摘要:本文主要介绍了tomcat内部处理HTTP请求的Container部分,即剩余的部分
上一篇文章讲到CoyoteAdapter对HTTP请求的处理,主要查看了postParseRequest()方法对request的处理填充。我们继续往下看:
//代码清单1
// Parse and set Catalina and configuration specific
// request parameters
req.getRequestProcessor().setWorkerThreadName(Thread.currentThread().getName());
postParseSuccess = postParseRequest(req, request, res, response);
if (postParseSuccess) {
//check valves if we support async
request.setAsyncSupported(connector.getService().getContainer().getPipeline().isAsyncSupported());
// Calling the container
//111
connector.getService().getContainer().getPipeline().getFirst().invoke(request, response);
//..略代码
}
上一篇文章分析过了,标注1的地方最终调用的是StandardEngineValve的invoke()方法:
//代码清单2
@Override
public final void invoke(Request request, Response response)
throws IOException, ServletException {
// Select the Host to be used for this Request
Host host = request.getHost();
if (host == null) {
response.sendError
(HttpServletResponse.SC_BAD_REQUEST,
sm.getString("standardEngine.noHost",
request.getServerName()));
return;
}
if (request.isAsyncSupported()) {
request.setAsyncSupported(host.getPipeline().isAsyncSupported());
}
// Ask this Host to process this request
//调用host的pipeline 来处理
//11111111
host.getPipeline().getFirst().invoke(request, response);
}
在清单2的标注1的地方我们可以看到最后调用的是host的pipeline来处理,而StandardHost和StandardEngine则有所不同,不同的地方在于,StandardEngine只有一个基本阀也就是StandardEngineValve,而StandardHost除了基本阀门StandardHostValve还额外有两个阀门分别是AccessLogValve和ErrorReportValve。这两个阀门的来源分别是server.xml中配置以及在StandardHost类startInternal()方法中添加。所以标注1的地方getFirst()返回的应该是AccessLogValve这个类的实例,至于为什么是AccessLogValve不是ErrorReportValve,这个大家可以自己思考下,下面我们继续查看AccessLogValve的invoke()方法:
//代码清单3
@Override
public void invoke(Request request, Response response) throws IOException,
ServletException {
getNext().invoke(request, response);
}
这里的getNext()返回的应该是ErrorReportValve,继续查看其invoke()方法:
//代码清单4
@Override
public void invoke(Request request, Response response) throws IOException, ServletException {
//111111
// Perform the request
getNext().invoke(request, response);
if (response.isCommitted()) {
if (response.setErrorReported()) {
// Error wasn't previously reported but we can't write an error
// page because the response has already been committed. Attempt
// to flush any data that is still to be written to the client.
try {
response.flushBuffer();
} catch (Throwable t) {
ExceptionUtils.handleThrowable(t);
}
// Close immediately to signal to the client that something went
// wrong
response.getCoyoteResponse().action(ActionCode.CLOSE_NOW, null);
}
return;
}
Throwable throwable = (Throwable) request.getAttribute(RequestDispatcher.ERROR_EXCEPTION);
// If an async request is in progress and is not going to end once this
// container thread finishes, do not trigger error page handling - it
// will be triggered later if required.
if (request.isAsync() && !request.isAsyncCompleting()) {
return;
}
if (throwable != null && !response.isError()) {
// Make sure that the necessary methods have been called on the
// response. (It is possible a component may just have set the
// Throwable. Tomcat won't do that but other components might.)
// These are safe to call at this point as we know that the response
// has not been committed.
response.reset();
response.sendError(HttpServletResponse.SC_INTERNAL_SERVER_ERROR);
}
// One way or another, response.sendError() will have been called before
// execution reaches this point and suspended the response. Need to
// reverse that so this valve can write to the response.
response.setSuspended(false);
try {
report(request, response, throwable);
} catch (Throwable tt) {
ExceptionUtils.handleThrowable(tt);
}
}
可以看到在方法一开始也就是标注1的地方继续是调用getNext()然后调用其invoke()方法,下面的代码可以考虑为后续处理,所以我们继续往下看,也就是StandardHostValve的invoke()方法:
//代码清单5
@Override
public final void invoke(Request request, Response response)
throws IOException, ServletException {
// Select the Context to be used for this Request
// 获取处理这个request的context对象
Context context = request.getContext();
if (context == null) {
response.sendError
(HttpServletResponse.SC_INTERNAL_SERVER_ERROR,
sm.getString("standardHost.noContext"));
return;
}
// Bind the context CL to the current thread
if( context.getLoader() != null ) {
// Not started - it should check for availability first
// This should eventually move to Engine, it's generic.
if (Globals.IS_SECURITY_ENABLED) {
PrivilegedAction<Void> pa = new PrivilegedSetTccl(
context.getLoader().getClassLoader());
AccessController.doPrivileged(pa);
} else {
Thread.currentThread().setContextClassLoader
(context.getLoader().getClassLoader());
}
}
if (request.isAsyncSupported()) {
request.setAsyncSupported(context.getPipeline().isAsyncSupported());
}
boolean asyncAtStart = request.isAsync();
boolean asyncDispatching = request.isAsyncDispatching();
if (asyncAtStart || context.fireRequestInitEvent(request)) {
// Ask this Context to process this request. Requests that are in
// async mode and are not being dispatched to this resource must be
// in error and have been routed here to check for application
// defined error pages.
try {
if (!asyncAtStart || asyncDispatching) {
//1111111
//调用Context的pipeline来处理
context.getPipeline().getFirst().invoke(request, response);
} else {
// Make sure this request/response is here because an error
// report is required.
if (!response.isErrorReportRequired()) {
throw new IllegalStateException(sm.getString("standardHost.asyncStateError"));
}
}
} catch (Throwable t) {
ExceptionUtils.handleThrowable(t);
container.getLogger().error("Exception Processing " + request.getRequestURI(), t);
// If a new error occurred while trying to report a previous
// error allow the original error to be reported.
if (!response.isErrorReportRequired()) {
request.setAttribute(RequestDispatcher.ERROR_EXCEPTION, t);
throwable(request, response, t);
}
}
// Now that the request/response pair is back under container
// control lift the suspension so that the error handling can
// complete and/or the container can flush any remaining data
response.setSuspended(false);
Throwable t = (Throwable) request.getAttribute(RequestDispatcher.ERROR_EXCEPTION);
// Protect against NPEs if the context was destroyed during a
// long running request.
if (!context.getState().isAvailable()) {
return;
}
// Look for (and render if found) an application level error page
if (response.isErrorReportRequired()) {
if (t != null) {
throwable(request, response, t);
} else {
status(request, response);
}
}
if (!request.isAsync() && (!asyncAtStart || !response.isErrorReportRequired())) {
context.fireRequestDestroyEvent(request);
}
}
// Access a session (if present) to update last accessed time, based on a
// strict interpretation of the specification
if (ACCESS_SESSION) {
request.getSession(false);
}
// Restore the context classloader
if (Globals.IS_SECURITY_ENABLED) {
PrivilegedAction<Void> pa = new PrivilegedSetTccl(
StandardHostValve.class.getClassLoader());
AccessController.doPrivileged(pa);
} else {
Thread.currentThread().setContextClassLoader
(StandardHostValve.class.getClassLoader());
}
}
代码比较长,先获取了该需要处理该request的Context实例,然后调用了该实例的pipeline来处理request。而StandardContext对象在初始化的时候如果没有在server.xml中配置Valve阀门的话,那么Context的getFirst()方法返回的是StandardContextValve的实例,所以查看StandardContextValve的invoke()方法:
//代码清单6
@Override
public final void invoke(Request request, Response response)
throws IOException, ServletException {
// Disallow any direct access to resources under WEB-INF or META-INF
MessageBytes requestPathMB = request.getRequestPathMB();
if ((requestPathMB.startsWithIgnoreCase("/META-INF/", 0))
|| (requestPathMB.equalsIgnoreCase("/META-INF"))
|| (requestPathMB.startsWithIgnoreCase("/WEB-INF/", 0))
|| (requestPathMB.equalsIgnoreCase("/WEB-INF"))) {
response.sendError(HttpServletResponse.SC_NOT_FOUND);
return;
}
// Select the Wrapper to be used for this Request
Wrapper wrapper = request.getWrapper();
if (wrapper == null || wrapper.isUnavailable()) {
response.sendError(HttpServletResponse.SC_NOT_FOUND);
return;
}
// Acknowledge the request
try {
response.sendAcknowledgement();
} catch (IOException ioe) {
container.getLogger().error(sm.getString(
"standardContextValve.acknowledgeException"), ioe);
request.setAttribute(RequestDispatcher.ERROR_EXCEPTION, ioe);
response.sendError(HttpServletResponse.SC_INTERNAL_SERVER_ERROR);
return;
}
if (request.isAsyncSupported()) {
request.setAsyncSupported(wrapper.getPipeline().isAsyncSupported());
}
//调用wrapper的pipeline来处理
//11111
wrapper.getPipeline().getFirst().invoke(request, response);
}
从标注1的地方可以看到最终调用的还是子容器StandardWrapper的pipeline来处理request,也就是StandardWrapperValve的invoke()方法:
//代码清单7
@Override
public final void invoke(Request request, Response response)
throws IOException, ServletException {
// Initialize local variables we may need
boolean unavailable = false;
Throwable throwable = null;
// This should be a Request attribute...
long t1=System.currentTimeMillis();
requestCount++;
StandardWrapper wrapper = (StandardWrapper) getContainer();
Servlet servlet = null;
Context context = (Context) wrapper.getParent();
// Check for the application being marked unavailable
if (!context.getState().isAvailable()) {
response.sendError(HttpServletResponse.SC_SERVICE_UNAVAILABLE,
sm.getString("standardContext.isUnavailable"));
unavailable = true;
}
// Check for the servlet being marked unavailable
if (!unavailable && wrapper.isUnavailable()) {
container.getLogger().info(sm.getString("standardWrapper.isUnavailable",
wrapper.getName()));
long available = wrapper.getAvailable();
if ((available > 0L) && (available < Long.MAX_VALUE)) {
response.setDateHeader("Retry-After", available);
response.sendError(HttpServletResponse.SC_SERVICE_UNAVAILABLE,
sm.getString("standardWrapper.isUnavailable",
wrapper.getName()));
} else if (available == Long.MAX_VALUE) {
response.sendError(HttpServletResponse.SC_NOT_FOUND,
sm.getString("standardWrapper.notFound",
wrapper.getName()));
}
unavailable = true;
}
// Allocate a servlet instance to process this request
try {
if (!unavailable) {
//加载servlet
//111111111111
servlet = wrapper.allocate();
}
} catch (UnavailableException e) {
//异常处理 略
} catch (ServletException e) {
//异常处理 略
} catch (Throwable e) {
//异常处理 略
}
// Identify if the request is Comet related now that the servlet has been allocated
boolean comet = false;
if (servlet instanceof CometProcessor && Boolean.TRUE.equals(request.getAttribute(
Globals.COMET_SUPPORTED_ATTR))) {
comet = true;
request.setComet(true);
}
MessageBytes requestPathMB = request.getRequestPathMB();
DispatcherType dispatcherType = DispatcherType.REQUEST;
if (request.getDispatcherType()==DispatcherType.ASYNC) dispatcherType = DispatcherType.ASYNC;
request.setAttribute(Globals.DISPATCHER_TYPE_ATTR,dispatcherType);
request.setAttribute(Globals.DISPATCHER_REQUEST_PATH_ATTR,
requestPathMB);
// Create the filter chain for this request
//2222222 创建filterChain
ApplicationFilterFactory factory = ApplicationFilterFactory.getInstance();
ApplicationFilterChain filterChain = factory.createFilterChain(request, wrapper, servlet);
// Reset comet flag value after creating the filter chain
request.setComet(false);
// Call the filter chain for this request
// NOTE: This also calls the servlet's service() method
try {
if ((servlet != null) && (filterChain != null)) {
// Swallow output if needed
if (context.getSwallowOutput()) {
try {
SystemLogHandler.startCapture();
if (request.isAsyncDispatching()) {
//TODO SERVLET3 - async
((AsyncContextImpl)request.getAsyncContext()).doInternalDispatch();
} else if (comet) {
filterChain.doFilterEvent(request.getEvent());
request.setComet(true);
} else {
filterChain.doFilter(request.getRequest(),response.getResponse());
}
} finally {
String log = SystemLogHandler.stopCapture();
if (log != null && log.length() > 0) {
context.getLogger().info(log);
}
}
} else {
if (request.isAsyncDispatching()) {
//TODO SERVLET3 - async
((AsyncContextImpl)request.getAsyncContext()).doInternalDispatch();
} else if (comet) {
request.setComet(true);
filterChain.doFilterEvent(request.getEvent());
} else {
//3333333333 调用fiterChain来处理 request 和 response
filterChain.doFilter(request.getRequest(), response.getResponse());
}
}
}
} catch (ClientAbortException e) {
//异常处理 略
exception(request, response, e);
} catch (IOException e) {
//异常处理 略
} catch (UnavailableException e) {
//异常处理 略
} catch (ServletException e) {
//异常处理 略
} catch (Throwable e) {
//异常处理 略
}
// Release the filter chain (if any) for this request
if (filterChain != null) {
if (request.isComet()) {
// If this is a Comet request, then the same chain will be used for the
// processing of all subsequent events.
filterChain.reuse();
} else {
//444444444 释放过滤器链
filterChain.release();
}
}
// Deallocate the allocated servlet instance
//
try {
if (servlet != null) {
//55555555555 释放 sevlet 实例
wrapper.deallocate(servlet);
}
} catch (Throwable e) {
//异常处理 略
}
// If this servlet has been marked permanently unavailable,
// unload it and release this instance
try {
if ((servlet != null) &&
(wrapper.getAvailable() == Long.MAX_VALUE)) {
/ /666666666666 卸载wrapper
wrapper.unload();
}
} catch (Throwable e) {
//异常处理 略
}
long t2=System.currentTimeMillis();
long time=t2-t1;
processingTime += time;
if( time > maxTime) maxTime=time;
if( time < minTime) minTime=time;
}
好了,我们终于看到了最终去处理request和response代码的地方,虽然代码很长,但是思路很清楚,大多数代码都是在做检测判断等,invoke()方法我总结了核心是做了以下几件事,我已经在代码中注释出来了:
- 加载最终处理请求
request的servlet实例 - 创建过滤器链(
filterChain) - 调用过滤器链的
doFilter方法来处理对应的request和response。 - 后续处理释放过滤器链
- 后续处理卸载该次处理的
servlet实例 - 后续处理查看是否需要卸载对应的
wrapper实例
个人总结出该方法做的比较重要的6件事,关于后续处理的部分我们就不查看了,有兴趣的可以自行查看,我们主要看处理过程,也就是123三条。
加载对应的Servlet
对应的方法wrapper.allocate():
//代码清单8
@Override
public Servlet allocate() throws ServletException {
// If we are currently unloading this servlet, throw an exception
if (unloading) {
throw new ServletException(sm.getString("standardWrapper.unloading", getName()));
}
boolean newInstance = false;
// If not SingleThreadedModel, return the same instance every time
//111 判断servlet是否是STM模式,如果是从来没加载过的servlet 默认是非STM模式的
if (!singleThreadModel) {
// Load and initialize our instance if necessary
if (instance == null || !instanceInitialized) {
synchronized (this) {
if (instance == null) {
try {
if (log.isDebugEnabled()) {
log.debug("Allocating non-STM instance");
}
// Note: We don't know if the Servlet implements
// SingleThreadModel until we have loaded it.
//22222222 加载servlet
instance = loadServlet();
newInstance = true;
if (!singleThreadModel) {
// For non-STM, increment here to prevent a race
// condition with unload. Bug 43683, test case
// #3
countAllocated.incrementAndGet();
}
} catch (ServletException e) {
throw e;
} catch (Throwable e) {
ExceptionUtils.handleThrowable(e);
throw new ServletException(sm.getString("standardWrapper.allocate"), e);
}
}
//3333 如果没有初始化 初始化
if (!instanceInitialized) {
initServlet(instance);
}
}
}
//44444 如果是STM模式的并且是分配的新对象 将该对象压入pool中
//之所以在 非STM模式的判断里面又加入了STM模式判断是因为
// 没有加载过的Servlet默认是非STM模式的,在loadServlet的时候回去判断 该Servlet是否 是STM模式的
if (singleThreadModel) {
if (newInstance) {
// Have to do this outside of the sync above to prevent a
// possible deadlock
synchronized (instancePool) {
instancePool.push(instance);
nInstances++;
}
}
} else {
if (log.isTraceEnabled()) {
log.trace(" Returning non-STM instance");
}
// For new instances, count will have been incremented at the
// time of creation
if (!newInstance) {
countAllocated.incrementAndGet();
}
return instance;
}
}
synchronized (instancePool) {
//countAllocated 分配的活跃实例数量,对于一个非STM servlet 即使返回的是同一个数量,该字段也会增加
//nInstances 分配的STM模式的servlet数量
//maxInstances 可以分配的STM模式的servlet数量上限 默认是20
while (countAllocated.get() >= nInstances) {
// Allocate a new instance if possible, or else wait
if (nInstances < maxInstances) {
try {
instancePool.push(loadServlet());
nInstances++;
} catch (ServletException e) {
throw e;
} catch (Throwable e) {
ExceptionUtils.handleThrowable(e);
throw new ServletException(sm.getString("standardWrapper.allocate"), e);
}
} else {
try {
instancePool.wait();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
// Ignore
}
}
}
if (log.isTraceEnabled()) {
log.trace(" Returning allocated STM instance");
}
countAllocated.incrementAndGet();
return instancePool.pop();
}
}
在讲解之前,我们先介绍个概念:STM。
STM是SingleThreadModel类的缩写,SingleThreadModel类是一个标志类(类似Serializable)。在Servlet2.4的规范中有说明:所有的servlet都可以实现该类,实现了该类的servlet不会同时有2个线程在调用同一个实例的service()方法。注意,这个意思并不是实现了SingleThreadModel类就代表该servlet线程安全。tomcat这样处理主要是为了保证高性能而不是线程安全,真正的线程安全还是要service()方法中的代码自己去控制。
我们继续查看源码,可以看到为了兼容STM和非STM模式servlet的分配allocate()方法写的略显复杂。总体是先判断该servlt是否加载过,如果没有加载过那么就是走标注1调用loadServlet()方法加载对应需要处理request的servlet。也许会奇怪为什么加载完了会再判断该servlet是否是STM模式的,主要是因为在没有加载过的servlet是无法判断其是否是STM模式的,但是默认是非STM模式的,所以在加载完毕servlet以后需要再判断一下是否是STM模式的然后作相应的处理。至于后面的synchronized代码块的处理我们先不看,我们先看下比较重要的标注2的地方的loadServlet()方法的源码:
//代码清单9
/**
* 加载一个servlet
* @return
* @throws ServletException
*/
public synchronized Servlet loadServlet() throws ServletException {
//判断servlet 状态
if (unloading) {
throw new ServletException(
sm.getString("standardWrapper.unloading", getName()));
}
// Nothing to do if we already have an instance or an instance pool
//如果不是stm模式并且instance非空,那么直接返回instance(之前已经加载过该类)
if (!singleThreadModel && (instance != null))
return instance;
//获取输出流,记日志
PrintStream out = System.out;
if (swallowOutput) {
SystemLogHandler.startCapture();
}
Servlet servlet;
try {
long t1 = System.currentTimeMillis();
// Complain if no servlet class has been specified
//检测
if (servletClass == null) {
unavailable(null);
throw new ServletException
(sm.getString("standardWrapper.notClass", getName()));
}
InstanceManager instanceManager = ((StandardContext)getParent()).getInstanceManager();
try {
//111111新建实例
servlet = (Servlet) instanceManager.newInstance(servletClass);
} catch (ClassCastException e) {
//异常处理 略
} catch (Throwable e) {
//异常处理 略
}
//处理servlet3.0 注解 MultipartConfig 配置该servlet的一些属性(上传文件的注解,上传文件的一些属性)
if (multipartConfigElement == null) {
MultipartConfig annotation =
servlet.getClass().getAnnotation(MultipartConfig.class);
if (annotation != null) {
multipartConfigElement =
new MultipartConfigElement(annotation);
}
}
//处理 ServletSecurity 注解
processServletSecurityAnnotation(servlet.getClass());
// Special handling for ContainerServlet instances
if ((servlet instanceof ContainerServlet) &&
(isContainerProvidedServlet(servletClass) ||
((Context) getParent()).getPrivileged() )) {
((ContainerServlet) servlet).setWrapper(this);
}
classLoadTime=(int) (System.currentTimeMillis() -t1);
if (servlet instanceof SingleThreadModel) {
//22222如果是STM模式,为了达到高性能 需要从缓存池中取对象 缓存池是个stack
if (instancePool == null) {
instancePool = new Stack<Servlet>();
}
singleThreadModel = true;
}
//333333初始化servlet 会调用自定义servlet的 init()方法
initServlet(servlet);
fireContainerEvent("load", this);
loadTime=System.currentTimeMillis() -t1;
} finally {
if (swallowOutput) {
String log = SystemLogHandler.stopCapture();
if (log != null && log.length() > 0) {
if (getServletContext() != null) {
getServletContext().log(log);
} else {
out.println(log);
}
}
}
}
return servlet;
}
loadServlet()方法也很简单,主要就是标注123,标注1的地方是在新建servlet实例,标注2的地方是新建STM模式的servlet缓存池,标注3的地方是把新建的servlet实例初始化,值得注意的是在initServlet()方法里会调用servlet实例的init(),我们来查看下initServlet()方法:
//代码清单10
private synchronized void initServlet(Servlet servlet)
throws ServletException {
//已经初始化
if (instanceInitialized && !singleThreadModel) return;
// Call the initialization method of this servlet
try {
instanceSupport.fireInstanceEvent(InstanceEvent.BEFORE_INIT_EVENT,
servlet);
if( Globals.IS_SECURITY_ENABLED) {
boolean success = false;
try {
Object[] args = new Object[] { facade };
SecurityUtil.doAsPrivilege("init",
servlet,
classType,
args);
success = true;
} finally {
if (!success) {
// destroy() will not be called, thus clear the reference now
SecurityUtil.remove(servlet);
}
}
} else {
//11111 servlet 初始化后 会调用一次 init()方法,可以自己复写,也可以不复写
servlet.init(facade);
}
instanceInitialized = true;
//触发事件
instanceSupport.fireInstanceEvent(InstanceEvent.AFTER_INIT_EVENT,
servlet);
} catch (UnavailableException f) {
//异常处理 略
} catch (ServletException f) {
//异常处理 略
} catch (Throwable f) {
//异常处理 略
}
}
可以看到在标注1的地方调用了servlet实例的init()方法,其实这个就是用户自定义servlet可以复写也可以不复写的init()方法,值得注意的是传递的对象StandardWrapperFacade的实例,这个类实现了ServletConfig类,同时包装了StandardWrapper,我个人理解是这里传递StandardWrapperFacade对象主要目的是为了把StandardWrapper对servlet开发人员隐藏,不允许servlet开发人员随意使用StandardWrapper,是为了安全着想。
说到这里我们看下代码清单8的最后一段代码
//代码清单11
synchronized (instancePool) {
//countAllocated 分配的活跃实例数量,对于一个非STM servlet 即使返回的是同一个数量,该字段也会增加
//nInstances 分配的STM模式的servlet数量
//maxInstances 可以分配的STM模式的servlet数量上限 默认是20
while (countAllocated.get() >= nInstances) {
// Allocate a new instance if possible, or else wait
if (nInstances < maxInstances) {
try {
instancePool.push(loadServlet());
nInstances++;
} catch (ServletException e) {
throw e;
} catch (Throwable e) {
ExceptionUtils.handleThrowable(e);
throw new ServletException(sm.getString("standardWrapper.allocate"), e);
}
} else {
try {
instancePool.wait();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
// Ignore
}
}
}
if (log.isTraceEnabled()) {
log.trace(" Returning allocated STM instance");
}
countAllocated.incrementAndGet();
return instancePool.pop();
}
在当前StandardWrapper分配的活跃实例数量大于STM的servlet分配的实例数量,并且分配的STM实例数量小于限定值(20)的时候会不停的实例化该STM模式的servlet并且塞到缓存池(instancePool)中。最后把缓存池中的栈顶对象弹出使用,也就是一开始实例化20个对象,每个请求弹出一个对象使用,这样主要是为了保持高性能,以及每个请求使用一个servlet对象。
看到这里代码清单7的servlet = wrapper.allocate()方法就看完了,主要作用是初始化需要被使用的servlet,我们继续看代码清单7的标注23的内容。
FilterChain的创建以及调用
//代码清单12
//2222222 创建filterChain
ApplicationFilterFactory factory = ApplicationFilterFactory.getInstance();
ApplicationFilterChain filterChain = factory.createFilterChain(request, wrapper, servlet);
filterChain.doFilter(request.getRequest(), response.getResponse());
先查看createFilterChain()方法:
//代码清单13
public ApplicationFilterChain createFilterChain(ServletRequest request, Wrapper wrapper, Servlet servlet) {
//略
boolean comet = false;
// Create and initialize a filter chain object
ApplicationFilterChain filterChain = null;
if (request instanceof Request) {
Request req = (Request) request;
comet = req.isComet();
if (Globals.IS_SECURITY_ENABLED) {
// Security: Do not recycle
filterChain = new ApplicationFilterChain();
if (comet) {
req.setFilterChain(filterChain);
}
} else {
filterChain = (ApplicationFilterChain) req.getFilterChain();
if (filterChain == null) {
//11111111 新建ApplicationFilterChain 实例
filterChain = new ApplicationFilterChain();
req.setFilterChain(filterChain);
}
}
} else {
// Request dispatcher in use
filterChain = new ApplicationFilterChain();
}
filterChain.setServlet(servlet);
filterChain.setSupport
(((StandardWrapper)wrapper).getInstanceSupport());
// Acquire the filter mappings for this Context
StandardContext context = (StandardContext) wrapper.getParent();
//22222 获取所有的filter
FilterMap filterMaps[] = context.findFilterMaps();
// If there are no filter mappings, we are done
if ((filterMaps == null) || (filterMaps.length == 0))
return (filterChain);
// Acquire the information we will need to match filter mappings
String servletName = wrapper.getName();
// Add the relevant path-mapped filters to this filter chain
//33333333 添加匹配servlet路径的filter
for (int i = 0; i < filterMaps.length; i++) {
if (!matchDispatcher(filterMaps[i] ,dispatcher)) {
continue;
}
if (!matchFiltersURL(filterMaps[i], requestPath))
continue;
//44444444 获取 filter对应的 ApplicationFilterConfig 对象
ApplicationFilterConfig filterConfig = (ApplicationFilterConfig)
context.findFilterConfig(filterMaps[i].getFilterName());
if (filterConfig == null) {
// FIXME - log configuration problem
continue;
}
boolean isCometFilter = false;
if (comet) {
try {
isCometFilter = filterConfig.getFilter() instanceof CometFilter;
} catch (Exception e) {
// Note: The try catch is there because getFilter has a lot of
// declared exceptions. However, the filter is allocated much
// earlier
Throwable t = ExceptionUtils.unwrapInvocationTargetException(e);
ExceptionUtils.handleThrowable(t);
}
if (isCometFilter) {
filterChain.addFilter(filterConfig);
}
} else {
// 5555555 添加filter
filterChain.addFilter(filterConfig);
}
}
// Add filters that match on servlet name second
//666666666 添加匹配 servelt名字的filter
for (int i = 0; i < filterMaps.length; i++) {
if (!matchDispatcher(filterMaps[i] ,dispatcher)) {
continue;
}
if (!matchFiltersServlet(filterMaps[i], servletName))
continue;
ApplicationFilterConfig filterConfig = (ApplicationFilterConfig)
context.findFilterConfig(filterMaps[i].getFilterName());
if (filterConfig == null) {
// FIXME - log configuration problem
continue;
}
boolean isCometFilter = false;
if (comet) {
try {
isCometFilter = filterConfig.getFilter() instanceof CometFilter;
} catch (Exception e) {
// Note: The try catch is there because getFilter has a lot of
// declared exceptions. However, the filter is allocated much
// earlier
}
if (isCometFilter) {
filterChain.addFilter(filterConfig);
}
} else {
filterChain.addFilter(filterConfig);
}
}
// Return the completed filter chain、
//最终返回 filterchain
return (filterChain);
}
代码其实很简单,注释我都在代码中添加了,先是创建ApplicationFilterChain实例,再向filterChain中添加和该servlet匹配的各种filter,主要这里需要解释一下filter体系里几个对象的关系。
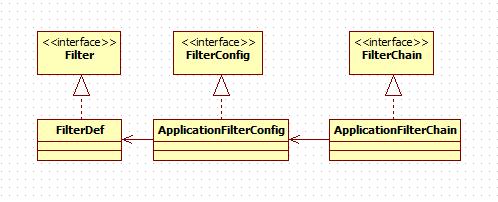
- FilterDef:代表一个filter,filter的定义类。类中的
parameters变量存储了在初始化过滤器的时候需要的所有参数,参数解析在解析web.xml的时候进行添加。 - ApplicationFilterConfig:实现
FilterConfig接口,用于管理web应用第一次启动时创建的所有过滤器实例,简单理解就是用来管理filter类的统一管理类。 - ApplicationFilterChain:代表一个过滤器链实体,请求在到达对应servlet之前会先经过该实例拥有的所有filter。
除了filter相关知识以外,代码清单13中context.findFilterMaps()表示了context对象和filter在启动的时候已经被关联在一起了,具体的关联代码前面说了一点,本文主要讲解的是请求流程的处理,所以这里具体代码就不查看了,只提一下。filter的初始化和关联context的代码都在context对象的初始化时进行,类似deploy项目一样的监听器HostConfig类,StandardContext类初始化的时候使用的监听器是ContextConfig,具体代码可以在该类中查找。
看完代码清单13我们看到了ApplicationFilterChain的创建过程,从创建过程中我们知道了创建出来的filterChain实例拥有对于该请求应该应用的所有filter的实例引用。我们继续查看doFilter()方法。
//代码清单14
@Override
public void doFilter(ServletRequest request, ServletResponse response)
throws IOException, ServletException {
if( Globals.IS_SECURITY_ENABLED ) {
final ServletRequest req = request;
final ServletResponse res = response;
try {
java.security.AccessController.doPrivileged(
new java.security.PrivilegedExceptionAction<Void>() {
@Override
public Void run()
throws ServletException, IOException {
internalDoFilter(req,res);
return null;
}
}
);
} catch( PrivilegedActionException pe) {
//异常处理略
}
} else {
internalDoFilter(request,response);
}
}
最后调用的是internalDoFilter()方法:
//代码清单15
/**
* The int which is used to maintain the current position
* in the filter chain.
* 当前正在调用的filter的编号
*/
private int pos = 0;
/**
* The int which gives the current number of filters in the chain.
* filter的总的数量
*/
private int n = 0;
private void internalDoFilter(ServletRequest request,
ServletResponse response)
throws IOException, ServletException {
// Call the next filter if there is one
if (pos < n) {
//1111 获取ApplicationFilterConfig对象
ApplicationFilterConfig filterConfig = filters[pos++];
Filter filter = null;
try {
//2222222222222 获取对应的filter实例
filter = filterConfig.getFilter();
support.fireInstanceEvent(InstanceEvent.BEFORE_FILTER_EVENT,
filter, request, response);
if (request.isAsyncSupported() && "false".equalsIgnoreCase(
filterConfig.getFilterDef().getAsyncSupported())) {
request.setAttribute(Globals.ASYNC_SUPPORTED_ATTR,
Boolean.FALSE);
}
if( Globals.IS_SECURITY_ENABLED ) {
final ServletRequest req = request;
final ServletResponse res = response;
Principal principal =
((HttpServletRequest) req).getUserPrincipal();
Object[] args = new Object[]{req, res, this};
SecurityUtil.doAsPrivilege
("doFilter", filter, classType, args, principal);
} else {
//33333 调用该filter的`doFilter()`方法
filter.doFilter(request, response, this);
}
support.fireInstanceEvent(InstanceEvent.AFTER_FILTER_EVENT,
filter, request, response);
} catch (IOException e) {
//异常处理略
} catch (ServletException e) {
//异常处理略
} catch (RuntimeException e) {
//异常处理略
} catch (Throwable e) {
//异常处理略
}
return;
}
// We fell off the end of the chain -- call the servlet instance
// 所有的filter都调用完毕以后调用 对应的 servlet
try {
if (ApplicationDispatcher.WRAP_SAME_OBJECT) {
lastServicedRequest.set(request);
lastServicedResponse.set(response);
}
support.fireInstanceEvent(InstanceEvent.BEFORE_SERVICE_EVENT,
servlet, request, response);
if (request.isAsyncSupported()
&& !support.getWrapper().isAsyncSupported()) {
request.setAttribute(Globals.ASYNC_SUPPORTED_ATTR,
Boolean.FALSE);
}
// Use potentially wrapped request from this point
if ((request instanceof HttpServletRequest) &&
(response instanceof HttpServletResponse)) {
if( Globals.IS_SECURITY_ENABLED ) {
final ServletRequest req = request;
final ServletResponse res = response;
Principal principal =
((HttpServletRequest) req).getUserPrincipal();
Object[] args = new Object[]{req, res};
SecurityUtil.doAsPrivilege("service",
servlet,
classTypeUsedInService,
args,
principal);
} else {
//444444 调用对应servlet的`service()`方法
servlet.service(request, response);
}
} else {
servlet.service(request, response);
}
support.fireInstanceEvent(InstanceEvent.AFTER_SERVICE_EVENT,
servlet, request, response);
} catch (IOException e) {
//异常处理略
} catch (ServletException e) {
//异常处理略
} catch (RuntimeException e) {
//异常处理略
} catch (Throwable e) {
//异常处理略
} finally {
if (ApplicationDispatcher.WRAP_SAME_OBJECT) {
lastServicedRequest.set(null);
lastServicedResponse.set(null);
}
}
}
从代码清单15中我们可以看到,如果请求还在filter链中流转那么就会一直调用filter.dofilter()方法,可以把代码清单14和代码清单15理解为一个递归方法,如果没满足pos < n这个条件就会一直调用filter.dofilter()方法,我们先看一下正常一个filter的dofilter()方法:
//代码清单16
@Override
public void doFilter(ServletRequest request, ServletResponse response,
FilterChain chain) throws IOException, ServletException {
//自定义代码略
chain.doFilter(request, response);
}
而在清单15标注3的地方传递的正是自身filterChain的实例,所以在filter中再调用chain.doFilter()方法,相当于又去调用代码清单14的代码了,这也是类似递归的地方。而pos < n这个条件表示的意思就是filter链中filter还没有调用完毕。当filter调用完毕就会去调用请求对应的servlet的service方法。
看到这里我们终于把代码清单7中提及的filterChain部分看完了,代码清单7中后续的处理就不一一查看了,同时这个也是相当于整个处理流程的完结,因为已经调用到了对应servlet的service()方法。
既然到最后了,我们来总结下tomcat是如何处理HTTP请求的:
Socket-->Http11ConnectionHandler-->Http11Processor-->CoyoteAdapter-->StandardEngineValve-->StandardHostValve-->StandardContextValve-->ApplicationFilterChain-->Servlet
其实用uml画个时序图比较好,但是实在太懒了,大家可以随便找个tomcat请求的时序图配图看文更清晰。
新年快乐(完)