在一个应用里面,可能涉及到连接多个不同数据库进行操作,而每次连接写不同的实现会很麻烦。前面已经会了用JDBC连接数据库,那么利用反射和工厂模式,可以实现连接不同的数据库,这样处理起来将会很方便。同时建造数据库连接池,处理多个业务数据处理。

那么具体怎么实现呢,下面一起来看一下:
整体结构如下:

第一步,先处理连接不同数据库
1、首先,将数据库配置信息创建一个公用类:JdbcUrl.java
主数据库可以用默认的构造方法,如果是连接其他库,则通过传递参数的方式来处理。
数据库参数有如下几个:

1 /** 2 * 数据库连接配置信息类 3 * @author Damon 4 */ 5 public class JdbcUrl 6 { 7 8 /** 定义数据库参数 */ 9 10 // 数据库类型 11 private String DBType; 12 // 数据库服务器IP 13 private String IP; 14 // 数据库服务器端口 15 private String Port; 16 // 数据库名称 17 private String DBName; 18 // 用户名 19 private String UserName; 20 // 密码 21 private String PassWord; 22 23 24 /** 25 * 默认构造方法,连接默认数据库 26 */ 27 public JdbcUrl() 28 { 29 // TODO Auto-generated constructor stub 30 DBType = SysCon.DATABASE_TYPE_MYSQL; 31 IP = "127.0.0.1"; 32 DBName = "mysql"; 33 Port = "3306"; 34 UserName = "damon"; 35 PassWord = "damon"; 36 } 37 38 /** 39 * 连接指定数据库 40 * @param urlType 传入连接类型标识 41 */ 42 public JdbcUrl(String urlType) 43 { 44 if ("mysql".equals(urlType)) 45 { 46 DBType = SysCon.DATABASE_TYPE_MYSQL; 47 IP = "127.0.0.1"; 48 DBName = "mysql"; 49 Port = "3306"; 50 UserName = "damon"; 51 PassWord = "damon"; 52 } 53 } 54 55 /** 56 * 获取连接句柄 57 * @return String 58 */ 59 public String getJdbcUrl() 60 { 61 String sUrl = ""; 62 63 if (DBType.trim().toUpperCase().equals("MYSQL")) 64 { 65 sUrl = "jdbc:mysql://" + IP + ":" + Port + "/" + DBName; 66 } 67 else if (DBType.trim().toUpperCase().equals("DB2")) 68 { 69 sUrl = "jdbc:db2://" + IP + ":" + Port + "/" + DBName; 70 } 71 72 else if (DBType.trim().toUpperCase().equals("ORACLE")) 73 { 74 sUrl = "jdbc:oracle:thin:@" + IP + ":" + Port + ":" + DBName; 75 } 76 77 else if (DBType.trim().toUpperCase().equals("SQLSERVER")) 78 { 79 sUrl = "jdbc:microsoft:sqlserver://" + IP + ":" + Port + ";databaseName=" + DBName + ";selectMethod=cursor"; 80 } 81 else if (DBType.trim().toUpperCase().equals("WEBLOGICPOOL")) 82 { 83 sUrl = "jdbc:weblogic:pool:" + DBName; 84 } 85 else 86 { 87 System.out.println("暂无对应数据库驱动"); 88 } 89 return sUrl; 90 } 91 92 // getters and setters 93 94 public String getDBType() 95 { 96 return DBType; 97 } 98 99 public void setDBType(String dBType) 100 { 101 DBType = dBType; 102 } 103 104 public String getIP() 105 { 106 return IP; 107 } 108 109 public void setIP(String iP) 110 { 111 IP = iP; 112 } 113 114 public String getPort() 115 { 116 return Port; 117 } 118 119 public void setPort(String port) 120 { 121 Port = port; 122 } 123 124 public String getDBName() 125 { 126 return DBName; 127 } 128 129 public void setDBName(String dBName) 130 { 131 DBName = dBName; 132 } 133 134 public String getUserName() 135 { 136 return UserName; 137 } 138 139 public void setUserName(String userName) 140 { 141 UserName = userName; 142 } 143 144 public String getPassWord() 145 { 146 return PassWord; 147 } 148 149 public void setPassWord(String passWord) 150 { 151 PassWord = passWord; 152 } 153 154 }
2、重写一个Connection类,实现Connection接口的方法,同时连接数据库。
参数有已实现的JdbrUrl类,主要新增方法为:createConnection()
根据DBType来对不同数据库进行处理:加载对应的数据库,然后获取数据库连接。

1 ** 2 * 数据库连接类,连接数据库 3 * @author Damon 4 */ 5 public class DBConn implements Connection 6 { 7 8 // 获取JdbcUrl信息 9 private JdbcUrl JUrl; 10 11 // 数据库连接 12 private Connection con = null; 13 14 // 连接是否已使用 15 private boolean bNotInUse; 16 17 private CharArrayWriter m_buf = new CharArrayWriter(); 18 19 private PrintWriter m_pw = new PrintWriter(m_buf, true); 20 21 // 默认连接 22 public DBConn() 23 { 24 // TODO Auto-generated constructor stub 25 this.JUrl = new JdbcUrl(); 26 } 27 28 // 指定数据库连接 29 public DBConn(String urlType) 30 { 31 this.JUrl = new JdbcUrl(urlType); 32 } 33 34 // 创建连接 35 public boolean createConnection() 36 { 37 38 // 根据数据库类型加载驱动及连接 39 try 40 { 41 // 连接MySQL数据库 42 if (SysCon.DATABASE_TYPE_MYSQL.equals(JUrl.getDBType())) 43 { 44 // 加载数据库驱动 45 Class.forName("com.mysql.jdbc.Driver"); 46 47 // 尝试连接数据库 48 con = DriverManager.getConnection(JUrl.getJdbcUrl(), JUrl.getUserName(), JUrl.getPassWord()); 49 } 50 // 其他数据库类型判断及处理 51 // SQLSERVER 52 else if (SysCon.DATABASE_TYPE_SQLSERVER.equals(JUrl.getDBType())) 53 { 54 Class.forName("com.microsoft.jdbc.sqlserver.SQLServerDriver"); 55 con = DriverManager.getConnection(JUrl.getJdbcUrl(), JUrl.getUserName(), JUrl.getPassWord()); 56 } 57 // DB2 58 else if (SysCon.DATABASE_TYPE_DB2.equals(JUrl.getDBType())) 59 { 60 Class.forName("com.ibm.db2.jcc.DB2Driver"); 61 con = DriverManager.getConnection(JUrl.getJdbcUrl(), JUrl.getUserName(), JUrl.getPassWord()); 62 } 63 // ORACLE 64 else if (SysCon.DATABASE_TYPE_ORACLE.equals(JUrl.getDBType())) 65 { 66 Class.forName("oracle.jdbc.driver.OracleDriver"); 67 // 一个是缓存取到的记录数,一个是设置默认的批量提交数 68 Properties props = new Properties(); 69 props.setProperty("user", JUrl.getUserName()); 70 props.setProperty("password", JUrl.getPassWord()); 71 props.setProperty("defaultRowPrefetch", "50"); 72 props.setProperty("defaultExecuteBatch", "50"); 73 con = DriverManager.getConnection(JUrl.getJdbcUrl(), props); 74 } 75 else 76 { 77 System.out.println("未匹配到数据库类型!"); 78 return false; 79 } 80 81 } 82 catch (ClassNotFoundException e) 83 { 84 // TODO Auto-generated catch block 85 System.out.println("加载驱动失败!"); 86 e.printStackTrace(); 87 return false; 88 } 89 catch (SQLException e) 90 { 91 // TODO Auto-generated catch block 92 System.out.println("创建连接失败..." + e.getMessage()); 93 e.printStackTrace(); 94 return false; 95 } 96 return true; 97 } 98 99 protected void setInUse() 100 { 101 /** 102 * Record stack information when each connection is get We reassian 103 * System.err, so Thread.currentThread().dumpStack() can dump stack info 104 * into our class FilterPrintStream. 105 */ 106 new Throwable().printStackTrace(m_pw); 107 108 bNotInUse = false; 109 110 /** 111 * record lastest access time 112 */ 113 } 114 115 /* 下面都是 实现Connection的方法,返回conn的实现 */ 116 public <T> T unwrap(Class<T> iface) throws SQLException 117 { 118 // TODO Auto-generated method stub 119 return con.unwrap(null); 120 } 121 122 public boolean isWrapperFor(Class<?> iface) throws SQLException 123 { 124 // TODO Auto-generated method stub 125 return false; 126 } 127 128 public Statement createStatement() throws SQLException 129 { 130 // TODO Auto-generated method stub 131 return con.createStatement(); 132 } 133 134 public PreparedStatement prepareStatement(String sql) throws SQLException 135 { 136 // TODO Auto-generated method stub 137 return con.prepareStatement(sql); 138 } 139 140 public CallableStatement prepareCall(String sql) throws SQLException 141 { 142 // TODO Auto-generated method stub 143 return con.prepareCall(sql); 144 } 145 146 public String nativeSQL(String sql) throws SQLException 147 { 148 // TODO Auto-generated method stub 149 return con.nativeSQL(sql); 150 } 151 152 public void setAutoCommit(boolean autoCommit) throws SQLException 153 { 154 // TODO Auto-generated method stub 155 con.setAutoCommit(autoCommit); 156 } 157 158 public boolean getAutoCommit() throws SQLException 159 { 160 // TODO Auto-generated method stub 161 return con.getAutoCommit(); 162 } 163 164 public void commit() throws SQLException 165 { 166 // TODO Auto-generated method stub 167 con.commit(); 168 } 169 170 public void rollback() throws SQLException 171 { 172 // TODO Auto-generated method stub 173 con.rollback(); 174 } 175 176 public void close() throws SQLException 177 { 178 // TODO Auto-generated method stub 179 con.close(); 180 } 181 182 public boolean isClosed() throws SQLException 183 { 184 // TODO Auto-generated method stub 185 186 return con.isClosed(); 187 } 188 189 public DatabaseMetaData getMetaData() throws SQLException 190 { 191 // TODO Auto-generated method stub 192 return con.getMetaData(); 193 } 194 195 public void setReadOnly(boolean readOnly) throws SQLException 196 { 197 // TODO Auto-generated method stub 198 con.setReadOnly(readOnly); 199 } 200 201 public boolean isReadOnly() throws SQLException 202 { 203 // TODO Auto-generated method stub 204 return con.isReadOnly(); 205 } 206 207 public void setCatalog(String catalog) throws SQLException 208 { 209 // TODO Auto-generated method stub 210 con.setCatalog(catalog); 211 } 212 213 public String getCatalog() throws SQLException 214 { 215 // TODO Auto-generated method stub 216 return con.getCatalog(); 217 } 218 219 public void setTransactionIsolation(int level) throws SQLException 220 { 221 // TODO Auto-generated method stub 222 con.setTransactionIsolation(level); 223 } 224 225 public int getTransactionIsolation() throws SQLException 226 { 227 // TODO Auto-generated method stub 228 return con.getTransactionIsolation(); 229 } 230 231 public SQLWarning getWarnings() throws SQLException 232 { 233 // TODO Auto-generated method stub 234 return con.getWarnings(); 235 } 236 237 public void clearWarnings() throws SQLException 238 { 239 // TODO Auto-generated method stub 240 con.clearWarnings(); 241 } 242 243 public Statement createStatement(int resultSetType, int resultSetConcurrency) throws SQLException 244 { 245 // TODO Auto-generated method stub 246 return con.createStatement(resultSetType, resultSetConcurrency); 247 } 248 249 public PreparedStatement prepareStatement(String sql, int resultSetType, int resultSetConcurrency) 250 throws SQLException 251 { 252 // TODO Auto-generated method stub 253 return con.prepareStatement(sql, resultSetType, resultSetConcurrency); 254 } 255 256 public CallableStatement prepareCall(String sql, int resultSetType, int resultSetConcurrency) throws SQLException 257 { 258 // TODO Auto-generated method stub 259 return con.prepareCall(sql, resultSetType, resultSetConcurrency); 260 } 261 262 public Map<String, Class<?>> getTypeMap() throws SQLException 263 { 264 // TODO Auto-generated method stub 265 return con.getTypeMap(); 266 } 267 268 public void setTypeMap(Map<String, Class<?>> map) throws SQLException 269 { 270 // TODO Auto-generated method stub 271 con.setTypeMap(map); 272 } 273 274 public void setHoldability(int holdability) throws SQLException 275 { 276 // TODO Auto-generated method stub 277 con.setHoldability(holdability); 278 } 279 280 public int getHoldability() throws SQLException 281 { 282 // TODO Auto-generated method stub 283 return con.getHoldability(); 284 } 285 286 public Savepoint setSavepoint() throws SQLException 287 { 288 // TODO Auto-generated method stub 289 return con.setSavepoint(); 290 } 291 292 public Savepoint setSavepoint(String name) throws SQLException 293 { 294 // TODO Auto-generated method stub 295 return con.setSavepoint(name); 296 } 297 298 public void rollback(Savepoint savepoint) throws SQLException 299 { 300 // TODO Auto-generated method stub 301 con.rollback(savepoint); 302 } 303 304 public void releaseSavepoint(Savepoint savepoint) throws SQLException 305 { 306 // TODO Auto-generated method stub 307 con.releaseSavepoint(savepoint); 308 } 309 310 public Statement createStatement(int resultSetType, int resultSetConcurrency, int resultSetHoldability) 311 throws SQLException 312 { 313 // TODO Auto-generated method stub 314 return con.createStatement(resultSetType, resultSetConcurrency, resultSetHoldability); 315 } 316 317 public PreparedStatement prepareStatement(String sql, int resultSetType, int resultSetConcurrency, 318 int resultSetHoldability) throws SQLException 319 { 320 // TODO Auto-generated method stub 321 return con.prepareStatement(sql, resultSetType, resultSetConcurrency, resultSetHoldability); 322 } 323 324 public CallableStatement prepareCall(String sql, int resultSetType, int resultSetConcurrency, 325 int resultSetHoldability) throws SQLException 326 { 327 // TODO Auto-generated method stub 328 return null; 329 } 330 331 public PreparedStatement prepareStatement(String sql, int autoGeneratedKeys) throws SQLException 332 { 333 // TODO Auto-generated method stub 334 return con.prepareStatement(sql, autoGeneratedKeys); 335 } 336 337 public PreparedStatement prepareStatement(String sql, int[] columnIndexes) throws SQLException 338 { 339 // TODO Auto-generated method stub 340 return con.prepareStatement(sql, columnIndexes); 341 } 342 343 public PreparedStatement prepareStatement(String sql, String[] columnNames) throws SQLException 344 { 345 // TODO Auto-generated method stub 346 return con.prepareStatement(sql, columnNames); 347 } 348 349 public Clob createClob() throws SQLException 350 { 351 // TODO Auto-generated method stub 352 return con.createClob(); 353 } 354 355 public Blob createBlob() throws SQLException 356 { 357 // TODO Auto-generated method stub 358 return con.createBlob(); 359 } 360 361 public NClob createNClob() throws SQLException 362 { 363 // TODO Auto-generated method stub 364 return con.createNClob(); 365 } 366 367 public SQLXML createSQLXML() throws SQLException 368 { 369 // TODO Auto-generated method stub 370 return con.createSQLXML(); 371 } 372 373 public boolean isValid(int timeout) throws SQLException 374 { 375 // TODO Auto-generated method stub 376 return con.isValid(timeout); 377 } 378 379 public void setClientInfo(String name, String value) throws SQLClientInfoException 380 { 381 // TODO Auto-generated method stub 382 con.setClientInfo(name, value); 383 } 384 385 public void setClientInfo(Properties properties) throws SQLClientInfoException 386 { 387 // TODO Auto-generated method stub 388 con.setClientInfo(properties); 389 } 390 391 public String getClientInfo(String name) throws SQLException 392 { 393 // TODO Auto-generated method stub 394 return con.getClientInfo(name); 395 } 396 397 public Properties getClientInfo() throws SQLException 398 { 399 // TODO Auto-generated method stub 400 return con.getClientInfo(); 401 } 402 403 public Array createArrayOf(String typeName, Object[] elements) throws SQLException 404 { 405 // TODO Auto-generated method stub 406 return con.createArrayOf(typeName, elements); 407 } 408 409 public Struct createStruct(String typeName, Object[] attributes) throws SQLException 410 { 411 // TODO Auto-generated method stub 412 return con.createStruct(typeName, attributes); 413 } 414 415 }
3、公共的数据库连接池
数据库配置和数据库连接已经搞定,那么可以建一个数据库连接池来进行数据库的连接及处理。
主要有2个方法,连接默认数据库和连接指定的数据库。

1 /** 2 * 获取默认数据库连接 3 * @param uri 4 * @return 5 */ 6 public static DBConn getConnection() 7 { 8 DBConn dbConn = new DBConn(); 9 if (!dbConn.createConnection()) 10 { 11 // 如果创建连接失败 12 DBSemaphore.unLock(); 13 return null; 14 } 15 16 // 连接成功,设置该连接属性 17 try 18 { 19 // 特殊处理连接的AutoCommit是否已经被设置 20 dbConn.setAutoCommit(true); 21 dbConn.setInUse(); 22 DBSemaphore.unLock(); 23 return dbConn; 24 } 25 catch (Exception ex) 26 { 27 ex.printStackTrace(); 28 DBSemaphore.unLock(); 29 return null; 30 } 31 32 } 33 34 /** 35 * 通过URI地址获取指定数据库连接 36 * @param uri 37 * @return 38 */ 39 public static DBConn getConnection(String uri) 40 { 41 DBConn dbConn = new DBConn(uri); 42 if (!dbConn.createConnection()) 43 { 44 // 如果创建连接失败 45 // DBSemaphore.UnLock(); 46 return null; 47 } 48 try 49 { 50 // 特殊处理连接的AutoCommit是否已经被设置 51 dbConn.setAutoCommit(true); 52 // dbConn.setInUse(); 53 // DBSemaphore.UnLock(); 54 return dbConn; 55 } 56 catch (Exception ex) 57 { 58 ex.printStackTrace(); 59 // DBSemaphore.UnLock(); 60 return null; 61 } 62 63 }
可以写一个测试方式,这也数据库连接就完成了,通过传入不同的参数就可以获取到不同数据库的连接了。

1 public static void main(String[] args) 2 { 3 // 测试连接池 4 5 // 1、连接mysql 数据库 6 Connection conn = DBConnPool.getConnection(); 7 8 if (conn == null) 9 { 10 System.out.println("获取连接失败!"); 11 } 12 else 13 { 14 System.out.println("获取连接成功"); 15 } 16 17 }
第二步,构建数据库连接池
前面已经实现连接不同数据库,那么怎么处理为连接池呢?
数据库连接池负责分配、管理和释放数据库连接,它允许应用程序重复使用一个现有的数据库连接,而不是再重新建立一个;释放空闲时间超过最大空闲时间的数据库连接来避免因为没有释放数据库连接而引起的数据库连接遗漏。这项技术能明显提高对数据库操作的性能。下面我们就来实现数据库连接池的功能:
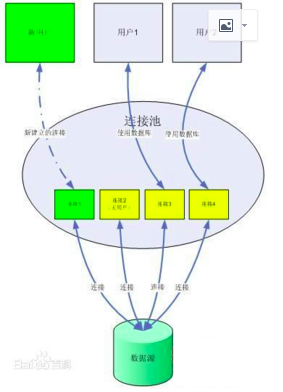
数据库连接池的实现思想主要有如下几个方面:
1、可定义最大和最小的连接数:如果请求小于最小连接数,则直接分配连接,达到最大连接数则新请求等待;
2、用户在连接数据库时,不用新建连接,而是直接从连接池中获取连接,使用完毕后也不用关闭,而是释放给连接池,供下一个用户使用;
下面来进行实现:
其实就是实现了一个数据连接数的判断,最大连接数进行限制,实际的数据库连接池需结合对应的数据库连接池组件(比如 WebSphere等中间件),在判断是否有连接在使用的时候,会涉及到并发,这里需要用到volatile关键字。
其中,增加了DBsemaphor类,用以处理连接的使用和释放。
在原有DBConn基础上,加上是否已使用方法,在获取连接成功时调用,具体代码如下:

1 // 连接成功,设置该连接属性 2 try 3 { 4 // 特殊处理连接的AutoCommit是否已经被设置 5 dbConn.setAutoCommit(true); 6 dbConn.setInUse(); 7 DBSemaphore.unLock(); 8 return dbConn; 9 } 10 catch (Exception ex) 11 { 12 ex.printStackTrace(); 13 DBSemaphore.unLock(); 14 return null; 15 }
新增DBSemaphore类属性及方法如下:

1 /** 2 * 数据库同步对象 3 * @author Damon 4 */ 5 public class DBSemaphore 6 { 7 private static volatile boolean m_bInUse = false; 8 9 public DBSemaphore() 10 {} 11 12 /** 13 * 设置"使用标志"。 传入true表示请求“使用标志”,传入false表示释放“使用标志”。 14 * @param bNewValue boolean 15 * @return boolean 16 */ 17 protected static synchronized boolean setInUseFlag(boolean bNewValue) 18 { 19 if (bNewValue == true) 20 { 21 // 请求“使用标志” 22 if (m_bInUse == true) 23 { 24 // “使用标志”已经被占用 25 return false; 26 } 27 else 28 { 29 m_bInUse = true; 30 return true; 31 } 32 } 33 else 34 { 35 // 释放“使用标志” 36 m_bInUse = false; 37 return true; 38 } 39 } 40 41 protected static void lock() throws Exception 42 { 43 lock(0); 44 } 45 46 protected static void lock(int nSeconds) throws Exception 47 { 48 if (nSeconds <= 0) 49 { 50 while (!setInUseFlag(true)) 51 { 52 Thread.sleep(100); 53 } 54 } 55 else 56 { 57 while (!setInUseFlag(true) && nSeconds-- > 0) 58 { 59 Thread.sleep(100); 60 } 61 62 if (nSeconds == 0) 63 { 64 throw new Exception("Lock time out"); 65 } 66 } 67 } 68 69 protected static void unLock() 70 { 71 setInUseFlag(false); 72 } 73 }
到这里,整个配置处理结束了,更多的就需要在实际项目中发挥了~
