委托的概念
一、了解委托(delegate)
1、委托是一种全新的面向对象语言特性,运行在.NET平台
2、基于委托,开发事件驱动程序变得非常简单
3、使用委托可以大大简化多线程的难度
二、理解委托
1、委托,也可以看成是一种数据类型,可以定义变量,但是它是一种特殊的变量
2、委托定义的变量能接收的数值只能是一个方法(函数),可以理解成委托就是一个方法(函数)的指针(存储方法的变量)
方法1
方法调用---->委托对象----> 方法2
方法3
委托的使用
【1】声明委托(定义一个函数的原型:返回值+参数类型和个数)注意:委托的声明要定义在类的外面
public delegate int CalculatorDelegate(int a,int b);
【2】根据委托定义一个“具体方法”实现加法功能(写在类里面)
static int Add(int a,int b)
{
return a+b;
}
【2】根据委托定义一个“具体方法”实现减法功能(写在类里面)
static int Sub(int a,int b)
{
return a-b;
}
【3】创建委托对象,关联“具体方法”
CalculatorDelegate objCal=new CalculatorDelegate(Add);
【4】通过委托调用方法(而不是直接使用方法)
int result=objCal(10,20);
【5】委托对象所关联的方法可以动态的变化
objCal-=Add;//将委托变量所代表的具体方法“解绑”
objCal+=Sub;//重新指向一个新的方法
委托的应用
一、从窗体到主窗体的通信

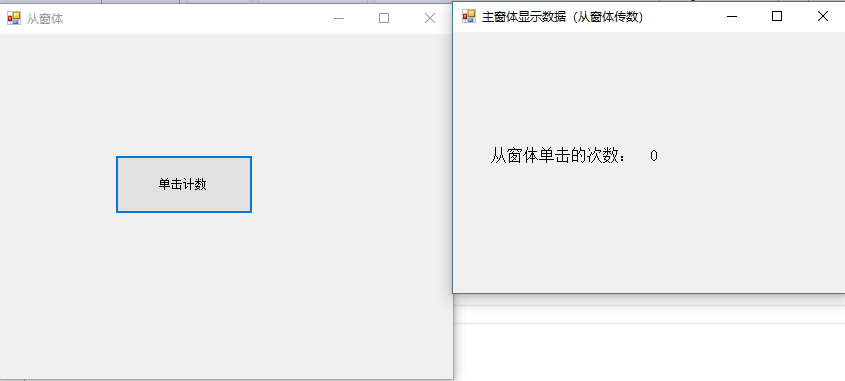
主窗体:FrmMain.cs
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.ComponentModel;
using System.Data;
using System.Drawing;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
using System.Windows.Forms;
namespace DelegateApp
{
public partial class FrmMain : Form
{
public FrmMain()
{
InitializeComponent();
FrmOther objFrmOther = new FrmOther();
//[4]将从窗体委托对象属性和主窗体委托方法关联
objFrmOther.msgsender = this.Receiver;
objFrmOther.Show();
}
//[2]根据委托构建方法
private void Receiver(string content)
{
this.lblCount.Text = content;
}
private void FrmMain_Load(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
}
}
//[1]声明委托
public delegate void ShowCountDelegate(string content);
}
从窗体:FrmOther
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.ComponentModel;
using System.Data;
using System.Drawing;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
using System.Windows.Forms;
namespace DelegateApp
{
public partial class FrmOther : Form
{
public FrmOther()
{
InitializeComponent();
}
//[3]根据委托创建对象
public ShowCountDelegate msgsender;
private int content = 0;
private void btnClick_Click(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
content++;
if (msgsender!=null){
msgsender(content.ToString());//[5]调用
}
}
private void FrmOther_Load(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
}
}
}
二、主窗体到从窗体的通信
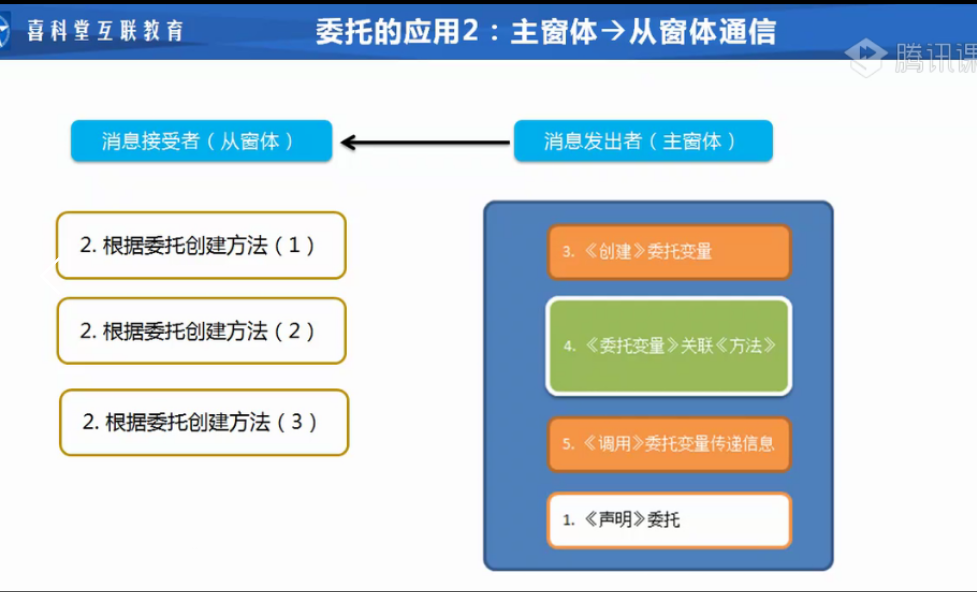
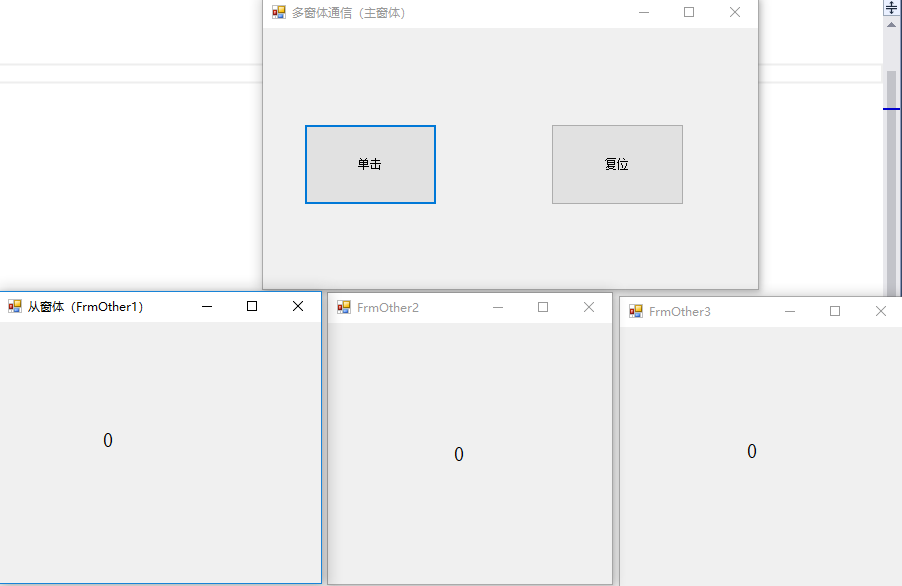
主窗体:FrmMain.cs
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.ComponentModel;
using System.Data;
using System.Drawing;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
using System.Windows.Forms;
namespace DelegateApp2
{
public partial class FrmMain : Form
{
//[3]创建委托对象
public ShowCountDelegate objShowCountDelegate;
public FrmMain()
{
InitializeComponent();
FrmOther1 objFrmOther1 = new FrmOther1();
FrmOther2 objFrmOther2 = new FrmOther2();
FrmOther3 objFrmOther3 = new FrmOther3();
//[4]委托对象关联从窗体方法
objShowCountDelegate += objFrmOther1.Receiver;
objShowCountDelegate += objFrmOther2.Receiver;
objShowCountDelegate += objFrmOther3.Receiver;
objFrmOther1.Show();
objFrmOther2.Show();
objFrmOther3.Show();
}
private int count = 0;
private void btnClick_Click(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
count++;
objShowCountDelegate.Invoke(count.ToString());//[5]利用委托调用方法
}
private void btnReset_Click(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
count = 0;
objShowCountDelegate.Invoke("0");
}
}
//[1]声明委托
public delegate void ShowCountDelegate(string count);
}
从窗体
FrmOther1
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.ComponentModel;
using System.Data;
using System.Drawing;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
using System.Windows.Forms;
namespace DelegateApp2
{
public partial class FrmOther1 : Form
{
public FrmOther1()
{
InitializeComponent();
}
//[2]根据委托创建方法
public void Receiver(string count)
{
this.lblCount.Text = count;
}
private void lblCount_Click(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
}
}
}
FrmOther2
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.ComponentModel;
using System.Data;
using System.Drawing;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
using System.Windows.Forms;
namespace DelegateApp2
{
public partial class FrmOther2 : Form
{
public FrmOther2()
{
InitializeComponent();
}
//[2]根据委托创建方法
public void Receiver(string count)
{
this.lblCount.Text = count;
}
private void FrmOther2_Load(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
}
}
}
FrmOther3
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.ComponentModel;
using System.Data;
using System.Drawing;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
using System.Windows.Forms;
namespace DelegateApp2
{
public partial class FrmOther3 : Form
{
public FrmOther3()
{
InitializeComponent();
}
//[2]根据委托创建方法
public void Receiver(string count)
{
this.lblCount.Text = count;
}
private void FrmOther3_Load(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
}
}
}
总结:多窗体通信个人理解:哪个窗体接受消息,委托方法就写在那里。然后另一个窗体通过委托调用这个方法。