1. Concurrent
用ReentrantLock+Condition实现Blocking Queue。
class TaskQueue{
final Queue<String> queue = new LinkedList<>();
final Lock lock = new ReentrantLock();
final Condition noEmpty = lock.newCondition();
public String getTask(){...}
public void addTask(String name){...}
}
Blocking Queue:当一个线程调用这个Queue的getTask()时,该方法内部可能让给线程变成等待状态,直到条件满足。线程被唤醒以后,getTask()才会返回。
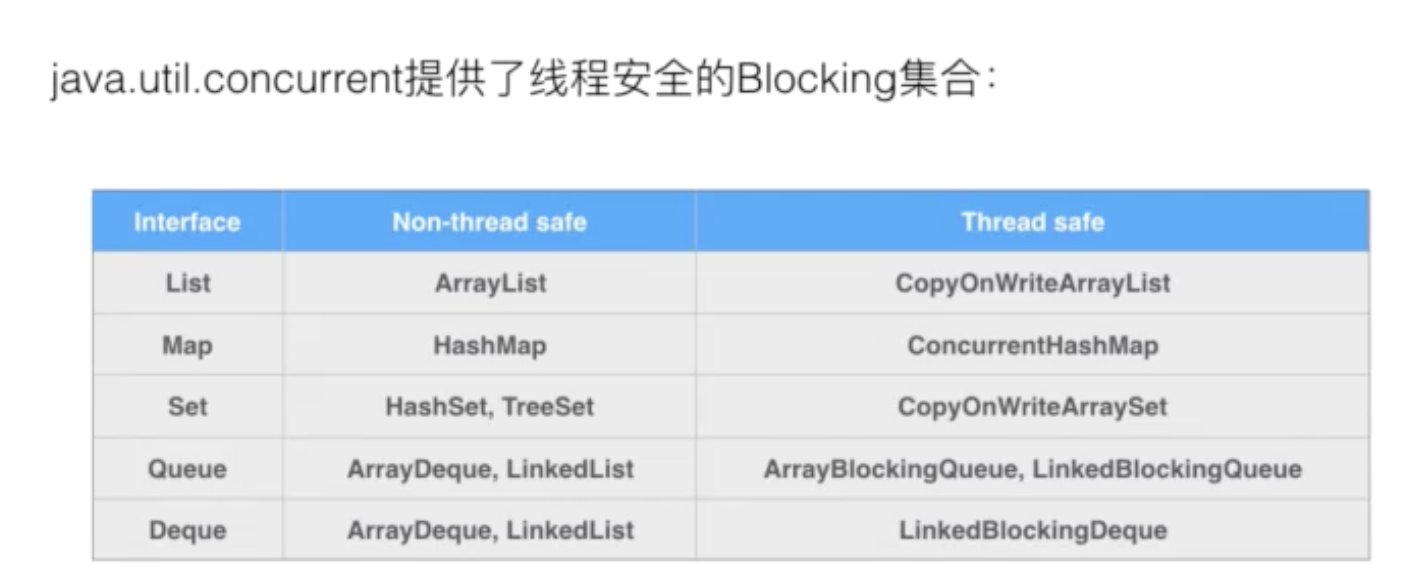
而java.util.concurrent提供了线程安全的Blocking集合,如ArrayBlockingQueue就已经包含了一个线程安全的BlockingQueue。
2. 示例
当我们使用BlockingQueue的时候,我们的代码又被大大的简化了。take()是BlockingQueue提供的一个Blocking方法。当我们调用take()方法的时候,在内部可能会被阻塞,直到条件满足线程才会返回。
import java.util.concurrent.ArrayBlockingQueue;
import java.util.concurrent.BlockingQueue;
class WorkerThread extends Thread{
BlockingQueue<String> taskQueue;
public WorkerThread(BlockingQueue<String> taskQueue){
this.taskQueue = taskQueue;
}
public void run(){
while(!isInterrupted()){
String name;
try{
name = taskQueue.take();
}catch (InterruptedException e){
break;
}
String result = "Hello,"+name+"!";
System.out.println(result);
}
}
}
public class Main{
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception{
//在main方法中,我们不需要自己编写一个BlockingQueue。我们可以直接使用ArrayBlockingQueue,然后向Queue中添加3个任务
BlockingQueue<String> taskQueue = new ArrayBlockingQueue<>(1000);
WorkerThread worker = new WorkerThread(taskQueue);
worker.start();
taskQueue.put("Bob");
Thread.sleep(1000);
taskQueue.put("Alice");
Thread.sleep(1000);
taskQueue.put("Tim");
Thread.sleep(1000);
worker.interrupt();
worker.join();
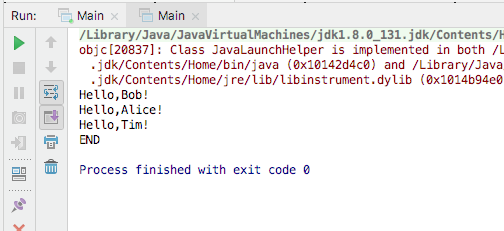
System.out.println("END");
}
}
 ## 3.java.util.concurrent提供了线程安全的Blocking集合
## 3.java.util.concurrent提供了线程安全的Blocking集合
 ## 4.java.util.Collections工具类
java.util.Collections工具类还提供了旧的线程安全集合转换器:
如把一个HashMap转化为一个线程安全的Map。实际上使用一个线程类,包装了非线程安全的map,然后对所有的读写方法都用synchronized加锁,这样获得了线程安全的集合。它的性能比Concurrent低很多,不推荐使用。。
```#java
Map unsafeMap = new HashMap();
Map threadSafeMap = Collections.synchronizedMap(unsafeMap);
```
## 4.java.util.Collections工具类
java.util.Collections工具类还提供了旧的线程安全集合转换器:
如把一个HashMap转化为一个线程安全的Map。实际上使用一个线程类,包装了非线程安全的map,然后对所有的读写方法都用synchronized加锁,这样获得了线程安全的集合。它的性能比Concurrent低很多,不推荐使用。。
```#java
Map unsafeMap = new HashMap();
Map threadSafeMap = Collections.synchronizedMap(unsafeMap);
```
5. 总结:
使用java.util.concurrent提供的Blocking集合可以简化多线程编程
- 多线程同时访问Blocking集合是安全的
- 尽量使用JDK提供的concurrent集合,避免自己编写同步代码