《Effective Java 第三版》——第二章 创建和销毁对象
《Effective Java 第三版》——第三章 所有对象都通用的方法
《Effective Java 第三版》——第四章 类和接口
《Effective Java 第三版》——第六章 枚举和注解
《Effective Java 第三版》——第七章 Lambda 和 Stream


49条神神叨叨的没个主线

package effectivejava.chapter8.item50; import java.util.*; // Broken "immutable" time period class (Pages 231-3) public final class Period { private final Date start; private final Date end; /** * @param start the beginning of the period * @param end the end of the period; must not precede start * @throws IllegalArgumentException if start is after end * @throws NullPointerException if start or end is null */ public Period(Date start, Date end) { if (start.compareTo(end) > 0) throw new IllegalArgumentException( start + " after " + end); this.start = start; this.end = end; } public Date start() { return start; } public Date end() { return end; } public String toString() { return start + " - " + end; } // // Repaired constructor - makes defensive copies of parameters (Page 232) // public Period(Date start, Date end) { // this.start = new Date(start.getTime()); // this.end = new Date(end.getTime()); // // if (this.start.compareTo(this.end) > 0) // throw new IllegalArgumentException( // this.start + " after " + this.end); // } // // // Repaired accessors - make defensive copies of internal fields (Page 233) // public Date start() { // return new Date(start.getTime()); // } // // public Date end() { // return new Date(end.getTime()); // } // Remainder omitted }
package effectivejava.chapter8.item50; import java.util.*; // Two attacks on the internals of an "immutable" period (232-3) public class Attacks { public static void main(String[] args) { // Attack the internals of a Period instance (Page 232) Date start = new Date(); Date end = new Date(); Period p = new Period(start, end); end.setYear(78); // Modifies internals of p! System.out.println(p); // Second attack on the internals of a Period instance (Page 233) start = new Date(); end = new Date(); p = new Period(start, end); p.end().setYear(78); // Modifies internals of p! System.out.println(p); } }
/Library/Java/JavaVirtualMachines/jdk-13.0.2.jdk/Contents/Home/bin/java -Dfile.encoding=UTF-8 -classpath /Users/didi/git/effective-java-3e-source-code/bin effectivejava.chapter8.item50.Attacks Thu Jul 09 13:52:39 CST 2020 - Sun Jul 09 13:52:39 CST 1978 Thu Jul 09 13:52:39 CST 2020 - Sun Jul 09 13:52:39 CST 1978 Process finished with exit code 0


package effectivejava.chapter8.item52; import java.util.*; import java.math.*; // Broken! - What does this program print? (Page 238) public class CollectionClassifier { public static String classify(Set<?> s) { return "Set"; } public static String classify(List<?> lst) { return "List"; } public static String classify(Collection<?> c) { return "Unknown Collection"; } public static void main(String[] args) { Collection<?>[] collections = { new HashSet<String>(), new ArrayList<BigInteger>(), new HashMap<String, String>().values() }; for (Collection<?> c : collections) System.out.println(classify(c)); } }
编译期就定下来了要调用:
classify(Collection<?> c)
// 重载编译期静态决定 /Library/Java/JavaVirtualMachines/jdk-13.0.2.jdk/Contents/Home/bin/java -Dfile.encoding=UTF-8 -classpath /Users/didi/git/effective-java-3e-source-code/bin effectivejava.chapter8.item52.CollectionClassifier Unknown Collection Unknown Collection Unknown Collection Process finished with exit code 0 //覆盖运行期动态决定 /Library/Java/JavaVirtualMachines/jdk-13.0.2.jdk/Contents/Home/bin/java -Dfile.encoding=UTF-8 -classpath /Users/didi/git/effective-java-3e-source-code/bin effectivejava.chapter8.item52.Overriding wine sparkling wine champagne Process finished with exit code 0
解决方案:
package effectivejava.chapter8.item52; import java.math.BigInteger; import java.util.*; // Repaired static classifier method. (Page 240) public class FixedCollectionClassifier { public static String classify(Collection<?> c) { return c instanceof Set ? "Set" : c instanceof List ? "List" : "Unknown Collection"; } public static void main(String[] args) { Collection<?>[] collections = { new HashSet<String>(), new ArrayList<BigInteger>(), new HashMap<String, String>().values() }; for (Collection<?> c : collections) System.out.println(classify(c)); } }
/Library/Java/JavaVirtualMachines/jdk-13.0.2.jdk/Contents/Home/bin/java -Dfile.encoding=UTF-8 -classpath /Users/didi/git/effective-java-3e-source-code/bin effectivejava.chapter8.item52.FixedCollectionClassifier
Set
List
Unknown Collection
Process finished with exit code 0
remove(元素还是索引),经典问题

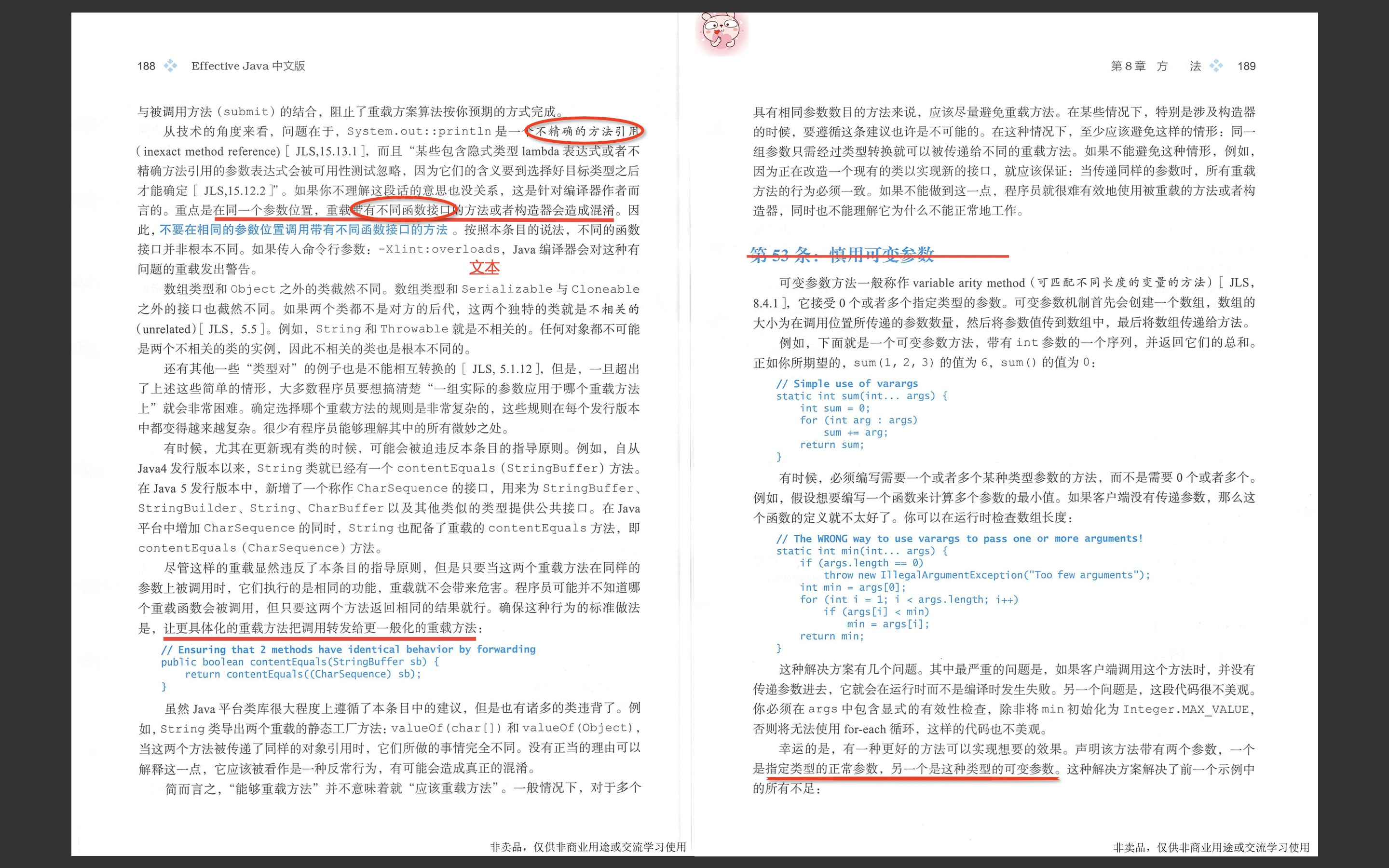

package effectivejava.chapter8.item53; import java.util.stream.IntStream; // Sample uses of varargs (Pages 245-6) public class Varargs { // Simple use of varargs (Page 245) static int sum(int... args) { int sum = 0; for (int arg : args) sum += arg; return sum; } // // The WRONG way to use varargs to pass one or more arguments! (Page 245) // static int min(int... args) { // if (args.length == 0) // throw new IllegalArgumentException("Too few arguments"); // int min = args[0]; // for (int i = 1; i < args.length; i++) // if (args[i] < min) // min = args[i]; // return min; // } // The right way to use varargs to pass one or more arguments (Page 246) static int min(int firstArg, int... remainingArgs) { int min = firstArg; for (int arg : remainingArgs) if (arg < min) min = arg; return min; } public static void main(String[] args) { System.out.println(sum(1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10)); System.out.println(min(1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10)); } }



package effectivejava.chapter8.item55; import java.util.*; // Using Optional<T> as a return type (Pages 249-251) public class Max { // // Returns maximum value in collection - throws exception if empty (Page 249) // public static <E extends Comparable<E>> E max(Collection<E> c) { // if (c.isEmpty()) // throw new IllegalArgumentException("Empty collection"); // // E result = null; // for (E e : c) // if (result == null || e.compareTo(result) > 0) // result = Objects.requireNonNull(e); // // return result; // } // // Returns maximum value in collection as an Optional<E> (Page 250) // public static <E extends Comparable<E>> // Optional<E> max(Collection<E> c) { // if (c.isEmpty()) // return Optional.empty(); // // E result = null; // for (E e : c) // if (result == null || e.compareTo(result) > 0) // result = Objects.requireNonNull(e); // // return Optional.of(result); // } // Returns max val in collection as Optional<E> - uses stream (Page 250) public static <E extends Comparable<E>> Optional<E> max(Collection<E> c) { return c.stream().max(Comparator.naturalOrder()); } public static void main(String[] args) { List<String> words = Arrays.asList(args); System.out.println(max(words)); // Using an optional to provide a chosen default value (Page 251) String lastWordInLexicon = max(words).orElse("No words..."); System.out.println(lastWordInLexicon); } }
/Library/Java/JavaVirtualMachines/jdk-13.0.2.jdk/Contents/Home/bin/java -Dfile.encoding=UTF-8 -classpath /Users/didi/git/effective-java-3e-source-code/bin effectivejava.chapter8.item55.Max
Optional.empty
No words...
Process finished with exit code 0
package effectivejava.chapter8.item55; import java.util.Optional; // Avoiding unnecessary use of Optional's isPresent method (Page 252) public class ParentPid { public static void main(String[] args) { ProcessHandle ph = ProcessHandle.current(); // Inappropriate use of isPresent Optional<ProcessHandle> parentProcess = ph.parent(); System.out.println("Parent PID: " + (parentProcess.isPresent() ? String.valueOf(parentProcess.get().pid()) : "N/A")); // Equivalent (and superior) code using orElse System.out.println("Parent PID: " + ph.parent().map(h -> String.valueOf(h.pid())).orElse("N/A")); } }
/Library/Java/JavaVirtualMachines/jdk-13.0.2.jdk/Contents/Home/bin/java -Dfile.encoding=UTF-8 -classpath /Users/didi/git/effective-java-3e-source-code/bin effectivejava.chapter8.item55.ParentPid Parent PID: 372 Parent PID: 372 Process finished with exit code 0




package effectivejava.chapter8.item56; import java.lang.annotation.Retention; import java.lang.annotation.RetentionPolicy; import java.lang.annotation.Target; import java.lang.annotation.ElementType; // Documentation comment examples (Pages 255-9) public class DocExamples<E> { // Method comment (Page 255) /** * Returns the element at the specified position in this list. * * <p>This method is <i>not</i> guaranteed to run in constant * time. In some implementations it may run in time proportional * to the element position. * * @param index index of element to return; must be * non-negative and less than the size of this list * @return the element at the specified position in this list * @throws IndexOutOfBoundsException if the index is out of range * ({@code index < 0 || index >= this.size()}) */ E get(int index) { return null; } // Use of @implSpec to describe self-use patterns & other visible implementation details. (Page 256) /** * Returns true if this collection is empty. * * @implSpec This implementation returns {@code this.size() == 0}. * * @return true if this collection is empty */ public boolean isEmpty() { return false; } // Use of the @literal tag to include HTML and javadoc metacharacters in javadoc comments. (Page 256) /** * A geometric series converges if {@literal |r| < 1}. */ public void fragment() { } // Controlling summary description when there is a period in the first "sentence" of doc comment. (Page 257) /** * A suspect, such as Colonel Mustard or {@literal Mrs. Peacock}. */ public enum FixedSuspect { MISS_SCARLETT, PROFESSOR_PLUM, MRS_PEACOCK, MR_GREEN, COLONEL_MUSTARD, MRS_WHITE } // Generating a javadoc index entry in Java 9 and later releases. (Page 258) /** * This method complies with the {@index IEEE 754} standard. */ public void fragment2() { } // Documenting enum constants (Page 258) /** * An instrument section of a symphony orchestra. */ public enum OrchestraSection { /** Woodwinds, such as flute, clarinet, and oboe. */ WOODWIND, /** Brass instruments, such as french horn and trumpet. */ BRASS, /** Percussion instruments, such as timpani and cymbals. */ PERCUSSION, /** Stringed instruments, such as violin and cello. */ STRING; } // Documenting an annotation type (Page 259) /** * Indicates that the annotated method is a test method that * must throw the designated exception to pass. */ @Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME) @Target(ElementType.METHOD) public @interface ExceptionTest { /** * The exception that the annotated test method must throw * in order to pass. (The test is permitted to throw any * subtype of the type described by this class object.) */ Class<? extends Throwable> value(); } }
