1.布局与控件的关系
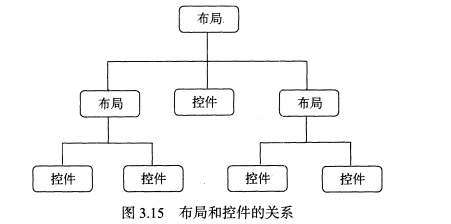
2.布局
为了适应不同的界面风格,Android系统为开发人员提供了五种常用布局:
- 线性布局:LinearLayout
- 相对布局:RelativeLayout
- 帧布局:FrameLayout
- 表格布局:TableLayout
- 绝对布局:AbsoluteLayout
(1)线性布局(LinearLayout)
线性布局在实际开发中比较常用,主要以水平和垂直方式来显示界面中的控件。当空间水平排列时,显示顺序依次从左到右,当控件垂直排列时,显示顺序一次从上到下。
- android∶orientation属性指定了排列方向是vertical.如果指定的是horizontal,控件就会在水平方向上排列了。
- 需要注意的是:如果LinearLayout的排列方向是horizontal(水平的),内部的控件就绝对不能将宽度设置为match_parent。反之同理
①android:layout_gravity属性:
这个属性与android:gravity相似:
- android∶gravity 用于指定文字在控件中的对齐方式
- 而android∶layout_gravity用于指定控件在布局中的对齐方式。
- android∶layout gravity的可选值和 android∶gravity差不多,但是需要注意,当LinearLayout的排列方向是horizontal时,只有垂直方向上的对齐方式才会生效,因为此时水平方向上的长度是不固定的,每添加一个控件,水平方向上的长度都会改变,因而无法指定该方向上的对齐方式。同样的道理,当LinearLayout的排列方向是vertical时,只有水平方向上的对齐方式才会生效。
示例:三个水平排列的按钮,分别给三个对齐方式
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?> <LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android" xmlns:app="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res-auto" xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools" android:layout_width="match_parent" android:layout_height="match_parent" android:orientation="horizontal" tools:context=".MainActivity"> <Button android:id="@+id/button1" android:layout_width="wrap_content" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:text="button1" android:layout_gravity="top" ></Button> <Button android:id="@+id/button2" android:layout_width="wrap_content" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:text="button2" android:layout_gravity="center_vertical" ></Button> <Button android:id="@+id/button3" android:layout_width="wrap_content" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:text="button3" android:layout_gravity="bottom" ></Button> </LinearLayout>

②android:layout_weight
这个属性允许我们使用比例的方式来指定控件的大小,在手机屏幕适配方面有重要作用
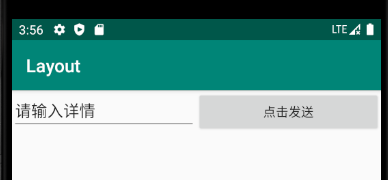
示例:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?> <LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android" xmlns:app="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res-auto" xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools" android:layout_width="match_parent" android:layout_height="match_parent" android:orientation="horizontal" tools:context=".MainActivity"> <EditText android:id="@+id/edittext" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:layout_width="0dp" android:layout_weight="1" android:text="请输入详情"></EditText> <Button android:id="@+id/send" android:layout_weight="1" android:layout_width="0dp" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:text="点击发送"></Button> </LinearLayout>
说明:
- 这里竟然将 EditTxt和Buton的宽度都指定成了0dp,由于我们使用了android∶layout _weight属性,此时控件的宽度就不应该再由android∶layout_width 来决定,这里指定成0dp是一种比较规范的写法。
- 另外,dp是Android中用于指定控件大小、间距等属性的单位,后面我们还会经常用到它。
- 然后在 EditText和 Button里都将 android∶layout_weight 属性的值指定为1,这表示EditText和 Button将在水平方向平分宽度。
- 原理:
- 为什么将android∶layout weight属性的值同时指定为1就会平分屏幕宽度呢?
- 系统会先把LinearLayout下所有控件指定的layout weight 值相加,得到一个总值,然后每个控件所占大小的比例就是用该控件的layout weight 值除以刚才算出的总值。
- 为什么将android∶layout weight属性的值同时指定为1就会平分屏幕宽度呢?
效果:
(2)相对布局(RelativeLayout)——默认布局
- Android程序创建时,默认采用的就是相对布局,相对布局是通过相对定位的方式指定控件位置,即以其他控件或者父容器为参照物,摆放控件位置。
- 在设计相对布局时,要遵循控件之间的依赖关系,后放入的控件的位置依赖于先放入的控件。
- 它可以通过相对定位的方式让控件出现在布局的任何位置。
- 也正因为如此,RelativeLayout 中的属性非常多,不过这些属性都是有规律可循的,其实并不难理解和记忆。
示例1:
1 <?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?> 2 <RelativeLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android" 3 xmlns:app="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res-auto" 4 xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools" 5 android:layout_width="match_parent" 6 android:layout_height="match_parent" 7 android:orientation="horizontal" 8 tools:context=".MainActivity"> 9 10 <Button 11 android:id="@+id/button1" 12 android:layout_height="wrap_content" 13 android:layout_width="wrap_content" 14 android:layout_alignParentLeft="true" 15 android:layout_alignParentTop="true" 16 android:text="button1"></Button> 17 18 <Button 19 android:id="@+id/button2" 20 android:layout_height="wrap_content" 21 android:layout_width="wrap_content" 22 android:layout_alignParentRight="true" 23 android:layout_alignParentTop="true" 24 android:text="button2"></Button> 25 26 <Button 27 android:id="@+id/button3" 28 android:layout_height="wrap_content" 29 android:layout_width="wrap_content" 30 android:layout_centerInParent="true" 31 android:text="button3"></Button> 32 33 <Button 34 android:id="@+id/button4" 35 android:layout_height="wrap_content" 36 android:layout_width="wrap_content" 37 android:layout_alignParentLeft="true" 38 android:layout_alignParentBottom="true" 39 android:text="button4"></Button> 40 41 <Button 42 android:id="@+id/button5" 43 android:layout_height="wrap_content" 44 android:layout_width="wrap_content" 45 android:layout_alignParentRight="true" 46 android:layout_alignParentBottom="true" 47 android:text="button5"></Button> 48 49 </RelativeLayout>
效果:

说明:
- button1和父布局左上角对齐
- button2和父布局右上角对齐
- button4和父布局左下角对齐
- button5和父布局右下角对齐
- button3在父布局中间对齐
示例2:控件相对于控件排列
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?> <RelativeLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android" xmlns:app="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res-auto" xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools" android:layout_width="match_parent" android:layout_height="match_parent" android:orientation="horizontal" tools:context=".MainActivity"> <Button android:id="@+id/button3" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:layout_width="wrap_content" android:layout_centerInParent="true" android:text="button3"></Button> <Button android:id="@+id/button1" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:layout_width="wrap_content" android:layout_above="@+id/button3" android:layout_toLeftOf="@+id/button3" android:text="button1"></Button> <Button android:id="@+id/button2" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:layout_width="wrap_content" android:layout_above="@+id/button3" android:layout_toRightOf="@+id/button3" android:text="button2"></Button> <Button android:id="@+id/button4" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:layout_width="wrap_content" android:layout_below="@+id/button3" android:layout_toLeftOf="@+id/button3" android:text="button4"></Button> <Button android:id="@+id/button5" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:layout_width="wrap_content" android:layout_below="@+id/button3" android:layout_toRightOf="@+id/button3" android:text="button5"></Button> </RelativeLayout>
效果:
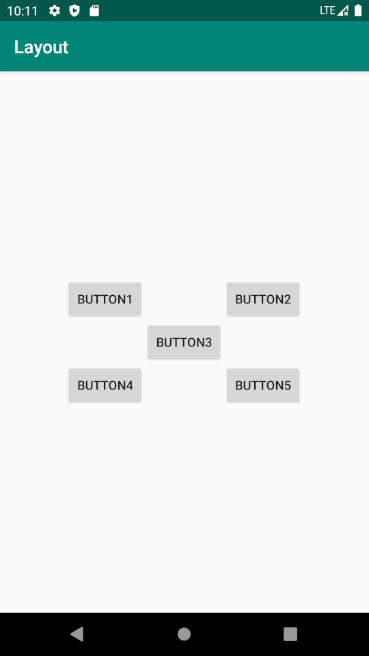
注意:当一个控件去引用另一个控件的 id 时,该控件一定要定义在引用控件的后面,不然会出现找不到id的情况。重新运行程序,效果如图3.22所示。
常用控件属性:
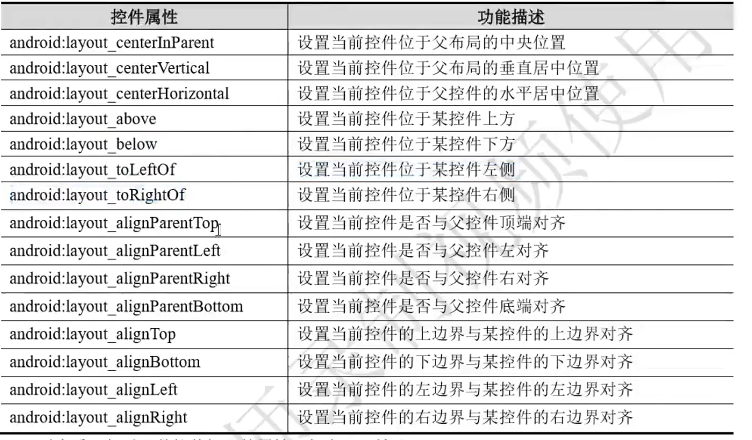
所有控件见官网
(3)帧布局(FrameLayout)
- 帧布局是Android中最为简单的一种布局,该布局为每个加入其中的控件创建一个空白区域(称为一帧,每个控件占据一帧)。
- 采用帧布局的方式设计页面时,所有的控件都默认显示在屏幕左上角,并且按照先后顺序重叠摆放,先放入的控件显示在最底层,后放入的控件显示在最顶层,重叠摆放。
- 帧布局适用于图层设计,例如应用图表上信息提示数量。帧布局的大小由内部最大控件决定。
示例:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?> <FrameLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android" xmlns:app="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res-auto" xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools" android:layout_width="match_parent" android:layout_height="match_parent" android:orientation="horizontal" tools:context=".MainActivity"> <TextView android:id="@+id/text1" android:layout_width="wrap_content" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:text="这时一个TextView" android:layout_gravity="left"></TextView> <ImageView android:id="@+id/image_view" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:layout_width="wrap_content" android:src="@mipmap/ic_launcher" android:layout_gravity="right"></ImageView> </FrameLayout>
效果:

(4)百分比布局
- 在这种布局中,我们可以不再使用wrap_content、match_parent等方式来指定控件的大小,而是允许直接指定控件在布局中所占的百分比,这样的话就可以轻松实现平分布局甚至是任意比例分割布局的效果了。
- 由于LinearLayout本身已经支持按比例指定控件的大小了,因此百分比布局只为Frame-Layout和RelativeLayout 进行了功能扩展,提供了PercentFrameLayout和PercentRelativeLayout 这两个全新的布局。
- 不同于前3种布局,百分比布局属于新增布局,那么怎么才能做到让新增布局在所有Android 版本上都能使用呢?
- 为此,Android团队将百分比布局定义在了support库当中,我们只需要在项目的build.gradle中添加百分比布局库的依赖,就能保证百分比布局在Android所有系统版本上的兼容性了
此工件及其类已弃用。请改用 ConstraintLayout 和关联布局。