19 二叉树的镜像
递归实现
public class Solution { public void Mirror(TreeNode root) { if(root == null || (root.left == null && root.right == null)){ return; } TreeNode temp = root.left; root.left = root.right; root.right = temp; if(root.left != null){ Mirror(root.left); } if(root.right != null){ Mirror(root.right); } } }
循环实现

import java.util.Stack; public class Solution { public void Mirror(TreeNode root) { if(root == null){ return; } Stack<TreeNode> stack = new Stack<TreeNode>(); stack.push(root); while(!stack.isEmpty()){ TreeNode node = stack.pop(); if(node.left != null||node.right != null){ TreeNode temp = node.left; node.left = node.right; node.right = temp; } if(node.left!=null){ stack.push(node.left); } if(node.right!=null){ stack.push(node.right); } } } }
20 顺时针打印矩阵

import java.util.ArrayList; public class Solution { public ArrayList<Integer> printMatrix(int [][] matrix) { ArrayList<Integer> result = new ArrayList<Integer> (); if(matrix.length==0) return result; int row = matrix.length,col = matrix[0].length; if(col==0) return result; // 定义四个关键变量,表示左上和右下的打印范围 int left = 0, top = 0, right = col - 1, bottom = row - 1; while(left <= right && top <= bottom){ // left to right for (int i = left; i <= right; ++i) result.add(matrix[top][i]); // top to bottom for (int i = top + 1; i <= bottom; ++i) result.add(matrix[i][right]); // right to left if (top != bottom) for (int i = right - 1; i >= left; --i) result.add(matrix[bottom][i]); // bottom to top if (left != right) for (int i = bottom - 1; i > top; --i) result.add(matrix[i][left]); left++;top++;right--;bottom--; } return result; } }

class Solution { public: vector<int> printMatrix(vector<vector<int> > matrix) { int row = matrix.size(); int col = matrix[0].size(); vector<int> res; // 输入的二维数组非法,返回空的数组 if (row == 0 || col == 0) return res; // 定义四个关键变量,表示左上和右下的打印范围 int left = 0, top = 0, right = col - 1, bottom = row - 1; while (left <= right && top <= bottom) { // left to right for (int i = left; i <= right; ++i) res.push_back(matrix[top][i]); // top to bottom for (int i = top + 1; i <= bottom; ++i) res.push_back(matrix[i][right]); // right to left if (top != bottom) for (int i = right - 1; i >= left; --i) res.push_back(matrix[bottom][i]); // bottom to top if (left != right) for (int i = bottom - 1; i > top; --i) res.push_back(matrix[i][left]); left++,top++,right--,bottom--; } return res; } };
21 包含min函数的栈
Stack实现

import java.util.Stack; public class Solution { Stack<Integer> stack1 = new Stack<Integer>(); Stack<Integer> stack2 = new Stack<Integer>(); public void push(int node) { stack1.push(node); if(stack2.isEmpty() || node < stack2.peek()){ stack2.push(node); }else{ stack2.push(stack2.peek()); } } public void pop() { assert(!stack1.isEmpty() && !stack2.isEmpty()); stack1.pop(); stack2.pop(); } public int top() { return stack1.peek(); } public int min() { return stack2.peek(); } }
ArrayList实现

import java.util.ArrayList; public class Solution { ArrayList<Integer> list = new ArrayList<Integer>(); public void push(int node) { list.add(0,node); } public void pop() { list.get(0); list.remove(0); } public int top() { return list.get(0).intValue(); } public int min() { int temp = top(); for(int i=1;i<list.size();i++){ if(temp>list.get(i).intValue()){ temp = list.get(i).intValue(); } } return temp; } }
22 栈的压入、弹出序列
Stack实现
import java.util.ArrayList; import java.util.Stack; public class Solution { public boolean IsPopOrder(int [] pushA,int [] popA) { boolean bResult = false; int nLength = pushA.length; if(pushA != null && popA != null && nLength>0){ int nextpush =0; int nextpop = 0; Stack<Integer> stackData = new Stack<Integer>(); while(nextpop < nLength){ while(stackData.empty() || stackData.peek() != popA[nextpop]){ if(nextpush == nLength){ break; } stackData.push(pushA[nextpush]); nextpush++; } if(stackData.peek() != popA[nextpop]){ break; } stackData.pop(); nextpop++; } if(stackData.empty() && nextpop == nLength){ bResult = true; } } return bResult; } }
23 从上往下打印二叉树
按层打印,实际就是广度优先搜索 BFS, 借助一个队列就可以实现.
广度优先搜索 BFS:主要借助一个队列、一个布尔类型数组、邻接矩阵完成(判断一个点是否查看过,用于避免重复到达同一个点,造成死循环等),先将各点以及各点的关系存入邻接矩阵。
再从第一个点开始,将一个点存入队列,然后在邻接表中找到他的相邻点,存入队列,每次pop出队列头部并将其打印出来(文字有些抽象,实际过程很简单),整个过程有点像往水中投入石子水花散开。
public class Solution { public ArrayList<Integer> PrintFromTopToBottom(TreeNode root) { ArrayList<Integer> list = new ArrayList<>(); ArrayList<TreeNode> queue = new ArrayList<>(); if (root == null) { return list; } queue.add(root); while (queue.size() != 0) { TreeNode temp = queue.remove(0); if (temp.left != null){ queue.add(temp.left); } if (temp.right != null) { queue.add(temp.right); } list.add(temp.val); } return list; } }
扩展:
广度优先遍历一个有向图,同样可以基于队列实现。树是图的一种特殊退化形式,从上到下按层遍历二叉树,本质上就是广度优先遍历二叉树。
24 二叉搜索树的后序遍历序列
后序遍历:先遍历子结点,再遍历父结点。在后序遍历得到的序列中,最后一个数字是树的根结点。
public class Solution { public boolean VerifySquenceOfBST(int [] sequence) { if(sequence == null || sequence.length <= 0){ return false; } int root = sequence[sequence.length-1]; int[] sequenceleft = new int[sequence.length]; int[] sequenceright = new int[sequence.length]; //在二叉搜索树中左子树的结点小于结点 int i=0; for(;i<sequence.length -1;++i){ if(sequence[i] > root){ break; } sequenceleft[i] = sequence[i]; } //早二叉搜索树中右子树的结点大于根结点 int j=i; int k=0; for(;j < sequence.length -1;++j){ if(sequence[j] < root){ return false; } k++; sequenceright[k] = sequence[j]; } //判断左子树是不是二叉搜索树 boolean left = true; if(i>0){ left = VerifySquenceOfBST(sequenceleft); } boolean right = true; if(i<sequence.length-1){ right = VerifySquenceOfBST(sequenceright); } return (left && right); } }
前中后序遍历
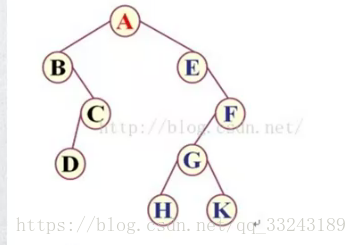
前、中、后指的是根节点的顺序。前序遍历有根节点开始。
前序遍历:ABCDEFGHK
中序遍历:BDCAEHGKF
后序遍历:DCBHKGFEA
中序排列思想:

25 二叉树中和为某一值的路径
public class Solution { public ArrayList<ArrayList<Integer>> FindPath(TreeNode root,int target) { ArrayList<ArrayList<Integer>> paths=new ArrayList<ArrayList<Integer>>(); if(root==null)return paths; find(paths,new ArrayList<Integer>(),root,target); return paths; } public void find(ArrayList<ArrayList<Integer>> paths,ArrayList<Integer> path,TreeNode root,int target){ path.add(root.val); if(root.left==null&&root.right==null){ if(target==root.val){ paths.add(path); } return; } ArrayList<Integer> path2=new ArrayList<>(); path2.addAll(path); if(root.left!=null)find(paths,path,root.left,target-root.val); if(root.right!=null)find(paths,path2,root.right,target-root.val); } }
import java.util.ArrayList; import java.util.Stack; /** public class TreeNode { int val = 0; TreeNode left = null; TreeNode right = null; public TreeNode(int val) { this.val = val; } } */ public class Solution { public ArrayList<ArrayList<Integer>> FindPath(TreeNode root,int target) { ArrayList<ArrayList<Integer>> pathList= new ArrayList<ArrayList<Integer>>(); if(root==null) return pathList; Stack<Integer> stack=new Stack<Integer>(); FindPath(root,target,stack,pathList ); return pathList; } private void FindPath(TreeNode root, int target, Stack<Integer> path, ArrayList<ArrayList<Integer>> pathList) { if(root==null) return; if(root.left==null&&root.right==null){ if(root.val==target){ ArrayList<Integer> list= new ArrayList<Integer>(); for(int i:path){ list.add(new Integer(i)); } list.add(new Integer(root.val)); pathList.add(list); } } else{ path.push(new Integer(root.val)); FindPath(root.left, target-root.val, path, pathList); FindPath(root.right, target-root.val, path, pathList); path.pop(); } } }
26 复杂链表的复制
分治法,通常分治法的思路都可以用递归实现
在复杂链表的结点中,除了有指向下一个结点的指针,还有指向任意结点的指针。、
/* public class RandomListNode { int label; RandomListNode next = null; RandomListNode random = null; RandomListNode(int label) { this.label = label; } } */ public class Solution { public RandomListNode Clone(RandomListNode pHead) { CloneNodes(pHead); ConnectSiblingNodes(pHead); return ReconnectNodes(pHead); } void CloneNodes(RandomListNode pHead){ RandomListNode pNode = pHead; while(pNode != null){ RandomListNode pCloned = new RandomListNode(pNode.label); pCloned.next = pNode.next; pCloned.random = null; pNode.next = pCloned; pNode = pCloned.next; } } void ConnectSiblingNodes(RandomListNode pHead){ RandomListNode pNode = pHead; while(pNode!= null){ RandomListNode pCloned = pNode.next; if(pNode.random != null){ pCloned.random = pNode.random.next; } pNode = pCloned.next; } } RandomListNode ReconnectNodes(RandomListNode pHead){ RandomListNode pNode = pHead; RandomListNode pClonedHead = null; RandomListNode pClonedNode = null; if(pNode != null){ pClonedNode = pNode.next; pClonedHead = pClonedNode; pNode.next = pClonedNode.next; pNode = pNode.next; } while(pNode != null){ pClonedNode.next = pNode.next; pClonedNode = pClonedNode.next; pNode.next = pClonedNode.next; pNode = pNode.next; } return pClonedHead; } }
27 二叉搜索树与双向链表
二叉搜索树:左子结点的值小于父结点的值,右子节点的值大于父结点的值。
直接递归
public class Solution { public TreeNode Convert(TreeNode pRootOfTree) { if(pRootOfTree == null) return pRootOfTree; pRootOfTree = ConvertNode(pRootOfTree); while(pRootOfTree.left!= null) pRootOfTree = pRootOfTree.left; return pRootOfTree; } TreeNode ConvertNode(TreeNode root) { if(root == null) return root; if(root.left != null) { TreeNode left = ConvertNode(root.left); while(left.right!= null) left = left.right; left.right = root; root.left = left; } if(root.right != null) { TreeNode right = ConvertNode(root.right); while(right.left!= null) right = right.left; right.left = root; root.right = right; } return root; } }
此解法暂时未通过
public class Solution { public TreeNode Convert(TreeNode pRootOfTree) { TreeNode pLastNodeInList = null; ConvertNode(pRootOfTree, pLastNodeInList); //pLastNodeInList双向链表尾结点 //需要返回头结点 TreeNode pHeadOfList = pLastNodeInList; while(pHeadOfList != null && pHeadOfList.left != null){ pHeadOfList = pHeadOfList.left; } return pHeadOfList; } void ConvertNode(TreeNode pNode, TreeNode pLastNodeInList){ if(pNode == null){ return; } TreeNode pCurrent = pNode; if(pCurrent.left != null){ ConvertNode(pCurrent.left, pLastNodeInList); } pCurrent.left = pLastNodeInList; if(pLastNodeInList != null){ pLastNodeInList.right = pCurrent; } pLastNodeInList = pCurrent; if(pCurrent.right != null){ ConvertNode(pCurrent.right,pLastNodeInList); } } }
28 字符串的排列
解法一:递归
import java.util.ArrayList; import java.util.Collections; import java.util.Set; import java.util.HashSet; public class Solution { public ArrayList<String> Permutation(String str) { ArrayList<String> list = new ArrayList<String>(); if(str!=null && str.length()>0){ PermutationHelper(str.toCharArray(),0,list); Collections.sort(list); } return list; } private void PermutationHelper(char[] chars,int i,ArrayList<String> list){ if(i == chars.length-1){ list.add(String.valueOf(chars)); }else{ Set<Character> charSet = new HashSet<Character>(); for(int j=i;j<chars.length;++j){ if(j==i || !charSet.contains(chars[j])){ charSet.add(chars[j]); swap(chars,i,j); PermutationHelper(chars,i+1,list); swap(chars,j,i); } } } } private void swap(char[] cs,int i,int j){ char temp = cs[i]; cs[i] = cs[j]; cs[j] = temp; } }
解法二:字典序排列算法
import java.util.ArrayList; import java.util.Arrays; public class Solution { public ArrayList<String> Permutation(String str) { ArrayList<String> list = new ArrayList<String>(); if(str==null || str.length()==0){ return list; } char[] chars = str.toCharArray(); Arrays.sort(chars); list.add(String.valueOf(chars)); int len = chars.length; while(true){ int lIndex = len-1; int rIndex; while(lIndex>=1 && chars[lIndex-1]>=chars[lIndex]){ lIndex--; } if(lIndex == 0) break; rIndex = lIndex; while(rIndex<len && chars[rIndex]>chars[lIndex-1]){ rIndex++; } swap(chars,lIndex-1,rIndex-1); reverse(chars,lIndex); list.add(String.valueOf(chars)); } return list; } private void reverse(char[] chars,int k){ if(chars==null || chars.length<=k) return; int len = chars.length; for(int i=0;i<(len-k)/2;i++){ int m = k+i; int n = len-1-i; if(m<=n){ swap(chars,m,n); } } } private void swap(char[] cs,int i,int j){ char temp = cs[i]; cs[i] = cs[j]; cs[j] = temp; } }
参考:
https://www.cnblogs.com/cxjchen/p/3932949.html
https://www.cnblogs.com/pmars/archive/2013/12/04/3458289.html
