We've got a rectangular n × m-cell maze. Each cell is either passable, or is a wall (impassable). A little boy found the maze and cyclically tiled a plane with it so that the plane became an infinite maze. Now on this plane cell (x, y) is a wall if and only if cell 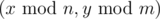 is a wall.
is a wall.
In this problem 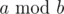 is a remainder of dividing number a by number b.
is a remainder of dividing number a by number b.
The little boy stood at some cell on the plane and he wondered whether he can walk infinitely far away from his starting position. From cell (x, y) he can go to one of the following cells: (x, y - 1), (x, y + 1), (x - 1, y) and (x + 1, y), provided that the cell he goes to is not a wall.
The first line contains two space-separated integers n and m (1 ≤ n, m ≤ 1500) — the height and the width of the maze that the boy used to cyclically tile the plane.
Each of the next n lines contains m characters — the description of the labyrinth. Each character is either a "#", that marks a wall, a ".", that marks a passable cell, or an "S", that marks the little boy's starting point.
The starting point is a passable cell. It is guaranteed that character "S" occurs exactly once in the input.
Print "Yes" (without the quotes), if the little boy can walk infinitely far from the starting point. Otherwise, print "No" (without the quotes).
5 4
##.#
##S#
#..#
#.##
#..#
Yes
5 4
##.#
##S#
#..#
..#.
#.##
No
In the first sample the little boy can go up for infinitely long as there is a "clear path" that goes vertically. He just needs to repeat the following steps infinitely: up, up, left, up, up, right, up.
In the second sample the vertical path is blocked. The path to the left doesn't work, too — the next "copy" of the maze traps the boy.
思路:从起点开始走,对于可以走到的位置,都必定能从这个位置回到起点。这样,对地图进行搜索,当地图中的某一个被访问了两次,就能说明这个地图可以从起点走到无穷远。
搜索的坐标(x,y),x的绝对值可能大于n,的绝对值可能大于m,(x,y)对应在基础地图的位置为rx=(nx%n+n)%n,ry=(ny%m+m)%m。
1 #include <iostream> 2 #include <algorithm> 3 #include <map> 4 #include <vector> 5 #include <functional> 6 #include <string> 7 #include <cstring> 8 #include <queue> 9 #include <stack> 10 #include <set> 11 #include <cmath> 12 #include <cstdio> 13 using namespace std; 14 #define IOS ios_base::sync_with_stdio(false) 15 #define TIE std::cin.tie(0) 16 #define MAX2(a,b) (a>b?a:b) 17 #define MAX3(a,b,c) (a>b?(a>c?a:c):(b>c?b:c)) 18 typedef long long LL; 19 typedef unsigned long long ULL; 20 const int INF=0x3f3f3f3f; 21 const double PI=4.0*atan(1.0); 22 23 const int MAX_N=1505; 24 int n,m,sx,sy; 25 int dx[4]={0,0,1,-1},dy[4]={1,-1,0,0}; 26 bool v[MAX_N][MAX_N]; 27 char board[MAX_N][MAX_N]; 28 typedef struct Point{ 29 int x,y; 30 Point(int x=0,int y=0):x(x),y(y){} 31 bool operator==(const Point &A) const{ 32 return x==A.x&&y==A.y; 33 } 34 }P; 35 P vis[MAX_N][MAX_N]; 36 bool solve() 37 { 38 memset(v,0,sizeof(v)); 39 queue<P>que; 40 v[sx][sy]=true; 41 vis[sx][sy]=P(sx,sy); 42 que.push(P(sx,sy)); 43 while(que.size()){ 44 P p=que.front(); que.pop(); 45 for(int i=0;i<4;i++){ 46 int nx=p.x+dx[i],ny=p.y+dy[i]; 47 int rx=(nx%n+n)%n,ry=(ny%m+m)%m; 48 if(board[rx][ry]=='#') continue; 49 P next=P(nx,ny); 50 if(v[rx][ry]){ 51 if(!(vis[rx][ry]==next)) 52 return true; 53 }else{ 54 v[rx][ry]=true; 55 vis[rx][ry]=next; 56 que.push(next); 57 } 58 } 59 } 60 return false; 61 } 62 int main() 63 { 64 while(scanf("%d%d",&n,&m)==2){ 65 for(int i=0;i<n;i++){ 66 for(int j=0;j<m;j++){ 67 scanf(" %c",&board[i][j]); 68 if(board[i][j]=='S') sx=i,sy=j; 69 } 70 } 71 if(solve())puts("Yes"); 72 else puts("No"); 73 } 74 return 0; 75 }