题目
点这里看题目。
分析
考虑做不来就该直接赛后看题解。
下面称花费为 (a) 的移动为小跳,花费为 (b) 的移动为大跳。
考虑 (i) 这个位置被经过,必须要满足,对于任意 (j<i,p_j>p_i) , (j) 都被经过(我们可以认为 (p_0=n+1) )。
注意到对于最右边的一个 (j) , (j) 要被经过,也要满足类似的条件。这意味着我们只需要在图上建立链式的结构就可以表示 (i) 的限制;多个链式的结构,凑在一起,就变成了一棵树。
下图展示了 (p=[2,1,5,3,4]) 的树形结构(图源官方题解)
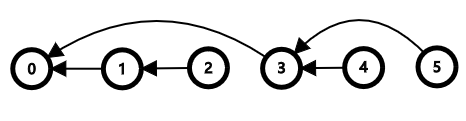
对于这棵树,基本分析如下:
-
0 一定会被经过。
-
如果 (i) 要被经过,那么 (i) 的祖先一定都会选择小跳。
-
如果 (i) 这里选择了大跳,就相当于直接跳过 (i) 的子树而进入到了它相邻下一个兄弟。
因此,可以单独考虑小跳的节点集合 (S) (其他节点为大跳或不经过)。
根据上面的分析,可以知道 (S) 一定为包含 0 的一棵子树。
针对某一特定的 (S) ,可以得到花费为:
[sum_{uin S}a_u+sum_{u
ot=S,fa_uin S}b_u
]
简单地做一下差分使各项独立——设 (c_x=a_x-b_x+sum_{fa_y=x}b_y) ,那么花费可以改写成:
[sum_{uin S}c_u
]
回过头来考虑题目的限制,可以发现它等价于强制 (S) 必须包含某棵以 0 为根的子树。那么我们可以用 set 在 DFS 序上面维护一下强制要选的部分的和,剩下的,则可以预处理出每一个子树的最优选法的和,然后计算一下[1]。
时间就是 (O((n+q)log_2n)) 。
小结:
- 将原题的限制转化成树形结构,联系祖先,确实是很巧的方法。
- 差分技巧的使用。
代码
#include <set>
#include <cmath>
#include <cstdio>
using namespace std;
#define rep( i, a, b ) for( int i = (a) ; i <= (b) ; i ++ )
#define per( i, a, b ) for( int i = (a) ; i >= (b) ; i -- )
typedef long long LL;
typedef set<int> :: iterator Iter;
const int MAXN = 2e5 + 5, MAXLOG = 20;
template<typename _T>
void read( _T &x )
{
x = 0;char s = getchar();int f = 1;
while( s > '9' || s < '0' ){if( s == '-' ) f = -1; s = getchar();}
while( s >= '0' && s <= '9' ){x = ( x << 3 ) + ( x << 1 ) + ( s - '0' ), s = getchar();}
x *= f;
}
template<typename _T>
void write( _T x )
{
if( x < 0 ){ putchar( '-' ); x = ( ~ x ) + 1; }
if( 9 < x ){ write( x / 10 ); }
putchar( x % 10 + '0' );
}
struct Edge
{
int to, nxt;
}Graph[MAXN << 1];
set<int> s;
int buc[MAXN];
bool vis[MAXN];
int f[MAXN][MAXLOG];
LL su[MAXN], bst[MAXN];
int DFN[MAXN], dep[MAXN], seq[MAXN], head[MAXN];
int stk[MAXN], top;
int A[MAXN], B[MAXN], P[MAXN];
int N, Q, cnt, lg2, ID; LL ans = 0;
void AddEdge( const int from, const int to )
{
Graph[++ cnt].to = to, Graph[cnt].nxt = head[from];
head[from] = cnt;
}
void DFS( const int u, const int fa )
{
seq[DFN[u] = ++ ID] = u;
dep[u] = dep[fa] + 1, f[u][0] = fa;
for( int i = head[u], v ; i ; i = Graph[i].nxt )
if( ( v = Graph[i].to ) ^ fa )
{
DFS( v, u ), su[u] += B[v];
if( bst[v] < 0 ) bst[u] += bst[v], bst[v] = 0;
}
bst[u] += A[u] - B[u] + su[u];
}
void Init()
{
DFS( 0, 0 ), lg2 = log2( N );
rep( j, 1, lg2 ) rep( i, 1, N )
f[i][j] = f[f[i][j - 1]][j - 1];
rep( i, 2, N ) bst[seq[i]] += bst[f[seq[i]][0]];
}
void Balance( int &u, const int stp )
{
for( int i = 0 ; ( 1 << i ) <= stp ; i ++ )
if( stp >> i & 1 ) u = f[u][i];
}
int LCA( int u, int v )
{
if( dep[u] > dep[v] ) Balance( u, dep[u] - dep[v] );
if( dep[v] > dep[u] ) Balance( v, dep[v] - dep[u] );
if( u == v ) return u;
per( i, lg2, 0 ) if( f[u][i] ^ f[v][i] ) u = f[u][i], v = f[v][i];
return f[u][0];
}
LL Dist( const int u, const int v ) { return bst[u] + bst[v] - 2 * bst[LCA( u, v )]; }
void Insert( const int u )
{
Iter it = ( s.insert( DFN[u] ), s.find( DFN[u] ) );
int pre = 0, nxt = 0;
if( it != s.begin() ) pre = seq[* -- it]; it ++;
if( it != s.end() && ( ++ it ) != s.end() ) nxt = seq[* it];
ans += Dist( u, pre ) + Dist( u, nxt ) - Dist( pre, nxt );
}
void Delete( const int u )
{
set<int> :: iterator it = s.find( DFN[u] );
int pre = 0, nxt = 0;
if( it != s.end() )
{
it ++;
if( it != s.end() )
nxt = seq[* it];
it --;
}
if( it != s.begin() ) pre = seq[* -- it];
ans -= Dist( u, pre ) + Dist( u, nxt ) - Dist( pre, nxt );
s.erase( DFN[u] );
}
int main()
{
read( N ), read( Q );
rep( i, 1, N ) read( P[i] );
rep( i, 1, N ) read( A[i] );
rep( i, 1, N ) read( B[i] );
for( int i = 1 ; i <= N ; i ++ )
{
while( top && P[stk[top]] <= P[i] ) top --;
AddEdge( stk[top], i ), stk[++ top] = i;
}
Init();
for( int cur ; Q -- ; )
{
read( cur );
if( vis[cur] )
{
vis[cur] = false;
if( ! ( -- buc[f[cur][0]] ) )
Delete( f[cur][0] );
}
else
{
vis[cur] = true;
if( ! ( buc[f[cur][0]] ++ ) )
Insert( f[cur][0] );
}
write( ans / 2 + bst[0] ), putchar( '
' );
}
return 0;
}
实际上这里 (c) 可以直接预处理成子树内的最优解,然后将被父亲选中的子树的 (c) 改成 0 就 OK 了。 ↩︎