Map是STL的一个关联容器,它提供一对一(其中第一个可以称为关键字(key),每个关键字只能在map中出现一次,第二个可能称为该关键字的值(value))的数据 处理能力,由于这个特性,它完成有可能在我们处理一对一数据的时候,在编程上提供快速通道。这里说下map内部数据的组织,map内部自建一颗红黑树(一 种非严格意义上的平衡二叉树),这颗树具有对数据自动排序的功能,所以在map内部所有的数据都是有序的。
1、map简介
map是一类关联式容器。它的特点是增加和删除节点对迭代器的影响很小,除了那个操作节点,对其他的节点都没有什么影响。
对于迭代器来说,可以修改实值,而不能修改key。
2、map的功能
自动建立Key - value的对应。key 和 value可以是任意你需要的类型。
根据key值快速查找记录,查找的复杂度基本是Log(N),如果有1000个记录,最多查找10次,1,000,000个记录,最多查找20次。
快速插入Key -Value 记录。
快速删除记录
根据Key 修改value记录。
遍历所有记录。
3、使用map
使用map得包含map类所在的头文件
#include <map> //STL头文件没有扩展名.h
map对象是模板类,需要关键字和存储对象两个模板参数:
std:map<int,string> personnel;
这样就定义了一个用int作为索引,并拥有相关联的指向string的指针.
4、map的构造函数
map共提供了6个构造函数,这块涉及到内存分配器这些东西,略过不表,在下面我们将接触到一些map的构造方法,这里要说下的就是,我们通常用如下方法构造一个map:
map<int, string> mapStudent;
5、数据的插入
在构造map容器后,我们就可以往里面插入数据了。这里讲两种插入数据的方法:
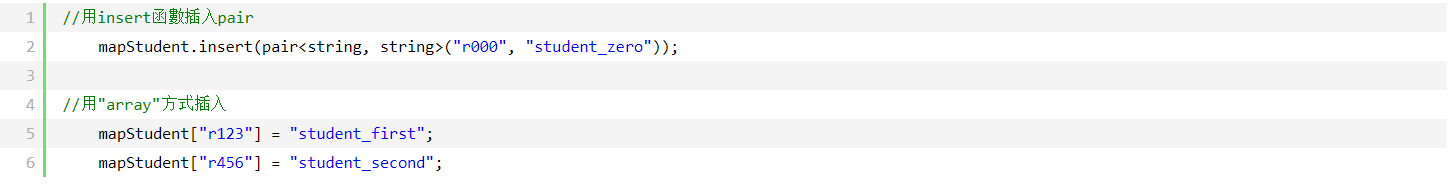
我们通过pair的第二个变量来知道是否插入成功,它的第一个变量返回的是一个map的迭代器,如果插入成功的话Insert_Pair.second应该是true的,否则为false。
通过下面代码可以看出用以一种方法进行插入时,当key对应的value已经存在不能重新给key相对应的value赋值
#include <iostream> #include <cmath> #include <algorithm> #include <set> #include <cstdio> #include <map> #include <string> #include <cstring> /*@author:浅滩 *family: *time: */ //我好像是一个在海边玩耍的孩子, //不时为拾到比通常更光滑的石子或更美丽的贝壳而欢欣鼓舞, //而展现在我面前的是完全未探明的真理之海 using namespace std; int main() { map<int, string> mapStudent; pair<map<int, string>::iterator, bool> Insert_Pair; Insert_Pair = mapStudent.insert(pair<int, string>(1, "student_one")); if(Insert_Pair.second == true) cout<<"Insert Successfully"<<endl; else cout<<"Insert Failure"<<endl; Insert_Pair = mapStudent.insert(pair<int, string>(1, "student_two")); if(Insert_Pair.second == true) cout<<"Insert Successfully"<<endl; else cout<<"Insert Failure"<<endl; map<int, string>::iterator iter; for(iter = mapStudent.begin(); iter != mapStudent.end(); iter++) cout<<iter->first<<' '<<iter->second<<endl; }
下面代码说明可以用第二种方法进行key对应value的覆盖
//验证数组形式插入数据的效果 #include <map> #include <string> #include <iostream> using namespace std; int main() { map<int, string> mapStudent; mapStudent[1] = "student_one"; mapStudent[1] = "student_two"; mapStudent[2] = "student_three"; map<int, string>::iterator iter; for(iter = mapStudent.begin(); iter != mapStudent.end(); iter++) cout<<iter->first<<' '<<iter->second<<endl; }
6、数据的查找(按key查找)
这里给出两种数据查找方法:
第一种:用count函数来判定关键字是否出现,其缺点是无法定位数据出现位置,由于map的特性,一对一的映射关系,就决定了count函数的返回值只有两个,要么是0,要么是1,出现的情况,当然是返回1了
第二种:用find函数来定位数据出现位置,它返回的一个迭代器,当数据出现时,它返回数据所在位置的迭代器,如果map中没有要查找的数据,它返回的迭代器等于end函数返回的迭代器。
#include <map> #include <string> #include <iostream> using namespace std; int main() { map<int, string> mapStudent; mapStudent.insert(pair<int, string>(1, "student_one")); mapStudent.insert(pair<int, string>(2, "student_two")); mapStudent.insert(pair<int, string>(3, "student_three")); map<int, string>::iterator iter; iter = mapStudent.find(1); if(iter != mapStudent.end()) //key不存在时返回最后一个数据迭代的下一个 cout<<"Find, the value is "<<iter->second<<endl; else cout<<"Do not Find"<<endl; return 0; }
通过map对象的方法获取的iterator数据类型是一个std::pair对象,包括两个数据 iterator->first和 iterator->second分别代表关键字和存储的数据。
7、 从map中删除元素
移除某个map中某个条目用erase()
该成员方法的定义如下:
iterator erase(iterator it);//通过一个条目对象删除
iterator erase(iterator first,iterator last)//删除一个范围
size_type erase(const Key&key);//通过关键字删除
clear()就相当于enumMap.erase(enumMap.begin(),enumMap.end());

8、排序之后再说吧