
在 http 配置块中,我们配置了 http 连接相关的信息,HTTP 框架也正是从这里启动的
在 nginx 初始化的过程中,执行了 ngx_init_cycle 函数,其中进行了配置文件解析,调用了 ngx_conf_parse 函数
函数 ngx_conf_handler 根据配置项的 command 调用了对应的 set 回调函数
// static ngx_command_t ngx_http_commands // http 模块命令结构 {{{ static ngx_command_t ngx_http_commands[] = { { ngx_string("http"), NGX_MAIN_CONF|NGX_CONF_BLOCK|NGX_CONF_NOARGS, ngx_http_block, 0, 0, NULL }, ngx_null_command }; // }}}
HTTP模块的总入口就是http{}命令集的回调函数:ngx_http_block
为所有的 http 模块都分配并创建了配置结构,同时,调用了每个模块相应的初始化回调
最后,调用 ngx_http_optimize_servers 创建了 http 连接,加入 cycle 的监听数组,并设为监听状态
nginx 配置文件对 http 模块的配置分为三层:main、sever、location,因此,http 模块上下文 ngx_http_module_t 中定义了以下六个回调函数,用来创建和保存配置信息
create_main_conf ------ init_main_conf -----create_srv_conf -----merge_srv_conf ------create_loc_conf ------ merge_loc_conf
在 ngx_http_block 中,循环调用了所有 NGX_HTTP_MODULE 的这六个回调函数,创建相关的配置结构
/* 4.3.1 解析HTTP配置的流程 图4-1是HTTP框架解析配置项的示意流程图(图中出现了ngx_http_module和ngx_ http_core_module模块,所谓的HTTP框架主要由这两个模块组成),下面解释图中每个流程 的意义。 1)图4-1中的主循环是指Nginx进程的主循环,主循环只有调用配置文件解析器才能 解析nginx.conf文件(这里的“主循环”是指解析全部配置文件的循环代码,图8-6的第4 步,为了便于理解,可以认为是Nginx框架代码在循环解析配置项)。 2)当发现配置文件中含有http{)关键字时,HTTP框架开始启动,这一过程详见10.7 节描述的ngx_http_block方法。 3) HTTP框架会初始化所有HTTP模块的序列号,并创建3个数组用于存储所有HTTP 模块的create—main- conf、create—srv—conf、create—loc—conf方法返回的指针地址,并把这3 个教组的地址保存到ngx_http_conf_ ctx-t结构中。 4)调用每个HTTP模块(当然也包括例子中的mytest模块)的create main conf. create—srv_conf. create一loc—conf(如果实现的话)方法。 5)把各HTTP模块上述3个方法返回的地址依次保存到ngx_http_conf ctx_t结构体的 3个数组中。 6)调用每个HTTP模块的preconfiguration方法(如果实现的话)。 7)注意,如果preconfiguration返回失败,那么Nginx进程将会停止。 8) HTTP框架开始循环解析nginx.conf文件中http{...}里面的所有配置项, 过程到第19步才会返回。 9)配置文件解析器在检测到1个配置项后,会遍历所有的HTTP模块, ngx_command_t数组中的name项是否与配置项名相同。 注意,这个 检查它们的 10)如果找到有1个HTTP模块(如mytest模块)对这个配置项感兴趣(如test- myconfig 配置项),就调用ngx_command_t结构中的set方法来处理。 11) set方法返回是否处理成功。如果处理失败,那么Nginx进程会停止。 12)配置文件解析器继续检测配置项。如果发现server{...)配置项,就会调用ngx_http_ core__ module模块来处理。因为ngx_http_core__ module模块明确表示希望处理server{}块下 的配置项。注意,这次调用到第18步才会返回。 13) ngx_http_core_module棋块在解析server{...}之前,也会如第3步一样建立ngx_ http_conf_ctx_t结构,并建立数组保存所有HTTP模块返回的指针地址。然后,它会调用每 个HTTP模块的create—srv_ conf、create- loc—conf方法(如果实现的话)。 14)将上一步各HTTP模块返回的指针地址保存到ngx_http_conf_ ctx-t对应的数组中。 15)开始调用配置文件解析器来处理server{...}里面的配置项,注意,这个过程在第17 步返回。 16)继续重复第9步的过程,遍历nginx.conf中当前server{...)内的所有配置项。 17)配置文件解析器继续解析配置项,发现当前server块已经遍历到尾部,说明server 块内的配置项处理完毕,返回ngx_http_core__ module模块。 18) http core模块也处理完server配置项了,返回至配置文件解析器继续解析后面的配 置项。 19)配置文件解析器继续解析配置项,这时发现处理到了http{...)的尾部,返回给 HTTP框架继续处理。 20)在第3步和第13步,以及我们没有列幽来的某些步骤中(如发现其他server块 或者location块),都创建了ngx_http_conf_ ctx_t结构,这时将开始调用merge_srv_conf、 merge_loc_conf等方法合并这些不同块(http、server、location)中每个HTTP模块分配的数 据结构。 21) HTTP框架处理完毕http配置项(也就是ngx_command_t结构中的set回调方法处 理完毕),返回给配置文件解析器继续处理其他http{...}外的配置项。 22)配置文件解析器处理完所有配置项后会告诉Nginx主循环配置项解析完毕,这时 Nginx才会启动Web服务器。 注意 图4-1并没有列出解析location{...)块的流程,实际上,解析location与解析 server并没有本质上的区别,为了简化起见,没有把它画到图中。 图形化参考:4.3.1 解析HTTP配置的流程图4-1 */ //从ngx_http_module模块里面的http命令解析走到这里 /* cf空间始终在一个地方,就是ngx_init_cycle中的conf,使用中只是简单的修改conf中的ctx指向已经cmd_type类型,然后在解析当前{}后,重新恢复解析当前{}前的配置 参考"http" "server" "location"ngx_http_block ngx_http_core_server ngx_http_core_location ngx_http_core_location */ static char * ngx_http_block(ngx_conf_t *cf, ngx_command_t *cmd, void *conf) //这里的cf是从ngx_conf_handler里面的if (cmd->type & NGX_DIRECT_CONF)判断里面确定了该cf为 {//图形化参考:深入理解NGINX中的图9-2 图10-1 图4-2,结合图看,并可以配合http://tech.uc.cn/?p=300看 char *rv; ngx_uint_t mi, m, s; ngx_conf_t pcf; ngx_http_module_t *module; ngx_http_conf_ctx_t *ctx; ngx_http_core_loc_conf_t *clcf; ngx_http_core_srv_conf_t **cscfp; ngx_http_core_main_conf_t *cmcf; /* the main http context */ ctx = ngx_pcalloc(cf->pool, sizeof(ngx_http_conf_ctx_t)); if (ctx == NULL) { return NGX_CONF_ERROR; } //conf为ngx_conf_handler中的conf = confp[ngx_modules[i]->ctx_index];也就是conf指向的是ngx_cycle_s->conf_ctx[], //所以对conf赋值就是对ngx_cycle_s中的conf_ctx赋值 *(ngx_http_conf_ctx_t **) conf = ctx; //图形化参考:深入理解NGINX中的图9-2 图10-1 图4-2,结合图看,并可以配合http://tech.uc.cn/?p=300看 /* count the number of the http modules and set up their indices */ ngx_http_max_module = 0; for (m = 0; ngx_modules[m]; m++) { if (ngx_modules[m]->type != NGX_HTTP_MODULE) { continue; } ngx_modules[m]->ctx_index = ngx_http_max_module++; //二级类型按照在ngx_modules中的顺序排序 } /* the http main_conf context, it is the same in the all http contexts */ ctx->main_conf = ngx_pcalloc(cf->pool, sizeof(void *) * ngx_http_max_module); if (ctx->main_conf == NULL) { return NGX_CONF_ERROR; } /* * the http null srv_conf context, it is used to merge * the server{}s' srv_conf's */ ctx->srv_conf = ngx_pcalloc(cf->pool, sizeof(void *) * ngx_http_max_module); if (ctx->srv_conf == NULL) { return NGX_CONF_ERROR; } /* * the http null loc_conf context, it is used to merge * the server{}s' loc_conf's */ ctx->loc_conf = ngx_pcalloc(cf->pool, sizeof(void *) * ngx_http_max_module); if (ctx->loc_conf == NULL) { return NGX_CONF_ERROR; } /* * create the main_conf's, the null srv_conf's, and the null loc_conf's * of the all http modules */ //执行所有ngx_modules[m]->type = NGX_HTTP_MODULE的http模块的crate函数来创建对应模块的conf参数,用于后面保存从配置文件中解析出的参数信息 //http{}下为所有的NGX_HTTP_MODULES模块开辟了main srv loc空间 //按照模块类型进行合并 http{} server{} location{}都属于同一个ngx_http_core_module模块,他们的init_main_conf都是一样的 /* http { xxxx server { location /xxx { } } } 这种情况的配置文件,在执行到http的时候开辟ngx_http_conf_ctx_t会分别调用一次main crv loc_creat,执行到server时开辟ngx_http_conf_ctx_t会调用srv_creat loc_creat, 执行到location时开辟ngx_http_conf_ctx_t会调用一次loc_creat 所以这种情况会调用1次main_creat 2才srv_creat 3次loc_creat。 http { xxxx server { location /xxx { } } server { location /yyy { } } } 这种情况的配置文件,在执行到http的时候开辟ngx_http_conf_ctx_t会分别调用一次main crv loc_creat,执行到server时开辟ngx_http_conf_ctx_t会调用srv_creat loc_creat, 执行到location时开辟ngx_http_conf_ctx_t会调用一次loc_creat 所以这种情况会调用1次main_creat 1+2才srv_creat 1+2+2次loc_creat。 需要ngx_http_block ngx_http_core_server ngx_http_core_location配合看代码可以看出来 */ for (m = 0; ngx_modules[m]; m++) { //注意这里为所有的NGX_HTTP_MODULE开辟了main_conf srv_conf loc_conf空间,也就是在http{}的时候为所有main srv loc开辟了空间 if (ngx_modules[m]->type != NGX_HTTP_MODULE) { //http{}相关配置结构创建首先需要执行ngx_http_core_module,而后才能执行对应的http子模块 continue; } module = ngx_modules[m]->ctx; mi = ngx_modules[m]->ctx_index; //mi实际上是依次递增的,见签名的ctx_index赋值处 if (module->create_main_conf) { ctx->main_conf[mi] = module->create_main_conf(cf); if (ctx->main_conf[mi] == NULL) { return NGX_CONF_ERROR; } } if (module->create_srv_conf) { ctx->srv_conf[mi] = module->create_srv_conf(cf); if (ctx->srv_conf[mi] == NULL) { return NGX_CONF_ERROR; } } if (module->create_loc_conf) { ctx->loc_conf[mi] = module->create_loc_conf(cf); if (ctx->loc_conf[mi] == NULL) { return NGX_CONF_ERROR; } } } pcf = *cf; //零时保存在解析到http{}时候,在这之前的cf cf->ctx = ctx;//零时指向这块新分配的ctx,为存储ngx_http_core_commands开辟的空间 //执行各个模块的preconfiguration for (m = 0; ngx_modules[m]; m++) { if (ngx_modules[m]->type != NGX_HTTP_MODULE) { continue; } module = ngx_modules[m]->ctx; if (module->preconfiguration) { if (module->preconfiguration(cf) != NGX_OK) { return NGX_CONF_ERROR; } } } /* parse inside the http{} block */ cf->module_type = NGX_HTTP_MODULE; cf->cmd_type = NGX_HTTP_MAIN_CONF; rv = ngx_conf_parse(cf, NULL); if (rv != NGX_CONF_OK) { goto failed; } /* * init http{} main_conf's, merge the server{}s' srv_conf's * and its location{}s' loc_conf's */ cmcf = ctx->main_conf[ngx_http_core_module.ctx_index]; //见ngx_http_core_create_main_conf cscfp = cmcf->servers.elts;//一级main_conf中的server中保存的所有二级server结构信息 for (m = 0; ngx_modules[m]; m++) { //按照模块类型进行合并 http{} server{} location{}都属于同一个ngx_http_core_module模块,他们的init_main_conf都是一样的 if (ngx_modules[m]->type != NGX_HTTP_MODULE) { continue; } module = ngx_modules[m]->ctx; mi = ngx_modules[m]->ctx_index; /* init http{} main_conf's */ if (module->init_main_conf) { rv = module->init_main_conf(cf, ctx->main_conf[mi]); //见ngx_http_core_init_main_conf if (rv != NGX_CONF_OK) { goto failed; } } //cf->ctx为http{}的上下文ctx,cmcf为server{}中的所有上下文ctx rv = ngx_http_merge_servers(cf, cmcf, module, mi);//合并server{}及其以下的local{} if (rv != NGX_CONF_OK) { goto failed; } } /* create location trees */ /* 经过配置的读取之后,所有server都被保存在http core模块的main配置中的servers数组中,而每个server里面的location都被按配置中 出现的顺序保存在http core模块的loc配置的locations队列中,上面的代码中先对每个server的location进行排序和分类处理,这一步 发生在 ngx_http_init_location()函数中: */ for (s = 0; s < cmcf->servers.nelts; s++) { /* clcf是server块下的ngx_http_core_loc_conf_t结构体,locations成员以双向链表关联着隶属于这个server块的所有location块对应的ngx_http_core_loc_conf_t结构体 */ //cscfp[]->ctx就是解析到二级server{}时所在的上下文ctx clcf = cscfp[s]->ctx->loc_conf[ngx_http_core_module.ctx_index];//每个server中的loc空间,其实他也是该server下location{}中的loc空间的头部,参考ngx_http_add_location /* 将ngx_http_core_loc_conf_t组成的双向链表按照location匹配字符串进行排序。注意:这个操作是递归进行的,如果某个location块下还具有其他location,那么它的locations链表也会被排序 */ if (ngx_http_init_locations(cf, cscfp[s], clcf) != NGX_OK) { //srver{}下所有loc空间(包括server自己的以及其下的location),这里的clcf是解析到server{}行的时候创建的loc_conf return NGX_CONF_ERROR; } /* 根据已经按照location字符串排序过的双向链表,快速地构建静态的二叉查找树。与ngx_http_init_locations方法类似,速个操作也是递归进行的 */ /* 下面的ngx_http_init_static_location_trees函数就会将那些普通的location(就是ngx_http_init_locations中name noname regex以外的location(exact/inclusive)), 即staticlocation,进行树化(一种三叉树)处理,之所以要做这样的处理,是为了在处理http请求时能高效的搜索的匹配的location配置。 */ /* 根据已经按照location字符串排序过的双向链表,快速地构建静态的三叉查找树。与ngx_http_init_locations方法类似,速个操作也是递归进行的 */ //clcf中现在只有普通staticlocation if (ngx_http_init_static_location_trees(cf, clcf) != NGX_OK) { return NGX_CONF_ERROR; } } if (ngx_http_init_phases(cf, cmcf) != NGX_OK) { return NGX_CONF_ERROR; } if (ngx_http_init_headers_in_hash(cf, cmcf) != NGX_OK) { return NGX_CONF_ERROR; } for (m = 0; ngx_modules[m]; m++) { if (ngx_modules[m]->type != NGX_HTTP_MODULE) { continue; } module = ngx_modules[m]->ctx; if (module->postconfiguration) { if (module->postconfiguration(cf) != NGX_OK) { return NGX_CONF_ERROR; } } } if (ngx_http_variables_init_vars(cf) != NGX_OK) { return NGX_CONF_ERROR; } /* * http{}'s cf->ctx was needed while the configuration merging * and in postconfiguration process */ *cf = pcf;//恢复到上层的ngx_conf_s地址 if (ngx_http_init_phase_handlers(cf, cmcf) != NGX_OK) { return NGX_CONF_ERROR; } /* optimize the lists of ports, addresses and server names */ if (ngx_http_optimize_servers(cf, cmcf, cmcf->ports) != NGX_OK) { return NGX_CONF_ERROR; } return NGX_CONF_OK; failed: *cf = pcf; return rv; }
2、初始化监听socket(ngx_listening_t)
在http模块初始化中,我们介绍了在函数ngx_http_block函数中调用ngx_http_optimize_servers函数完成ngx_listening_t初始化,下面看一下这个函数的实现。
这个函数就是遍历所有的端口号,将端口号对应的地址结构的hash、wc_head和wc_tail初始化,这个在初始化后面的ngx_listening_t的servers字段时会用到。然后调用ngx_http_init_listening函数完成ngx_listening_t初始化。
static ngx_int_t ngx_http_optimize_servers(ngx_conf_t *cf, ngx_http_core_main_conf_t *cmcf, ngx_array_t *ports) { ngx_uint_t p, a; ngx_http_conf_port_t *port; ngx_http_conf_addr_t *addr; if (ports == NULL) { return NGX_OK; } port = ports->elts; for (p = 0; p < ports->nelts; p++) { //将addrs排序,带通配符的地址排在后面, (listen 1.2.2.2:30 bind) > listen 1.1.1.1:30 > listen *:30 ngx_sort(port[p].addrs.elts, (size_t) port[p].addrs.nelts, sizeof(ngx_http_conf_addr_t), ngx_http_cmp_conf_addrs); /* * check whether all name-based servers have the same * configuration as a default server for given address:port */ addr = port[p].addrs.elts; for (a = 0; a < port[p].addrs.nelts; a++) { /* 多个server{}下面有listen IP:port ,并且每个server{}中的端口都相等,则他们保存在同一个port[i]中,只是ip地址不一样,以addrs区分 */ if (addr[a].servers.nelts > 1 #if (NGX_PCRE) || addr[a].default_server->captures #endif ) { //相同端口,不同IP地址对应的server{},把每个server中的server_names配置进行hash存储 /* * 初始addr(ngx_http_conf_addr_t)中的hash、wc_head和wc_tail哈希表。 * 这些哈希表以server name(虚拟主机名)为key,server块的ngx_http_core_srv_conf_t为 * value,用于在处理请求时,根据请求的host请求行快速找到处理该请求的server配置结构。 */ if (ngx_http_server_names(cf, cmcf, &addr[a]) != NGX_OK) { return NGX_ERROR; } } } if (ngx_http_init_listening(cf, &port[p]) != NGX_OK) { return NGX_ERROR; } } return NGX_OK; }
3. ngx_http_init_listening
static ngx_int_t ngx_http_init_listening(ngx_conf_t *cf, ngx_http_conf_port_t *port) { ngx_uint_t i, last, bind_wildcard; ngx_listening_t *ls; ngx_http_port_t *hport; ngx_http_conf_addr_t *addr; addr = port->addrs.elts; last = port->addrs.nelts; /* * If there is a binding to an "*:port" then we need to bind() to * the "*:port" only and ignore other implicit bindings. The bindings * have been already sorted: explicit bindings are on the start, then * implicit bindings go, and wildcard binding is in the end. //例如有listen 80(implicit bindings); listen *:80,则第一个无效,直接用第二个就行了 */ if (addr[last - 1].opt.wildcard) { //"*:port" addr是拍了序的,见ngx_http_optimize_servers,最后面的是通配符 addr[last - 1].opt.bind = 1; //如果是通配符,这里把bind值1 bind_wildcard = 1; //表示有通配符listen } else { bind_wildcard = 0; } i = 0; /* 这个函数就是遍历某个端口port对应的所有address,如果所有address中不包含通配符,则对所有的address:port调用ngx_http_add_listening分配一 个listen结构和ngx_http_port_t结构,并初始化它们。如果存在address包含通配符,则如果address:port需要bind,分配一个listen结构和 ngx_http_port_t结构,并初始化它们,对所有address:port不需要bind的,它们和包含通配符*:port共同使用一个listen结构和ngx_http_port_t结构, 并且listen结构中包含的地址是*:port,所以最好bind的地址是*:port。所有的listen都会存放在全局变量ngx_cycle的listening数组中,这样后面就 可以利用这些address:port信息建立每个套接字了。 */ while (i < last) { //last代表的是address:port的个数, 如果没有通配符配置项,则有多少个last,就有多少次循环。bind=1的有多少次就执行多少次,如果有通配符和bind = 0的listen配置, //则在后面的if (bind_wildcard && !addr[i].opt.bind)进行continue,也就是这些未精确配置项合在一起在后面置执行一次分配ngx_http_port_t空间,把他们算在 //addr[i]中,这里的i是通配符所在位置。 //对所有address:port不需要bind的,它们和包含通配符*:port共同使用一个listen结构和ngx_http_port_t结构, 并且listen结构中包含的地址是*:port,所以最好bind的地址是*:port if (bind_wildcard && !addr[i].opt.bind) { //如果是通配符*:port,或者是listen配置没有加bind参数 i++;//如果有通配符配置,并且bind = 0则把这些bind=0和通配符配置算作一项,执行后面的操作。通配符的bind在该函数前面置1,见addr[last - 1].opt.bind = 1 continue; } //为该listen创建对应的ngx_listening_t结构并赋值 ls = ngx_http_add_listening(cf, &addr[i]); if (ls == NULL) { return NGX_ERROR; } hport = ngx_pcalloc(cf->pool, sizeof(ngx_http_port_t)); if (hport == NULL) { return NGX_ERROR; } /* * servers会用来保存虚拟主机的信息,在处理请求时会赋值给request 用于进行虚拟主机的匹配 */ ls->servers = hport; //如果是未精确配置的listen(bind = 0并且有配置一项通配符,则这里的i是通配符所在addr[]的位置),如果没有配置通配符,则有多少个listen配置就会执行这里多少次。 //只是在出现通配符listen的配置中,把未精确配置的所有项合到通配符所在addr[]位置 hport->naddrs = i + 1; //保护listen通配符配置,并且没有bind的listen项数 switch (ls->sockaddr->sa_family) { #if (NGX_HAVE_INET6) case AF_INET6: if (ngx_http_add_addrs6(cf, hport, addr) != NGX_OK) { return NGX_ERROR; } break; #endif default: /* AF_INET */ if (ngx_http_add_addrs(cf, hport, addr) != NGX_OK) { //后面有addr++,所以这里的addr对应的是addr[i]的地址 return NGX_ERROR; } break; } if (ngx_clone_listening(cf, ls) != NGX_OK) { return NGX_ERROR; } addr++; last--; } return NGX_OK; } //ngx_event_process_init //master进程执行ngx_clone_listening中如果配置了多worker,监听80端口会有worker个listen赋值,master进程在ngx_open_listening_sockets //中会监听80端口worker次,那么子进程创建起来后,不是每个字进程都关注这worker多个 listen事件了吗?为了避免这个问题,nginx通过 //在子进程运行ngx_event_process_init函数的时候,通过ngx_add_event来控制子进程关注的listen,最终实现只关注master进程中创建的一个listen事件
4、 打开并配置监听socket
在nginx启动过程中,介绍过在ngx_init_cycle函数中,会调用ngx_open_listening_sockets和ngx_configure_listening_sockets函数完成监听socket的打开和配置,
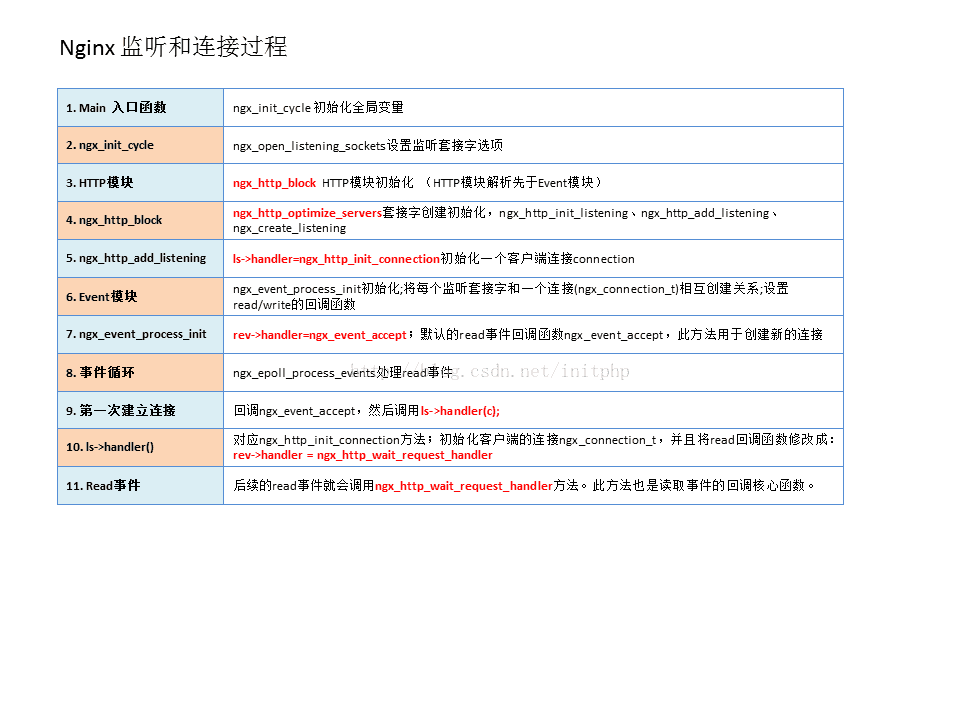
5、Nginx socket连接的过程
1. 在Nginx main函数的ngx_init_cycle()方法中,调用了ngx_open_listening_sockets函数,这个函数负责将创建的监听套接字进行套接字选项的设置(比如非阻塞、接受发送的缓冲区、绑定、监听处理)
2. HTTP模块初始化优先于Event模块,HTTP模块通过ngx_http_block()方法进行初始化,然后调用ngx_http_optimize_servers()进行套接字的创建和
初始化(ngx_http_init_listening、ngx_http_add_listening、ngx_create_listening)。根据每一个IP地址:port这种配置创建监听套接字。
3. ngx_http_add_listening函数,还会将ls->handler监听套接字的回调函数设置为ngx_http_init_connection。ngx_http_init_connection此函数主要初始化一个客户端连接connection。
4. Event模块的初始化主要调用ngx_event_process_init()函数。该函数每个worker工作进程都会初始化调用。然后设置read/write的回调函数。
5. ngx_event_process_init函数中,会将接收客户端连接的事件,设置为rev->handler=ngx_event_accept方法,ngx_event_accept方法,只有在第一次客户端和Nginx服务端创建连接关系的时候调用。
6. 当客户端有连接上来,Nginx工作进程就会进入事件循环(epoll事件循环函数:ngx_epoll_process_events),发现有read读取的事件,则会调用ngx_event_accept函数。
7. 调用ngx_event_accept函数,会调用ngx_get_connection方法,得到一个客户端连接结构:ngx_connection_t结构。ngx_event_accept函数最终会调用监听套接字的handler回调函数,ls->handler(c); 。
8. 从流程3中,我们知道ls->handler的函数对应ngx_http_init_connection方法。此方法主要初始化客户端的连接ngx_connection_t,并将客户端连接read读取事件的回调函数修改成rev->handler = ngx_http_wait_request_handler
9. 也就是说,当客户端连接上来,第一次事件循环的read事件会调用回调函数:ngx_event_accept函数;而后续的read事件的handler已经被ngx_http_init_connection方法修改掉,
改成了ngx_http_wait_request_handler函数了。所以客户端的读取事件都会走ngx_http_wait_request_handler函数。
10. ngx_http_wait_request_handler函数也是整个HTTP模块的数据处理的入口函数了。
reading from code and ---->
https://blog.csdn.net/initphp/article/details/53728970
https://blog.csdn.net/chosen0ne/article/details/7754608