍历,这样平均每次要遍历的数据量就减少了一半
-
如果多设置几个索引,甚至设置多级索引,那么遍历链表所花费的时间将大大降低,而额外付出的空间不过是几个指针
-
跳表示意图
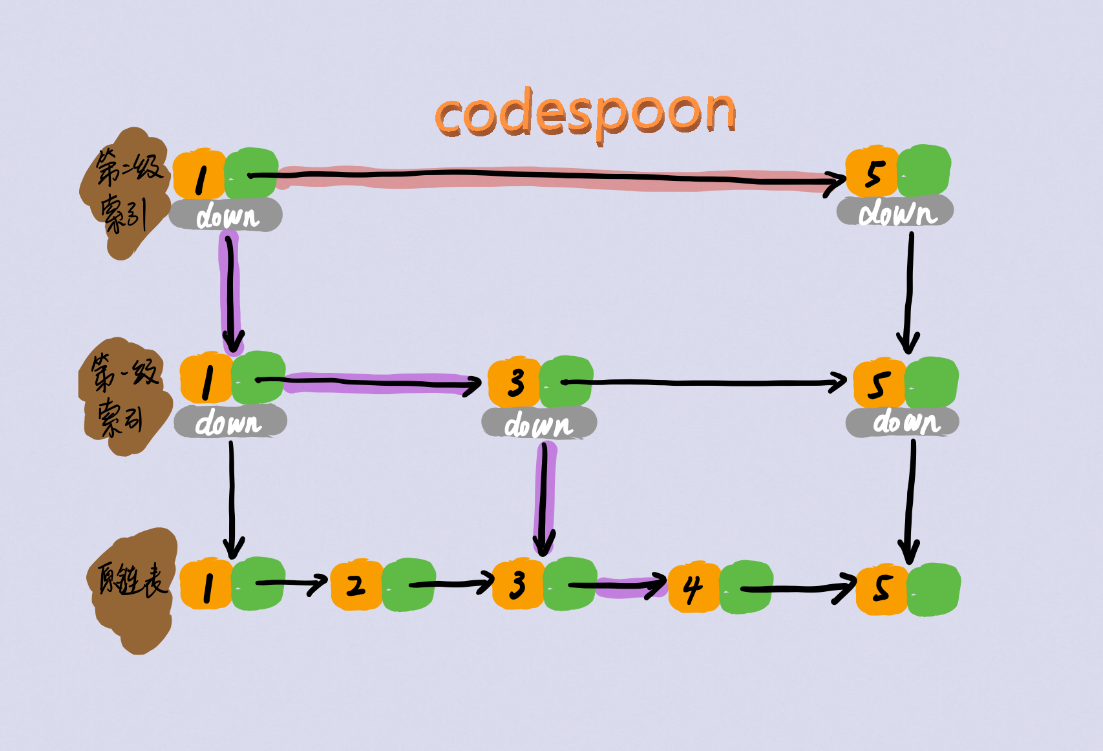
-
原链表查找4,需要1->2->3->4,而加了索引之后1->3->4;查找5更是只需1->5;在链表很大时跳表的查找效率会显著提高。
-
-
跳表实现上的注意点
-
与红黑树相比跳表的实现难度要简单不少,但还是有几处注意点
-
节点设置
-
数据(data):存储该节点数据
-
索引数组(forward[]):存储该节点各层的索引(每个索引也是一个节点),索引指是指向下一节点的指针
-
查找结点(值设为value)
-
-
实际上跳表实现的核心就是结点的查找
-
查找时从头节点、最上层索引开始
-
1.找到该层索引中data小于value的最大节点(这个节点后面的节点值要么等于value要么大于value)
-
2.若本层已经是第0层索引(也就是到了原链表)则此时的节点就是值小于等于value的最后一个节点,这个节点后面一个就是我们要找的值
-
3.若本层不是第0层索引,则去下一层,重复1-2-3过程
-
-
跳表的随机函数
-
数据不断的插入过程中,如果索引一直没有更新,考虑极端情况:所有数据都在两个索引之间,跳表退化为了链表
-
使用随机函数解决上述退化问题:在插入值新值时,不仅将新节点插入原链表,并且插入n层对应的索引
-
n是一个随机值,理论上要使得一级索引的数目为链表长度的n/2,二级索引的数目为n/4……
-
-
跳表Java实现(insert优化)
/**
* 跳表是在单链表的基础上加入索引,使查找效率大大提高的一种各方面性能都很优秀的数据结构
* 跳表存储正整数,且不重复
* @author hzk
*/
public class mySkipList {
private final int MAX_LEVEL = 16;//最大索引层数(0~原链表 15~最高一级索引)
private int levelCount = 1;//跳表当前索引层数
public Node head = new Node();//跳表头
/**
* 查找跳表中值为value的节点
*
* @param value 要查找的值
* @return 找到返回对应节点,否则返回null
*/
public Node find(int value) {
Node p = head;
//找到该层索引中小于value的最大节点
for (int i = levelCount - 1; i >= 0; i--) {
while (p.forwards[i] != null && p.forwards[i].data < value) {
p = p.forwards[i];
}
}
if (p.forwards[0] != null && p.forwards[0].data == value)
return p.forwards[0];
else
return null;
}
/**
* 将value插入跳表中
*
* @param value 待加入数据
*/
public void insert(int value) {
int level = randomLevel();
if (levelCount < level) levelCount = level;
Node p = head;
Node newNode = new Node();
newNode.data = value;
newNode.maxLevel = level;
Node path[] = new Node[level];//存储查找value时经过各层的索引
for (int i = level - 1; i >= 0; i--) {
while (p.forwards[i] != null && p.forwards[i].data < value) {
p = p.forwards[i];
}
path[i] = p;
}
//将value插入各层索引中
for (int i = level - 1; i >= 0; i--) {
newNode.forwards[i] = path[i].forwards[i];
path[i].forwards[i] = newNode;
}
}
/**
* insert的优化版本,去掉了path[]
* @param value 待加入数据
*/
public void insert_optimized(int value) {
int level = randomLevel();
if (levelCount < level) levelCount = level;
Node p = head;
Node newNode = new Node();
newNode.data = value;
newNode.maxLevel = level;
for (int i = level - 1; i >= 0; i--) {
while (p.forwards[i] != null && p.forwards[i].data < value)
p = p.forwards[i];
//这层索引是最后一个则直接插入
if (p.forwards[i] == null) {
p.forwards[i] = newNode;
}
//否则插在中间
else {
newNode.forwards[i] = p.forwards[i];
p.forwards[i] = newNode;
}
}
}
/**
* 删除跳表中值为value的节点及索引
*
* @param value 待删除结点的值
*/
public void delete(int value) {
Node path[] = new Node[levelCount];
Node p = head;
for (int i = levelCount - 1; i >= 0; i--) {
while (p.forwards[i] != null && p.forwards[i].data < value)
p = p.forwards[i];
path[i] = p;
}
//找到
if (p.forwards[0] != null && p.forwards[0].data == value) {
//删除节点所有索引
for (int i = levelCount - 1; i >= 0; i--) {
if (p.forwards[i] != null && p.forwards[i].data == value) {
p.forwards[i] = p.forwards[i].forwards[i];
}
}
}
}
/**
* 随机生成索引层数,索引层数和生成概率负相关
* 尽量使一级索引占全部索引的50%,二级索引占25%,三级索引占12.5%……
* 随机函数能防止链表数据全部集中在某两个索引之间
*
* @return
*/
private int randomLevel() {
int level = 1;
while (Math.random() < 0.5 && level < MAX_LEVEL)
level++;
return level;
}
public void printAll() {
Node p = head;
while (p.forwards[0] != null) {
System.out.print(p.forwards[0].data + " ");
p = p.forwards[0];
}
System.out.println();
}
public void skipListText() {
mySkipList list = new mySkipList();
list.insert(1);
list.insert(2);
list.insert(3);
list.printAll();
System.out.println(list.find(2));
list.delete(2);
list.printAll();
list.insert_optimized(2);
list.printAll();
}
public class Node {
private int data = -1;//节点数据
private Node forwards[] = new Node[MAX_LEVEL];//存储节点上层索引
private int maxLevel = 0;//最大索引层数
@Override
public String toString() {
StringBuilder builder = new StringBuilder();
builder.append("{ data: ");
builder.append(data);
builder.append("; levels: ");
builder.append(maxLevel);
builder.append(" }");
return builder.toString();
}
}
}