实体识别的基本技术是分块(chunking)
名词短语分块(NP-分块)
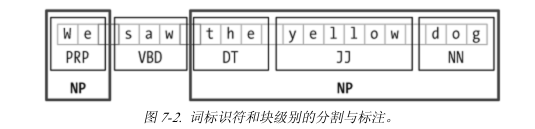
这里有一段已经标注的例子:
方括号中是名词标注的例子。
NP-分块信息最有用的来源之一是词性标记。
为了创建一个NP块,我们将首先定义一个块语法,规定了句子应该如何分块。
我们使用正则表达式来定义,规则可以我们自己定:一个NP块由一个可选的限定词(DT)后面跟着任何数目的形容词(JJ),然后是一个名词(NN组成)。
下面是示例代码:
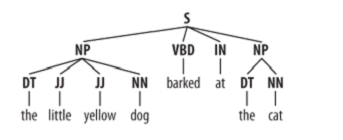
>>>sentence = [("the", "DT"), ("little", "JJ"), ("yellow", "JJ"), ... ("dog", "NN"), ("barked", "VBD"), ("at", "IN"), ("the", "DT"), ("cat", "NN")] >>>grammar= "NP: {<DT>?<JJ>*<NN>}" >>>cp = nltk.RegexpParser(grammar) >>>result = cp.parse(sentence) >>>print result (S (NP the/DT little/JJ yellow/JJdog/NN) barked/VBD at/IN (NP the/DT cat/NN)) >>>result.draw()
标记模式类似于正则表达式模式。<DT>?<JJ>*<NN>
用正则表达式分块
在这个例子中,不仅仅只有一个规则,定义了两个规则。依然可以类似于上面的做法进行分块。
NNP为专有名词;DT为限定词;PP$为所有格代名词($为特殊符号,必须加转义\进行匹配);JJ为形容词;
grammar= r""" NP:{<DT|PP\$>?<JJ>*<NN>} # chunk determiner/possessive,adjectives and nouns {<NNP>+} #chunksequences of propernouns """ cp= nltk.RegexpParser(grammar) sentence = [("Rapunzel", "NNP"), ("let", "VBD"), ("down", "RP"), ("her", "PP$"), ("long", "JJ"), ("golden", "JJ"), ("hair", "NN")] >>>print cp.parse(sentence) (S (NP Rapunzel/NNP) let/VBD down/RP (NP her/PP$long/JJ golden/JJhair/NN))
如果标记模式匹配位置重叠,最左边的优先。
例如:
>>>nouns= [("money", "NN"), ("market", "NN"), ("fund", "NN")] >>>grammar= "NP: {<NN><NN>} #Chunktwo consecutive nouns" >>>cp = nltk.RegexpParser(grammar) >>>print cp.parse(nouns) (S (NP money/NNmarket/NN)fund/NN)
为了解决这个问题,可以改进一下这个规则:NP:{<NN>+}。
搜索文本语料库
我们也可以使用分块器更容易的做同样的具体的工作:
>>>cp = nltk.RegexpParser('CHUNK: {<V.*><TO><V.*>}') >>>brown= nltk.corpus.brown 240 >>>for sent in brown.tagged_sents(): ... tree = cp.parse(sent) ... for subtree in tree.subtrees(): ... if subtree.node =='CHUNK': print subtree ... (CHUNK combined/VBN to/TO achieve/VB) (CHUNK continue/VB to/TO place/VB) (CHUNK serve/VB to/TO protect/VB) (CHUNK wanted/VBDto/TO wait/VB) (CHUNK allowed/VBN to/TO place/VB) (CHUNK expected/VBN to/TO become/VB) ... (CHUNK seems/VBZ to/TO overtake/VB) (CHUNK want/VBto/TO buy/VB)
加缝隙
加缝隙,是从一大块中出去一个标识符序列的过程。如果匹配的标识符序列贯穿成一整块,那么这一块会被去除。
下面这个例子将会演示代码过程:
grammar= r""" NP: {<.*>+} #Chunkeverything }<VBD|IN>+{ #Chinksequences of VBDand IN """ sentence = [("the", "DT"), ("little", "JJ"), ("yellow", "JJ"), ("dog", "NN"), ("barked", "VBD"), ("at", "IN"), ("the", "DT"), ("cat", "NN")] cp= nltk.RegexpParser(grammar) >>>print cp.parse(sentence) (S (NP the/DT little/JJ yellow/JJdog/NN) barked/VBD at/IN (NP the/DT cat/NN))
块的表示:标记与树
块结构是标注和分析之间的中间状态。
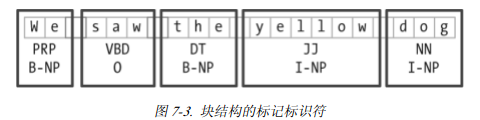
块结构可以用标记或者树来表示。使用最多的,是使用IOB标记。
每个标识符被用三个特殊的块标签之一标注。
I内部,O外部,B开始。一般没有必要指定出现在块外的标识符类型,都标志为O。
如图所示:
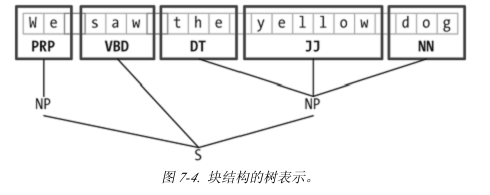
同样,块也可以使用树来表示。如图: