概述
- “行为变化”模式:组件构建过程中,组件行为的变化经常会导致组件本身剧烈的变化。“行为变化”模式将组件的行为和组件本身进行解耦,从而支持组件行为的变化,实现两者之间的松耦合
- 动机:在软件构建过程中,“行为请求者”与“行为实现者”通常呈现一种“紧耦合”。但在某些场合——如需要对行为进行“记录、撤销(redo/undo)”等处理,这种无法抵御变化的紧耦合是不合适的
- 如何将“行为请求者”与“行为实现者”解耦?将一组行为抽象为对象,可实现二者间的松耦合
- GoF:一个请求(行为)封装为对象,从而使你可用不同的请求对客户进行参数化;对请求排队或记录请求日志,及支持可撤销的操作
- 封装:创建对象的过程
- 对象能干什么:当做参数传递,当做字段存储,序列化,存在数据结构里(灵活性)
- Command模式的根本目的在于将“行为请求者”与“行为实现者”解耦,在面向对象语言中,常见的实现手段是“将行为抽象为对象”
- 实现Command接口的具体命令对象ConcreteCommand有时根据需要可能会保存一些额外的信息,通过使用Composite模式,可能将多个“命令”封装为一个“复合命令”MacroCommand
- Command模式与C++中的函数对象有些类似(都实现了行为对象化),但两者定义行为接口的规范有所区别:Command以面向对象中的“接口-实现”来定义行为接口规范,更严格,但有性能损失(运行时绑定);C++函数对象以函数签名来定义行为接口规范,更灵活,性能更高(编译时绑定)
- C++中一般用函数对象+泛型编程替代(性能高),在 Java, C#, Swift 中应用广泛
- 一种观点:设计模式是弥补语言模式的不足而出现
场景
- 餐厅点菜,通过服务员把点菜单传递给厨师做菜
- GUI中,通过菜单,工具栏,快捷键等实现复制功能
- 通过操作来参数化对象
- 将操作放入队列中,远程执行操作
- 实现操作回滚功能
结构
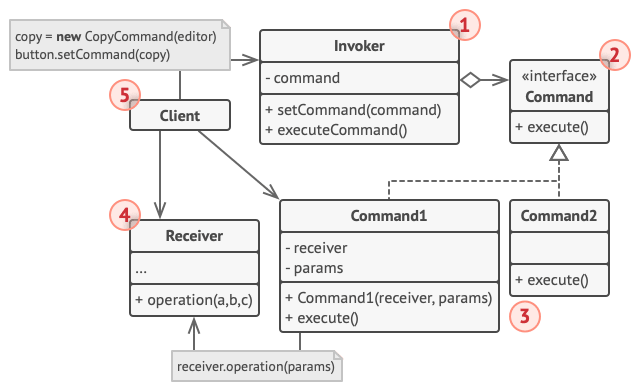
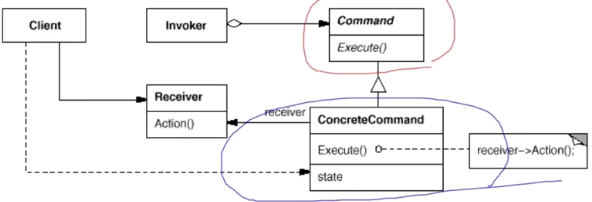
- 发送者(触发者)类:对请求进行初始化,包含成员变量存储对命令对象的引用
- 命令接口:声明一个执行命令的方法
- 具体命令:实现各种类型的请求
- 接收者:包含业务逻辑
- 客户端:创建并配置
场景
示例1
Command.cpp

1 #include <iostream> 2 #include <vector> 3 #include <string> 4 using namespace std; 5 6 class Command 7 { 8 public: 9 virtual void execute() = 0; 10 }; 11 12 class ConcreteCommand1 : public Command 13 { 14 string arg; 15 public: 16 ConcreteCommand1(const string & a) : arg(a) {} 17 void execute() override 18 { 19 cout<< "#1 process..."<<arg<<endl; 20 } 21 }; 22 23 class ConcreteCommand2 : public Command 24 { 25 string arg; 26 public: 27 ConcreteCommand2(const string & a) : arg(a) {} 28 void execute() override 29 { 30 cout<< "#2 process..."<<arg<<endl; 31 } 32 }; 33 34 class MacroCommand : public Command 35 { 36 vector<Command*> commands; 37 public: 38 void addCommand(Command *c) { commands.push_back(c); } 39 void execute() override 40 { 41 for (auto &c : commands) 42 { 43 c->execute(); 44 } 45 } 46 }; 47 48 int main() 49 { 50 51 ConcreteCommand1 command1(receiver, "Arg ###"); 52 ConcreteCommand2 command2(receiver, "Arg $$$"); 53 54 MacroCommand macro; 55 macro.addCommand(&command1); 56 macro.addCommand(&command2); 57 58 macro.execute(); 59 60 }
- 43:运行时辨析,c的具体类型决定excute()操作是什么
- 51-52:创建命令
- 54-56:组合命令
- 58:执行命令
示例2


1 // 命令基类会为所有具体命令定义通用接口。 2 abstract class Command is 3 protected field app: Application 4 protected field editor: Editor 5 protected field backup: text 6 7 constructor Command(app: Application, editor: Editor) is 8 this.app = app 9 this.editor = editor 10 11 // 备份编辑器状态。 12 method saveBackup() is 13 backup = editor.text 14 15 // 恢复编辑器状态。 16 method undo() is 17 editor.text = backup 18 19 // 执行方法被声明为抽象以强制所有具体命令提供自己的实现。该方法必须根 20 // 据命令是否更改编辑器的状态返回 true 或 false。 21 abstract method execute() 22 23 24 // 这里是具体命令。 25 class CopyCommand extends Command is 26 // 复制命令不会被保存到历史记录中,因为它没有改变编辑器的状态。 27 method execute() is 28 app.clipboard = editor.getSelection() 29 return false 30 31 class CutCommand extends Command is 32 // 剪切命令改变了编辑器的状态,因此它必须被保存到历史记录中。只要方法 33 // 返回 true,它就会被保存。 34 method execute() is 35 saveBackup() 36 app.clipboard = editor.getSelection() 37 editor.deleteSelection() 38 return true 39 40 class PasteCommand extends Command is 41 method execute() is 42 saveBackup() 43 editor.replaceSelection(app.clipboard) 44 return true 45 46 // 撤销操作也是一个命令。 47 class UndoCommand extends Command is 48 method execute() is 49 app.undo() 50 return false 51 52 53 // 全局命令历史记录就是一个堆桟。 54 class CommandHistory is 55 private field history: array of Command 56 57 // 后进... 58 method push(c: Command) is 59 // 将命令压入历史记录数组的末尾。 60 61 // ...先出 62 method pop():Command is 63 // 从历史记录中取出最近的命令。 64 65 66 // 编辑器类包含实际的文本编辑操作。它会担任接收者的角色:最后所有命令都会 67 // 将执行工作委派给编辑器的方法。 68 class Editor is 69 field text: string 70 71 method getSelection() is 72 // 返回选中的文字。 73 74 method deleteSelection() is 75 // 删除选中的文字。 76 77 method replaceSelection(text) is 78 // 在当前位置插入剪贴板中的内容。 79 80 // 应用程序类会设置对象之间的关系。它会担任发送者的角色:当需要完成某些工 81 // 作时,它会创建并执行一个命令对象。 82 class Application is 83 field clipboard: string 84 field editors: array of Editors 85 field activeEditor: Editor 86 field history: CommandHistory 87 88 // 将命令分派给 UI 对象的代码可能会是这样的。 89 method createUI() is 90 // ... 91 copy = function() { executeCommand( 92 new CopyCommand(this, activeEditor)) } 93 copyButton.setCommand(copy) 94 shortcuts.onKeyPress("Ctrl+C", copy) 95 96 cut = function() { executeCommand( 97 new CutCommand(this, activeEditor)) } 98 cutButton.setCommand(cut) 99 shortcuts.onKeyPress("Ctrl+X", cut) 100 101 paste = function() { executeCommand( 102 new PasteCommand(this, activeEditor)) } 103 pasteButton.setCommand(paste) 104 shortcuts.onKeyPress("Ctrl+V", paste) 105 106 undo = function() { executeCommand( 107 new UndoCommand(this, activeEditor)) } 108 undoButton.setCommand(undo) 109 shortcuts.onKeyPress("Ctrl+Z", undo) 110 111 // 执行一个命令并检查它是否需要被添加到历史记录中。 112 method executeCommand(command) is 113 if (command.execute) 114 history.push(command) 115 116 // 从历史记录中取出最近的命令并运行其 undo(撤销)方法。请注意,你并 117 // 不知晓该命令所属的类。但是我们不需要知晓,因为命令自己知道如何撤销 118 // 其动作。 119 method undo() is 120 command = history.pop() 121 if (command != null) 122 command.undo()
参考
https://refactoringguru.cn/design-patterns/command
