1. 数据库概述及环境搭建
1.1 为什么要使用数据库
- 动态网站中的数据都是存储在数据库中的
- 数据库可以用来持久存储客户端通过表单收集的用户信息
- 数据库软件本身可以对数据进行高效的管理
1.2 什么是数据库
数据库即存储数据的仓库,可以将数据进行有序的分门别类的存储。它是独立于语言之外的软件,可以通过API去操作它。
常见的数据库软件有:mysql、mongoDB、oracle

1.3 MongoDB数据库下载安装
下载地址:https://www.mongodb.com/download-center/community
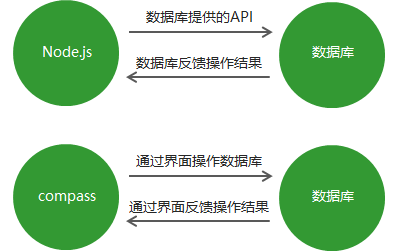
1.4 MongoDB可视化软件
MongoDB可视化软件,是使用图形界面操作数据库的一种方式。
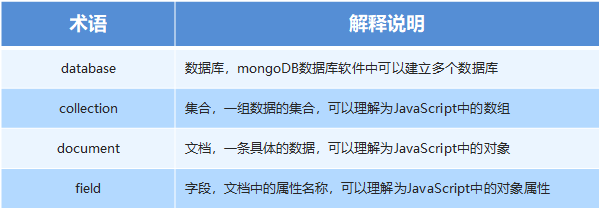
1.5 数据库相关概念
在一个数据库软件中可以包含多个数据仓库,在每个数据仓库中可以包含多个数据集合,每个数据集合中可以包含多条文档(具体的数据)。
1.6 Mongoose第三方包
- 使用Node.js操作MongoDB数据库需要依赖Node.js第三方包mongoose
- 使用 npm install mongoose 命令下载
1.7 启动MongoDB
在命令行工具中运行 net start mongoDB即可运行MonoDB,否则MongoDB将无法链接 必须以管理员身份运行

1.8 数据库连接
使用mongoose提供的connect方法即可连接数据库。
const mongoose = require('mongoose');
// mongoose.connect('mongodb://localhost/数据库的名字')
// 在MongoDB中不需要显示创建数据库,如果正在使用的数据库不存在,在MongoDB自动创建。
mongoose.connect('mongodb://localhost/playground', { useNewUrlParser: true, useUnifiedTopology: true })
.then(() => console.log('数据库连接成功'))
.catch(err => console.log(err, '数据库连接失败'));
1.9 创建数据库
在MongoDB中不需要显示创建数据库,如果正在使用的数据库不存在,MongoDB会自动创建。
2. MongoDB增删改查操作
2.1 创建集合
创建集合分为两步:一是对集合设定规则,二是<font color="red>创建集合,创建集合mongoose.Schema构造函数的实例即可创建集合。
2.2 创建文档
创建文档实际上就是向集合中插入数据。
分为两步:
- 创建集合的实例。
- 调用实例对象下的save方法将数据保存到数据库中。
// 引入mongoose第三方模块,用来操作数据库
const mongoose = require('mongoose');
// 数据库的连接
mongoose.connect('mongodb://localhost/playground', { useNewUrlParser: true, useUnifiedTopology: true })
// 连接成功
.then(() => console.log('数据库连接成功'))
// 连接失败
.catch(err => console.log(err, '数据库连接失败'));
// 创建集合规则
const courseSchema = new mongoose.Schema({
name: String,
author: String,
isPublished: Boolean
});
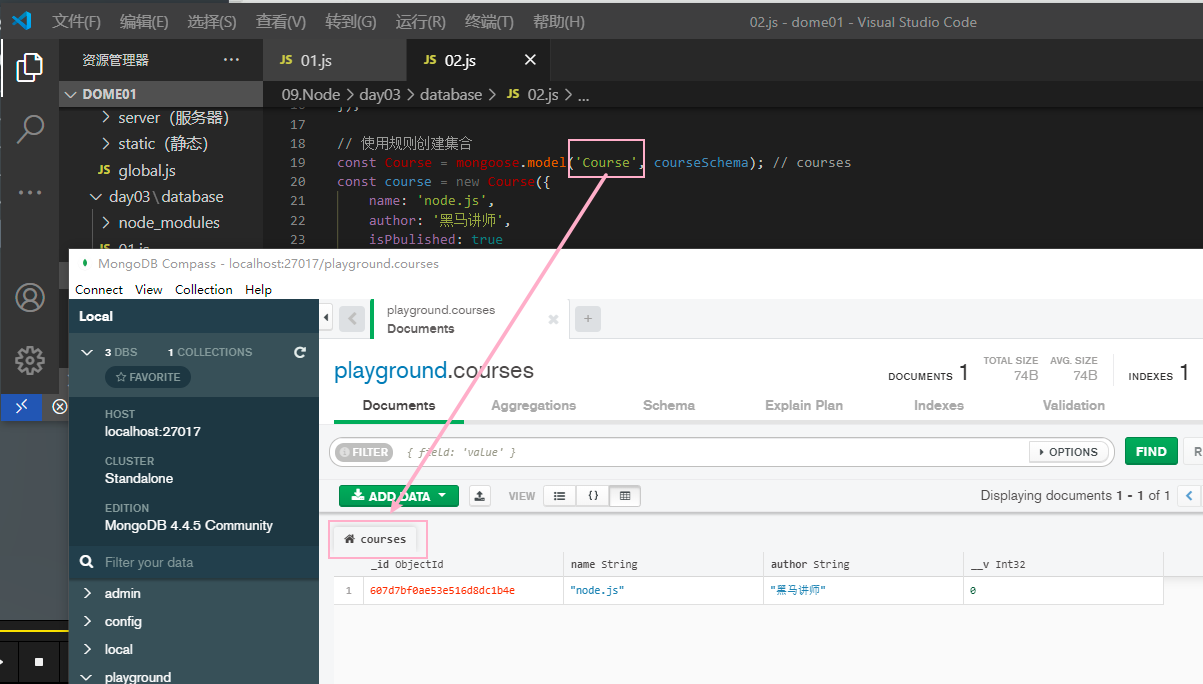
// 使用规则创建集合
const Course = mongoose.model('Course', courseSchema); // courses
const course = new Course({
name: 'node.js',
author: '黑马讲师',
isPbulished: true
});
course.save();
第二种方式
// 引入mongoose第三方模块,用来操作数据库
const mongoose = require('mongoose');
// 数据库的连接
mongoose.connect('mongodb://localhost/playground', { useNewUrlParser: true, useUnifiedTopology: true })
// 连接成功
.then(() => console.log('数据库连接成功'))
// 连接失败
.catch(err => console.log(err, '数据库连接失败'));
// 创建集合规则
const courseSchema = new mongoose.Schema({
name: String,
author: String,
isPublished: Boolean
});
// 使用规则创建集合
// 1. 集合名称
// 2. 集合规则
const Course = mongoose.model('Course', courseSchema); // courses
// 向集合中插入文档
// 向集合中插入文档
// Course.create({ name: 'JavaScript', author: '黑马讲师', isPublished: false }, (err, result) => {
// console.log(err);
// console.log(result);
// })
Course.create({ name: 'JavaScript123', author: '黑马讲师', isPublished: false })
.then((result) => {
console.log(result);
})
.catch((err) => {
console.log(err);
})
2.3 mongoDB数据库导入数据
mongoimport -d 数据库名 -c 集合名称 --file 要导入的数据文件
找到mongodb数据库的安装目录,将安装目录下的bin目录放置在环境变量中。

2.4 查询文档
// 引入mongoose第三方模块 用来操作数据库
const mongoose = require('mongoose');
// 数据库连接
mongoose.connect('mongodb://localhost/playground', { useNewUrlParser: true, useUnifiedTopology: true })
// 连接成功
.then(() => console.log('数据库连接成功'))
// 连接失败
.catch(err => console.log(err, '数据库连接失败'));
// 创建集合规则
const userSchema = new mongoose.Schema({
name: String,
age: Number,
email: String,
password: String,
hobbies: [String]
});
// 使用规则创建集合
const User = mongoose.model('User', userSchema);
// 查询用户集合中的所有文档
// User.find().then(result => console.log(result));
// 通过_id字段查找文档
// User.find({ _id: '5c09f267aeb04b22f8460968' }).then(result => console.log(result))
// findOne方法返回一条文档 默认返回当前集合中的第一条文档
// User.findOne({ name: '李四' }).then(result => console.log(result))
// 查找用户集合中年龄字段大于20并且小于40的文档
// User.find({ age: { $gt: 20, $lt: 40 } }).then(result => console.log(result))
// 查询用户集合中hobbies字段值包含足球的文档
// User.find({ hobbies: { $in: ['足球'] } }).then(result => console.log(result))
// 选择要查询的字段
// User.find().select('name email -_id').then(result => console.log(result))
// 根据年龄字段进行升序排列
// User.find().sort('age').then(result => console.log(result))
// 根据年龄字段进行降序排列
// User.find().sort('-age').then(result => console.log(result))
// 查询文档跳过前两条结果 限制显示3条结果
User.find().skip(2).limit(3).then(result => console.log(result))
2.5 删除文档
// 查找到一条文档并且删除
// 返回删除的文档
// 如何查询条件匹配多个文档 那么将会删除第一个匹配的文档
User.findOneAndDelete({ _id: '5c09f267aeb04b22f8460968' }).then(result => console.log(result));
// 删除多个文档
User.deleteMany({}).then(result => console.log(result));

2.6 更新文档
// 更新单个
userInfo.updateOne({ 查询条件 }, { 要修改的值 }).then(result => console.log(result));
// 引入mongoose第三方模块 用来操作数据库
const mongoose = require('mongoose');
// 数据库连接
mongoose.connect('mongodb://localhost/playground', { useNewUrlParser: true, useUnifiedTopology: true })
// 连接成功
.then(() => console.log('数据库连接成功'))
// 连接失败
.catch(err => console.log(err, '数据库连接失败'));
// 创建集合规则
const userSchema = new mongoose.Schema({
name: String,
age: Number,
email: String,
password: String,
hobbies: [String]
});
// 使用规则创建集合
const User = mongoose.model('User', userSchema);
// 更新集合中的文档(更新单个)
// User.updateOne({ name: '李四' }, { name: '李狗蛋' }).then(result => console.log(result));
// 更新集合中的多个文档(更新多个)
User.updateMany({}, { age: 56 }).then(result => console.log(result))
运行结果为:

2.7 mongoose验证
在创建集合规则时,可以设置当前字段的验证规则,验证失败就输入插入失败
- required:ture 必传字段
- minlength: 3 字符串最小长度
- maxlength: 20 字符串最大长度
- min: 2 数值最小为2
- max: 100 数值最大为100
- enum: ['html','css','javascript','node.js']
- trim: true 去除字符串两边的空格
- validate: 自定义验证器
- default: 默认值
获取错误信息: error.errors['字段名称'].message
// 引入mongoose第三方模块 用来操作数据库
const mongoose = require('mongoose');
// 数据库连接
mongoose.connect('mongodb://localhost/playground', { useNewUrlParser: true, useUnifiedTopology: true })
// 连接成功
.then(() => console.log('数据库连接成功'))
// 连接失败
.catch(err => console.log(err, '数据库连接失败'));
const postSchema = new mongoose.Schema({
title: {
type: String,
// 必传字段
required: [true, '请传入文章标题'],
// 字符串的最小长度
minlength: [2, '文章长度不能小于2'],
// 字符串的最大长度
maxlength: [6, '文章长度不能超过6'],
// 去除字符串两边的空格
trim: true
},
age: {
type: Number,
// 数字的最小值
min: 18,
// 数字的最大值
max: 100
},
publishDate: {
type: Date,
// 默认值
default: Date.now
},
category: {
type: String,
// 枚举 列举出当前字段可以拥有的值
enum: {
values: ['html', 'css', 'JavaScript'],
message: '分类名称要在一定的范围内才可以'
}
},
author: {
type: String,
validate: {
validator: v => {
// 返回布尔值
// true 验证成功
// false 验证失败
// v 要验证的值
return v && v.length > 4
},
// 错误信息
message: '传入的值不符合验证规则'
},
}
});
const Post = mongoose.model('Post', postSchema);
Post.create({ title: ' aa ', age: 45, category: 'java', author: 'ad' })
.then(result => console.log(result))
.catch(error => {
// 获取错误信息对象
const err = error.errors;
// 循环错误信息对象
for (var attr in err) {
// 将错误信息打印到控制台中
console.log(err[attr]['message']);
}
});
2.8 集合并联
通产不同集合的数据之间是有关联的,例如文章信息和用户信息存储在不同的集合中,但文章是某个用户发表的,要查询文章的所有信息包括发表用户,就需要用到集合并联。
- 使用id对集合进行并联
- 使用populate方法进行并联集合查询

require('./08.js');
// 引入mongoose第三方模块 用来操作数据库
const mongoose = require('mongoose');
// 数据库连接
mongoose.connect('mongodb://localhost/playgrounds', { useNewUrlParser: true, useUnifiedTopology: true })
// 连接成功
.then(() => console.log('数据库连接成功'))
// 连接失败
.catch(err => console.log(err, '数据库连接失败'));
// 用户集合规则
const userSchema = new mongoose.Schema({
name: {
type: String,
require: true
}
});
// 文章集合规则
const postSchema = new mongoose.Schema({
title: {
type: String
},
author: {
type: mongoose.Schema.Types.ObjectId,
ref: 'User'
}
});
// 用户集合
const User = mongoose.model('User', userSchema);
// 文章集合
const Post = mongoose.model('Post', postSchema);
// 创建用户
// User.create({ name: '黑马' }).then(result => console.log(result))
// 创建文章
// Post.create({ title: '平凡的世界', author: '60814e36f8cd4e3e706c1cfe' }).then(result => console.log(result));
// Post.find().then(result => console.log(result));
Post.find().populate('author').then(result => console.log(result));
