本篇博文接上篇的《Android项目开发全程(一)--创建工程》,主要介绍一下在本项目中用到的一个很重要的框架-Afinal,由于本系列博文重点是项目开发全程,所以在这里就先介绍一下本项目中用到的几个功能:
Afinal简介
- Afinal 是一个android的sqlite orm 和 ioc 框架。同时封装了android中的http框架,使其更加简单易用;
- 使用finalBitmap,无需考虑bitmap在android中加载的时候oom的问题和快速滑动的时候图片加载位置错位等问题。
- Afinal的宗旨是简洁,快速。约定大于配置的方式。尽量一行代码完成所有事情。
Afinal的四大模块
-
FinalDB模块:android中的orm框架,一行代码就可以进行增删改查。支持一对多,多对一等查询。
-
FinalActivity模块:android中的ioc框架,完全注解方式就可以进行UI绑定和事件绑定。无需findViewById和setClickListener等。
-
FinalHttp模块:通过httpclient进行封装http数据请求,支持ajax方式加载。
-
FinalBitmap模块:通过FinalBitmap,imageview加载bitmap的时候无需考虑bitmap加载过程中出现的oom和android容器快速滑动时候出现的图片错位等现象。FinalBitmap可以配置线程加载线程数量,缓存大小,缓存路径,加载显示动画等。FinalBitmap的内存管理使用lru算法,没有使用弱引用(android2.3以后google已经不建议使用弱引用,android2.3后强行回收软引用和弱引用,详情查看android官方文档),更好的管理bitmap内存。FinalBitmap可以自定义下载器,用来扩展其他协议显示网络图片,比如ftp等。同时可以自定义bitmap显示器,在imageview显示图片的时候播放动画等(默认是渐变动画显示)。
使用Afinal开发框架需要用到以下权限
<uses-permission android:name="android.permission.INTERNET" /> <uses-permission android:name="android.permission.WRITE_EXTERNAL_STORAGE" />
以上是github上的Afinal整体介绍,下面介绍一下本项目中需要到的几个功能,由于本次项目很小,仅仅用到了Afinal中的一点点功能:
1、注解方式就可以进行UI绑定和事件绑定,无需使用findViewById和setClickListener等方法,别忘了让Activity继承FinalActivity。
1 public class TestActivity extends FinalActivity { 2 @ViewInject(id=R.id.bn_click, click="testClick") Button bnClick; 3 @ViewInject(id=R.id.tv_show) TextView tvShow; 4 @Override 5 protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) { 6 // TODO Auto-generated method stub 7 super.onCreate(savedInstanceState); 8 setContentView(R.layout.test_main); 9 } 10 public void testClick(View v){ 11 tvShow.setText("您点击了确定"); 12 } 13 }
运行结果:
 点击确定后->
点击确定后-> 
2、FinalHttp的使用,接下来就要开挂了,还是用刚才的Activity,稍作修改让我们来做一下网络请求
get方法: 一行代码搞定,直接使用get方法提交请求地址,然后在相关的回调方法中进行结果操作。上面代码给出了三个回调方法
1 public class TestActivity extends FinalActivity { 2 FinalHttp fh; 3 String url = "http://xiaohua.hao.360.cn/m/itxt?page=1"; 4 @ViewInject(id=R.id.bn_click, click="testClick") Button bnClick; 5 @ViewInject(id=R.id.tv_show) TextView tvShow; 6 @Override 7 protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) { 8 // TODO Auto-generated method stub 9 super.onCreate(savedInstanceState); 10 setContentView(R.layout.test_main); 11 fh = new FinalHttp(); 12 } 13 public void testClick(View v){ 14 fh.get(url, new AjaxCallBack<String>(){ 15 @Override 16 public void onStart() { 17 // TODO Auto-generated method stub 18 super.onStart(); 19 tvShow.setText("正在请求……"); 20 } 21 22 @Override 23 public void onLoading(long count, long current) { 24 // TODO Auto-generated method stub 25 super.onLoading(count, current); 26 //请求响应过程中会执行此方法,每隔1秒自动回调一次 27 tvShow.setText(current + "/" + count); 28 } 29 30 @Override 31 public void onSuccess(String t) { 32 // TODO Auto-generated method stub 33 super.onSuccess(t); 34 tvShow.setText(t); 35 } 36 37 @Override 38 public void onFailure(Throwable t, int errorNo, String strMsg) { 39 // TODO Auto-generated method stub 40 super.onFailure(t, errorNo, strMsg); 41 tvShow.setText("网络异常"); 42 } 43 }); 44 } 45 }
post方法:
1 AjaxParams params = new AjaxParams(); 2 params.put("username", "testname"); 3 params.put("password", "123456"); 4 params.put("profile_picture", new File("/mnt/sdcard/test.jpg")); // 上传文件 5 params.put("profile_picture2", inputStream); // 上传数据流 6 params.put("profile_picture3", new ByteArrayInputStream(bytes)); // 提交字节流 7 8 fh.post("http://www.test.com", params, new AjaxCallBack(){......});
① onStart()请求开始时回调此方法。
② onSuccess()请求成功时回调此方法,其中“t”为返回结果。
③ onFailure()请求失败时回调此方法。
④ onLoading()在请求响应过程中,每隔1秒回调一次此方法。
执行结果如下:

3、FinalBitmap的使用。同样,加载网络图片也是就一行代码 fb.display(imageView,url)。
1 public void loadingImg(View v){ 2 FinalBitmap fb = FinalBitmap.create(this); 3 fb.display(ivImg, "http://pic4.nipic.com/20091120/805653_183746006558_2.jpg"); 4 }
其中,loadingImg方法是用注解方式绑定在按钮上的事件,ivImg是ImageView控件。点击按钮后就会加载一张网络图片,结果如下:
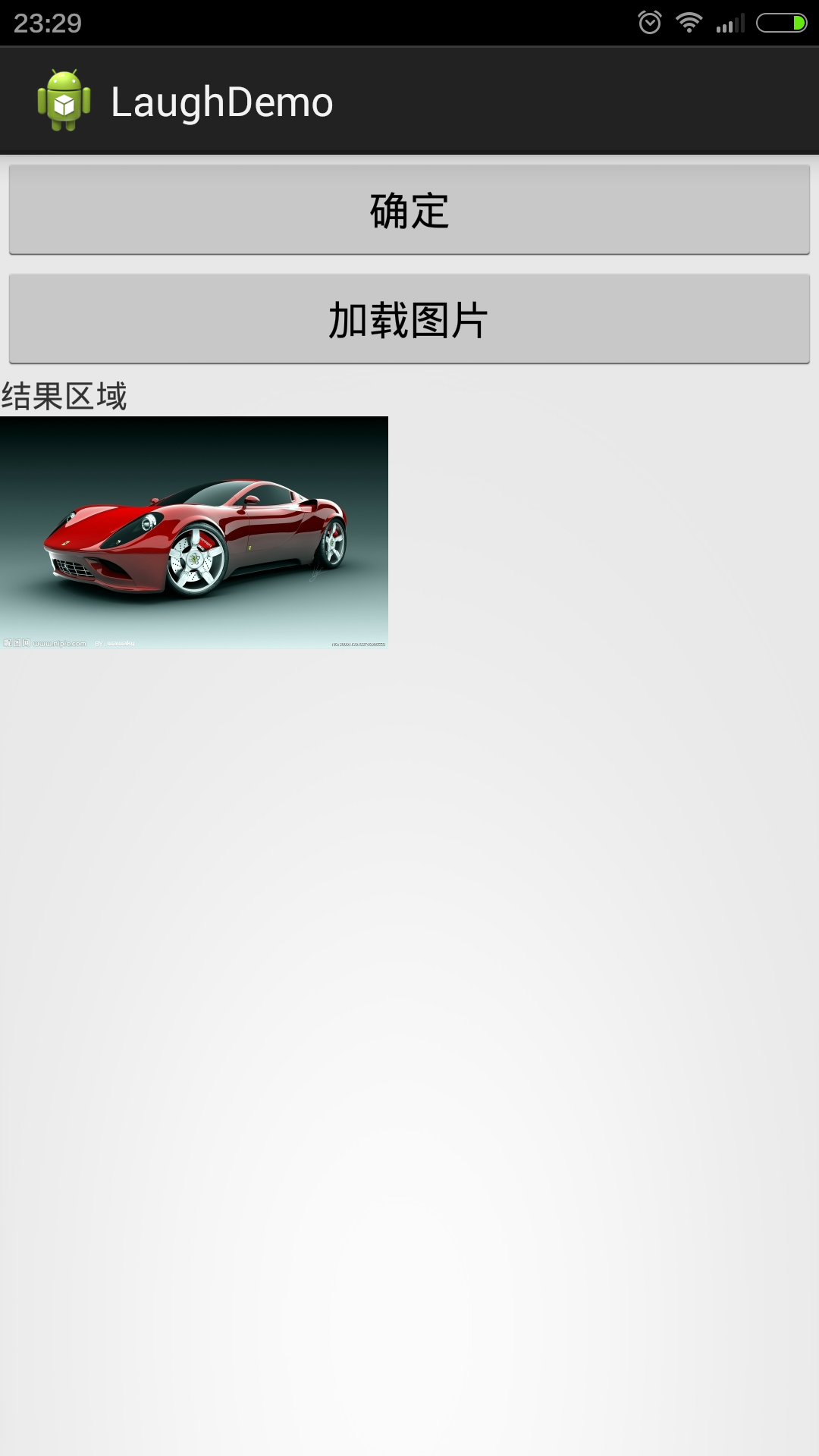
哈哈,是不是很简单,同时也很给力啊!
本项目目前设计到Afinal的一些用法就这几个,如果想了解更多可以参考:http://www.oschina.net/p/afinal
在项目开中还涉及到了另一个很给力的工具--Jackson,暂时先不介绍了,等在项目中需要到的时候再做介绍。
有了这两样工具,我们的开发工作就大大简化了很多,而且性能绝不比自己纯手工去写网络请求之类的方法性能差。当然,在实际的开发中我们不能这样暴力式的直接使用get和post方法,最好是做一下封装,这样的话既节省了工作量,减少重复代码,又保证了请求方式的规范性,在后续博文中会展开项目的详细介绍。
PS:本来打算只介绍上面这么多呢,因为在将要介绍到的项目中目前只用到上面这几个功能,不过有园友建议再介绍一下FinalDb,OK,再续上一段。
4、FinalDb的使用。
其实用Afinal操作数据也是非常方便的,仍然很好的体现着Afinal的风格,一行代码实现保存数据/读取数据。
首先建立一个实体对象,用来充当数据表角色。
1 public class Note { 2 private int id;//id属性必须要有 3 private String title; 4 private String content; 5 6 /* getter and setter方法一定要有,应为FinalDb会通过setter方法赋值*/ 7 public int getId() { 8 return id; 9 } 10 public String getTitle() { 11 return title; 12 } 13 public String getContent() { 14 return content; 15 } 16 public void setId(int id) { 17 this.id = id; 18 } 19 public void setTitle(String title) { 20 this.title = title; 21 } 22 public void setContent(String content) { 23 this.content = content; 24 } 25 }
实体类建好了,再写一个测试Activity:
1 public class DbTestActivity extends FinalActivity { 2 FinalDb fd; 3 Note note; 4 @ViewInject(id=R.id.et_title) EditText etTitle; 5 @ViewInject(id=R.id.et_content) EditText etContent; 6 @ViewInject(id=R.id.txt_title) TextView txtTitle; 7 @ViewInject(id=R.id.txt_content) TextView txtContent; 8 @ViewInject(id=R.id.bn_save, click="saveData") Button bnSave; 9 @ViewInject(id=R.id.bn_read, click="readData") Button bnRead; 10 @Override 11 protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) { 12 // TODO Auto-generated method stub 13 super.onCreate(savedInstanceState); 14 setContentView(R.layout.activity_dbtest); 15 fd = FinalDb.create(this); 16 } 17 18 //利用Afinal注解直接在按钮上绑定事件。 19 public void saveData(View v){ 20 dbSave(); 21 } 22 23 public void readData(View v){ 24 dbRead(); 25 } 26 27 private void dbSave(){ 28 note = new Note(); 29 note.setTitle(etTitle.getText().toString()); 30 note.setContent(etContent.getText().toString()); 31 //利用FinalDb的save方法保存数据 32 fd.save(note); 33 } 34 35 private void dbRead(){ 36 //利用FinalDb的findAll方法查询数据 37 List<Note> noteList = fd.findAll(Note.class); 38 txtTitle.setText("标题:" + noteList.get(0).getTitle()); 39 txtContent.setText("内容:" + noteList.get(0).getContent()); 40 } 41 }
布局文件也很简单,也一并贴出来吧。
1 <LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android" 2 xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools" 3 android:id="@+id/container" 4 android:layout_width="match_parent" 5 android:layout_height="match_parent" 6 android:orientation="vertical"> 7 8 <EditText 9 android:id="@+id/et_title" 10 android:layout_width="match_parent" 11 android:layout_height="wrap_content" 12 android:hint="Input title" 13 android:ems="10" > 14 <requestFocus /> 15 </EditText> 16 17 <EditText 18 android:id="@+id/et_content" 19 android:layout_width="match_parent" 20 android:layout_height="wrap_content" 21 android:hint="Input content" 22 android:ems="10" > 23 </EditText> 24 25 <Button 26 android:id="@+id/bn_save" 27 android:layout_width="fill_parent" 28 android:layout_height="wrap_content" 29 android:text="保存到数据库" /> 30 31 <Button 32 android:id="@+id/bn_read" 33 android:layout_width="fill_parent" 34 android:layout_height="wrap_content" 35 android:text="读取数据" /> 36 37 <TextView 38 android:id="@+id/txt_title" 39 android:layout_width="wrap_content" 40 android:layout_height="wrap_content" 41 android:text="标题:" /> 42 43 <TextView 44 android:id="@+id/txt_content" 45 android:layout_width="wrap_content" 46 android:layout_height="wrap_content" 47 android:text="内容:" /> 48 49 </LinearLayout>
执行结果如图,在编辑框输入内容后,单击保存到数据库按钮,程序会执行fd.save方法(如左图),然后我们单击读取数据按钮,就会从数据库中读取出来数据,并显示在下面(如右图)
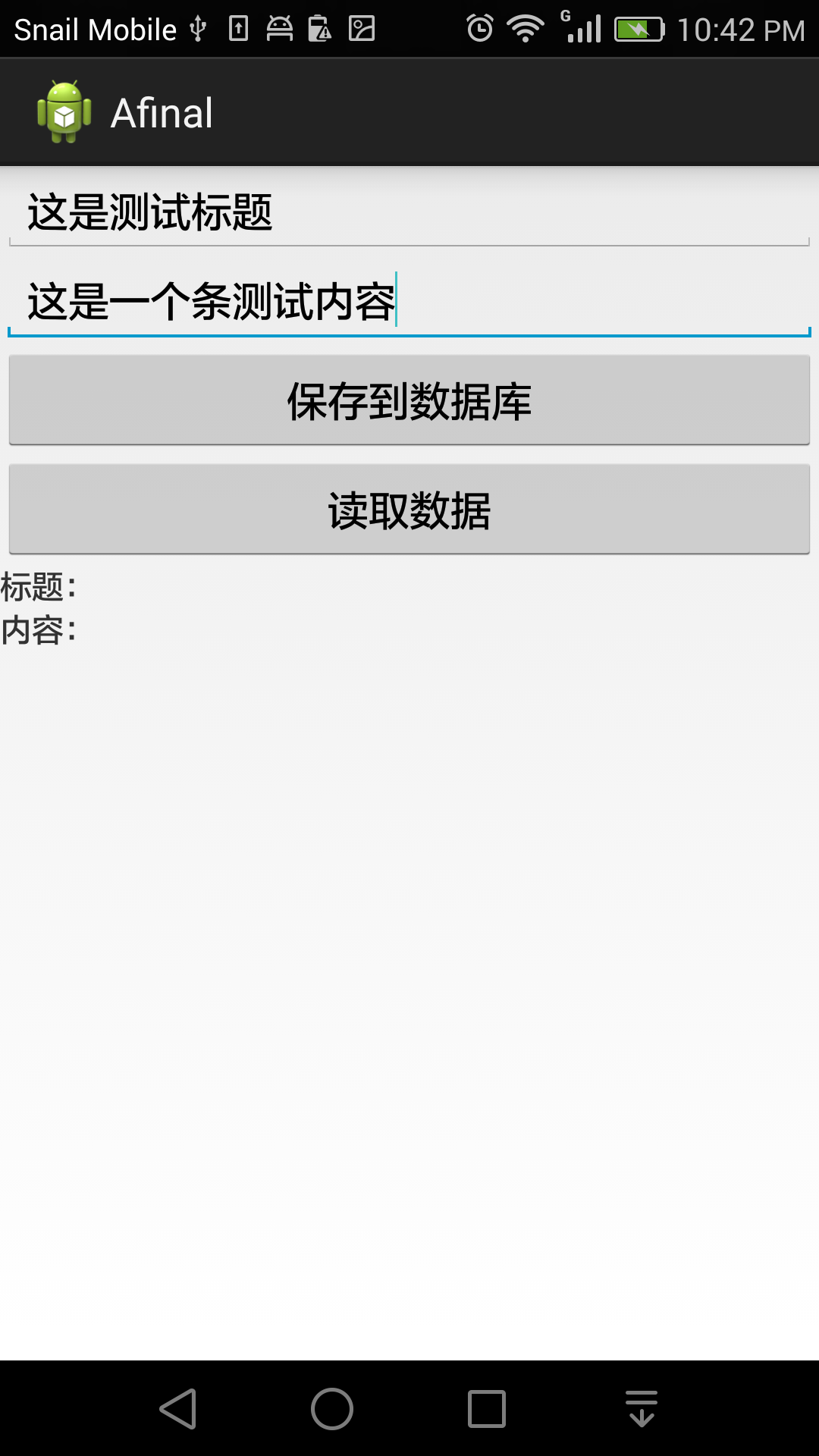

然后我们在验证一下,是否真的插入了数据库,关闭程序,重新打开后直接点击读取数据按钮,会看到仍然可以读取之前保存过的内容,由于在代码中,只取了数据表中的第一行内容,所以多次保存后仍然只显示第一次写入的数据。(由于手机目前没有root,所以无法直接通过eclipse的File Explorer查看数据库,敬请谅解!)

以上只是简单介绍了一下Afinal的几个用法,希望能起到抛砖引玉的作用,好了,步入正题,在下一遍博文中将要开始咱们的项目之旅......