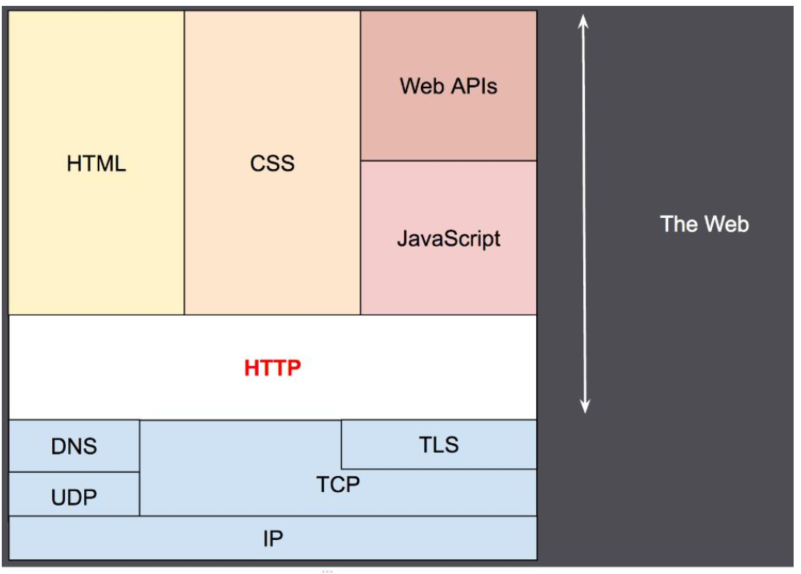
HTTP
- HyperText Transfer Protocol
- 用于传输HTML等内容的应用层协
- 规定了浏览器和服务器之间如何通信,
- 规定了通信时的数据格式
https://www.ietf.org
https://developer.mozilla.org/zh-CN
修改application.properties文件
#ThymeleafProperties
spring.thymeleaf.cache=false
关闭缓存,方便调试。上线的时候需要打开。
针对commyprojectcommunitycontrollerAlphaController.java 修改
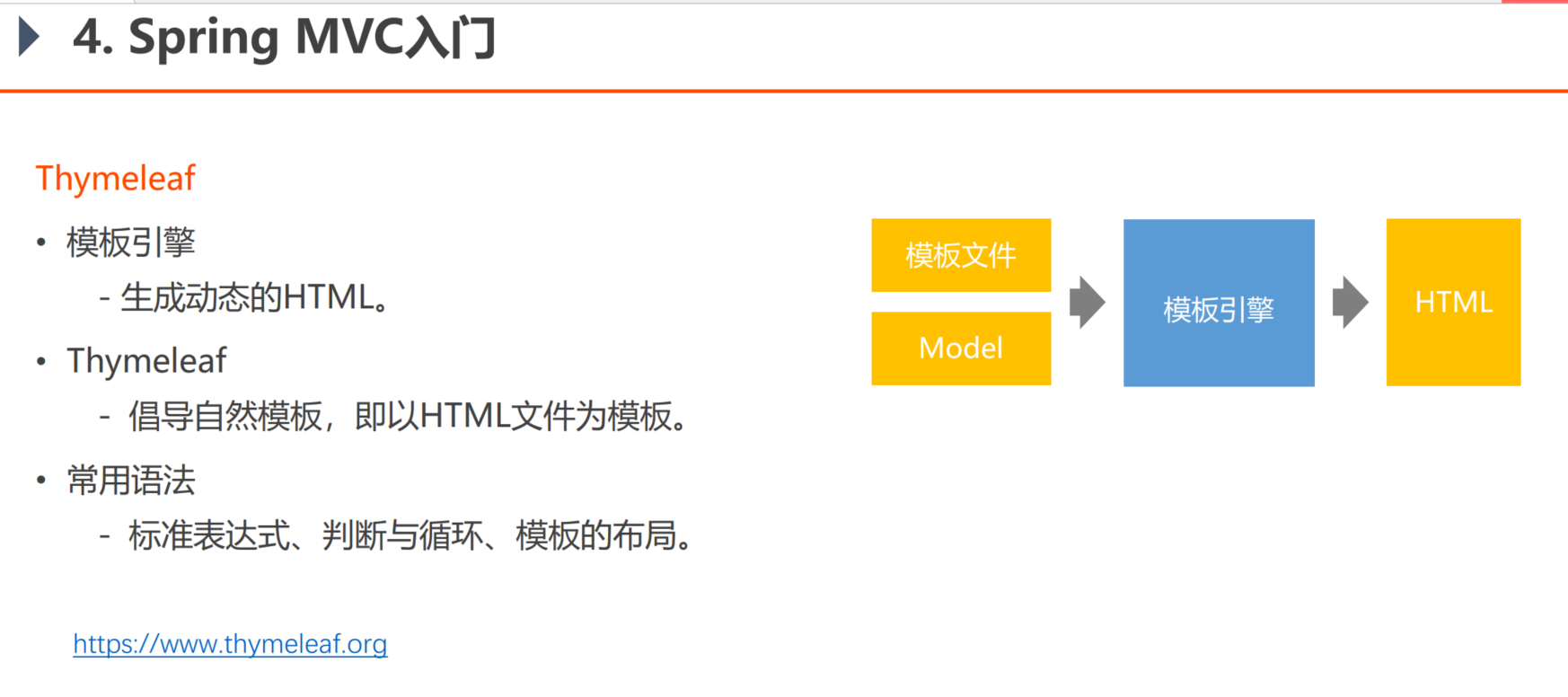
获取数据请求的底层逻辑(了解)

//获取请求,响应的数据(底层的) //通过respond 对象可以直接向浏览器输出任何数据,不依赖返回值 @RequestMapping("/http") public void http(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response){ // 获取请求数据 //———————————————————请求行—————————————————————————————— System.out.println(request.getMethod()); System.out.println(request.getServletPath()); //———————————————————消息头———————(若干行数据)——————————————————————— Enumeration<String> enumeration = request.getHeaderNames();//得到的是迭代器 while (enumeration.hasMoreElements()){ String name = enumeration.nextElement(); String value = request.getHeader(name); System.out.println(name +" : "+value); } //———————————————————亲球体—————————————(业务数据,含参数)————————————————— System.out.println(request.getParameter("code")); // 返回响应数据 response.setContentType("text/html; charset=utf-8");//设置返回类型,返回网页类型的文本 //通过封装好的输出流,向浏览器进行输出 try (PrintWriter writer = response.getWriter()){ writer.write("<h1>学习使我快乐</h1>"); }catch (IOException e){ e.printStackTrace(); } //这样一层一层的写很麻烦 }
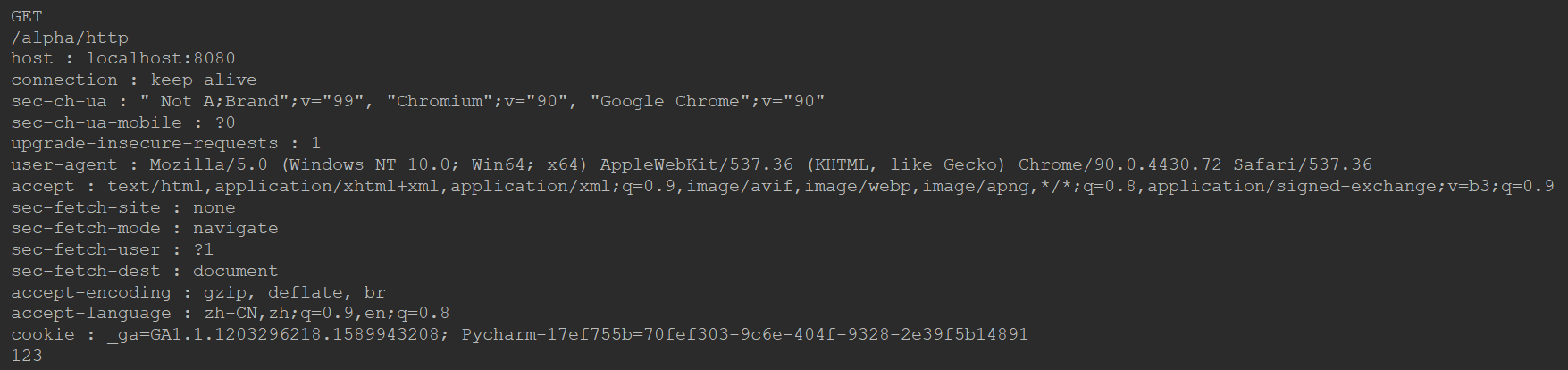
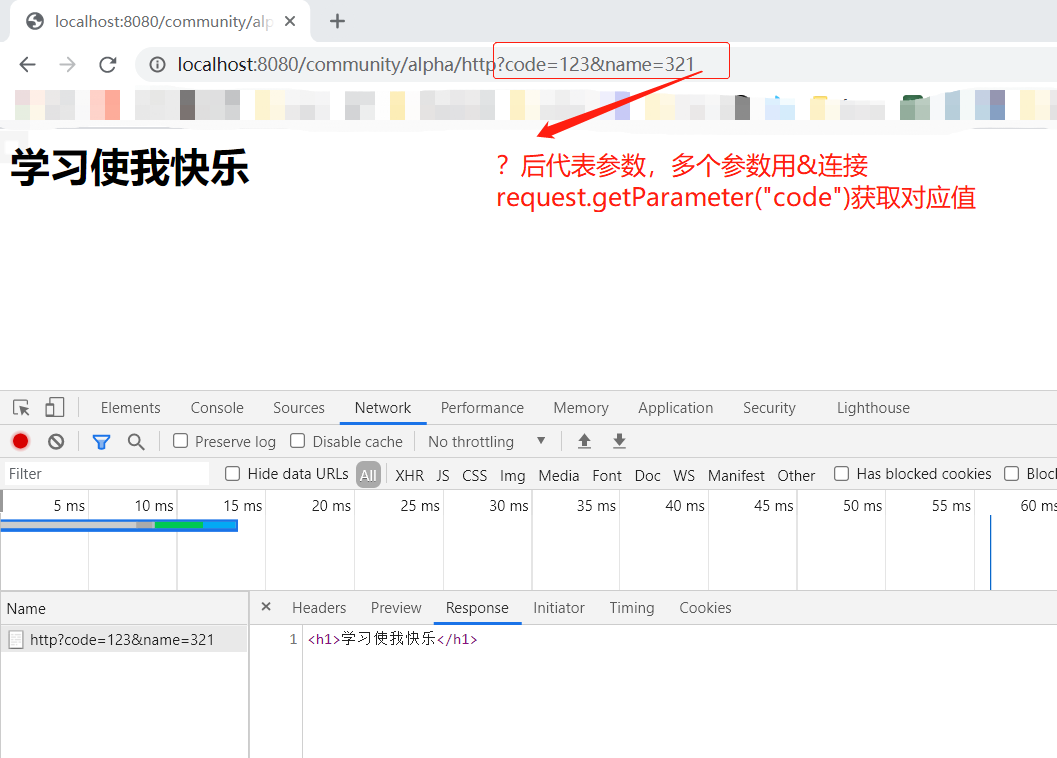
Get请求的两种方式

//GET 请求 // students?current=1&limit=20 分页条件,当前第几页,每页显示多少条 @RequestMapping(path = "/students", method = RequestMethod.GET) @ResponseBody public String getStudents( @RequestParam(name = "current",required = false,defaultValue = "1") int current, @RequestParam(name = "limit",required = false,defaultValue = "10")int limit){ System.out.println(current); System.out.println(limit); return "some student"; } // student/123 _______ student?id=123 ______当123成为路径的一部分时 @RequestMapping(path = "student/{id}", method = RequestMethod.GET) @ResponseBody public String getStudent (@PathVariable("id") int id){ System.out.println(id); return "a student"; }
为什么不是用GET提交而使用POST?
- 直接显示在访问地址,隐秘性不好
- 地址长度有限,大量数据不合适
POST请求的方式

//POST 请求 @RequestMapping(path = "/student",method = RequestMethod.POST) @ResponseBody public String saveStudent(String name, int age){ System.out.println(name); System.out.println(age); return "success"; }
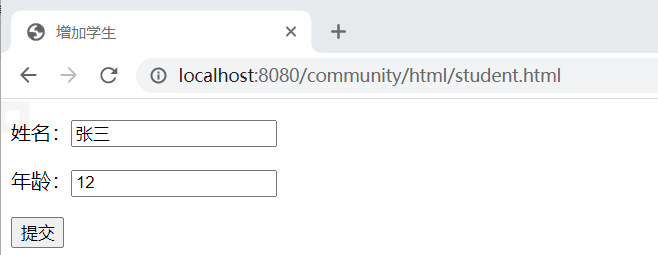
对应的HTML文件(静态的,放在statichtmlstudent.html)

<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <title>增加学生</title> </head> <body> <form method="post" action="/community/alpha/student"> <p> 姓名:<input type="text", name="name"> </p> <p> 年龄:<input type="text", name="age"> </p> <p> <input type="submit", name="保存"> </p> </form> </body> </html>
访问时访问,http://localhost:8080/community/html/student.html (没有static但是有html)静态页面,不是/alpha 下属子页
响应动态HTML数据,2种方式(不加注解ResponseBody,换返回值)

//响应动态HTML数据,不加注解ResponseBody @RequestMapping(path = "/teacher",method = RequestMethod.GET) public ModelAndView getTeacher(){ ModelAndView mav = new ModelAndView(); mav.addObject("name","张胜男"); mav.addObject("age",30); mav.setViewName("/demo/view");//放在 templates下,不用写templates,也不用写文件格式,默认格式html return mav; //直观,把modle和view 的对象都装到一个对象中 } @RequestMapping(path = "/school",method = RequestMethod.GET) public String getSchool(Model model){//String 类型返回的是 Model 的路径 model.addAttribute("name","北京大学"); model.addAttribute("age",120); return "/demo/view"; //把model装到model中,将view直接返回,返回值给了servelet,并且servelet持有model的引用。 }
对应的HTML文件(动态的,templatesdemoview.html)
html标签中列出证明引用动态模板Thymeleaf地址 <html lang="en" xmlns:th="http://thymeleaf.org">

<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en" xmlns:th="http://thymeleaf.org"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <title>Title</title> </head> <body> <p th:text ="${name}"></pth> <p th:text ="${age}"></p> </body> </html>
响应JSON数据(异步请求)
异步请求——当前网页不刷新,访问服务器————eg:当注册时输入名字未提交,显示名称被占用)
//JAVA对象 -————> JSON 字符串————————>JS对象 (浏览器解析对象)

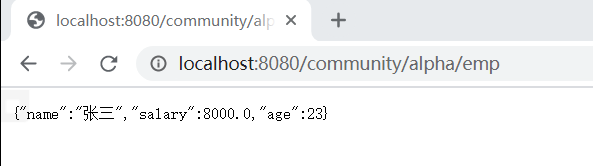
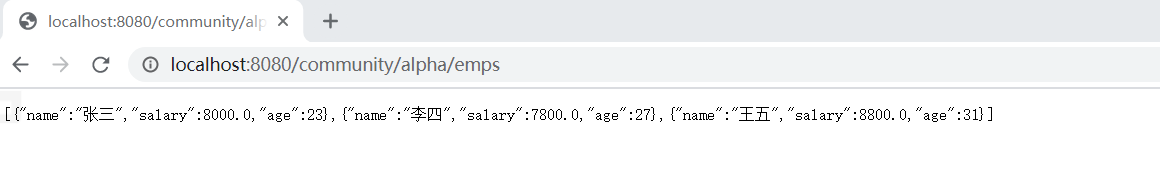
//响应JSON数据(异步请求) // ---当前网页不刷新,访问服务器————eg:当注册时输入名字未提交,显示名称被占用) //JAVA对象 -————> JSON 字符串————————>JS对象 (浏览器解析对象) @RequestMapping(path="/emp",method = RequestMethod.GET) @ResponseBody public Map<String ,Object> getEmp() { Map<String,Object> emp = new HashMap<>(); emp.put("name","张三"); emp.put("age",23); emp.put("salary",8000.00); return emp; } @RequestMapping(path="/emps",method = RequestMethod.GET) @ResponseBody public List<Map<String ,Object>> getEmps() { List<Map<String ,Object>> list = new ArrayList<>(); Map<String,Object> emp = new HashMap<>(); emp.put("name","张三"); emp.put("age",23); emp.put("salary",8000.00); list.add(emp); emp = new HashMap<>(); emp.put("name","李四"); emp.put("age",27); emp.put("salary",7800.00); list.add(emp); emp = new HashMap<>(); emp.put("name","王五"); emp.put("age",31); emp.put("salary",8800.00); list.add(emp); return list; }