什么是字典树
字典树是一种树形结构,利用字符串的公共前缀来减少查询时间,以空间换时间;根节点不包含字符,除根节点外每一个节点都只包含一个字符;从根节点到某一节点,路径上经过的字符连接起来,为该节点对应的字符串。
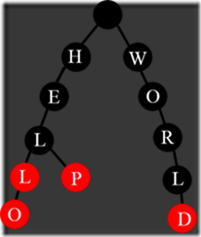
如图是一个字典树,共有12个节点不为NULL,其中根节点不包含字符。那么这棵树中有几个单词呢?hell、hello、help、world,共四个单词。节点标记为红色表示根节点到该节点所形成的字符串存在。
如何实现字典树
下面以字符串查找问题为例,介绍字典树使用。
问题描述如下:
实现一个 Trie,包含 insert, search, 和 startsWith 这三个方法, 假设所有单词均由小写字母组成。
insert插入单词,search查找单词,startsWith是否包含以查询词为前缀的单词。
样例
insert(“hello”)
search(“hell”) // return false
startsWith(“hell”) // return true
startsWith(“helloworld”) // return false
insert(“helloworld”)
search(“hello) // return true
startsWith(“helloworld”) // return true
字符种类数目
const int MAX_CHAR = 26;
字典树节点TrieNode
child是TrieNode指针数组,指向子节点,0-25这26个下标与a-z这26个小写字母一一对应。
也就是说,一个节点表示哪个字符,是由该节点在父节点的child数组的下标所决定的。
flag标记当前字符串是否存在,true相当于在前面的图中将节点标记为红色,false则为黑色。
字典树TrieTree
只是将TrieNode实现的方法进行封装。
#include<cstdio>
#include<cstring>
#include<iostream>
#include<string>
#include<algorithm>
using namespace std;
const int MAX_CHAR=26;
class TrieNode {
public:
TrieNode()
{
flag=false;
for(int i=0;i<MAX_CHAR; i++) {
childs[i]=NULL;
}
}
~TrieNode()
{
for(int i=0;i<MAX_CHAR; i++) if(childs[i]!=NULL) {
delete childs[i];
childs[i]=NULL;
}
}
//递归插入一个单词,每次建立其中的一个字符
void insert(const string& word, int i)
{
int pos=word[i]-'a';
if(childs[pos]==NULL)
childs[pos]=new TrieNode;
if((int)word.length()-1==i) childs[pos]->flag=true;
else childs[pos]->insert(word, i+1);
}
//递归查找一个单词,每次校验其中的一个字符
bool search(const string& word, int i)
{
int pos=word[i]-'a';
//当前位置字符在当前节点的孩子对应于NULL,查找失败
if(childs[pos]==NULL) return false;
//若查找到了最后一个字符,当前节点的对应孩子的flag标记了该单词是否存在
//否则递归校验
if((int)word.length()-1==i) return childs[pos]->flag;
else return childs[pos]->search(word, i+1);
}
bool startwith(const string& word, int i)
{
int pos=word[i]-'a';
if(childs[pos]==NULL) return false;
//只要查找到最后一个字符前未失败说明以该单词为前缀的单词存在
if((int)word.length()-1==i) return true;
else return childs[pos]->startwith(word, i+1);
}
private:
TrieNode* childs[MAX_CHAR];
bool flag;
};
class TrieTree {
public:
TrieTree()
{
root=new TrieNode();
}
~TrieTree()
{
delete root;
}
void insert(const string& word)
{
root->insert(word, 0);
}
bool search(const string& word)
{
return root->search(word, 0);
}
bool startwith(const string& word)
{
return root->startwith(word, 0);
}
private:
TrieNode* root;
};
const char* str[]
{
"hello",
"helloworld",
"acm",
"acmhello",
"helloo",
};
const char* str2[]
{
"acmhell",
"helloo",
"acmh"
};
const char* str3[]
{
"hell",
"heo",
"helo",
"xxx",
"acm"
};
int main()
{
TrieTree trie;
for(int i=0;i<sizeof(str)/sizeof(str[0]); i++)
trie.insert(str[i]);
for(int i=0;i<sizeof(str)/sizeof(str[0]); i++)
if(trie.search(str[i]))
cout<<"find "<<str[i]<<endl;
else
cout<<"not find "<<str[i]<<endl;
for(int i=0;i<sizeof(str2)/sizeof(str2[0]); i++)
if(trie.search(str2[i]))
cout<<"find "<<str2[i]<<endl;
else
cout<<"not find "<<str2[i]<<endl;
for(int i=0;i<sizeof(str3)/sizeof(str3[0]); i++)
if(trie.startwith(str3[i]))
cout<<"startwith "<<str3[i]<<endl;
else
cout<<"not startwith "<<str3[i]<<endl;
return 0;
}